Sources analysis and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals and metalloids in Yao'an area of central Yunnan
-
摘要:
为了解滇中姚安地区表层土壤重(类)金属的污染特征、来源及生态风险状况,在研究区共采集表层土壤样品428件,对其中As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn元素的含量进行测试分析。通过数据统计分析和地球化学图说明了这些重(类)金属元素的含量分布特征和空间分布特征。运用相关性分析、主成分分析和聚类分析方法探究了重(类)金属的来源。运用地累积指数法、富集系数法和潜在生态危害指数法对研究区土壤重(类)金属污染程度及潜在生态风险进行了评价。研究结果表明,As、Cu、Pb和Zn受自然背景与矿产开采共同影响;Cr、Ni主要来源于成土母质;而Cd受矿产开采和农业施肥的影响较大;Hg则受周边工厂以及煤炭燃烧的影响。地累积指数和富集系数分析表明,研究区污染程度普遍不高,但局部地区有重(类)金属元素的污染富集,代表元素为Cd和Hg。而潜在生态危害指数法分析结果也表明Cd和Hg是研究区最主要的风险元素,但以轻度和中度生态危害为主,强生态危害分布面积较小,研究区生态风险整体较低,风险可控。本研究对滇中地区的土壤重(类)金属的污染评价和土地利用发展规划有一定的参考作用。
Abstract:A suite of 428 surface soil samples were collected in the Yao'an area of central Yunnan area to evaluate the pollution characteristics, sources, and ecological risks associated with the heavy metals and metalloids such as As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn. The concentrations and spatial distribution characteristics of these heavy metal elements are illustrated through statistical data analysis and geochemical maps. The sources of heavy metals and metalloids were explored using correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis methods. The degree of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks were evaluated by the geo-accumulation index method, the enrichment factor method, and the potential ecological risk index method. The results show that As, Cu, Pb and Zn are influenced by the natural background and mineral mining. Cr and Ni mainly reflect soil parent materials; Cd enrichment is associated with mineral mining and agricultural fertilizer use. Hg is affected by surrounding factory emissions and coal combustion. The analysis of the Geo-accumulation Index and Enrichment Factor showed that the pollution degree in the study area was generally not high; however, there was local enrichment of the heavy metals such as Cd and Hg. The potential ecological risk index method also showed that Cd and Hg are the most important risk elements in the study area, but they are mainly mild and moderate ecological hazards. The distribution area of strong ecological hazards is small, and the overall ecological risk in the study area is low and controllable. Our study provides a current assessment of soil heavy metal and metalloid pollution in the study area that can be used to guide future land-using plan in central Yunnan.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- heavy metal and metalloid /
- source analysis /
- risk assessment /
- central Yunnan
-

-
表 1 地累积指数评价指标
Table 1. Geo-accumulation index and contamination grades
等级 Igeo值 富集(污染)程度 Ⅰ ≤0 无富集(无污染) Ⅱ 0~1 轻微富集(轻微污染) Ⅲ 1~2 中度富集(中度污染) Ⅳ 2~3 中强富集(中强污染) Ⅴ 3~4 强富集(强污染) Ⅵ 4~5 较强富集(较强污染) Ⅶ >5 极强富集(极强污染) 表 2 富集系数评价指标
Table 2. Enrichment factor and contamination grades
等级 EF值 富集(污染)程度 Ⅰ ≤0 无富集(无污染) Ⅱ 1~2 轻微富集(轻微污染) Ⅲ 2~5 中度富集(中度污染) Ⅳ 5~20 显著富集(中强污染) Ⅴ 20~40 强烈富集(强污染) Ⅵ >40 极强富集(较强污染) 表 3 重(类)金属的生态风险系数和潜在生态风险指数
Table 3. Potential ecological risk coefficient and its indices of the heavy metals and metalloids
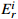 值
值潜在生态危害程度 RI值 潜在生态风险程度 <40 轻度 <150 轻度 40~80 中度 150~300 中度 80~160 强 300~600 强 160~320 很强 >600 很强 >320 极强 表 4 土壤重(类)金属元素含量分析统计
Table 4. Statistics of heavy metal and metalloid concentration in soils
项目 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn Fe 平均值/mg·kg-1 11.53 0.31 99.53 34.50 0.04 43.50 41.53 84.92 5.69 最小值/mg·kg-1 3.11 0.06 47.20 8.06 0.01 10.80 12.20 22.00 1.85 25% 8.90 0.19 91.30 27.93 0.03 38.73 24.80 71.80 5.26 百分位数 50% 10.60 0.24 99.85 33.15 0.03 43.95 27.25 81.60 5.80 75% 12.80 0.31 107.00 39.10 0.05 48.60 31.20 92.25 6.29 最大值/mg·kg-1 38.10 14.20 187.00 148.00 0.45 78.10 1819.00 268.00 8.11 标准偏差/mg·kg-1 4.66 0.74 14.62 11.89 0.04 9.24 96.78 26.51 0.86 变异系数 0.40 2.39 0.15 0.34 0.86 0.21 2.33 0.31 0.15 偏度 2.01 16.59 0.23 3.61 7.31 -0.12 15.28 3.08 -1.08 峰度 6.30 299.40 3.96 26.14 72.85 1.44 270.50 16.83 2.55 云南省土壤背景值/mg·kg-1 18.4 0.22 65.2 46.3 0.06 42.5 40.6 89.7 5.22 全国土壤背景值/mg·kg-1 11.2 0.10 61 22.6 0.07 26.9 26 74.2 2.94 土壤风险筛选值/mg·kg-1 30 0.3 150 50 0.5 60 70 200 pH≤5.5 30 0.3 150 50 0.5 70 90 200 5.5<pH≤6.5 25 0.3 200 100 0.6 100 120 250 6.5<pH≤7.5 20 0.6 250 100 1 190 170 300 pH>7.5 超标率/% 1.17 23.36 0.47 3.50 0 0.93 4.91 0.93 注:Fe含量单位为%。 表 5 土壤重(类)金属相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis of heavy metals and metalloids in soils
元素 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn Fe2O3 MgO As 1 0.103** 0.079 0.408** 0.339** 0.164** 0.475** 0.607** 0.283** -0.067 Cd 1 -0.029 0.165** 0.089 0.03 0.032 0.206** -0.002 0.001 Cr 1 0.252** -0.120* 0.783** -0.054 0.092 0.653** 0.368** Cu 1 0.123* 0.374** 0.529** 0.477** 0.459** 0.311** Hg 1 -0.048 0.245** 0.280** 0.028 -0.111* Ni 1 0.014 0.335** 0.760** 0.651** Pb 1 0.564** 0.093 -0.070 Zn 1 0.451** 0.271** 注:*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01。 表 6 土壤重(类)金属含量的主成分分析
Table 6. Principal component analysis of the heavy metal and metalloid concentrations in soils
重(类)金属元素 主成分 变量共同度 1 2 3 4 As 0.748 -0.241 -0.102 0.138 0.648 Cd 0.231 -0.115 0.956 -0.070 0.985 Cr 0.336 0.859 -0.026 0.165 0.878 Cu 0.760 0.091 0.002 -0.330 0.695 Hg 0.376 -0.444 0.001 0.747 0.896 Ni 0.504 0.790 0.024 0.152 0.902 Pb 0.699 -0.372 -0.252 -0.324 0.796 Zn 0.831 -0.147 0.031 -0.027 0.715 初始特征值 2.880 1.798 0.989 0.847 方差贡献率/% 36.00 22.48 12.37 10.59 累计方差贡献率/% 36.00 58.48 70.85 81.44 表 7 土壤重(类)金属元素地累积指数等级分布情况
Table 7. Class distribution of Igeo for heavy metals and metalloids in soils
元素 Igeo Igeo<0 0<Igeo<1 1<Igeo<2 2<Igeo<3 3<Igeo<4 4<Igeo<5 5<Igeo 变化范围 平均值 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% As -3.150~0.465 -1.356 99.065 0.935 0 0 0 0 0 Cd -2.459~5.427 -0.431 79.206 19.392 0.690 0.234 0 0.234 0.234 Cr -1.051~0.935 0.009 44.159 55.841 0 0 0 0 0 Cu -3.107~1.092 -1.074 98.598 1.168 0.234 0 0 0 0 Hg -3.170~2.322 -1.313 96.496 2.570 0.467 0.467 0 0 0 Ni -2.561~0.293 -0.589 98.364 1.636 0 0 0 0 0 Pb -2.320~4.901 -0.958 92.757 3.037 3.505 0 0.467 0.234 0 Zn -2.613~0.994 -0.719 95.794 4.206 0 0 0 0 0 表 8 土壤重(类)金属元素富集系数等级分布情况
Table 8. Class distribution of enrichment factors for heavy metals and metalloids in soils
元素 EF EF <1 1< EF <2 2< EF <5 5< EF <20 20< EF <40 40<EF 变化范围 平均值 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% As 0.176~2.803 0.581 93.458 6.308 0.234 0 0 0 Cd 0.253~56.722 1.330 48.832 46.963 3.271 0.467 0 0.467 Cr 1.003~2.613 1.416 0 98.832 1.168 0 0 0 Cu 0.326~3.299 0.684 96.495 3.038 0.467 0 0 0 Hg 0.130~11.757 0.660 91.122 7.009 1.402 0.467 0 0 Ni 0.539~1.674 0.937 75.935 24.065 0 0 0 0 Pb 0.389~36.259 0.935 87.383 11.448 0.935 0.234 0 0 Zn 0.516~3.930 0.871 89.720 10.280 0 0 0 0 表 9 土壤重(类)金属潜在生态风险系数等级分布情况
Table 9. Class distribution of potential ecological risk coefficient of heavy metals and metalloids in soils
元素 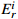
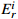 ≤40
≤4040<  ≤80
≤8080< 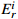 ≤160
≤160160< 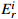 ≤320
≤320320< 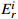
变化范围 平均值 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% As 1.69~20.71 6.27 100 0 0 0 0 Cd 8.18~ 1936.36 42.24 72.43 25.93 0.70 0.47 0.47 Cr 1.45~5.74 3.05 100 0 0 0 0 Cu 0.87~15.98 3.73 100 0 0 0 0 Hg 6.67~300.00 27.94 91.59 7.01 0.93 0.47 0 Ni 1.27~9.19 5.12 100 0 0 0 0 Pb 1.50~224.01 5.11 99.30 0.47 0 0.23 0 Zn 0.25~2.99 0.95 100 0 0 0 0 表 10 土壤重(类)金属潜在生态风险指数等级分布情况
Table 10. Class distribution of potential ecological risk index of heavy metals and metalloids in soils
RI RI<150 150≤RI<300 300≤RI<600 600< RI 变化范围 平均值 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 比例/% 31.34~ 2002.53 95.00 94.86 3.74 0.93 0.47 -
[1] 蔡立梅, 马瑾, 周永章, 等, 2008. 东莞市农业土壤重金属的空间分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 29(12): 3496-3502 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.034
Cai L M, Ma J, Zhou Y Z, et al. , 2008. Multivariate Geostatistics and GIS-based Approach to Study the Spatial Distribution and Sources of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soil in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Science, 29(12): 3496-3502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.12.034
[2] 岑静, 陈家玮, 杨忠芳, 等, 2008. 层次分析法在四川省通江县广纳镇土地评估中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 27(2): 277-285 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.02.017
Cen J, Chen J W, Yang Z F, et al. , 2008. Application of the analytic hierarchy process in the evaluation of land quality of Guangna Town, Tongjiang County, Sichuan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(2): 277-285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.02.017
[3] 陈航, 王颖, 王澍, 2022. 铜山矿区周边农田土壤重金属来源解析及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 43(5): 2719-2731
Chen H, Wang Y, Wang S, 2012. Source Analysis and Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil Around Tongshan Mining Area[J]. Environmental Science, 43(5): 2719-2731.
[4] Chen H Y, Teng Y G, Lu S J, et al. , 2015. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 512-513: 143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
[5] 陈志凡, 化艳旭, 徐薇, 等, 2020. 基于正定矩阵因子分析模型的城郊农田重金属污染源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(1): 276-283
Chen Z F, Hua Y X, Xu W, et al. , 2020. Analysis of heavy metal pollution sources in suburban farmland based on positive definite matrix factor model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(1): 276-283.
[6] 从源, 郑萍, 陈岳龙, 等, 2008. 北京农田生态系统土壤重金属元素的生态风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 27(5): 681-688 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.05.014
Cong Y, Zheng P, Chen Y L, et al. , 2008. Ecological risk assessments of heavy metals in soils of the farmland ecosystem of Beijing, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(5): 681-688. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.05.014
[7] Gasiorek M, Kowalska J, Mazurek R, et al., 2017. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution in topsoil of historical urban park on an example of the Planty Park in Krakow (Poland) [J]. Chemosphere, 179: 148−158.
[8] Hakanson L, 1980. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control—A Sedimentological Approach[J]. Water Research, 14(8) : 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[9] Hu W Y, Zhang Y X, Huang B, et al. , 2017. Soil environmental quality in greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China: Current status and management strategies[J]. Chemosphere, 170: 183-195. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.047
[10] Jin Y L, O’Connor D, Ok Y S, et al. , 2019. Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Environment International, 124: 320-328. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.024
[11] Khan K, Lu Y, Khan H, et al. , 2013. Heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops and their health risks in Swat District, northern Pakistan[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 58(8) : 449-458.
[12] 李苹, 黄勇, 林赟, 等, 2018. 北京市怀柔区土壤重金属的分布特征、来源分析及风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 32(1): 86-94 doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.01.08
Li Ping, Huang Y, Lin Y, et al. , 2018. Distribution, Source Identification and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Topsoil of Huairou District in Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 32(1): 86-94. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.01.08
[13] Liang J, Feng C T, Zeng G M, et al. , 2017. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 225: 681-690. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.057
[14] Liu M, Zhang A B, Liao Y J, et al. , 2015. The environment quality of heavy metals in sediments from the central Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100(1) : 534-543. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.001
[15] 柳云龙, 章立佳, 韩晓非, 等, 2012. 上海城市样带土壤重金属空间变异特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 33(2): 599-605
Liu Y L, Zhang L J, Han X F, et al. , 2012. Spatial Variability and Evaluation of Soil Heavy Metal Contamination in the Urban-transect of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science, 33(2): 599-605.
[16] 罗晨皓, 周晔, 沈阳, 等, 2019. 云南姚安Au-Pb-Ag矿床含矿富碱岩浆岩地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 44(6): 2063-2083
Luo C H, Zhou Y, Shen Y, et al. , 2019. The Geochemical Characteristics and Petrogenesis of the Mineralized Alkali-Rich Magmatic Rock in Yao’an Au⁃Pb⁃Ag Deposit, Yunnan Province[J]. Earth Science, 44(6): 2063-2083.
[17] Mwesigye A R, Young S D, Bailey E H, et al. , 2016. Population exposure to trace elements in the Kilembe copper mine area, western Uganda: A pilot study [J]. Science of Total Environment, 573: 366-375. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.125
[18] Madrid L, Díaz-Barrientos E, Madrid F, 2002. Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in parks of Seville[J]. Chemosphere, 49(10) : 1301-1308. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00530-1
[19] Mamat Z, Yimit H, Ji R Z, et al. , 2014. Source identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metal contamination in Yanqi basin, northwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 493: 1098-1111. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.087
[20] N’GUESSAN Y M, PROBST J L, BUR T, et al. , 2009. Trace elements in stream bed sediments from agricultural catchments (Gascogne region, S-W France) : where do they come from[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 407: 2939-2952. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.12.047
[21] Ogunkunle C O, Fatoba P O, 2013. Pollution Loads and the Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals around a Mega Cement Factory in Southwest Nigeria[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 22(2) : 487-493.
[22] Padoan E, Romè C, Ajmone-Marsan F, 2017. Bioaccessibility and size distribution of metals in road dust and roadside soils along a peri-urban transect[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 601-602: 89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.180
[23] 秦元礼, 张富贵, 彭敏, 等, 2020. 云南省武定县土壤重金属地球化学分布特征及其来源浅析[J]. 地质与勘探, 56(3): 540-550
Qin Y L, Zhang F G, Peng M, et al. , 2020. Geochemical distribution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in soils of Wuding County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 56(3): 540-550.
[24] Shi Y, Huang J, Zeng G, et al. , 2018. Evaluation of soluble microbial products (SMP) on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors (MBRs) at the fractional and overall level: A review[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 17(1) : 71-85. doi: 10.1007/s11157-017-9455-9
[25] Szolnoki Z, Farsang A, Puskás I, 2013.Cumulative impacts of human activities on urban garden soils: origin and accumulation of metals[J].Environmental Pollution, 177: 106-115.
[26] Tian K, Huang B, Xing Z, et al. , 2017. Geochemical baseline establishment and ecological risk evaluatiaon of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Dongtai, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 72: 510-520. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.037
[27] Tomlinson D L, Wilson J G, Harris C R, et al. , 2019. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index[J]. Helgolander Marine research, 33: 566-575.
[28] 魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等, 1991. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 12(4): 12-19 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1991.04.015
Wei F S, Chen J S, Wu Y Y, et al. , 1991. Study on soil environmental background value in China[J]. Environmental Science, 12(4): 12-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1991.04.015
[29] 王美, 李书田, 2014. 肥料重金属含量状况及施肥对土壤和作物重金属富集的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20(2): 466-480 doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2014.0224
Wang M, Li S T, 2014. Heavy metals in fertilizers and effect of the fertilization on heavy metal accumulation in soils and crops[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 20(2): 466-480. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.2014.0224
[30] 王玉, 辛存林, 于奭, 等, 2022. 南方丘陵区土壤重金属含量、来源及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 43(09): 4756-4766
Wang Y, Xin C L, Yu S, et al. , 2022. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content, Sources, and Potential Ecological Risks in Soils of Southern Hilly Areas[J]. Environmental Science, 43(09): 4756-4766.
[31] Wilding L P, 1985. Spatial variability: its documentation, accommodation, and implication to soil surveys[M]Nielsen D R Bouma J. Soil spatial variability. Wageningen: Pudoc Publishers, 166−194.
[32] 徐争启, 倪师军, 张成江, 等, 2004. 应用污染负荷指数法评价攀枝花地区金沙江水系沉积物中的重金属[J]. 四川环境, 23(3): 64-67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2004.03.019
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Zhang C J, et al. , 2004. Assessment on Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Jinsha River in Panzhihua Area by Pollution Load Index[J]. Sichuan Environment, 23(3): 64-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2004.03.019
[33] 严明书, 黄剑, 何忠庠, 等, 2018. 地质背景对土壤微量元素的影响—以川渝地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 42(1): 199-205
Yan M S, Huang J, He Z X, et al. , 2018. The influence of geological background on trace elements of soil, A case study of Yubei area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 42(1): 199-205.
[34] 严清高, 江小均, 吴鹏, 等, 2017. 滇中姚安老街子板内富碱火山岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学及火山机构划分[J]. 地质学报, 91(8): 1743-1759 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.007
Yan Q G, Jiang X J, W P, et al. , 2017. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Geochronology and Volcanic Edifice Division of the Laojiezi Intraplate Alkali-rich Volcanic Rocks in Yao’an, Central Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(8): 1743-1759. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.007
[35] 余小芬, 陈军, 彭荣珍, 等, 2012. 滇中农用地土壤重金属影响因素研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 25(5): 1765-1769 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2012.05.047
Yu X F, Chen J, Peng R Z, et al. , 2012. Study on Influencing Factors of Farmland Soil Heavy Metals in Central Yunnan Province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 25(5): 1765-1769. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2012.05.047
[36] 中国环境监测总站, 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 329−472.
China Environmental Monitoring Station, 1990. Background value of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 329−472(in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2018. GB 15618−2018 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准[S].
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. GB15618−2018 Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S].
[38] 赵庆令, 李清彩, 谢江坤, 等, 2015. 应用富集系数法和地累积指数法研究济宁南部区域土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 34(1): 129-137 doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.019
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, Xie J K, et al. , 2015. Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Its Ecological Risk Assessment in South Jining District Using Methods of Enrichment Factor and Index of Geoaccumulation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 34(1): 129-137. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.019
[39] Zheng Y M, Chen T B, He J Z, 2008. Multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in topsoils from Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 8(1) : 51-58. doi: 10.1065/jss2007.08.245
[40] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 等, 2018. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 39(6): 2884-2892 doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201707125
Zhou Y, Chen Q, Deng S P, et al. , 2018. Principal Component Analysis and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soils around a Pb-Zn Mine in Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 39(6): 2884-2892. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201707125
[41] 周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等, 2019. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 43(6): 1358-1366
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W, et al. , 2019. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 43(6): 1358-1366.
[42] Zhu L, Liu J W, Xu S G, et al. , 2017. Deposition behavior, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in reservoir sediments of northeast China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety, 142: 454-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.039
-




 下载:
下载:



