Characteristics and controlling factors of tight sandstone reservoir of the Jurassic strata in the Lenghu region, Northern Qaidam Basin
-
摘要:
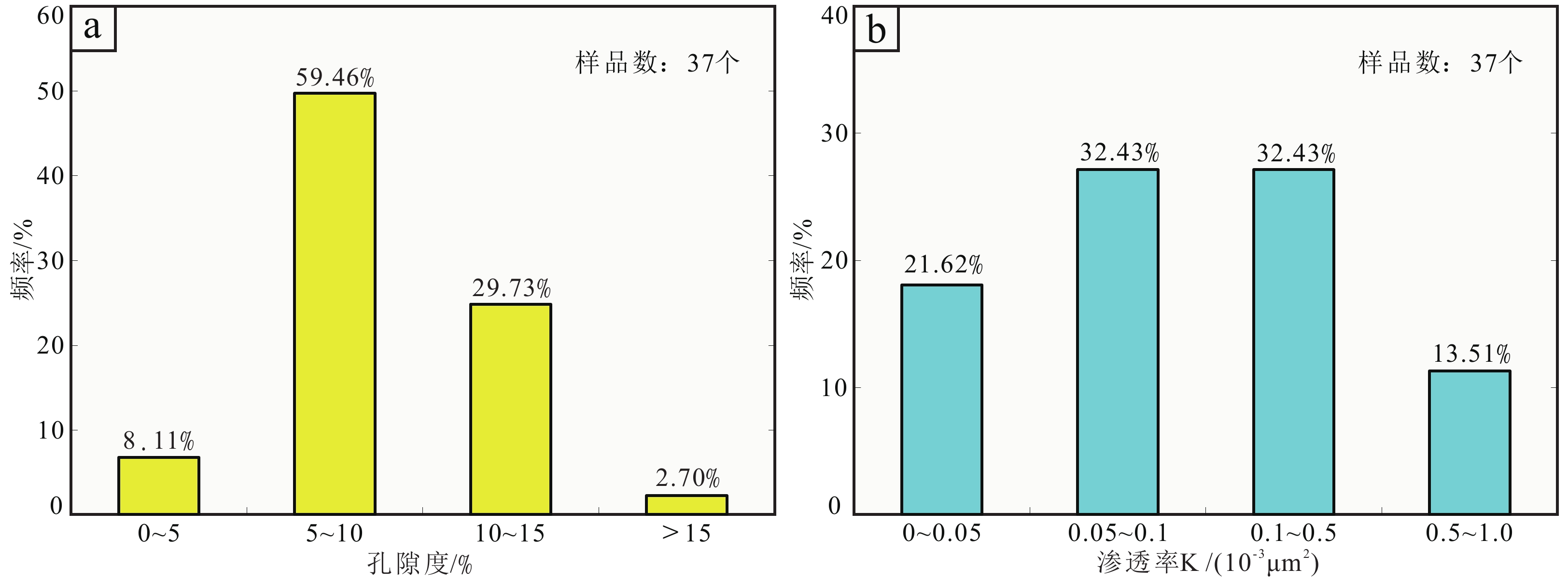
冷湖地区侏罗系地层油源丰富,储层致密化程度高,为查明低孔低渗储层成因机制,剖析储层发育控制因素,利用普通薄片、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、全岩X衍射矿物分析、物性分析、核磁共振分析等多种分析测试手段,对研究区侏罗系储层的岩石学特征、孔隙类型、物性与成岩作用特征进行研究。结果显示:(1)研究区侏罗系储层主要为长石岩屑砂岩和岩屑砂岩,孔隙类型以次生溶孔为主,原生孔隙残留少,微孔隙占比高,孔隙度平均为9.96%,渗透率平均为2.26×10−3 μm2,属于特低孔、超低渗致密储层。(2)储层成岩作用类型以压实作用、胶结作用和溶蚀作用为主,成岩演化主要处于中成岩A期,成岩序列可概括为:机械压实改造-少量早期方解石胶结-长石、岩屑轻微溶蚀-石英I期加大-有机酸流体侵入、长石岩屑强烈溶蚀-黏土矿物广泛出现-石英Ⅱ期加大-长石、岩屑、黏土矿物伊利石化-少量含铁碳酸盐胶结。(3)多种成岩作用综合制约着致密砂岩储层的发展进程。煤系地层富含水生、陆生动植物遗体,沉积后至成岩早期有机质分解产生腐殖酸并形成酸性环境,早期碳酸盐胶结物不甚发育,碎屑颗粒间欠缺方解石胶结物支撑,压实作用导致原生孔隙大幅降低;成岩中期广泛存在的黏土矿物占据孔隙空间,分割大孔隙为无数微孔隙,黏土矿物的胶结作用进一步加剧了储层致密化;有机质热演化过程中释放的有机酸性流体对长石的持续溶蚀形成较多次生孔隙,有效改善了储层物性。本项研究深化了柴北缘致密砂岩储层物性与成岩作用特征的认识,对开展进一步油气勘探具有指导意义。
Abstract:The Jurassic strata in Lenghu area are rich in oil and gas resources and have a high degree of reservoir densification. In order to find out the genetic mechanism of porous and low permeability reservoirs and to analyze the controlling factors of reservoir development, a variety of experimental methods are used in this work, such as analyses of normal thin-section, cast thin-section and scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction of clay minerals and nuclear magnetic resonance. Based on the description of petrology characteristics of reservoir pore structures characterization and physical characteristics, the characteristics of reservoir diagenesis are investigated. The results show the following: (1) The rock types of the Jurassic reservoir rocks in the study area are mainly feldspathic lithic sandstones and lithic sandstones. The main pore types of sandstones are mainly secondary solution pore and the proportion of micro pores are relatively high. The average porosity of sandstone is 9.96% and the average permeability of sandstone is 2.26×10−3 μm2, belonging to special low porosity-ultra-low permeability reservoirs. (2) The types of diagenesis are mainly compaction, cementation and dissolution. The diagenetic evolution mainly takes place during the mesodiagenetic phase A. The diagenetic sequence can be summarized as follows: compaction - a small amount of calcite cement is formed - feldspar and rock debris are slightly corroded - secondary enlargement of quartz - feldspar and rock debris are strongly corroded due to the formation of a large number of organic acids - clay minerals appear widely - secondary enlarged edges appear again in quartz particles - feldspar, rock debris and clay minerals are gradually transformed into illite - a small amount of iron-bearing calcite cement is formed. (3) Various types of diagenesis had once played important roles in the formation of ultra-low permeability tight sandstone reservoirs. The coal measure strata were rich in the remains of aquatic and terrestrial animals and plants. After the sediment was buried, the organic matter can decompose and produce humic acid, and then form an acidic environment. There were little calcite cements in the clastic reservoir because of the acidic water medium condition of the coal measures strata in the early diagenetic stage. The strong compaction greatly reduced the primary porosity. The widespread clay minerals occupy the pore space and divide the macropores into countless micro pores. The cementation of clay minerals further intensifies the reservoir densification, which intensifies the process of reservoir densification. The continuous dissolution of feldspar and rock debris components by organic acid fluids which came from thermal evolution of organic matter played a key role in improving reservoir physical properties. This study can deepen the understanding of diagenetic evolution of tight sandstone reservoir in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin, which has a guiding significance for further oil and gas exploration.
-
Key words:
- Lenghu region /
- tight sandstone /
- diagenesis /
- reservoir physical properties
-

-
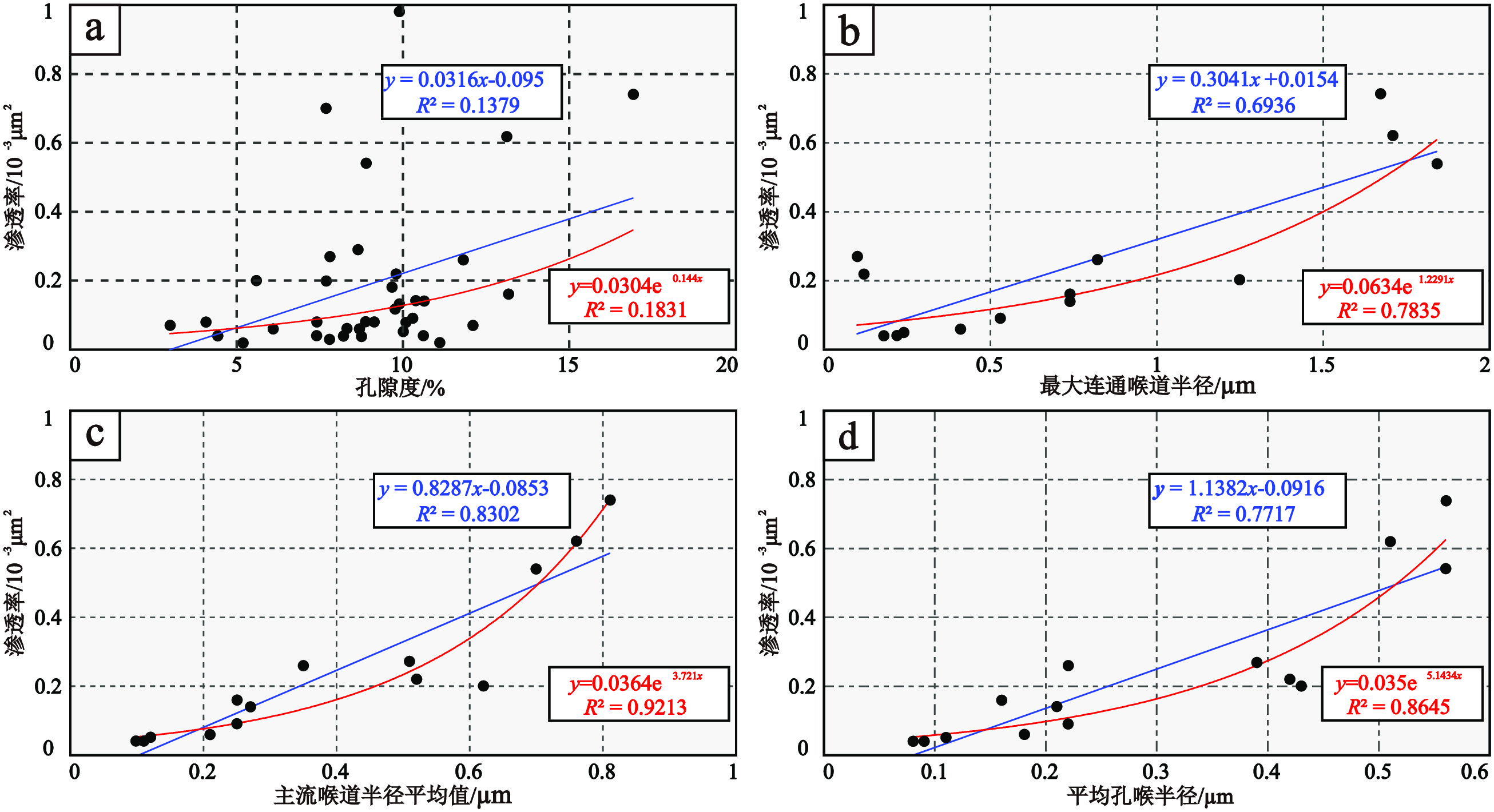
表 1 冷湖地区侏罗系储层压汞参数统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of mercury parameters of Jurassic reservoirs in the research area
井号 深度
/m孔隙度
/%渗透率
/×10−3 μm2SHgmax
/%退汞效率
/%排驱压力
/MPa最大连通
喉道半径/µm平均孔
喉半径/µm主流喉道
半径平均值/µm饱和度中值
半径/µm冷科1 3482.60 16.90 0.74 67.16 37.13 0.44 1.67 0.56 0.81 0.12 冷科1 4307.74 10.00 0.05 75.23 34.07 3.10 0.24 0.11 0.12 0.07 冷科1 4310.77 7.80 0.27 89.27 39.08 7.10 1.05 0.39 0.51 0.31 冷科1 4311.45 7.40 0.04 64.01 37.63 3.30 0.22 0.08 0.11 0.02 冷科1 4312.33 7.70 0.20 62.27 41.62 0.59 1.25 0.43 0.62 0.06 冷科1 4314.08 10.60 0.04 67.82 34.87 4.05 0.18 0.09 0.10 0.04 冷科1 4314.55 10.30 0.09 80.52 24.79 1.40 0.53 0.22 0.25 0.18 冷科1 4315.36 9.80 0.22 68.75 17.67 6.10 0.89 0.42 0.52 0.15 冷科1 4318.74 8.70 0.06 71.45 43.41 1.80 0.41 0.18 0.21 0.07 冷科1 3482.90 13.10 0.62 79.37 36.83 0.43 1.71 0.51 0.76 0.18 冷科1 4315.41 10.40 0.14 79.92 37.39 1.00 0.74 0.21 0.27 0.10 冷科1 4320.26 8.90 0.54 78.87 25.00 0.40 1.84 0.56 0.70 0.32 冷95 3358.00 11.80 0.26 76.15 45.08 0.90 0.82 0.22 0.35 0.06 冷95 3358.45 13.20 0.16 61.03 41.71 0.99 0.74 0.16 0.25 0.01 平均值 9.96 0.26 72.99 35.45 2.26 0.87 0.30 0.40 0.12 表 2 砂岩核磁共振参数统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of nuclear magnetic resonance parameters
井号 样号 深度/m 层位 核磁孔隙度/% 核磁渗透率/×10−3 μm2 束缚水饱和度/% 可动水饱和度/% 冷科1 7 4307.92 J 7.17 2.54 58.55 41.45 冷科1 14 4318.01 J 4.59 1.06 73.61 26.39 冷95 4 3357.89 J 11.12 0.20 79.92 20.08 平均值 7.63 1.27 70.69 29.31 -
[1] Beard D C, Weyl P K. , 1973. Influence of Texture on Porosity and Permeability of Unconsolidated Sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 57(2): 349-369
[2] Boles, J. R and Franks, S. G. , 1979. Clay diagenesis in Wilcox sandstones of southwest Texas: implications of smectite diagenesis on sandstone cementation. Journal of Sedimentary Petroleum, 49(1): 55-70.
[3] Chen J, Shi J A, Long G H, et al. , 2013. Sedimentary facies and models for the Palaeogene — Neogene deposits on the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 33(3): 16-26.
[4] Chen D Q, Long A L, Zhao G Z, et al. , 2014. Characterization of Jurassic reservoirs in the Jiulongshan area of the Qaidam Basin[J]. Qinghai Petroleum, 32(2): 20-27.
[5] Chen B, Chen F J, Wu Z X, et al. , 2015. Diagenesis and Favorable Diagenetic Facies of Paleogene Lulehe Formation Sandstone in Lenghu Region[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 34(4): 20-27.
[6] Dou W C, Liu L F, Wu K J, et al. , 2016. Pore Structure Characteristics and Its Effect on Permeability by Mercury Injection Measurement: An Example from Triassic Chang-7 Reservoir, Southwest Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Review, 62(2): 502-511.
[7] Du J J, Zhang S A, Xiao W F, et al. , 2017. Geochemistry Characteristics of Middle — Lower Jurassic Clastic Rocks in the Northern Margin of Qaidam Basin and Their Geological Significance[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 39(6): 721-734.
[8] Ehrlich R, Crabtree S J, Horkowitz K O, et al. , 1991. Petrography and reservoir physics I: Objective classification of reservoir porosity. AAPG Bulletin, 75(10): 1547-1562.
[9] Gao X Z, Chen F J. 2002. Accumulation Model of Petroleum in the Tertiary System of the Northwestern Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science — Journal of China University of Geosciences, 27(6): 757-76.
[10] Hu J J, Ma Y S, Wang Z X, et al. , 2017. Palaeoenvironment and palaeoclimate of the Middle to Late Jurassic revealed by geochemical records in northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 19(3): 480-490.
[11] Huang X, Duan D P, Liu B B, et al. , 2021. Origin Mechanism of Chlorite and Its Impact on Reservoir Properties in Huagang Formation[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 19(3): 480-490.
[12] Jin Z K, Qi C W, Xue J Q, et al. , 2006. Sedimentary facies of the Jurassic in northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 19(3): 480-490.
[13] Liang W, Zhang X Y. 1994. Generation Mechanism of Secondary Porosity in Sandstone Hydrocarbon Resevoirs of Upper Jurassic Tieling — Changtu Basin[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 14(3): 62-68.
[14] Liu M W, Sun G Q, Guo J J, et al. , 2018. Provenance analysis of the Palaeogene clastic rocks in the western part of northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 38(1): 53-61.
[15] Lü B F, Zhang Y Q, Yang S Y. Characteristics of Structural System and Its Implication for Formation Dynamics in Qaidam Basin[J]. Geological Review, 57(2): 167-174(in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Manning D A C, 1997. Acetate and propionate in landfill leachates: Implications for the recognition of microbiological influences on the composition of waters in sedimentary systems[J]. Geology, 25(3): 279-281. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0279:AAPILL>2.3.CO;2
[17] Manning D A C and Bewsher A. , 1997. Determination of anions in landfill leachates by ion chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 770(1): 203-210.
[18] Mu J, Wang L Q. 1999. Petroliferous prospect of Lenghu-Nanbaxian structure belt in Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 20(2): 18-22(in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Pittman, E. D and Larese, R E. , 1991. Compaction of lithic sands: Experimental results and applications. AAPG Bulletin, 75(8): 1279-1299.
[20] Scherer M, 1987. Parameters Influencing Porosity in Sandstones: A Model for Sandstone Porosity Prediction[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 71(5): 485-491.
[21] Shao L Y, Li M, Li Y H, et al. , 2014. Geological characteristics and controlling factors of shale gas in the Jurassic of the northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(4): 311-322.
[22] Shou J F, Zhang H L, Shen Yang, et al. , 2006. Diagenetic Mechanisms of Sandstone Reservoirs in China Oil and Gas — Bearing Basins[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(8): 2165-2170.
[23] Towe, K. M, 1962. Clay mineral diagenesis of a possible source of silica cement in sedimentary rocks. Journal of Sedimentary Petroleum, 32(1): 26-28.
[24] Torabi A, Fossen H, Braathen A. , 2013. Insight into petrophysical properties of deformed sadstone reservoirs. AAPG Bulletin, 97(4): 619-637.
[25] Walderhaug O, 1994. Precipitation rates for quartz cement in sandstones determined by fluid-inclusion microthermometry and temperature-history modeling[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 64(2a): 324-333. doi: 10.2110/jsr.64.324
[26] Wang A F, You Z L. 1995. Diagenetic Factors Controlling Development of the Pores in Sandstone From Xiangxi Group in The North Part of Eastern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Chengdu Institute of Technology, 22(2): 79-83(in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Wang F Q, Wang B Q. 2006. Diagenesis of reservoir rocks of the Lower Jurassic and its influence on porosity modification in North Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Sciences, 42(5): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Wang X W, Yang Z M, Li H B, et al. , 2010. Experimental study on pore structure of low permeability core with NMR spectra[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 32(2): 69-72.
[29] Wang M, Yang Y H, Wang Y T, et al. , 2019. The Jurassic clastic reservoirs in the Jiulongshan area, northern Qaidam Basin, Qinghai[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(2): 94-102.
[30] Wang M, Geng R Y, Ma F Q, et al. , 2021. Diagenesis Characteristics of Jurassic in Jiulongshan area, Northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 21(15): 6175-6184.
[31] Westcott, W. A, 1983. Diagenesis of Cotton Valley sandstone (Upper Jurassic), East Texas: implications for tight gas formation pay recognition. AAPG Bulletin, 67(6): 1002-1013.
[32] Wu Z T, Sun G Q, Wang F, et al. , 2016. Characteristics and Significance of the Carbonate Cements in the Lower member of the Palaeogene Xiaganchaigou Formation in the Pingtai region, northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 36(4): 30-36.
[33] 陈吉, 史基安, 龙国徽, 等, 2013. 柴北缘古近系-新近系沉积相特征及沉积模式[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 33(3): 16-26.
[34] 陈登钱, 龙安林, 赵国忠, 等, 2014. 柴达木盆地九龙山地区侏罗系储层特征研究[J]. 青海石油, 32(2): 20-27.
[35] 陈波, 陈汾君, 吴志雄, 等, 2015. 柴北缘冷湖地区古近系路乐河组成岩作用及有利成岩相研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 34(4): 20-27.
[36] 窦文超, 刘洛夫, 吴康军, 等, 2016. 基于压汞实验研究低渗储层孔隙结构及其对渗透率的影响-以鄂尔多斯盆地西南部三叠系延长组长7储层为例[J]. 地质论评, 62(2): 502-511.
[37] 杜建军, 张士安, 肖伟峰, 等, 2017. 柴达木盆地北缘中-下侏罗统碎屑岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 39(6): 721-734. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.06.004
[38] 高先志, 陈发景, 2002. 柴达木盆地北缘西段油气成藏机理研究[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 27(6): 757-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.06.018
[39] 胡俊杰, 马寅生, 王宗秀, 等, 2017. 地球化学记录揭示的柴达木盆地北缘地区中-晚侏罗世古环境与古气候[J]. 古地理学报, 19(3): 480-490. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.03.037
[40] 黄鑫, 段冬平, 刘彬彬, 等, 2021. 西湖凹陷花港组绿泥石成因及其对储层物性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 51(3): 69-679.
[41] 金振奎, 齐聪伟, 薛建勤, 等, 2006. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系沉积相[J]. 古地理学报, 8(2): 199-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2006.02.006
[42] 梁卫, 张晓宇, 1994. 铁岭—昌图盆地上侏罗统砂岩储层次生孔隙形成机制研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 14(3): 62-68.
[43] 吕宝凤, 张越青, 杨书逸, 2011. 柴达木盆地构造体系特征及其成盆动力学意义[J]. 地质论评, 57(2): 167-174.
[44] 刘伟明, 孙国强, 郭佳佳, 等, 2018. 柴北缘西段古近纪物源体系分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 38(1): 53-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2018.01.006
[45] 穆剑, 汪立群, 1999. 论柴达木盆地冷湖-南八仙构造带的含油气远景[J]. 石油学报, 20(2): 18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1999.02.002
[46] 寿建峰, 张惠良, 沈扬, 等, 2006. 中国油气盆地砂岩储层的成岩压实机制分析[J]. 岩石学报, 22(8): 2165-2170. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.08.006
[47] 邵龙义, 李猛, 李永红, 等, 2014. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系页岩气地质特征及控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 21(4): 311-322.
[48] 王安发, 游章隆, 1995. 川东北香溪群影响砂岩孔隙发育的成岩作用因素[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 22(2): 79-83.
[49] 王凤琴, 王宝清, 2006. 柴达木盆地北缘下侏罗统储集岩成岩作用及其对孔隙演化的影响[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 42(5): 1-6.
[50] 王学武, 杨正明, 李海波, 等, 2010. 核磁共振研究低渗透储层孔隙结构方法[J]. 西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 32(2): 69-72.
[51] 王猛, 杨永恒, 王晔桐, 等, 2019. 青海柴达木盆地北缘构造带九龙山地区侏罗系储层特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 39(2): 94-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.02.011
[52] 王猛, 耿榕悦, 马富强, 等, 2021. 柴北缘九龙山地区侏罗系成岩作用特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 21(15): 6175-6184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.15.011
[53] 仵宗涛, 孙国强, 王锋, 等, 2016. 柴北缘平台地区下干柴沟组下段碳酸盐胶结物特征及意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 36(4): 30-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2016.04.005
[54] 谢庆宾, 管守锐, 2000. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系沉积相类型及储集层评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 27(2): 40-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.02.011
[55] Xie Q B, Guan S Y. 2000. Sedimentary Facies Type and Reservoir Evaluation for the Northern Qaidam b-asin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 27(2): 40 − 44(in Chinese with English abstract).
[56] 杨永泰, 张宝民, 李伟, 等, 2000. 柴达木盆地北缘侏罗系层序地层与沉积相研究[J]. 地学前缘, 7(3): 145-151. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.03.015
[57] Yang Y T, Zhang B M, Li W, et al. , 2000. Study of Jurassic Stratigraphic Sequence and Sedimentary Facies in Norrh of Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 7(3): 145-151.
[58] 闫建萍, 刘池洋, 张卫刚, 等, 2010. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部上古生界低孔低渗砂岩储层成岩作用特征研究[J]. 地质学报, 84(2): 272-279.
[59] Yan J P, Liu C Y, Zhang W G, et al. , 2010. Diagenetic Characteristics of the Lower Porosity and Permeability Sandstones of the Upper Paleozoic in the South of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(2): 272-279.
[60] 闫占冬, 2017. 柴达木盆地北缘西段侏罗纪原型盆地研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学.
[61] Yan Z D. 2017. Study on the Jurassic Prototype Basin in the Western Part of the Northern Qaidam Basin[D], Xi’an: Northwest University(in Chinese with English abstract).
[62] 张梦林, 2012. 柴北缘苏干湖凹陷中生界源内岩性油气藏分布规律研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学.
[63] Zhang M L. 2012. A Study on the Distribution Regularity of Mesozoic Strata Within Oil Source Lithologi-c Hydrocarbon Reservoir of Suganhu Depression in North Qaidam[D], Changchun: Jilin University(in Chinese with English abstract).
[64] 张杰, 夏维民, 徐丽, 等, 2014. 柴北缘九龙山地区侏罗系致密砂岩储层成因分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 25(S1): 71-78.
[65] Zhang J, Xia W M, Xu L, et al. , 2014. Genesis of Jurassic Tight Sandstone Reservoirs of Jiulongshan Region in the Northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(S1): 71-78.
[66] 张莉, 王威, 舒志国, 等, 2019. 川东北元坝地区须家河组钙质交代—胶结致密层分布与成因[J]. 石油学报, 40(6): 692-705. doi: 10.7623/syxb201906005
[67] Zhang L, Wang W, Shu Z G, et al. , 2019. Distribution and Genesis of Calcite — Replaced and Calcite — Cemented Tight Reservoirs in Xujiahe Formation, Yuanba Area, Northeast Sichuan[J]. Acta Petrole-i Sinica, 40(6): 692-705.
[68] 张大智, 初丽兰, 周翔, 等, 2021. 松辽盆地北部徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密气储层成岩作用与成岩相特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 51(1): 22-34.
[69] Zhang D Z, Chu L L, Zhou X, et al. , 2021. Diagenesis and Diagenesis Facies of Tight Gas Reservoir of Shahezi Formation, in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression of North Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 51(1): 22-34.
[70] 郑浚茂, 应凤祥, 1997. 煤系地层(酸性水介质)的砂岩储层特征及成岩模式[J]. 石油学报, 18(4): 19-24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1997.04.004
[71] Zheng J M, Ying F X. 1997 ZHENG Reservoir Characteristics and Diagenetic Model of Sandstone Inter-calated in Coal-bearing Strata (Acid Water Medium)[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 18(4): 19 − 24(in Chinese with English abstract).
[72] 周飞, 王波, 李哲翔, 等, 2019. 柴达木盆地冷湖构造带天然气地球化学特征及成藏主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 30(10): 1496-1507. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.10.013
[73] Zhou F, Wang B, Li Z X, et al. , 2019. Geochemical Characteristics and Accumulation Elements Controllin-g the Natural Gas in Lenghu Tectonic Belts of Qaidam Basin[J], Natural Gas Geoscience. 30(10): 1496 − 1507(in Chinese with English abstract).
-




 下载:
下载: