Development characteristics, distribution patterns and favorable exploration zones of Permian reef shoals in Sichuan Basin
-
摘要:
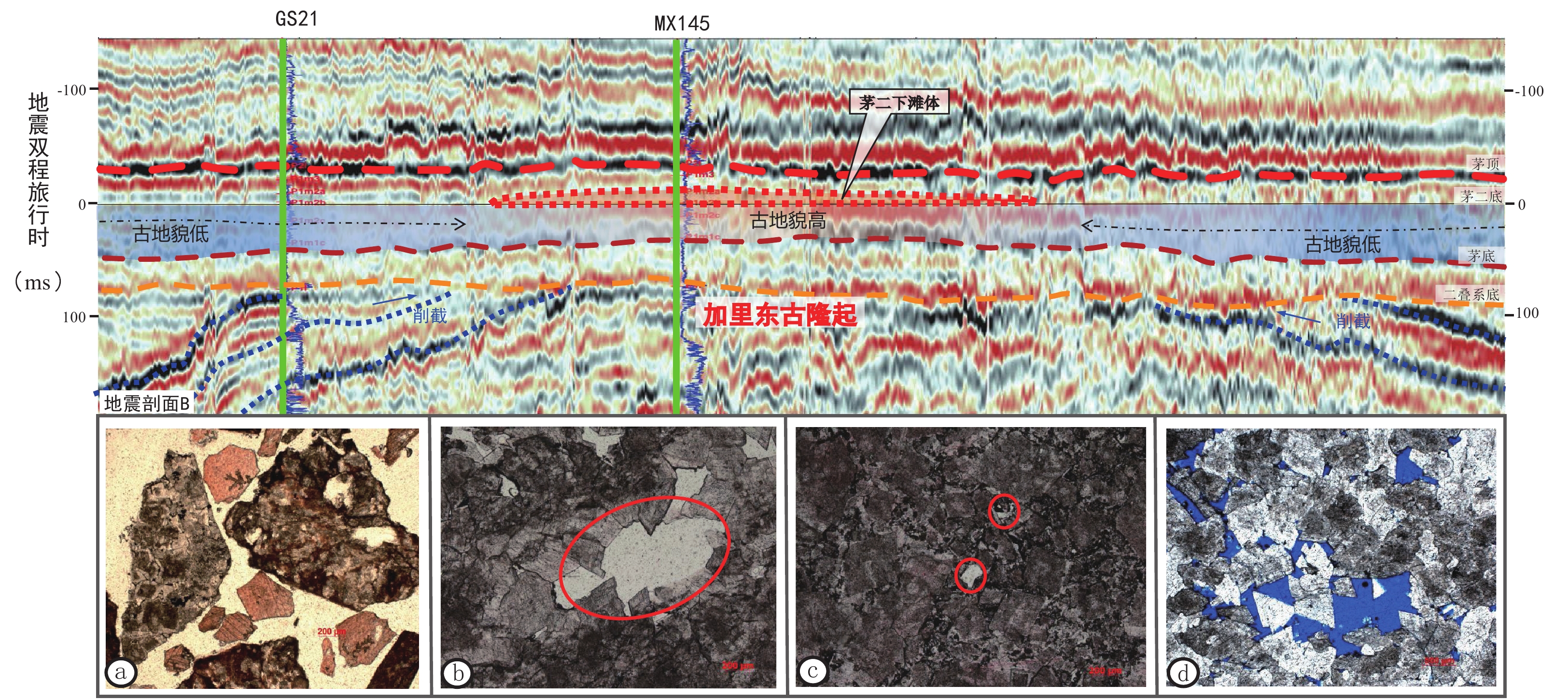
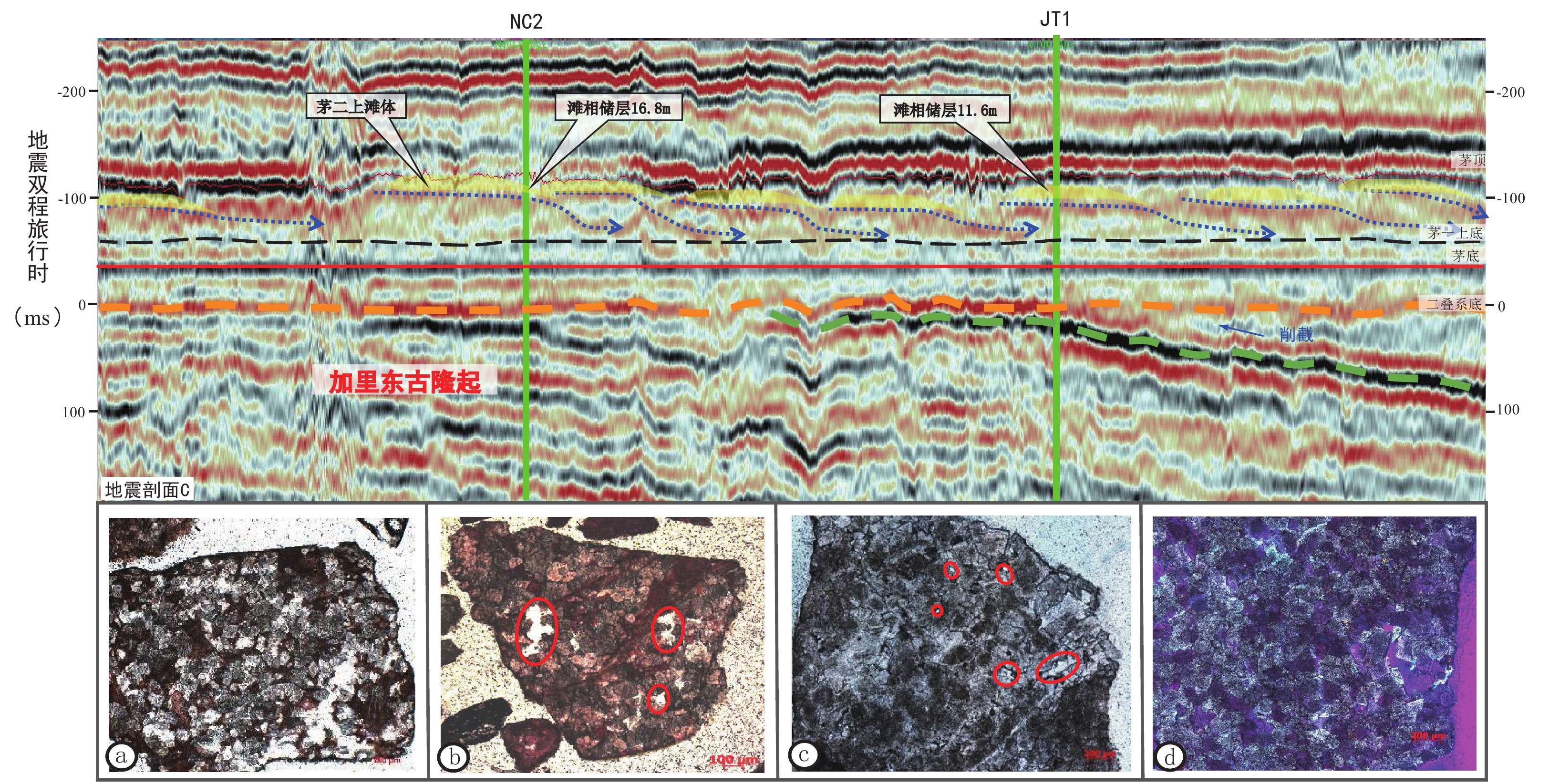
围绕四川盆地二叠纪开江-梁平海槽的台缘礁滩相勘探已获得巨大成功,但近十年勘探进入瓶颈期。为进一步深化二叠纪礁滩认识、取得规模性勘探新突破,本文以钻测井、地震及地质资料为基础,系统开展了二叠纪构造-沉积演化特征及礁滩分布规律研究,明确了下一步礁滩勘探的有利区带。研究表明:(1)栖霞期台内滩受加里东末期阶梯状环形侵蚀地貌控制,其台内滩表现出早、中、晚三期环带状展布的特点,川北九龙山—龙岗地区、蜀南宜宾—内江地区栖二段晚期环形台内滩成藏条件优越,勘探程度低,是下一步的重要勘探方向;(2)茅二段沉积期是二叠纪沉积格局转换的关键时期,茅二下亚段沉积受加里东古隆残留地貌控制,台内滩仍呈环带状分布,至茅二上亚段古地貌受峨眉地幔柱隆升活动影响,有利相带转变为北西-南东向“条带状”展布特征,磨溪北斜坡地区茅二上亚段台缘滩是茅口组重要的接替领域;(3)长兴期台缘礁向开江-梁平海槽内迁移形成多排礁滩体,具有优越的源储配置条件,是二叠系新的潜在勘探领域。
Abstract:The exploration of carbonate rocks around the Permian Kaijiang-Liangping trough in the Sichuan Basin has achieved great success, but exploration has entered a bottleneck period in the past decade. In order to further deepen the understanding of Permian reef shoals and achieve new breakthroughs in large-scale exploration, based on drilling, logging, seismic, and geological data, a systematic study has been carried out on the Permian tectonic-sedimentary evolution characteristics and the distribution patterns of Permian reef shoals, and the favorable zones for further reef shoals exploration have been identified. Research shows that: (1) The shoal in the Qixia Formation tableland is controlled by the late Caledonian ladder-like annular erosion, featuring a ring-like distribution in the early, middle, and late stages. The Jiulong Mountain–Longgang region in northern Sichuan and the Yibin–Neijiang region in southern Sichuan have good conditions for the inner shoal formation of the ring-like tableland in the late stage of the second member of the Qixia Formation, with a low degree of exploration, needing further exploration in the next step. (2) The second stage of the Maokou Formation is the key period for the transformation of the sedimentary pattern of the Permian system. The sedimentation of the lower sub-member of the Maokou Formation was controlled by the residual landform of the Caledonian paleo-uplift, thus, the inner shoal is distributed in a ring belt. The ancient landform of the area to the upper sub-member of the Maokou Formation was affected by the uplift of the Emei mantle plume, so, the favorable sedimentary facies transformed into a "strip-like" distribution pattern trending northwest-southeast. The platform margin shoal of the upper sub-member of the Maokou Formation in the north slope region of Moxi is a major successor area of the Maokou Formation. (3) The platform margin reef shoals of the Changxing Formation migrated into the Kaijiang-Liangping trough to form multiple rows of reef shoals, which have superior source and reservoir distribution conditions, being a potential exploration area of the Permian system.
-

-
图 1 四川盆地区域构造位置图(据魏国齐等,2019)
Figure 1.
-
[1] Campbell I H, Griffiths RW, 1990. Implications of mantle plume structure for the evolution of flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 99(1/2): 79-93.
[2] 陈轩, 赵文智, 张利萍, 等, 2012. 川中地区中二叠统构造热液白云岩的发现及其勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 33(4): 562-569 doi: 10.7623/syxb201204004
Chen X, Zhao W Z, Zhang L P, et al. , 2012. Discovery and exploration significance of structure-controlled hydrothermal dolomites in the Middle Permian of the central Sichuan Basin[J]. ACTA Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 33(4): 562-569. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204004
[3] 程锦翔, 郭彤楼, 谭钦银, 等, 2011. 川东北宣汉-达县地区长兴组-飞仙关组礁滩储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 31(3): 64-70 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2011.03.011
Cheng J X, Guo T L, Tan Q Y, et al. , 2011. Characteristics and controlling factors of the reef shoal reservoirs from the Changxing Formation-Feixianguan Formation in the Xuanhan-Daxian zone, northeastern Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 31(3): 64-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2011.03.011
[4] Cox K G, 1989. The role of mantle plumes in the development of continental drainage patterns[J]. Nature, 342(6252): 873-877. doi: 10.1038/342873a0
[5] 郝毅, 周进高, 张建勇, 等, 2013. 川西北中二叠统栖霞组白云岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 33(1): 68-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2013.01.011
Hao Y, Zhou J G, Zhang J Y, et al. , 2013. The dolostone reservoirs from the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin: Characteristics and controlling factors[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 33(1): 68-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2013.01.011
[6] He B, Xu Y G, Chung S L et al. , 2003. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 213(3/4): 391-395.
[7] 胡东风, 王良军, 黄仁春, 等, 2019. 四川盆地东部地区中二叠统茅口组白云岩储层特征及其主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 39(6): 13-21 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.06.002
Hu D F, Wang L J, Huang R C, et al. , 2019. Characteristics and main controlling factors of the Middle Permian Maokou dolomite reservoirs in the eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 39(6): 13-21. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.06.002
[8] 李洪奎, 李忠全, 龙伟, 等, 2019. 四川盆地纵向结构及原型盆地叠合特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报, 46(3): 257-267
LI H K, LI Z Q, Long W, et al. , 2019. Vertical configuration of Sichuan Basin and its superimposed characteristics of the prototype basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 46(3): 257-267.
[9] 李建忠, 谷志东, 鲁卫华, 等, 2021. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大气田形成主控因素与勘探思路[J]. 天然气工业, 41(6): 13-26
Li J Z, Gu Z D, Lu W H, et al. , 2021. Main factors controlling the formation of giant Marine carbonate gas fields in the Sichuan Basin and exploration ideas[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 41(6): 13-26.
[10] 李忠权, 应丹琳, 李洪奎, 等, 2011. 川西盆地演化及叠合特征研究[J]. 岩石学报, 27(8): 2362-2370
Li Z Q, Ying D L, Li H K, et al. , 2011. Evolution of the western Sichuan basin and its superimposed characteristics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(8): 2362-2370.
[11] 梁新权, 周云, 蒋英, 等, 2013. 二叠纪东吴运动的沉积响应差异: 来自扬子和华夏板块吴家坪组或龙潭组碎屑锆石LA-ICPMSU-Pb年龄研究[J]. 岩石学报, 29(10): 3592-3606
Liang X Q, Zhou Y, Jiang Y, et al. , 2013. Difference of sedimentary response to Dongwu Movement: Study on LA-ICPMS U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from Upper Permian Wujiaping or Longtan Formation from the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(10): 3592-3606.
[12] 刘建强, 郑浩夫, 刘波, 等, 2017. 川中地区中二叠统茅口组白云岩特征及成因机理[J]. 石油学报, 38(4): 386-398 doi: 10.7623/syxb201704003
Liu J Q, Zheng H F, Liu B, et al. , 2017. Characteristics and genetic mechanism of the dolomite in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation, central Sichuan area[J]. ACTA Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 38(4): 386-398. doi: 10.7623/syxb201704003
[13] 刘雁婷, 张文军, 熊治富, 等, 2014. 四川盆地东北部中二叠统层序地层特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 34(2): 47-53
Liu Y T, Zhang W J, Xiong Z F, et al. , 2014. Sequence Stratigraphy of the Middle Permian strata in northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 34(2): 47-53.
[14] 马新华, 杨雨, 文龙, 等, 2019. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大中型气田分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 46(1): 1-13 doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.01.01
Ma X H, Yang Y, Wen L, et al. , 2019. Distribution and exploration direction of medium and large-sized Marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(1): 1-13. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.01.01
[15] 牟传龙, 马永生, 王瑞华, 等, 2005. 川东北地区上二叠统盘龙洞生物礁成岩作用研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 25 (1-2): 198-202
Mou C L, Ma Y S, Wang R H, et al. , 2005. Diagenesis of the Upper Permian Panlongdong Organic Reefs in Northeastern Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 25(1-2): 198-202.
[16] 牟传龙, 许效松, 2010. 华南地区早古生代沉积演化与油气地质条件[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 30(3): 24-29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2010.03.004
Mou C L, Xu X S, 2010. Sedimentary evolution and petroleum geology in South China during the Early Palaeozoic[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 30(3): 24-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2010.03.004
[17] 倪新锋, 陈洪德, 田景春, 等, 2007. 川东北地区长兴组-飞仙关组沉积格局及成藏控制意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 28(4): 458-462 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.04.003
Ni X F, Chen H D, Tian J C, et al. , 2007. Sedimentary framework of Changxing-Feixianguan Formations and its control on reservoiring in northeastern Sichuan basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 28(4): 458-462. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.04.003
[18] 汪华, 沈浩, 黄东, 等, 2014. 四川盆地中二叠统热水白云岩成因及其分布[J]. 天然气工业, 34(9): 25-32 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.09.004
Wang H, Shen H, Huang D, et al. , 2014. Origin and distribution of hydrothermal dolomites of the Middle Permian in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(9): 25-32. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.09.004
[19] 王瑞华, 牟传龙, 谭钦银, 等, 2006. 达县-宣汉地区长兴组礁滩白云岩成岩作用与成岩环境研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 26(1): 30-36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2006.01.005
Wang R H, Mou C L, Tan Q Y, et al. , 2006. Diagenetic processes and environments of the reef shoal dolostones from the Changxing Formation in the Daxian-Xuanhan region, northeastern Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 26(1): 30-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2006.01.005
[20] 王一刚, 洪海涛, 夏茂龙, 等, 2008. 四川盆地二叠、三叠系环海槽礁滩富气带勘探[J]. 天然气工业, 28(1): 22-27 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.01.006
Wang Y G, Hong H T, Xia M L, et al. , 2008. EXPLORATION OF REEF-BANK GAS RESERVOIRS SURROUNDING PERMIAN AND TRIASSIC TROUGHS IN SICHUAN BASIN[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 28(1): 22-27. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.01.006
[21] 魏国齐, 杨威, 刘满仓, 等, 2019. 四川盆地大气田分布、主控因素与勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 39(6): 1-12 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.06.001
Wei G J, Yang W, Liu M C, et al. , 2019. Distribution rules, main controlling factors and exploration directions of giant gas fields in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 39(6): 1-12. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.06.001
[22] Williams G E, Gostin V A, 2000. Mantle plume uplift in the sedimentary record: Origin of kilometre-deep canyons within Late Neoproterozoic successions, South Australia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 157(4): 759-768. doi: 10.1144/jgs.157.4.759
[23] Xu Y G, Chung S L et al. , 2004. Geologic, geochemical, and geophysical Consequences of plume involvement in the Emeishan flood-basalt province[J]. Geology, 32(10): 917-920. doi: 10.1130/G20602.1
[24] 杨巍, 张廷山, 刘治成, 等, 2014. 地幔柱构造的沉积及环境响应——以峨眉地幔柱为例[J]. 岩石学报, 30(3): 835-850
Yang W, Zhang T S, Liu Z C, et al. , 2014. Sedimentary and environmental responses to mantle plume: A case study of Emeishan mantle plume[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(3): 835-850.
[25] 杨跃明, 杨雨, 文龙, 等, 2020. 四川盆地中二叠统天然气勘探新进展与前景展望[J]. 天然气工业, 40(7): 10-22 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.07.002
Yang Y M, Yang Y, Wen L, et al. , 2020. New exploration progress and prospect of Middle Permian natural gas in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 40(7): 10-22. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.07.002
[26] 张帆, 文应初, 强子同, 等, 1993. 四川及邻区晚二叠统吴家坪碳酸盐缓坡沉积[J]. 西南石油学院学报, 15(1): 34-41
Zhang F, Wen Y C, Qiang Z T, et al. , 1993. Carbonate RAMP sedimentation of permian in wujiapin, Sichuan and its neighbouring region[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 15(1): 34-41.
[27] 张亚, 陈双玲, 张晓丽, 等, 2020. 四川盆地茅口组岩溶古地貌刻画及油气勘探意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 32(3): 44-55 doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200305
Zhang Y, Chen S L, Zhang X L, et al. , 2020. Restoration of paleokarst geomorphology of Lower Permian Maokou Formation and its petroleum exploration implication in Sichuan Basin[J]. Northwest Oil & Gas Exploration, 32(3): 44-55. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200305
-




 下载:
下载: