Sensitivity evaluation of Karst rock desertification based on its formation mechanism: A case study of Qianxi County in Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
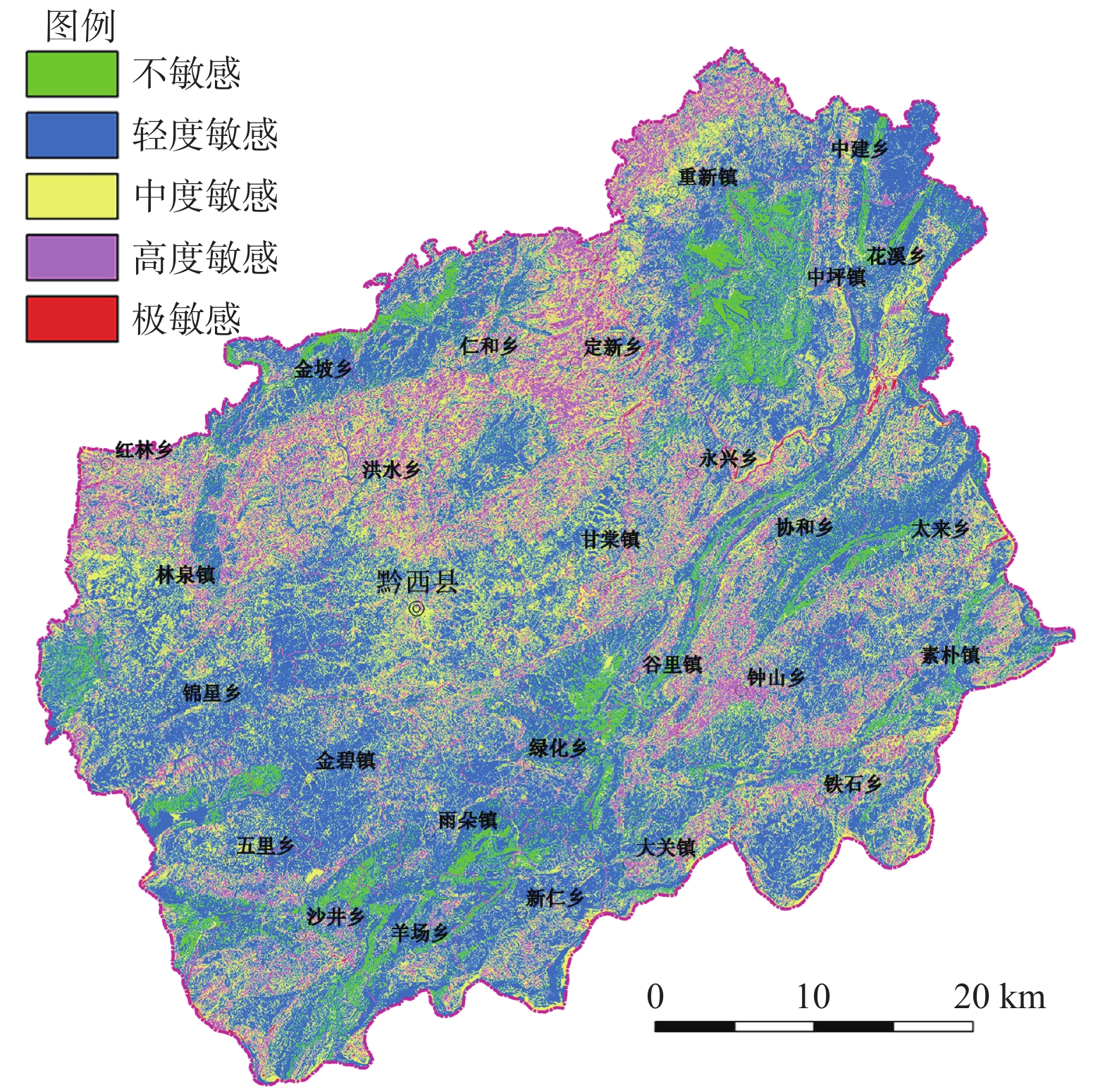
在遥感解译和野外调查基础上,通过分析石漠化的成因与形成机理,找出影响石漠化敏感性的主要自然因素,选取年降雨量、坡度、岩性组合、土壤质地和植被覆盖度5个指标,在GIS的支持下,采用改进的层次分析法,开展了黔西县石漠化敏感性评价。结果表明:黔西县石漠化仍然处于较为敏感状态,中度、高度和极敏感区域的面积合计为1176.39 km2,占46.97%,发生石漠化可能性依然存在;中度、高度和极敏感区主要分布于洪水—仁和、定新—重新、五里—沙井和钟山—铁石—素朴等区域,与石漠化土地的分布区域一致;绝大部分石漠化高度敏感区和极敏感区分布在三叠系碳酸盐岩地层中,嘉陵江组是敏感性最高的地层单元;通过综合研究石漠化各相关因素的作用机理和内在联系及继承关系来比较各相关因素的重要性,可以替代专家调查表方法,来降低层次分析法的随意性和主观性。
Abstract:Based on remote sensing interpretation and field investigation, this paper analyzes the causes and formation mechanisms of rocky desertification, aiming to identify the impact of key natural factors on the sensitivity of Karst rock desertification. The annual rainfall, slope, lithology, soil texture, and vegetation coverage are selected as indicators for evaluating the sensitivity of Karst rock desertification. The sensitivity evaluation of Karst rock desertification is carried out by using improved analytic hierarchy process, with the support of GIS, in Qianxi County, Guizhou Province. The results reveal that Karst rock desertification remains sensitive, with the total area of moderate, strong, and extremely high sensitivity amounting to 1176.39 km2, representing 46.97% of the studied areas, and the possibility of Karst rock desertification still exists. The moderate, strong and extremely sensitive areas are mainly distributed in Hongshui-Renhe, Dingxin-Chongxin, Wuli-Shajing and Zhongshan-Tieshi-Supu, which are consistent with the distribution pattern of rocky desertification land. Most of the strong sensitive and extremely sensitive areas of rocky desertification are distributed in the Triassic carbonate strata, and the Jialingjiang Formation is the most sensitive stratigraphic unit. Through comprehensively studying the mechanism of various related factors of rock desertification and comparing the importance of each related factor based on their internal relationships and inheritance relationships, we can replace expert questionnaire methods to reduce the arbitrariness and subjectivity of the analytic hierarchy process.
-

-
表 1 黔西县碳酸盐岩酸不溶物含量统计
Table 1. Content of acid insoluble residues in carbonate rocks of Qianxi County
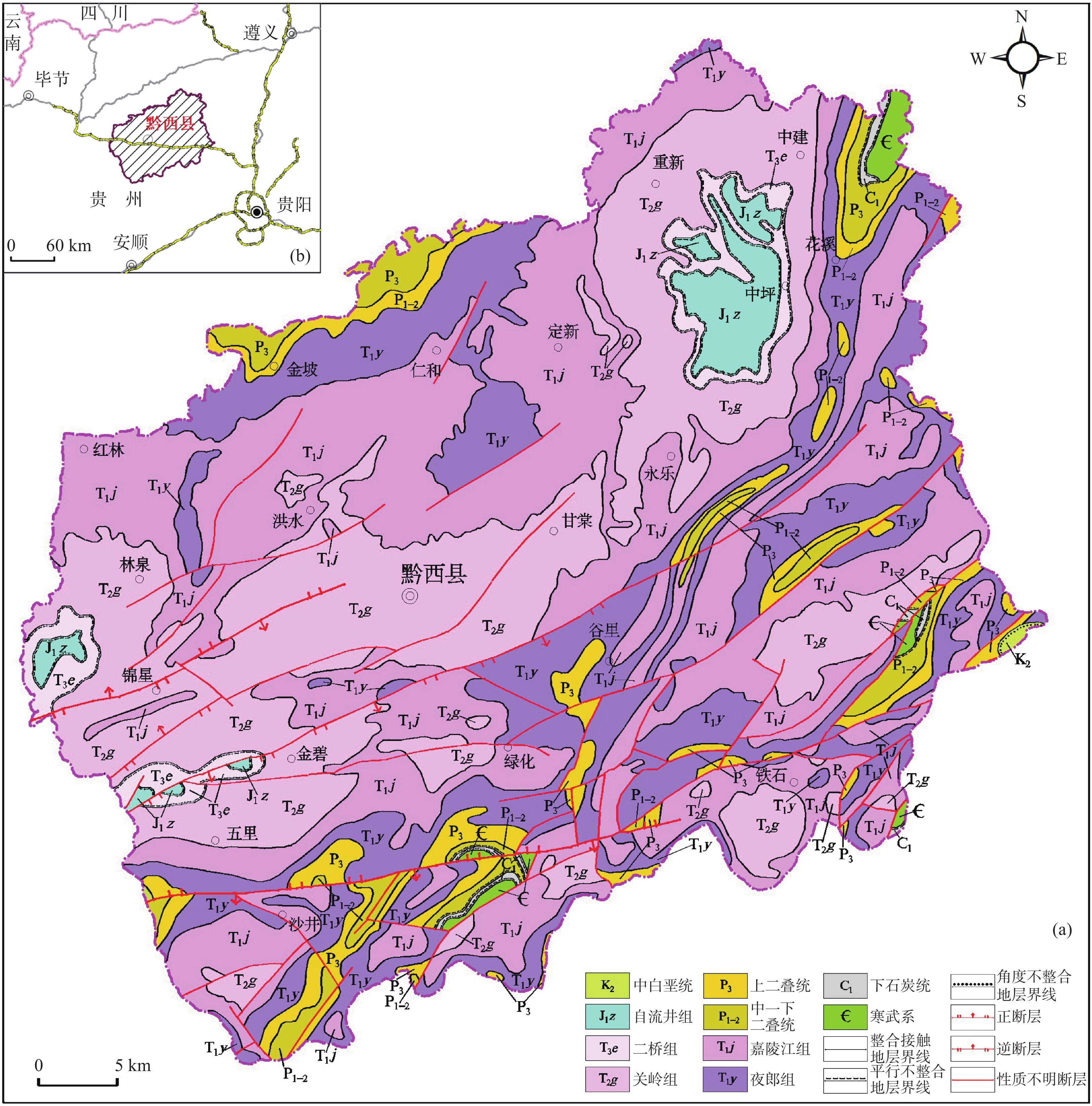
样品编号 采样地层 岩性 酸不溶物含量 H001 嘉陵江组 白云质灰岩 5.48% H002 嘉陵江组 生物碎屑灰岩 1.09% H003 嘉陵江组 灰岩 3.30% H004 嘉陵江组 灰岩 1.40% H005 嘉陵江组 灰岩 3.36% H006 嘉陵江组 灰质白云岩 2.19% H007 嘉陵江组 灰质白云岩 2.45% H008 嘉陵江组 灰岩 3.29% H009 嘉陵江组 灰岩 2.85% H010 嘉陵江组 灰岩 3.54% H011 嘉陵江组 灰岩 3.93% H012 嘉陵江组 灰岩 1.74% H013 嘉陵江组 灰岩 2.47% H014 嘉陵江组 灰岩 5.76% H015 嘉陵江组 灰岩 1.39% H016 嘉陵江组 灰岩 4.71% H017 嘉陵江组 灰岩 4.33% H018 嘉陵江组 灰岩 4.28% H019 嘉陵江组 灰岩 1.18% H020 关岭组 泥质白云岩 8.27% H021 关岭组 泥质灰岩 14.63% H022 关岭组 灰岩 1.87% H023 关岭组 泥质白云岩 8.73% H024 夜郎组二段 灰岩 2.65% H025 嘉陵江组 灰岩 0.89% H026 关岭组 泥质白云岩 8.41% H027 关岭组 泥质白云岩 7.98% H028 嘉陵江组 灰岩 2.00% H030 嘉陵江组 灰岩 2.86% H032 夜郎组二段 泥质灰岩 10.71% H033 夜郎组二段 灰岩 2.37% H034 关岭组 泥质白云岩 15.68% H035 关岭组 灰岩 3.33% H036 关岭组 灰岩 5.78% H037 嘉陵江组 灰岩 1.36% H038 关岭组 泥质白云岩 8.09% H039 关岭组 砂质白云岩 20.69% 平均值 5.00% 表 2 黔西县石漠化敏感性评价指标
Table 2. Indicators of sensitivity evaluation of Karst rock desertification in Qianxi County
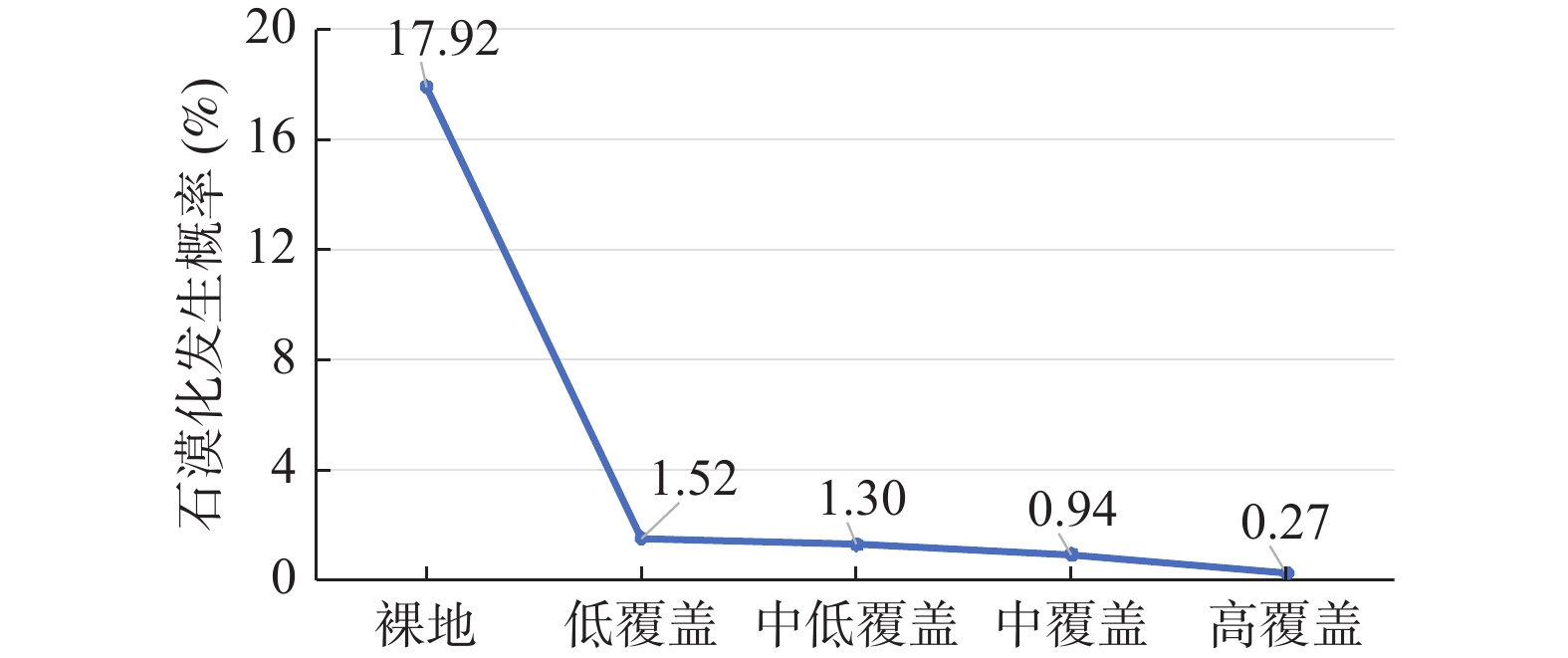
分级 不敏感 轻度敏感 中度敏感 高度敏感 极敏感 年降雨量 <400 mm 400~800 mm 800~ 1500 mm1500 ~2000 mm> 2000 mm坡度 0~5° 5°~15° 15°~25° 25°~35° >35° 岩性组合 非可溶性岩石 不纯碳酸盐岩 白云岩夹灰岩 灰岩、白云岩 灰岩夹白云岩 土壤质地 石砾、沙 粗砂土、细砂土、
黏土面砂土、壤土 砂壤土、粉黏土、
壤黏土砂粉土、粉土 植被覆盖度 高覆盖
(>60%)中高覆盖
(45%~60%)中低覆盖
(30%~45%)低覆盖
(10%~30%)裸地
(<10%)分级赋值(C) 1 3 5 7 9 分级标准(SS) 1.0~2.0 2.0~4.0 4.0~6.0 6.0~8.0 >8.0 表 3 判断矩阵与层次排序
Table 3. Judgment matrix and hierarchical sorting
A D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 W 排序 D1 1 1/3 1/5 1/3 1/7 0.0464 5 D2 3 1 1/3 3 1/3 0.1551 3 D3 5 3 1 3 1/3 0.2642 2 D4 3 1/3 1/3 1 1/3 0.0985 4 D5 7 3 3 3 1 0.4359 1 注:A表示总目标−黔西县石漠化敏感性;D1表示年降雨量单因子敏感性;D2表示坡度单因子敏感性;D3表示岩性单因子敏感性;D4表示土壤质地单因子敏感性;D5表示植被覆盖度单因子敏感性;W表示计算出来的权重。 表 4 黔西县石漠化敏感性统计
Table 4. The areas and their percentages of each Karst rock desertification sensitivity class in Qianxi County
石漠化敏感性 面积/km2 百分比/% 不敏感 118.78 4.74 轻度敏感 1209.39 48.29 中度敏感 866.34 34.59 高度敏感 303.65 12.12 极敏感 6.40 0.26 -
[1] 安宏锋, 安裕伦, 袁士聪, 等, 2010. 贵州省石漠化敏感性的动态演变与模拟预测[J]. 中国农学通报, 26(13): 388-395
An H F, An Y L, Yuan S C, et al, 2010. The dynamic change and simulation and prediction of sensitivity of the Karst rocky desertification of Guizhou[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 26(13): 388-395.
[2] 白晓永, 王世杰, 陈起伟, 等, 2010. 贵州碳酸盐岩性基底对土地石漠化时空演变的控制[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 35(4): 691-696 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.084
Bao X Y, Wang S J, Chen Q W, et al, 2010. Constrains of lithological background of carbonate rock on spatio-temporal evolution of Karst rocky desertification land[J]. Earth Science — Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(4): 691-696. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.084
[3] 白占国, 万国江, 1998. 贵州碳酸盐岩区域的侵蚀速率及环境效应研究[J]. 土壤侵蚀与水土保持学报, 4(1): l-7+46
Bai Z G, Wan G J, 1998. Study on watershed erosion rate and its environmental effects in Guizhou Karst region[J]. Journal of Soil Erosion and Soil and Water Conservation, 4(1): l-7+46.
[4] 高华端, 李锐, 2007. 喀斯特地区原状土的可蚀性[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 5(5): 1-4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2007.05.001
Gao H D, Li R, 2007. Erodibility of original soil in Karst area[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 5(5): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2007.05.001
[5] 蒋忠诚, 曹建华, 杨德生, 等, 2008. 西南岩溶石漠化区水土流失现状与综合防治对策[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 6(1): 37-42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2008.01.006
Jiang Z C, Cao J H, Yang D S, et al, 2008. Current status and comprehensive countermeasures of soil erosion for Karst rocky desertification areas in the Southwestern China[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 6(1): 37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2008.01.006
[6] LeGrand H E, 1973. Hydrological and ecological problems of Karst regions: hydrological actions on limestone regions cause distinctive ecological problems[J]. Science, (179): 859-864.
[7] Li Y B, Shao J A, Yang H, et al, 2009. The relations between land use and Karst rocky desertification in a typical Karst area, China[J]. Environmental Geology, (57): 621-627.
[8] 李会, 周运超, 刘娟, 等, 2013. 喀斯特土壤抗蚀性对不同土地利用方式的响应[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(5): 16-23
Li H, Zhou Y C, Liu J, et al, 2013. Responses of Karst soil anti-erodibility to different land use types[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(5): 16-23.
[9] 刘洪, 黄瀚霄, 欧阳渊, 等, 2020. 基于地质建造的土壤地质调查及应用前景分析—以大凉山区西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(1): 91-105
Liu H, Huang H X, Ouyang Y, et al, 2020. Soil’s geologic investigation in Daliangshan, Xichang, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(1): 91-105.
[10] 李苗苗, 2003. 植被覆盖度的遥感估算方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院.
Li M M, 2003. The Method of Vegetation Fraction Estimation by Remote Sensing[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] 李瑞玲, 王世杰, 周德全, 等, 2003. 贵州岩溶地区岩性与土地石漠化的相关分析[J]. 地理学报, 58(2): 314-320 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.02.019
Li R L, Wang S J, Zhou D Q, et al, 2003. The correlation between rock desertification and lithology in Karst area of Guizhou[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58(2): 314-320. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.02.019
[12] 李威, 李月臣, 唐谊娟, 2014. 基于GIS和RS的石漠化敏感性评价及空间分异特征——以贵州省为例[J]. 资源开发与市场, 30(11): 1334-1338 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2014.11.014
Li W, Li Y C, Tang Y J, 2014. Sensitivity assessment of Karst rocky desertification and its spatial differentiation characteristics based on GIS and RS —— a case study of Guizhou Province[J]. Resource Development & Market, 30(11): 1334-1338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2014.11.014
[13] 李阳兵, 邵景安, 王世杰, 等, 2007. 基于岩溶生态系统特性的水土流失敏感性评价[J]. 山地学报, 25(6): 671-677 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.06.005
Li Y B, Shao J A, Wang S J, et al, 2007. Assessment of soil erosion sensitivity based on the characteristics of Karst ecosystem[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 25(6): 671-677. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.06.005
[14] 路洪海, 冯绍国, 2002. 贵州喀斯特地区石漠化成因分析[J]. 四川师范学院院报(自然科学版), 23(2): 189-192
Lu H H, Feng S G, 2002. Causes of the rocky desertification in Guizhou Karst areas[J]. Journal of Sichuan Teachers College (Natural Science), 23(2): 189-192.
[15] 马士彬, 安裕伦, 杨广斌, 等, 2016. 喀斯特地区不同植被类型NDVI变化及驱动因素分析——以贵州为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(7): 1106-1114
Ma S B, An Y L, Yang G B, et al, 2016. The analysis of the difference vegetation variation and driver factors on NDVI Change in Karst region: a case on Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(7): 1106-1114.
[16] 赖长鸿, 覃家作, 张文, 等, 2013. 四川省石漠化敏感性评价及其空间分布特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 20(4): 99-104
Lai C H, Qin J Z, Zhang W, et al, 2013. Assessment on sensitivity and spatial distributed characteristics of Karst rocky desertification in Sichuan Province[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(4): 99-104.
[17] 单洋天, 2006, 我国西南岩溶石漠化及其地质影响因素分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 25(2): 163-167 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2006.02.013
Shan Y T, 2006, Karst rocky desertification and analysis on the geological factors in Southwest China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 25(2): 163-167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2006.02.013
[18] 苏维词, 杨华, 李晴, 等, 2006. 我国西南喀斯特山区土地石漠化成因及防治[J]. 土壤通报, 37(3): 447-451 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2006.03.008
Su W C, Yang H, Li Q, et al, 2006. Rocky land desertification and its controlling measurements in the Karst mountainous region, Southwest of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 37(3): 447-451. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2006.03.008
[19] 谭秋, 李阳兵, 杨晓英, 2009. 贵州连续性碳酸盐岩地区石漠化的岩性差异[J]. 矿物学报, 29(3): 393-398 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2009.03.018
Tan Q, Li Y B, Yang X Y, 2009. Lithological difference in rocky desertification for homogenous carbonate areas in Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 29(3): 393-398. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2009.03.018
[20] 王世杰, 季宏兵, 欧阳自远, 等, 1999. 碳酸盐岩风化成土作用的初步研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 29(5): 442 − 449
Wang S J, Ji H B, Ouyang Z Y, et al., 1999. Preliminary Study on weathering and pedogenesis of carbonate rock[J]. Science in China (series D), 29(5): 442 − 449 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] 王世杰, 2002. 喀斯特石漠化概念演绎及其科学内涵的探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 21(2): 101-105 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2002.02.006
Wang S J, 2002. Concept deduction and its connotation of Karst rocky desertification[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 21(2): 101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2002.02.006
[22] 王世杰, 李阳兵, 李瑞玲, 2003. 喀斯特石漠化的形成背景、演化与治理[J]. 第四纪研究, 23(6): 657-666 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.06.009
Wang S J, Li Y B, Li R L, 2003. Karst rocky desertification: formation background, evolution and comprehensive taming[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 23(6): 657-666. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.06.009
[23] 王瑞江, 姚长宏, 蒋忠诚, 等, 2001. 贵州六盘水石漠化的特点、成因与防治[J]. 中国岩溶, 20(1): 211-216
Wang R J, Yao C H, Jiang Z C, et al, 2001. Characteristics, formation, and control of rocky desertification in Liupanshui City, Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 20(1): 211-216.
[24] 肖荣波, 欧阳志云, 王效科, 等, 2005. 中国西南地区石漠化敏感性评价及其空间分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 24(5): 551-554 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2005.05.018
Xiao R B, Ouyang Z Y, Wang X K, et al, 2005. Sensitivity of rocky desertification and its spatial distribution in Southwestern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24(5): 551-554. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2005.05.018
[25] 王尧, 张茂省, 杨建锋, 2019. 中国地质环境脆弱性评价[J]. 西北地质, 52(2): 199-206
Wang Y, Zhang M S, Yang J F, 2019, Evaluation research on the fragility of geological environment in China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 52(2): 199-206.
[26] 徐建华, 2014. 计量地理学(第二版)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 234 − 239
Xu J H, 2014, Quantitative geography (second edition) [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 234 − 239 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] 徐燕, 龙健, 2005. 贵州喀斯特山区土壤物理性质对土壤侵蚀的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 19(1): 157-159+175 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.01.039
Xu Y, Long J, 2005. Effect of soil physical properties on soil erosion in Guizhou Karst mountainous region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 19(1): 157-159+175. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2005.01.039
[28] 张景华, 高慧, 欧阳渊, 等, 2018. 贵州省黔西县土壤侵蚀敏感性评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 16(2): 88-94
Zhang J H, Gao H, Ouyang Y, et al, 2018. Sensitivity evaluation of soil erosion in Qianxi County of Guizhou Province[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 16(2): 88-94.
[29] 张景华, 欧阳渊, 陈远智, 等, 2021. 基于无人机遥感的四川省昭觉县农业产业园土地适宜性评价[J]. 中国地质, 48(6): 1710-1719 doi: 10.12029/gc20210604
Zhang J H, Ouyang Y, Chen Y Z, et al, 2021. Land suitability evaluation of agricultural industrial park based on UAV remote sensing in Zhaojue County of Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 48(6): 1710-1719. doi: 10.12029/gc20210604
[30] 张景华, 欧阳渊, 刘洪, 等, 2021. 基于主控要素的生态地质脆弱性评价——以四川省西昌市为例[J]. 自然资源遥感, 33(4): 181-191
Zhang J H, Ouyang Y, Liu H, et al, 2021. Eco-geological vulnerability assessment based on major controlling factors: a case study of Xichang City, Sichuan Province[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 33(4): 181-191.
[31] 张茂省, 王尧, 薛强, 2019. 资源环境承载力评价理论方法与实践[J]. 西北地质, 52(2): 1-11
Zhang M S, Wang Y, Xue Q, 2019. Evaluation resource environment carrying capacity: Theoretical method and practice[J]. Northwestern Geology, 52(2): 1-11.
[32] 张腾蛟, 刘洪, 欧阳渊, 等, 2020. 中高山区土壤成土母质理化特征及主控因素初探——以西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(1): 106-114
Zhang T J, Liu H, Ouyang Y, et al, 2020. A preliminary discussion on the physical and chemical characteristics and main controlling factors of soil and parent material in the middle and high mountain area——take Xichang as an example[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(1): 106-114.
[33] 张信宝, 王世杰, 白晓永, 等, 2013. 贵州石漠化空间分布与喀斯特地貌、岩性、降水和人口密度的关系[J]. 地球与环境, 41(1): 1-6
Zhang X B, Wang S J, Bai X Y, et al, 2013. Relationships between the spatial distribution of Karst land desertification and geomorphology, lithology, precipitation, and population density in Guizhou Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 41(1): 1-6.
[34] 张晓博, 周萍, 张焜, 等, 2023. 基于 GIS 和 CF-Logistic 回归模型地质灾害易发性评价——以青海湟中县为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 43(4): 797 − 807.
Zhang X B, Zhou P, Zhang K, et al, 2023. Evaluation method of geological hazard susceptibility: A case study on GIS and CF-Logistic regression model in Huangzhong, Qinghai[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 43(4): 797 − 807 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 郑续, 苗俊霞, 王东, 等, 2020. 黄河中上游地质灾害高发县国土空间适宜性评价及功能分区——以陕西省延川县为例[J]. 西北地质, 53(2): 289-297
Zheng X, Wang J X, Wang D, et al, 2020. Suitability evaluation and functional division of land space development in the high-incidence area of geological hazards in the Yellow River: a case study of Yanchuan County, Shangxi Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 53(2): 289-297.
[36] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 生态功能区划暂行规程. [EB/OL]. [2017-04-12]. http://sts.mep.gov.cn/stbh/stglq/200308/t20030815_90755.shtml.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Tentative specification of ecological function regionalization [EB / OL]. [2017-04-12]. http://sts.mep.gov.cn/stbh/stglq/200308/t20030815_90755.shtml (in Chinese).
-



 下载:
下载: