Applied research of slope radar in emergency monitoring of major sudden landslides
-
摘要:
西南地区突发性重大地质灾害常发生于深切河谷区,在应急抢险过程中,存在人员难到达、地面调查与监测困难、灾害持续变形破坏造成的危害大等问题。以西藏自治区江达县白格滑坡和四川丹巴县阿娘寨滑坡应急抢险为例,应用边坡雷达对白格滑坡残留体和阿娘寨滑坡复活体进行应急监测和变形特征研究。结果表明:通过边坡雷达获取各测点的累计视向变形量、变形速率、变形加速度等监测数据绘制监测区变形云图和监测曲线,判识滑坡区变形破坏及发展趋势、研判各变形区所处的变形演化阶段,快速对临滑破坏区进行识别与预报。边坡雷达能对突发性重大地质灾害开展非接触式全天候实时监测,既能实时掌握灾害变形特征,也保证了监测人员安全,对今后类似的突发性地质灾害应急监测和预警预报具有参考借鉴意义。
Abstract:Landslides often occur in deep river valleys with high altitudes in remote regions in southwest China. In the process of emergency rescue, there are some difficulties, such as difficulty in arrival of personnel, difficulty in ground investigation and monitoring, and great damage caused by sustained deformation. In this paper, we use interferometric synthetic aperture radar to carry out real-time monitoring of a landslide mass and study deformation characteristics using the emergency monitoring of Baige Landslide in Jiangda County of Tibet Autonomous Region and Aniangzhai Landslide in Danba County of Sichuan Province as examples. Through the real-time deformation map in the monitoring area obtained by S-SAR-I, we have identified the ranges of strong deformation regions. Through the cumulative apparent deformation, deformation velocity and deformation acceleration of each monitoring point, we have monitored the whole deformation law of each deformation area in real time and judged the deformation evolution stage of each deformation area. In addition, we have successfully identified and forecasted the local sliding failures in each deformation area. The slope radar can carry out non-contact all-weather real-time monitoring of sudden major geological disasters. This method not only captures the deformation characteristics of the disaster in real time, but also ensures the safety of the monitoring personnel. This approach has great significance for the future emergency monitoring and early warning and forecast of sudden geological disasters.
-

-
表 1 S-SAR-I型边坡雷达基本参数
Table 1. The basic parameters of S-SAR-I
信号频段 Ku 信号类型 SFCW 监测距离 10~ 5000 m监测范围 60°×30° 监测精度 0.1 mm 合成孔径长度 1 m 方位向分辨率 4 mrad 距离向分辨率 0.3 m 数据采集周期 10 min 防护等级 IP65 供电电源 220 V/50 Hz 工作温度 −30℃~65℃ 工作湿度 0~95% 表 2 不同型号边坡雷达主要参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of main parameters of different types of slope radar
国家 瑞士 意大利 荷兰 中国 型号 GAMMA IBIS-FM FastGBSAR S-SAR-I 类型 真实孔径雷达 合成孔径雷达 合成孔径雷达 合成孔径雷达 最大监测距离 / 4 km / 5 km 距离分辨率 0.75 m 0.5 m×4.4 mrad 0.5 m 0.3 m 方位分辨率 6.9 m@1 km / / 4 mrad 采集时间 <20 min <3 min 5 s <10 min 监测精度 <2 mm ±0.1 mm / 0.1 mm 表 3 各强变形区特征表
Table 3. Characteristics of each deformation zone
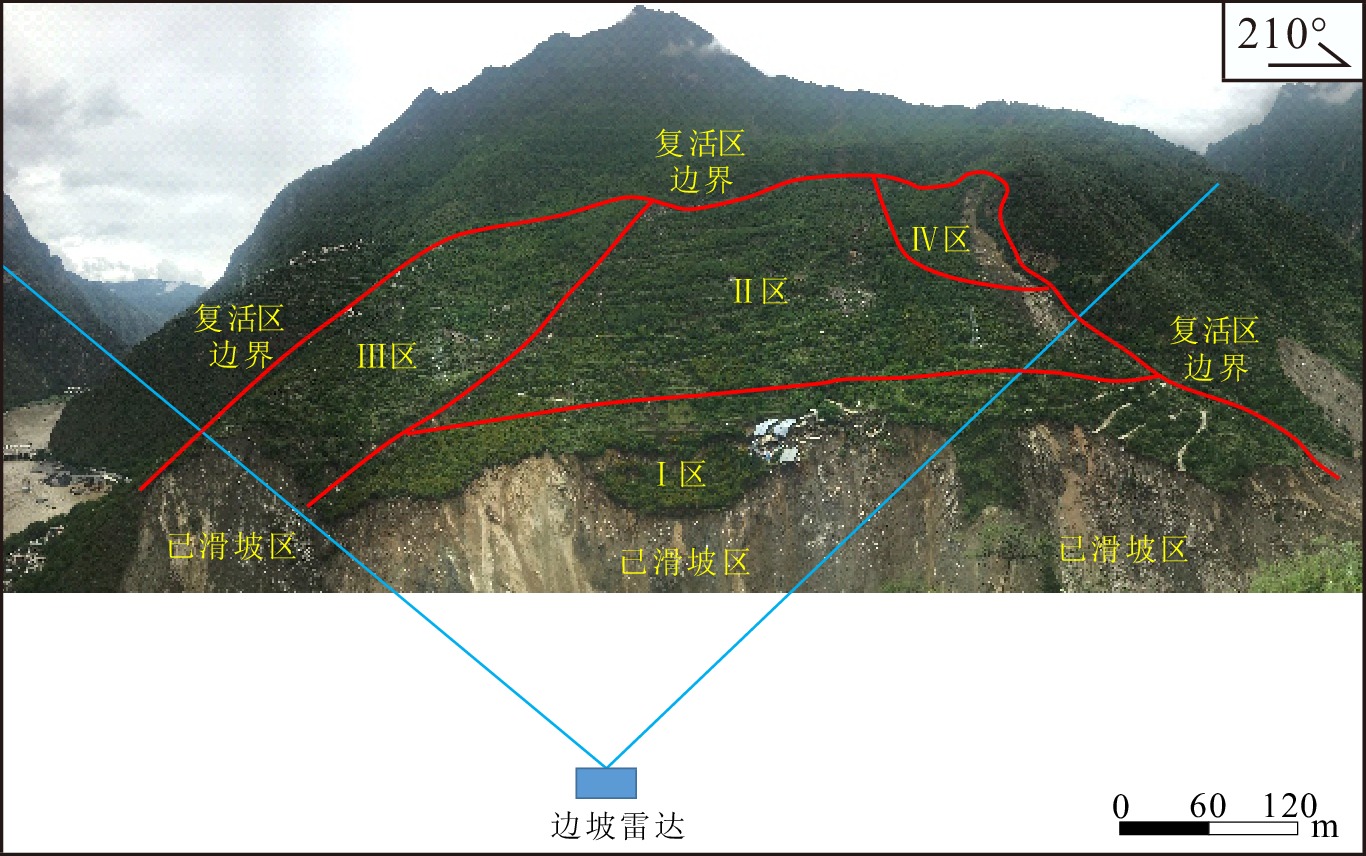
序号 位置 估算面积/m2 强变形原因 ① K3区下部及坡脚 61000 浅表层残坡积土和碎裂岩体垮塌 ② K1区下游侧临空面 14000 临空面松动块石掉落 ③,④ V形凹槽区域 13200 V形凹槽上部及两侧滚落的块石铲刮地表 ⑤ 剪出口处 15400 地表滑坡堆积物、浅表层残坡积土和碎裂岩体垮塌 -
[1] 邓国仕, 郑万模, 杨桂花, 等, 2011. 四川丹巴县甲居滑坡GPS监测结果及分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 31(2): 99-104 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2011.02.014
Deng G S, Zheng W M, Yang G H, et al, 2011. GPS monitoring of the Jiaju landslide in Danba, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 31(2): 99-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2011.02.014
[2] Fan X, Xu Q, Gianvito S, et al., Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24th 2017 Xinmo landslide, Maoxian, Sichuan, China[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(3) : 2129−2146.
[3] Fan X, Xu Q, Alonso−Rodriguez A, et al., Successive land sliding and damming of the Jinsha River in eastern Tibet, China: prime investigation, early warning, and emergency response[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(5) : 1003−1020.
[4] 胡凯衡, 张晓鹏, 罗鸿, 等, 2020. 丹巴县梅龙沟“6.17”泥石流灾害链调查[J]. 山地学报, 38(6): 945-951 doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000570
Hu K H, Zhang X P, Luo H, et al, 2020. Investigation of the “6.17” Debris Flow Chain at the Meilong Catchment of Danba County, China[J]. Mountain Research, 38(6): 945-951. doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000570
[5] 蒋留兵, 杨凯, 车俐, 2020. 地基合成孔径雷达对目标三维形变的监测[J]. 测绘通报, (3): 35-38
Jiang L B, Yang K, Che L, 2020. Monitoring of 3D deformation of target by ground-based synthetic aperture radar[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (3): 35-38
[6] 刘斌, 葛大庆, 张玲, 等, 2016. 地基雷达干涉测量技术在滑坡灾后稳定性评估中的应用[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 36(8): 674-677
Liu B, Ge D Q, Zhang L, et al, 2016. Application of Monitoring Stability after Landslide Based on Ground-Based InSAR [J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 36(8): 674-677.
[7] 林德才, 马海涛, 宋宝宏, 2016. 边坡雷达在滑坡应急救援行动中的应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 12(S1): 284-289
Lin D C, Ma H T, Song B H, 2016. Application of slope radar in emergency rescue of landslide[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 12(S1): 284-289.
[8] 李如仁, 杨震, 余博, 2017. GB-InSAR集成GIS的露天煤矿边坡变形监测[J]. 测绘通报, (5): 26-30
Li R R, Yang Z, Yu B, 2017. Slope Deformation Monitoring of Open Pit Coal Mine by GIS Integrated GB-InSAR[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (5): 26-30.
[9] 刘国祥, 张波, 张瑞, 等, 2019. 联合卫星SAR和地基SAR的海螺沟冰川动态变化及次生滑坡灾害监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(7): 980-995
Liu G X, Zhang B, Zhang R, et al, 2019. Monitoring Dynamics of Hailuogou Glacier and the Secondary Landslide Disasters Based on Combination of Satellite SAR and Ground-Based SAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 980-995.
[10] 陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等, 2019. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(9): 1342-1354
Lu H Y, Li W L, Xu Q, et al, 2019. Early Detection of Landslides in the Upstream and Downstream Areas of the Baige Landslide, the Jinsha River Based on Optical Remote Sensing and InSAR Technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(9): 1342-1354.
[11] 李强, 张景发, 2019. 高分三号卫星全极化SAR影像九寨沟地震滑坡普查[J]. 遥感学报, 23(5): 883-891.
Li Q, Zhang J F, 2019. Investigation on earthquake-induced landslide in Jiuzhaigou using fully polarimetric GF-3 SAR images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(5): 883-891.
[12] 李翔宇, 雷添杰, 陈文晋, 等, 2020. 基于地基雷达干涉测量技术的大坝边坡形变监测及应用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 48(9): 221-225 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.09.061
Li X Y, Lei T J, Chen W J, et al, 2020. Deformation Monitoring and Application of Dam Slope Based on Ground-based Radar Interferometry[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 48(9): 221-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.09.061
[13] LUO Y, SONG H, WANG R, et al, 2014. Arc FMCW SAR and applications in ground monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(9): 5989-5998. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2325905
[14] 邱志伟, 岳建平, 汪学琴, 2014. 地基雷达系统IBIS-L在大坝变形监测中的应用[J]. 长江科学院院报, 31(10): 104-107 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2014.10.015
Qiu Z W, Yue J P, Wang X Q, 2014. Application of Ground-based Radar System IBIS-L to Dam Deformation Analysis[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 31(10): 104-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2014.10.015
[15] 王念秦, 曾思伟, 吴玮江, 等, 1999. 滑坡宏观迹象综合分析预报方法研究[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 11(1): 34–38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0366.1999.01.009
Wang N Q, Zeng S W, Wu W J, 1999. A Study on Forecasting Method of The Comprehensive Analysis of Macroscopic Signs of Landslide[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 11(1): 34–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0366.1999.01.009
[16] 王尚庆, 徐进军, 2006. 滑坡灾害短期临滑预报监测新途径研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 28(5): 385–388
Wang S Q, Xu J J, 2006. New Method to Monitor and Forecast Landslide Disaster in Short-term[J]. J of China Three Gorges Univ. (Natural Sciences), 28(5): 385–388.
[17] 许强, 黄润秋, 李秀珍, 2004. 滑坡时间预测预报研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 19(3): 478–483 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.021
Xu Q, Huang R Q, Li X Z, 2004. Research Progress in Time Forecast and Prediction of Landslides [J]. Advance in Earth sciences, 19(3): 478–483. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.021
[18] 薛源, 胡丹, 郭科, 等, 2007. 基于新型仿生智能方法的边坡变形位移预测[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 29(5): 446–449 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2007.05.017
Xue Y, Hu D, Guo K, 2007. Displacement Forecast of Slope Deformation Based on A New Type of Bionic and Intelligent Method[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 29(5): 446–449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2007.05.017
[19] 许强, 曾裕平, 2009. 具有蠕变特点滑坡的加速度变化特征及临滑预警指标研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 28(6): 1099–1106 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.003
Xu Q, Zeng Y P, 2009. Research on Acceleration Variation Characteristics of Creep Landslide and Early-Warning Prediction Indicator of Critical Sliding [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 28(6): 1099–1106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.003
[20] 邢诚, 韩贤权, 周校, 等, 2014. 地基合成孔径雷达大坝监测应用研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 31(7): 128-134 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2014.07.025
Xing C, Han X Q, Zhou X, el al, 2014. Application of GB-SAR to Dam Monitoring [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 31(7): 128-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2014.07.025
[21] 许强, 李为乐, 董秀军, 等, 2017. 四川茂县叠溪镇新磨村滑坡特征与成因机制初步研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 36(11): 2612-2628 doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0855
Xu Q, Li W L, Dong X J, 2017. The Xinmocun landslide on June 24, 2017 in Maoxian, Sichuan: characteristics and failure mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 36(11): 2612-2628. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0855
[22] 许强, 郑光, 李为乐, 等, 2018.2018年10月和11月金沙江白格两次滑坡-堰塞堵江事件分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 26(6): 1534-1551 doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-406
Xu Q, Zheng G, Li W L, 2018. Study on Successive Landslide Damming Events of Jinsha River in Baige Village on Octorber 11 And November 3, 2018 [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(6): 1534-1551. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018-406
[23] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐, 2019. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(7): 957-966
Xu Q, Dong X J, Li W L, 2019. Integrated Space-Air Ground Early Detection, Monitoring Warning System for Potential Catastrophic Geohazards [J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University), 44(7): 957-966.
[24] 殷跃平, 2004. 中国地质灾害减灾战略初步研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, (2): 4-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.001
Yin Y P, 2004. Initial study on the hazard-relief strategy of geological hazard in China [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, (2): 4-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.001
[25] 张清志, 郑万模, 刘宇平, 等, 2010. GPS在滑坡监测中的应用-以四川省丹巴县亚喀则滑坡为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 30(1): 111-114
Zhang Q Z, Zheng W M, Liu Y P, et al, 2010. An application of GPS monitoring: A case study of the Yakaze landslide in Suopo village, Danba, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 30(1): 111-114.
[26] 张昊宇, 周克勤, 宋亚腾, 等, 2017. 基于新型FMCW地基合成孔径雷达的大坝变形监测[J]. 长江科学院院报, 34(12): 33-37 doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20160869
Zhang H Y, Zhou K Q, Song Y T, et al, 2017. A New Methodology of Landslide Hazard Mapping by Kernel Density Estimation and Value-at-Risk Measurement in Heifangtai Area, Gansu Province of China [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 34(12): 33-37. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20160869
[27] 张海泉, 何文秀, 赵波, 等, 2021. 四川丹巴县“6.17”梅龙沟泥石流-阿娘寨滑坡灾害链现场调查与监测分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 21(29): 12481-12489 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.29.017
Zhang H Q, He W X, Zhao B, et al, 2021. Analysis of field investigation and monitoring of "6.17”Meilong valley debris flow-Aniangzhai landslide disaster chain in Danba County, Sichuan Povince [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 21(29): 12481-12489. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.29.017
[28] 郑光, 许强, 巨袁臻, 等, 2018.2017年8月28日贵州纳雍县张家湾镇普洒村崩塌特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 26(1): 223-240 doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018.01.023
Zheng G, Xu Q, Ju N P, et al, 2018. The Pusacun Rock avalanche on August 28, 2017 in ZhangjiaWan Nayongxian, Guizhou: Characteristics and Failure Mechanism [J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(1): 223-240. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018.01.023
[29] 郑万模, 邓国仕, 刘宇平, 等, 2008. 四川丹巴县典型滑坡GPS监测效果研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 28(3): 30-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2008.03.006
Zheng W M, Deng G S, Liu Y P, et al, 2008. GPS monitoring on the representative landslides in Danba, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 28(3): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2008.03.006
[30] Zheng X, Yang X, Ma H, et al, 2018. Integrated Ground-Based SAR Interferometry, Terrestrial Laser Scanner, and Corner Reflector Deformation Experiments[J]. Sensors (Basel), 18(12): 4401 doi: 10.3390/s18124401
-




 下载:
下载: