The coupling mechanism between geomorphology of shale sedimentary and differential enrichment of shale gas in Longmaxi Formation in Changning area
-
摘要:
长宁地区下志留统龙马溪组页岩的发育过程存在空间非均质性,导致了高产能区域仅局限于个别构造单元区。通过长宁气田(地区)新获取的钻井等资料,结合龙马溪组沉积古地貌,探究不同地貌单元下的古生产力、氧化-还原环境,阐明地貌单元与页岩气富集的联系机制。结果表明:(1)长宁地区龙马溪组沉积古地貌呈现出多级隆洼相间格局,西南与东北部形成两大低幅隆起区,矿物组分空间变化所指示的物源方向与古地貌高度吻合。(2)相较于古沟谷区,古隆起区拥有更丰富的陆源营养物质供给和更高的古海洋生产力,有利于有机质优势富集,且古隆起区近物源的特性使其成为相对高石英含量的脆性区。但随着海平面降低,古隆起区的氧化作用相较于古沟谷区更强,并不利于有机质保存。(3)长宁地区龙马溪组孔隙度、TOC和含气量三者关系紧密,表明有机孔隙是优质页岩孔隙的重要组成。(4)与古沟谷区相比,古隆起区更有利于优质页岩中有机质的生烃和储存,同时也更便于后期的生产压裂。
Abstract:There are spatial heterogeneities in the development process of shale in Longmaxi Formation of Lower Silurian in Changning area, limiting high-productivity areas to specific structural units. Based on the newly obtained drilling data of Changning gas field (area), combined with the sedimentary paleogeomorphology of Longmaxi Formation, this paper explores the paleoproductivity and oxidation-reduction environment under different geomorphic units, and expounds the connection mechanism between geomorphic units and shale gas enrichment. The results show that :(1) The sedimentary palaeogeomorphology of Longmaxi Formation in Changning area presents a multi-level pattern of inter-uplift and depression, and two low amplitude uplifts are formed in the southwest and northeast. The provenance direction indicated by the spatial change of mineral composition is highly consistent with the palaeogeomorphology. (2) Compared with the ancient depression, the ancient uplift has more terrestrial nutrients and higher paleomarine productivity, which is conducive to the advantageous enrichment of organic matter. The near-source characteristic renders the ancient uplift a brittle area with relatively high quartz content. However, with the reduction of sea level, the oxidation of ancient uplift is stronger than that of ancient depression, which is not conducive to the preservation of organic matter. (3)The porosity, TOC (Total Organic Carbon content), and gas content of the Longmaxi Formation in Changning area are closely correlated, indicating that organic pores are important components of high-quality shale pores. (4) Compared to the ancient depression, the ancient uplift is more conducive to hydrocarbon generation and storage of high-quality shale organic matter, and it also facilitates later production fracturing.
-

-
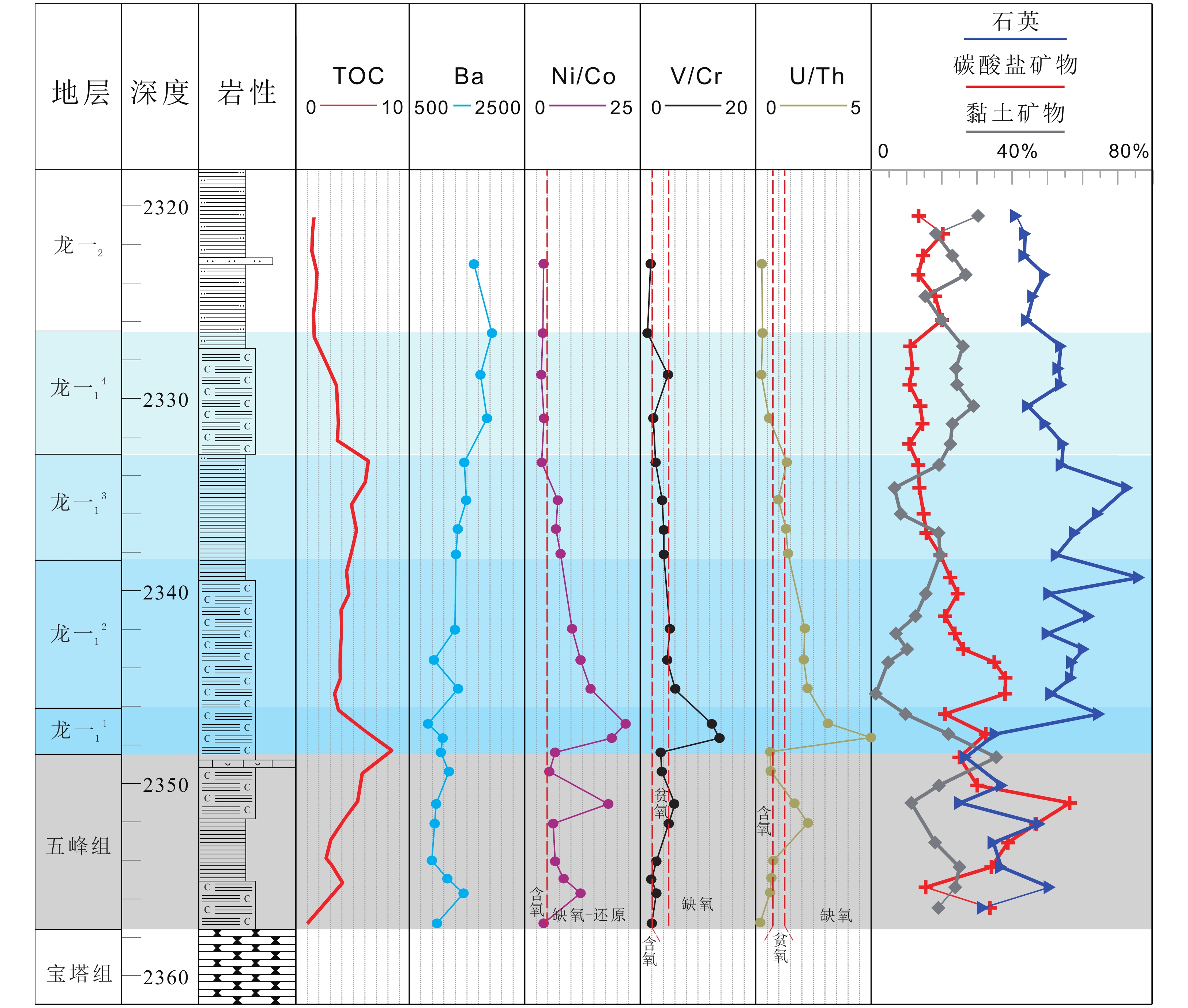
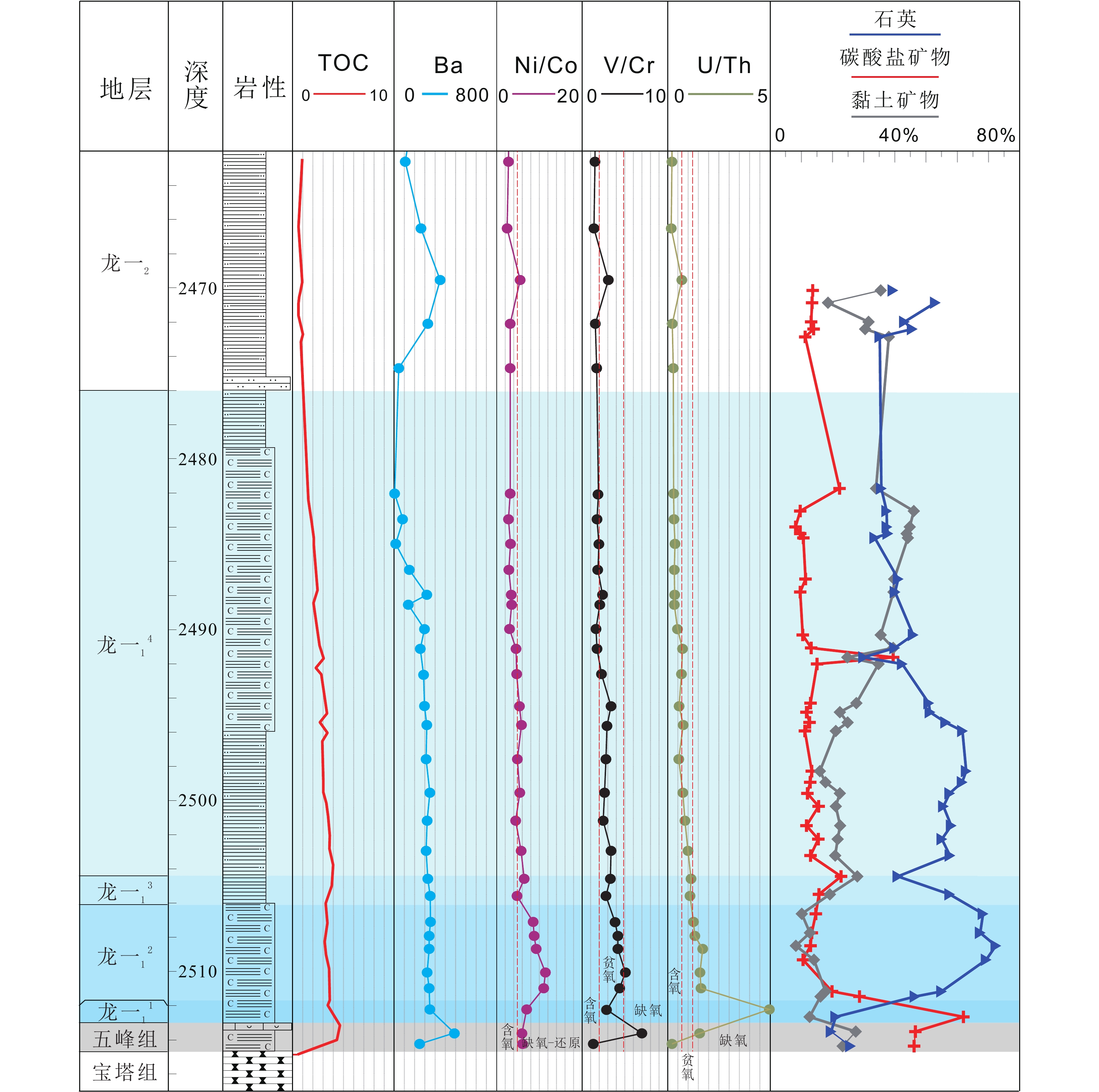
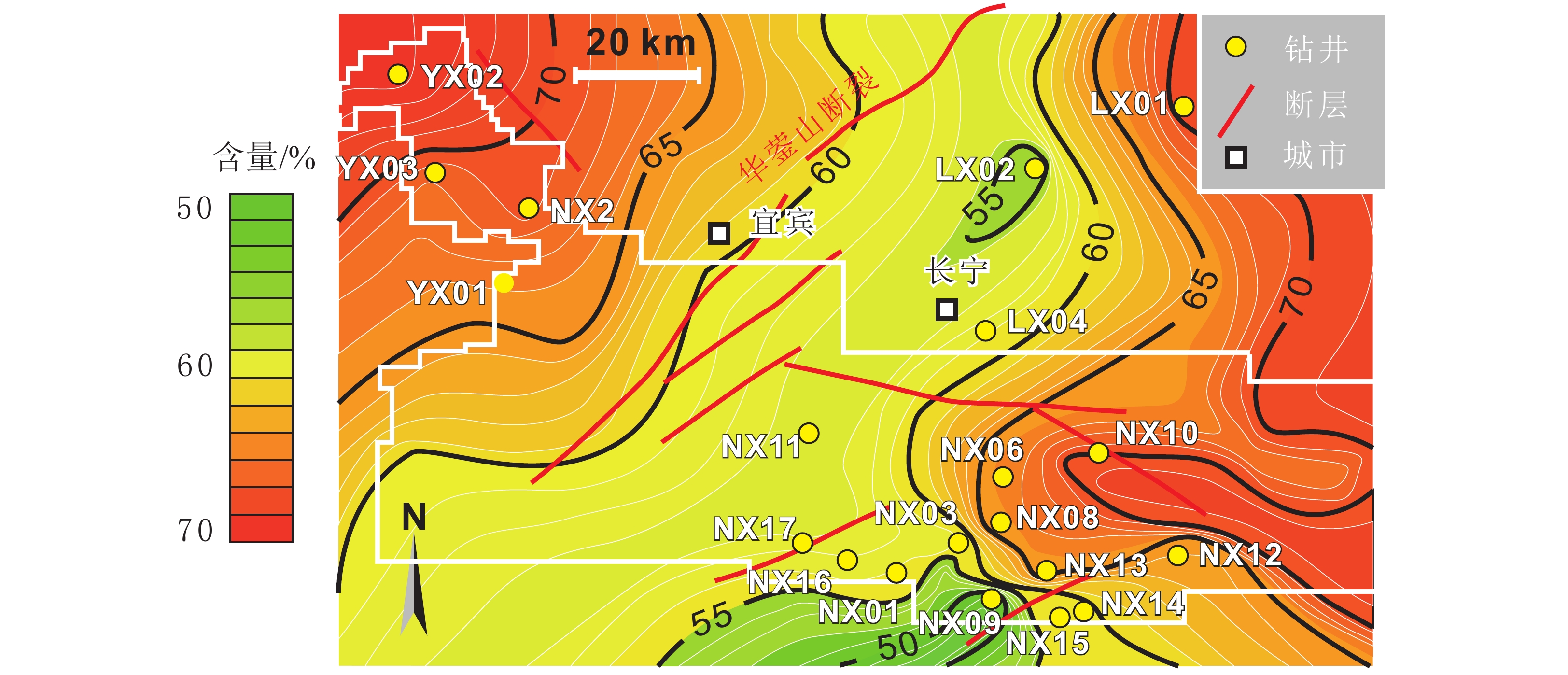
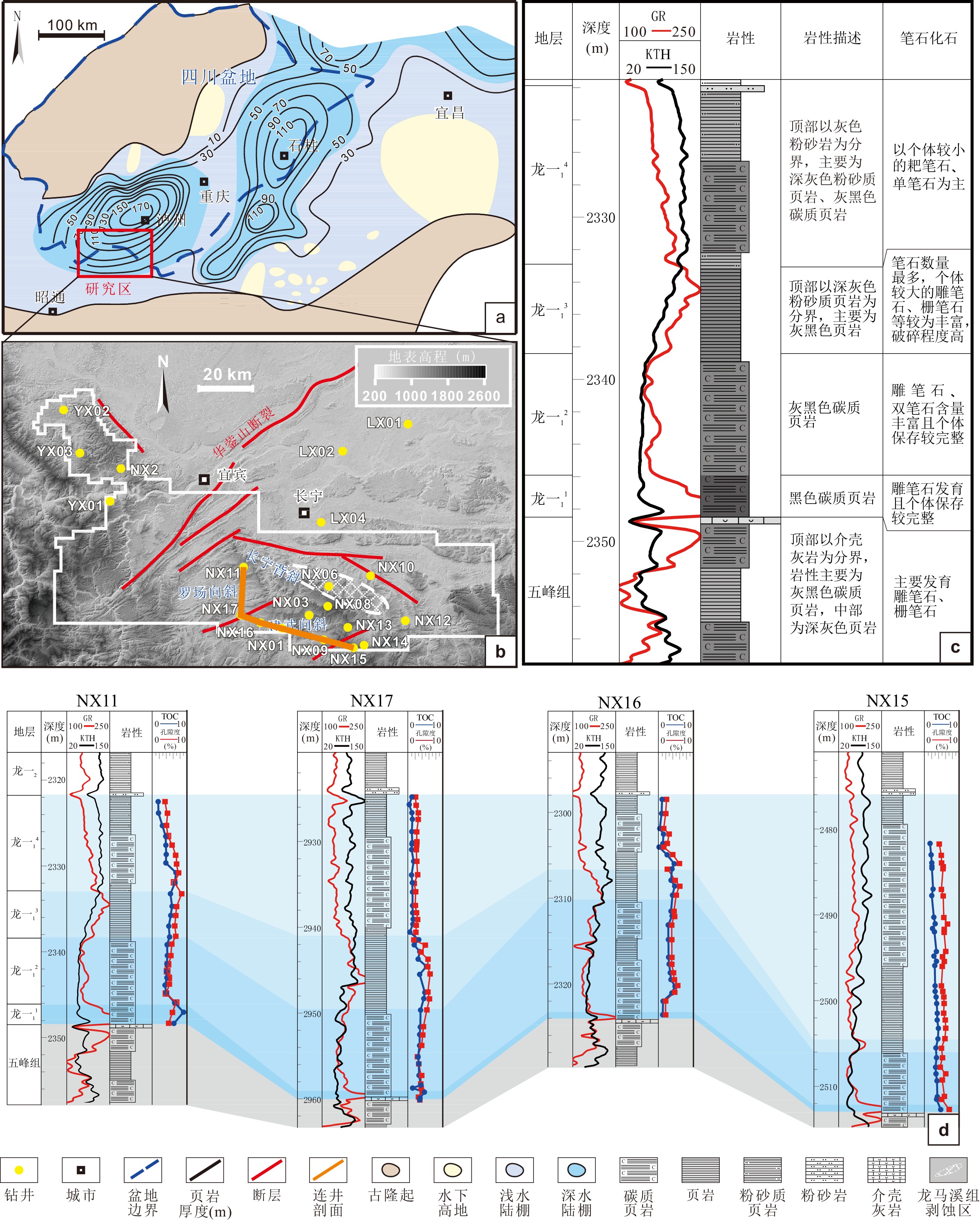
图 1 a. 上扬子地区早志留世沉积古地理简图(据聂海宽等,2017;Liu et al., 2020修改);b. 长宁地区现今构造及地貌简图(据Liu et al., 2021修改);c. 长宁地区龙一1亚段小层划分;d. NX15-NX16-NX17-NX11连井剖面(井位见图1b)
Figure 1.
-
[1] Arthur M A, Sageman B B. 1994. Marine black shales: depositional mechanisms and environments of ancient deposits[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 22(1): 499−551.
[2] Chen Y, Xu J, Wang P. 2020. Shale gas potential in China: A production forecast of the Wufeng−Longmaxi Formation and implications for future development[J]. Energy Policy, 147: 111868.
[3] 陈尚斌, 朱炎铭, 王红岩, 等. 2011. 四川盆地南缘下志留统龙马溪组页岩气储层矿物成分特征及意义[J]. 石油学报, 32(5): 775−782
Chen S B, Zhu Y M, Wang H Y, et al. , 2011. Characteristics and significance of mineral compositions of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale gas reservoir in the southern margin of Sichuan Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 32(5): 775−782.
[4] 邓旭升, 杜远生, 余文超, 等. 2020. “黔中隆起”和贵州晚古生代古地理演化及其对铝土矿的控矿作用[J]. 古地理学报, 22(5): 872−892
Deng X S, Du X S, Yu W C, et al. , 2020.‘Qianzhong Uplift’ and evolution of the Late Paleozoic palaeogeography and its control on formation of bauxite in Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 22 (5): 872−892
[5] Dong D Z, Shi Z S, Guan Q Z, et al. , 2018. Progress, challenges and prospects of shale gas exploration in the Wufeng-Longmaxi reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Nat. Gas Indust. B, 5(5): 415-424. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2018.04.011
[6] 丁文龙, 李超, 李春燕, 等. 2012. 页岩裂缝发育主控因素及其对含气性的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 19(2): 212−220
Ding W L, Li C, Li C Y, et al. , 2012. Main controlling factors of shale fracture development and their influence on gas bearing property [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(2): 212−220.
[7] 葛祥英, 牟传龙, 余谦, 等. 2021. 四川盆地东部五峰组−龙马溪组黑色页岩有机质富集规律探讨[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(3): 418−435
Ge X Y, Mou C L, Yu Q, et al. , 2021. , A study on the enrichment of organic materials in black shales of the Wufeng to Longmaxi Formations in eastern Sichuan Basin [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(03): 418−435.
[8] 耿军阳, 刘丽萍, 罗顺社, 等. 2022. 鄂尔多斯盆地环江地区侏罗系延安组古地貌特征与油气成藏规律[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发: 42(1): 23−31
Geng J Y, Liu L P, Luo S S, et al. , 2022. Paleogeomorphic characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation rules of Jurassic Yan'an Formation in Huanjiang area of Ordos Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing: 42(1): 23−31.
[9] 郭雯, 董大忠, 李明, 等. 2021. 富有机质页岩中石英的成因及对储层品质的指示意义—以四川盆地东南部及周缘龙马溪组龙一1亚段为例[J]. 天然气工业, 41(2): 65−74
Guo W, Dong D Z, Li M, et al. , 2021. Quartz genesis in organic-rich shale and its indicative significance to reservoir quality:A case study on the first submember of the first Member of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin and its periphery [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(2): 65−74.
[10] 何江林, 刘伟, 杨平, 等. 2017. 四川盆地西南缘五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气形成条件与有利区优选[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 37(3): 50−58.
[11] He J L, Liu W, Yang P, et al. , 2017. Formation conditions and favorable areas of shale gas from Wufeng Formation to Longmaxi Formation in the southwest margin of Sichuan Basin [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 37(03): 50-58.
[12] 何骁, 吴建发, 雍锐, 等. 2021. 四川盆地长宁—威远区块海相页岩气田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 42(2): 259−272
He X, Wu J F, Yong R, et al. , 2021.Accumulation conditions and key exploration and development technologies of marine shale gas field in Changning-Weiyuan block,Sichuan Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 42(2): 259−272.
[13] Jiang Z X, Tang X L, Cheng L J, et al. , 2015. Characterization and origin of the Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale multiscale heterogeneity in southeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Interpretation, 3(2): 61-74. doi: 10.1190/INT-2014-0151.1
[14] 李令, 潘仁芳, 杨依, 等. 2017. 四川盆地长宁地区志留系龙马溪组页岩孔隙特征及发育控制因素[J]. 地质学刊, 41(1): 39−45
Li L, Pan R F, Yang Y, et al. , 2017. Characteristics of pores and the controlling factors in Longmaxi Formation of Silurian Changning Area, Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Geology, 41(1): 39−45.
[15] 李桃, 杨贵来, 何伟, 等. 2021. 西昌盆地五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气保存条件研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(3): 465−476
Li T, Yang G L, He W, et al. , 2021. Preservation condition for shale gas of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Xichang Basin [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(3): 465−476.
[16] 李萧,吴礼明,王丙贤,等. 2021.渝东南地区龙马溪组构造应力场数值模拟及裂缝有利区预测[J].地质科技通报, 40(6):24-31. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0603
Li X, Wu L M, Wang B X, et al., 2021. Numerical simulation of tectonic stress field and prediction of fracture target in the Longmaxi Formation, southeastern Chongqing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 40(6): 24-31. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0603
[17] 梁霄, 徐剑良, 王滢, 等. 2021. 川南地区渐变型盆−山边界条件下龙马溪组页岩气(藏)富集主控因素: 构造−沉积分异与差异性演化[J]. 地质科学, 56(1): 60−81
Liang X, Xu J L, Wang Y, et al. , 2021. The shale gas enrichment factors of Longmaxi Formation under gradient basin-mountain boundary in South Sichuan Basin: Tectono-depositional differentiation and discrepant evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 56(1): 60−81.
[18] 刘文平, 周政, 吴娟, 等. 2020. 川南盆地长宁页岩气田五峰组−龙马溪组成藏动力学过程及其意义[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 56(3): 102−113
Liu W P, Zhou Z, Wu J, et al. , 2020. Hydrocarbon generation and shale gas accumulation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, Changning shale-gas field, Southern Sichuan Basin [J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 56(03): 102−113.
[19] Liu R, Jiang D C, Zheng J, et al. , 2021. Stress heterogeneity in the Changning shale-gas field, southern Sichuan Basin: Implications for a hydraulic fracturing strategy[J]. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 132, 105218.
[20] 刘治成, 李红佼, 张喜, 等. 2021. 川南−黔北地区下志留统龙马溪组沉积相展布及演化[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(3): 436−445
Liu Z C, Li H J, Zhang X, et al. , 2021. Distribution and evolution of sedimentary facies of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan and northern Guizhou area [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(3): 436−445.
[21] Liu R, Hao F, Engelder T, et al. , 2020. Influence of tectonic exhumation on porosity of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in the Fuling gas field of the eastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bull. 104(4), 939-959.
[22] 陆扬博, 马义权, 王雨轩, 等. 2017. 上扬子地区五峰组−龙马溪组主要地质事件及岩相沉积响应[J]. 地球科学, 42(7): 1169−1184
Lu Y B, Ma Y Q, Wang Y X, et al. , 2017. The sedimentary response to the major geological events and lithofacies characteristics of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Upper Yangtze area [J]. Earth Science, 42(7): 1169−1184.
[23] 马龙, 徐学金, 闫剑飞, 等. 2022. 古隆起边缘页岩气富集规律与选区——以雪峰西南缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(3): 426−443
Ma L, Xu X J, Yan J F, et al., 2022. Enrichment laws and regional selection of shale gas at the edge of palaeohigh: A case study on the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation on the southwestern margin of Xuefeng Uplift [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42 (03): 426−443.
[24] 马新华, 谢军. 2018. 川南地区页岩气勘探开发进展及发展前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 45(1): 161−169
Ma X H, Xie J. 2018. The progress and prospects of shale gas exploration and exploitation in southern Sichuan Basin, NW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(1): 161−169.
[25] 马新华, 谢军, 雍锐, 等. 2020. 四川盆地南部龙马溪组页岩气储集层地质特征及高产控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 47(5): 841−855
Ma X H, Xie J, Yong R, et al. , 2020. Geological characteristics and high production control factors of shale gas reservoirs in Silurian Longmaxi Formation, southern Sichuan Basin, SW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(5): 841−855.
[26] 聂海宽, 金之钧, 马鑫, 等. 2017. 四川盆地及邻区上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组底部笔石带及沉积特征[J]. 石油学报, 38(2): 160−174
Nie H K, Jin Z J, Ma X, et al. , 2017. Graptolites zone and sedimentary characteristics of Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 38(2): 160−174.
[27] Pan R F, Gong Q, Yan J, et al. , 2016. Elements and gas enrichment laws of sweet spots in shale gas reservoir: A case study of the Longmaxi Fm in Changning Block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 3(3): 195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2016.05.003
[28] Rickman R, Mullen M J, Petre J E, et al., 2008. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett Shale[R]. In SPE annual technical conference and exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 9: 115258: 23-24.
[29] Ross D J, Bustin R M. 2008. Characterizing the shale gas resource potential of Devonian–Mississippian strata in the Western Canada sedimentary basin: Application of an integrated formation evaluation[J]. AAPG bulletin, 92(1): 87−125.
[30] 戎嘉余, 陈旭, 王怿, 等. 2011. 奥陶−志留纪之交黔中古陆的变迁: 证据与启示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 41(10): 1407−1415
Rong J Y, Chen X, Wang Y, et al. , 2011. Changes of the Middle Guizhou Ancient Land at the Ordovician Silurian Transition: Evidence and Enlightenment [J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Terrae, 41(10): 1407−1415.
[31] Rybacki E, Reinicke A, Meier T, et al. , 2015. What controls the mechanical properties of shale rocks? –Part I: Strength and Young's modulus[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 135: 702-722. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.10.028
[32] Sageman B B, Murphy A E, Werne J P, et al. , 2003. A tale of shales: the relative roles of production, decomposition, and dilution in the accumulation of organic-rich strata, Middle-Upper Devonian, Appalachian basin[J]. Chemical Geology, 195(1-4): 229-273. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00397-2
[33] 施振生, 袁渊, 赵群, 等. 2022. 川南地区五峰组—龙马溪组沉积期古地貌及含气页岩特征[J]. 天然气地球科学: 33(12): 1969−1985
Shi Z S, Yuan Y, Zhao Q, et al. , 2022. Paleogeomorphology and oil-bearing shale characteristics of the Wufeng—Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan Basin, China [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience: 33(12): 1969−1985.
[34] Sone H, Zoback M D. 2013. Mechanical properties of shale−gas reservoir rocks−Part 2: Ductile creep, brittle strength, and their relation to the elastic modulus[J]. Geophysics, 78(5): 393−402.
[35] Stasiuk L D, Fowler M G. 2002. Thermal maturity evaluation (vitrinite and vitrinite reflectance equivalent) of Middle Devonian, Upper Devonian and Devonian – Mississippian strata in the Western Canada sedimentary basin[R]. Geological Survey of Canada Open−File Report, 4341: 20.
[36] 王川, 董田, 蒋恕, 等. 2021. 中扬子地区上奥陶−下志留统五峰组−龙马溪组页岩纵向非均质性及主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报: 41(3): 108−121
Wang C, Dong T, Jiang S, et al. , 2021. Vertical heterogeneity and the main controlling factors of the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in the Middle Yangtze region [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology: 41(3): 108−121.
[37] 王淑芳, 邹才能, 董大忠, 等. 2014. 四川盆地富有机质页岩硅质生物成因及对页岩气开发的意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 50(3): 476−486
Wang S F, Zou C N, Dong D Z, et al. , 2014. Biogenic silica of organic-rich shale in Sichuan Basin and its significance for shale gas [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 50(3): 476−486.
[38] Wang Y X, Xu S, Hao F, et al. , 2020. Multiscale petrographic heterogeneity and their implications for the nanoporous system of the Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in Jiaoshiba area, Southeast China[J]. Response to depositional-diagenetic process. Bulletin, 132(7-8): 1704-1721.
[39] 王玉满, 董大忠, 李新景, 等. 2015. 四川盆地及其周缘下志留统龙马溪组层序与沉积特征[J]. 天然气工业, 35(3): 12−21
Wang Y M, Dong D Z, Li X J, et al. , 2015. Stratigraphic sequence and sedimentary characteristics of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin and its peripheral areas [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 35(3): 12−21.
[40] 王玉满, 李新景, 董大忠, 等. 2017. 上扬子地区五峰组−龙马溪组优质页岩沉积主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 37(4): 9−20
Wang Y M, Li X J, Dong D Z, et al. , 2017. Main factors controlling the sedimentation of high-quality shale in Wufeng-Longmaxi Fm, Upper Yangtze region [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 37(4): 9−20.
[41] 吴建发, 赵圣贤, 范存辉, 等. 2021. 川南长宁地区龙马溪组富有机质页岩裂缝发育特征及其与含气性的关系[J]. 石油学报, 42(4): 428−446
Wu J F, Zhao S X, Fan C H, et al. , 2021. Fracture development characteristics of organic shale rich in Longmaxi Formation in Changning area, southern Sichuan and its relationship with gas bearing property [J]. Acta Petrol Sin, 42(4): 428−446.
[42] 魏祥峰, 刘若冰, 张廷山, 等. 2013. 页岩气储层微观孔隙结构特征及发育控制因素—以川南−黔北XX地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 24(5): 1048−1059
Wei X F, Liu R B, Zhang T S, et al. , 2013. Micro-pores structure characteristics and development control factors of shale gas reservoir:A case of Longmaxi Formation in XX area of southern Sichuan and northern Guizhou [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 24(5): 1048−1059.
[43] 魏志红, 魏祥峰. 2014. 页岩不同类型孔隙的含气性差异—以四川盆地焦石坝地区五峰组−龙马溪组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 34(6): 37−41
Wei Z H, Wei X F. 2014. Comparison of gas-bearing property between different pore types of shale: A case from the Upper Ordovician Wufeng and Longmaxi Fms in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(6): 37−41.
[44] 熊国庆, 刘春来, 董国明, 等. 2021. 南大巴山上奥陶统五峰组−下志留统龙马溪组泥岩元素地球化学特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(3): 398−417
Xiong G Q, Liu C L, Dong G M, et al. , 2021. A study of element geochemistry of mudstones of upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation and lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southern Daba Mountain [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(3): 398−417.
[45] 熊国庆, 周小琳, 李小刚. 2022. 米仓山−大巴山地区赫兰特期岩相古地理及其页岩气地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质: 42(3): 368-384
Xiong G Q, Zhou X L, Li X G. 2022. Hirantian lithofacies palaeogeography and their geological significance for shale gas in Micangshan-Dabashan area [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(3): 368-384
[46] 严德天, 汪建国, 王卓卓. 2009. 扬子地区上奥陶−下志留统生物钡特征及其古生产力意义[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 24(4): 16−19+108−109
Yan D T, Wang J G, Wang Z Z. 2009. Biogenetic barium distribution from the Upper Ordovician to Lower Silurian in the Yangtze area and its significance to paleoproductivity [J]. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum University (Natural Science Edition), 24 (4): 16−19+108−109.
[47] 杨宝刚, 潘仁芳, 刘龙, 等. 2015. 四川盆地长宁示范区地质条件对页岩有机质的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 15(26): 35−41+65
Yang B G, Pan R F, Liu L, et al. , 2015. The Influence of Geological Condition of Sichuan Basin Changning Demonstration Area on the Development of Organic Matters in Shale [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 15(26): 35−41+65.
[48] 于雷, 施泽进, 李恕军, 等. 2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴旗油区早侏罗世古地貌特征与油气富集关系[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 34(1): 31−35
Yu L, Shi Z J, Li S J, et al. , 2014. Palaeogeomorphological features and their bearings on the hydrocarbon accumulation in the Wuqi oil field, Ordos Basin during the Lower Jurassic[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 34(1): 31−35.
[49] Yu T, Liu H, Liu B, et al., 2022. Restoration of karst paleogeomorphology and its significance in petroleum geology—Using the top of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the northwestern Sichuan Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 208: 109638.
[50] 曾靖珂, 潘仁芳, 金晓凡, 等. 2016. 页岩储层非均质性分析: 以四川长宁地区下志留统龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 23(2): 146−150
Zeng J K, Pan R F, Jin X F, et al. , Research of shale reservoir heterogeneity:a case of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Changning Area, Sichuan Basin [J]. Fault−Block Oil and Gas Field, 2016, 23(2): 146−150.
[51] 张福, 黄艺, 蓝宝锋, 等. 2021. 正安地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 196(1): 49−56
Zhang F, Huang Y, Lan B F, et al. , 2021. Characteristics and controlling factors of shale reservoir in Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation of the Zheng'an area [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 196(1): 49−56.
[52] Zhang S, Jin Q, Hu M, et al. , 2021. Differential structure of Ordovician karst zone and hydrocarbon enrichment in paleogeomorphic units in Tahe area, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(5): 1113-1125. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(21)60095-2
[53] 赵圣贤, 杨跃明, 张鉴, 等. 2016. 四川盆地下志留统龙马溪组页岩小层划分与储层精细对比[J]. 天然气地球科学, 27(3): 470−487
Zhao S X, Yang Y M, Zhang J, et al. , 2016. Micro-layers division and fine reservoirs contrast of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale,Sichuan Basin,SW China [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 27(3): 470−487.
-



 下载:
下载: