Sedimentary environment and shale gas exploration potential of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in northern Guizhou
-
摘要:
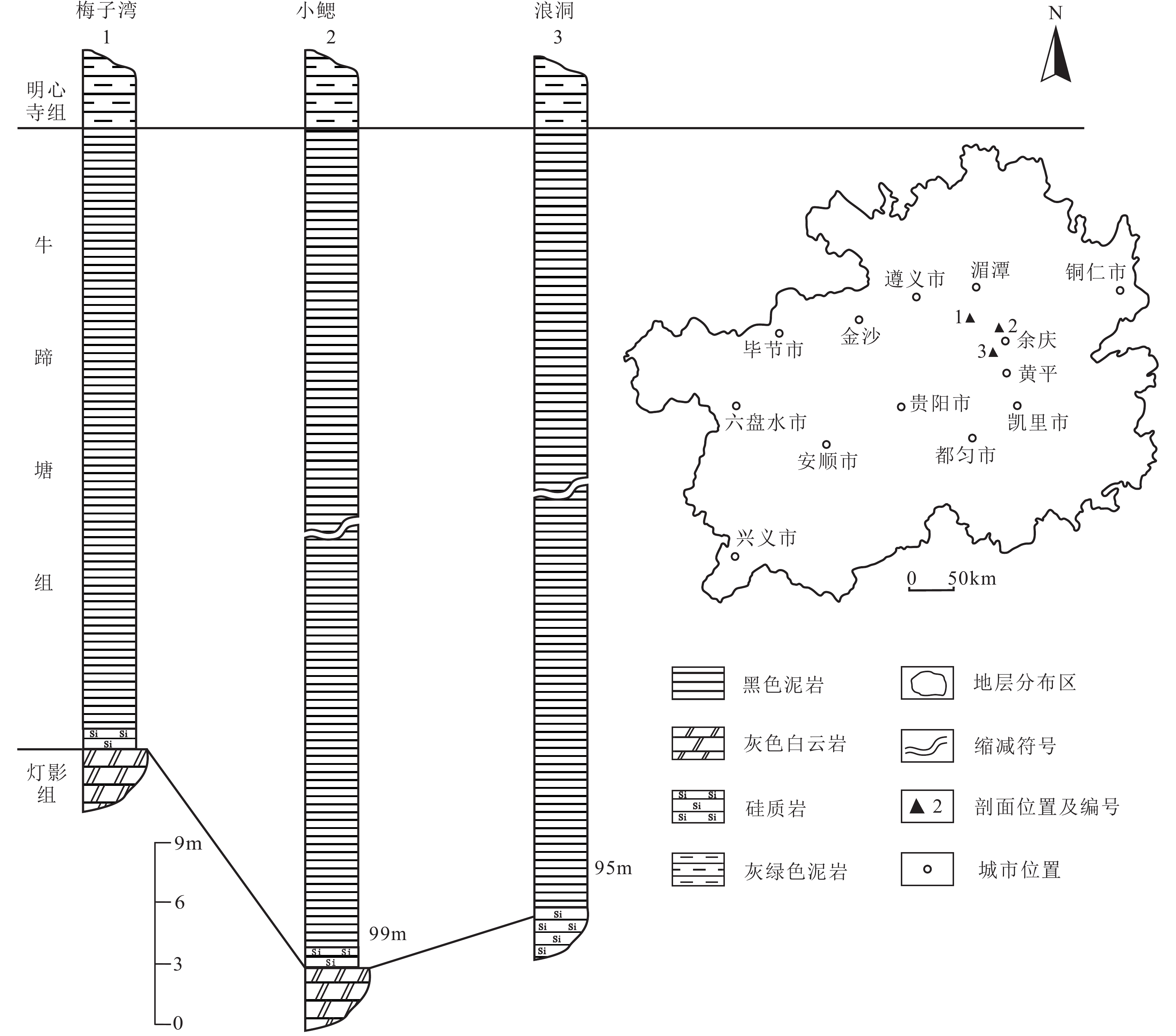
寒武系下统牛蹄塘组是中国南方海相碳质页岩赋存的主要层位之一,在贵州北部、中部及东部广泛分布,层位稳定。牛蹄塘组以黑色炭质泥岩为主,岩层多为薄层状,具水平层理,其组分主要为黏土矿物、石英及少量的碳质组分和黄铁矿。与澳大利亚后太古代页岩(PAAS)平均值相比,泥岩V、Mo、U含量较高,而Co、Cu、Zn和Th含量较低。V/Cr、Ni/Co、U/Th、V/(V+Ni)的元素比值以及AU含量表明,牛蹄塘组黑色泥岩沉积环境呈缺氧还原状态。样品(La/Yb)N值明显大于1,轻、重稀土元素分异程度较大,指示沉积速率较低。有机质丰度较高,有机质成熟度为高—过成熟阶段,脆性矿物含量较高,有效厚度约为30~100 m。综上,黔北牛蹄塘组黑色泥岩存在形成页岩气藏的较好物质条件,具有良好的页岩气勘探潜力。
Abstract:The Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation is one of the major marine carbonaceous shale horizons in southern China, which is widely distributed in northern, central and eastern Guizhou with stable horizons. The Niutitang Formation is mainly composed of black carbonaceous mudstone, which is thin-bedded and horizontally bedded. Its components are mainly clay minerals, quartz and a small amount of carbonaceous components and pyrite. Compared with the mean values of Australian Post-Archean Shale (PAAS), the contents of V, Mo, and U in the mudstone of Niutitang Formation are higher, while the contents of Co, Cu, Zn, and Th are lower. The content of AU, as well as the element content ratios of V/Cr, Ni/Co, U/Th, and V/(V+Ni) indicate that the sedimentary environment of the black mudstone in the Niutitang Formation is in a state of hypoxia reduction. The (La/Yb)N ratio is significantly greater than 1, with a large degree of differentiation between light rare earth elements and heavy rare earth elements, indicating a low deposition rate. The TOC abundance of the mudstone in the Niutitang Formation is high, at the stage of high maturity to over maturity, with a high content of brittle minerals, and an effective thickness of approximately 30 to 100 meters. In conclusion, the black mudstone of the Niutitang Formation in northern Guizhou Province possesses good material conditions for the formation of shale gas reservoirs, indicating its promising potential for shale gas exploration.
-
Key words:
- Niutitang Formation /
- shale gas /
- sedimentary environment /
- exploration potential /
- northern Guizhou
-

-
[1] Algeo T J, Tribovillard N, 2009. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum-uranium covariation[J]. Chemical Geology, 268(3-4): 211-225. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.001
[2] Bowker K A, 2003. Recent development of the Barnett Shale play, Fort Worth Basin[J]. West Texas Geological Society Bulletin, 42(6): 4-11.
[3] Boyer C, Kieschnick J, Suarez R R, et al. , 2006. Producing gas from its source[J]. Oilfield Review, 18: 36-49.
[4] Calvert S E, Pedersen T F, 1993. Geochemistry of Recent oxic and anoxic marine sediments: Implications for the geological record[J]. Marine Geology, 113(1-2): 67-88. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90150-T
[5] Chaillou G, Anschutz P, Lavaux G, et al. , 2002. The distribution of Mo, U, and Cd in relation to major redox species in muddy sediments of the Bay of Biscay[J]. Marine Chemistry, 80(1): 41-59. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(02)00097-X
[6] 常华进, 储雪蕾, 冯连君, 等, 2009. 氧化还原敏感微量元素对古海洋沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 地质论评, 55(1): 91-99
Chang H J, Chu X L, Feng L J, et al. , 2009. Redox Sensitive Trace Elements as Paleoenvironments Proxies[J]. Geological Review, 55(1): 91-99
[7] 陈兰, 钟宏, 胡瑞忠, 等, 2006. 黔北早寒武世缺氧事件: 生物标志化合物及有机碳同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报, 22(9): 2413-2423.
Chen L, Zhong H, Hu R Z, et al. , 2006. Early Cambrian oceanic anoxic event in northern Guizhou: biomarkers and organic carbon isotope[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(9): 2413-2423.
[8] 陈衍景, 邓健, 胡桂兴, 1996. 环境对沉积物微量元素含量和配分型式的制约[J]. 地质地球化学, 24(3): 97-105
Chen Y J, Deng J, Hu G X, 1996. Environmental constraints on the content and distribution patterns of trace elements in sediments[J]. Earth and Environment, 24(3): 97-105
[9] 戴传固, 郑启钤, 陈建书, 等, 2013. 贵州雪峰—加里东构造旋回期成矿地质背景研究[J]. 地学前缘, 20(6): 219-225
Dai C G, Zheng Q Q, Chen J S, et al. , 2013. The metallogenic geological background of the Xuefeng-Caledonian tectonic cycle in Guizhou, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(6): 219-225
[10] Ding X J, Liu G D, Zha M, et al. , 2015. Relationship between total organic carbon content and sedimentation rate in ancient lacustrine sediments, a case study of Erlian Basin, northern China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 149: 22−29
[11] 董大忠, 程克明, 王玉满, 等, 2010. 中国上扬子区下古生界页岩气形成条件及特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 31(3): 288-299+308
Dong D Z, Cheng K M, Wang Y M, et al. , 2010. Forming conditions and characteristics of shale gas in the Lower Paleozoic of the Upper Yangtze region, China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 31(3): 288-299+308
[12] 付勇, 周文喜, 王华建, 等, 2021. 黔北下寒武统黑色岩系的沉积环境与地球化学响应[J]. 地质学报, 95(2): 536-548
Fu Y, Zhou W X, Wang H J, et al. , 2021. The relationship between environment and geochemical characteristics of black rock series of Lower Cambrian in northern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(2): 536-548
[13] 刚文哲, 林壬子, 2011. 应用油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
Gang W Z, Lin R Z, 2011. Hydrocarbon Geochemistry Application[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press.
[14] 高波, 刘忠宝, 舒志国, 等, 2020. 中上扬子地区下寒武统页岩气储层特征及勘探方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 41(2): 284-294 doi: 10.11743/ogg20200205
Gao B, Liu Z B, Shu Z G, et al. , 2020. Reservoir characteristics and exploration of the Lower Cambrian shale gas in the Middle-Upper Yangtze area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(2): 284-294 doi: 10.11743/ogg20200205
[15] Ge M N, Chen K, Chen X L, et al. , 2020. The influence factors of gas-bearing and geological characteristics of Niutitang Formation shale in the southern margin of Xuefeng Mountain ancient uplift: A case of Well Huangdi 1[J]. China Geology, 3(04): 533-544. doi: 10.31035/cg2020072
[16] Gromet L P, Dymek R F, Haskin L A, et al. , 1984. The“North American shale composite”: Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(12): 2469-2482. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9
[17] 郭慧, 王延斌, 张崇崇, 等, 2015. 贵州下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏条件与有利区分析[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 34(4): 491-497
Guo H, Wang Y B, Zhang C C, et al. , 2015. Reservoir forming condition and favorable zones of shale gas in Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Guizhou[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic university(Natural Science), 34(4): 491-497
[18] Hatch J R, Levevthal J S, 1992. Relationship between inferred redox potential of depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U. S. A[J]. Chemical Geology, 99: 65-82. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-Y
[19] 何德军, 陈洪德, 钱利军, 2013. 新场地区须二段泥岩稀土元素地球化学特征及意义[J]. 断块油气田, 20(2): 157-161
He D J, Chen H D, Qian L J, 2013. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements and its geological signification for mudstones of the second member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang Area[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 20(2): 157-161
[20] 何金先, 段毅, 张晓丽, 等, 2011. 渝南—黔北地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏的生烃条件[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 27(7): 34-40
He J X, Duan Y, Zhang X L, et al. , 2011. Hydrocarbon generation conditions of the shale in Niutitang Formation of Lower Cambrian, southern Chongqing ang northern Guizhou[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 27(7): 34-40
[21] Hiroto K, Yoshio W, 2001. Oceanic anoxia at the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary[J]. Geology, 29(11): 995-998. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0995:OAATPC>2.0.CO;2
[22] 贾智彬, 侯读杰, 孙德强, 等, 2018. 贵州地区牛蹄塘组底部烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 29(7): 1031-1041
Jia Z B, Hou D J, Sun D Q, et al. , 2018. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, Guizhou Province[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 29(7): 1031-1041
[23] 姜呈馥, 王香增, 张丽霞, 等, 2013. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组长7段陆相页岩气地质特征及勘探潜力评价[J]. 中国地质, 40(6): 1880-1888
Jiang C F, Wang X Z, Zhang L X, et al. , 2013. Geological characteristics of shale and exploration potential of continental shale gas in 7th member of Yanchang Formation, southeast Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 40(6): 1880-1888
[24] Jin C S, Li C, Algeo T J, et al. , 2020. Controls on organic matter accumulation on the early-Cambrian western Yangtze Platform, South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 111(C): 75-87.
[25] 久凯, 丁文龙, 李玉喜, 等, 2012. 黔北地区构造特征与下寒武统页岩气储层裂缝研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 23(4): 797-803
Jiu K, Ding W L, Li Y X, et al. , 2012. Structural features in northern Guizhou area and reservoir fracture of Lower Cambrian shale gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 23(4): 797-803
[26] Jones B, Manning D A C, 1994. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of paleoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 111: 111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
[27] 李俊良, 谢瑞永, 游君君, 等, 2012. 贵州黔北地区页岩气成藏条件与勘探前景[J]. 中国矿业, 21(2): 55-59 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2012.02.016
Li J L, Xie R Y, You J J, et al. , 2012. Reservoir forming condition and exploration prospect of shale-gas in Guizhou qianbei area[J]. China Mining Magazine, 21(2): 55-59 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2012.02.016
[28] 李娟, 于炳松, 张金川, 等, 2012. 黔北地区下寒武统黑色页岩储层特征及其影响因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 33(3): 364-374
Li J, Yu B S, Zhang J C, et al. , 2012. Reservoir characteristics and their influence factors of the Lower Cambrian dark shale in northern Guizhou[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 33(3): 364-374
[29] 刘江斌, 李文厚, 任战利, 等, 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地泾川地区三叠系延长组烃源岩特征及其沉积环境[J]. 地质科学, 55(4): 989-1000 doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2020.060
Liu J B, Li W H, Ren Z L, et al. , 2020. Characteristics and sedimentary environment of the hydrocarbon source rock of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in Jingchuan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 55(4): 989-1000 doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2020.060
[30] 卢树藩, 陈厚国, 2017. 黔南地区麻页1井寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩特征及页岩气勘探前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 22(3): 81-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.010
Lu S F, Chen H G, 2017. Shale characteristics and shale gas exploration prospect in Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Well MY-1, southern Guizhou[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 22(3): 81-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.010
[31] 吕艳南, 张金川, 张鹏, 等, 2015. 黔西北下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏条件与有利勘探区预测[J]. 海相油气地质, 20(2): 37-44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.02.006
Lü Y N, Zhang J C, Zhang P, et al. , 2015. Gas Accumulation Conditions of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Shale and Prediction of Potential Zones in Northwestern Guizhou[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 20(2): 37-44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.02.006
[32] 罗超, 刘树根, 孙玮, 等, 2014. 上扬子区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气基本特征研究—以贵州丹寨南皋剖面为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 25(3): 453-470
Luo C, Liu S G, Sun W, et al. , 2014. Basic characteristics of shale gas in the Upper Yangtze Region: Taking Nangao section in Danzhai as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(3): 453-470
[33] 国家能源局, 1996. 透射光—荧光干酪根显微组分鉴定及类型划分方法: SY/T 5125—1996[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
National Energy Administration, 1996. Identification and classification of transmitted light−fluorescent kerogen macerals: SY/T 5125−1996[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press.
[34] 聂海宽, 张金川, 包书景, 等, 2012. 四川盆地及其周缘上奥陶统—下志留统页岩气聚集条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 33(3): 335-345
Nie H K, Zhang J C, Bao S J, et al. , 2012. Shale gas accumulation conditions of the Upper Ordovician - Lower Silurian in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 33(3): 335-345
[35] 宁凡, 2021. 黔北地区牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏规律及开采技术分析[J]. 科技与创新, (24): 108-110
Ning F, 2021. Shale gas accumulation rule and exploitation technology analysis of Niutitang Formation in northern Guizhou area[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, (24): 108-110
[36] 宁诗坦, 夏鹏, 郝芳, 等, 2021. 贵州牛蹄塘组黑色页岩岩相划分及岩相—沉积环境—有机质耦合关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 32(9): 1297-1307 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2021.02.013
Ning S T, Xia P, Hao F, et al. , 2021. Shale facies and its relationship with sedimentary environment and organic matter of Niutitang black shale, Guizhou Province[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 32(9): 1297-1307 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2021.02.013
[37] 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等, 2009. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 36(1): 1-16+255+17-28
Pan G T, Xiao Q H, Lu S N, et al. , 2009. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 36(1): 1-16+255+17-28
[38] 潘继平, 2019. 中国非常规天然气开发现状与前景及政策建议[J]. 国际石油经济, 27(02): 51-59.
Pan J P, 2019. Status quo,prospects and policysuggestions for unconventional natural gas E&DinChina[J]. International PetroleumEconomics, 27(02): 51-59 (inChinese withEnglishabstract).
[39] 彭安钰, 2017. 贵州黔北地区页岩气的勘探前景[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 37(10): 67-69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2017.10.032
Peng A Y, 2017. Exploration prospect of shale gas in the northern Guizhou area, Guizhou Province[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standards and Quality, 37(10): 67-69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2017.10.032
[40] Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C, 2000. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 51(3): 507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
[41] 秦川, 余谦, 刘伟, 等, 2016. 黔北地区龙马溪组富有机质泥岩储层特征与勘探前景[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 40(5): 86-93+9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.05.010
Qin C, Yu Q, Liu W, et al. , 2016. Reservoir characteristics and exploration prospect of organic-rich mudstone, Longmaxi Formation in northern Guizhou[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 40(5): 86-93+9 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.05.010
[42] Taylor S R, McLennan S M, 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
[43] 腾格尔, 刘文汇, 徐永昌, 等, 2004. 缺氧环境及地球化学判识标志的探讨—以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报, 22(2): 365-372
Teng G E, Liu W H, Xu Y C, et al. , 2004. The Discussion on Anoxic Environments and Its Geochemical Identifying Indices[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 22(2): 365-372
[44] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. , 2006. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update[J]. Chemical Geology, 232: 12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
[45] 王丽波, 久凯, 曾维特, 等, 2013. 上扬子黔北地区下寒武统海相黑色泥页岩特征及页岩气远景区评价[J]. 岩石学报, 29(9): 3263-3278
Wang L B, Jiu K, Zeng W T, et al. , 2013. Characteristics of Lower Cambrian marine black shales and evaluation of shale gas prospective area in Qianbei area, Upper Yangtze region[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9): 3263-3278
[46] 王宁, 许锋, 王喆, 等, 2020. 上扬子地台北缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组海相页岩气地质条件及勘探潜力[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 42(3): 329-341
Wang N, Xu F, Wang Z, et al. , 2020. Geological conditions and exploration potential of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation marine-facies shale gas in the northern margin of Upper Yangtze platform, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 42(3): 329-341
[47] Wang Y F, Zhai G Y, Liu G H, et al. , 2021. Geological Characteristics of Shale Gas in Different Strata of Marine Facies in South China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 32(4): 725-741. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1104-5
[48] Wignall P B, 1994. Black Shales. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 45−89.
[49] Wright J, Schrader H, Holser W T, 1987. Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite[J]. Geochemica et Cosmochimica Acta, 51: 631-644. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90075-5
[50] 郗兆栋, 唐书恒, 王静, 等, 2018. 中国南方海相页岩气选区关键参数探讨[J]. 地质学报, 92(6): 1313-1323 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.014
Xi Z D, Tang S H, Wang J, et al. , 2018. Evaluation parameters study of selecting favorable shale gas areas in southern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(6): 1313-1323 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.014
[51] 夏威, 于炳松, 王运海, 等, 2017. 黔北牛蹄塘组和龙马溪组沉积环境及有机质富集机理——以RY1井和XY1井为例[J]. 矿物岩石, 37(3): 77-89
Xia W, Yu B S, Wang Y H, et al. , 2017. Study on the depositional environment and organic accumulation mechanism in the Niutitang and Longmaxi Formation, northern Guizhou Province: A case study of well Renye 1 and well Xiye 1[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 37(3): 77-89
[52] 杨长清, 2016. 黔中隆起及周缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气勘探前景[J]. 矿产与地质, 30(4): 640-645 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2016.04.020
Yang C Q, 2016. Shale gas exploration potential of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Qianzhong Uplift and its periphery[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 30(4): 640-645 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2016.04.020
[53] 杨瑞东, 程伟, 周汝贤, 2012. 贵州页岩气源岩特征及页岩气勘探远景分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 23(2): 340-347
Yang R D, Cheng W, Zhou R X, 2012. Characteristics of organic-rich shale and exploration area of shale gas in Guizhou Province[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 23(2): 340-347
[54] Yeasmin R, Chen D Z, Fu Y, et al. , 2017. Climatic-oceanic forcing on the organic accumulation across the shelf during the Early Cambrian (Age 2 through 3) in the mid-upper Yangtze Block, NE Guizhou, South China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 134: 365-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.08.019
[55] 易同生, 赵霞, 2014. 贵州下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩储层特征及其分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, 34(8): 8-14
Yi T S, Zhao X, 2014. Characteristics and distribution patterns of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale reservoirs in Guizhou, China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(8): 8-14
[56] 张大权, 邹妞妞, 杜威, 等, 2022. 黔北凤冈地区海相牛蹄塘组页岩气成藏地质特征及评价[J]. 天然气地球科学, 02(14): 1-17
Zhang D Q, Zou N N, Du W, et al. , 2022. Geological features and evaluation of Niutitang Formation shale gas in Fenggang Block, Northern Guizhou[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 02(14): 1-17
[57] 张金川, 史淼, 王东升, 等, 2021. 中国页岩气勘探领域和发展方向[J]. 天然气工业, 41(8): 69-80
Zhang J C, Shi M, Wang D S, et al. , 2021. Fields and directions for shale gas exploration in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(8): 69-80
[58] 张鹏, 黄宇琪, 张金川, 等, 2019. 黔西北寒武系牛蹄塘组与志留系龙马溪组页岩生烃和储集能力差异分析[J]. 海相油气地质, 24(3): 83-90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.03.010
Zhang P, Huang Y Q, Zhang J C, et al. , 2019. Difference analysis of hydrocarbon generation and reservoir capacity between the Cambrian Niutitang Formation and the Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Northwest Guizhou[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 24(3): 83-90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.03.010
[59] 张素荣, 董大忠, 廖群山, 等, 2021. 四川盆地南部深层海相页岩气地质特征及资源前景[J]. 天然气工业, 41(9): 35-45
Zhang S R, Dong D Z, Liao Q S, et al. , 2021. Geological characteristics and resource prospect of deep marine shale gas in the southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(9): 35-45
[60] 张位华, 姜立君, 高慧, 等, 2003. 贵州寒武系底部黑色硅质岩成因及沉积环境探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 22(2): 174-178 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.02.020
Zhang W H, Jiang L J, Gao H, et al. , 2003. Study on Sedimentary Environment and Origin of Black Siliceous Rocks of the Lower Cambrian in Giuzhou Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 22(2): 174-178 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.02.020
[61] 赵磊, 贺永忠, 杨平, 等, 2015. 黔北下古生界烃源层系特征与页岩气成藏初探[J]. 中国地质, 42(6): 1931-1943
Zhao L, He Y Z, Yang P, et al. , 2015. Characteristics of Lower Palaeozoic hydrocarbon source strata and a primary study of the shale gas accumulation in northern Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 42(6): 1931-1943
-



 下载:
下载:


