Petrogeochemistry, chronology, Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions, and geological significance of the ore-causative intrusion in the Langdu skarn deposit, northwest Yunnan
-
摘要:
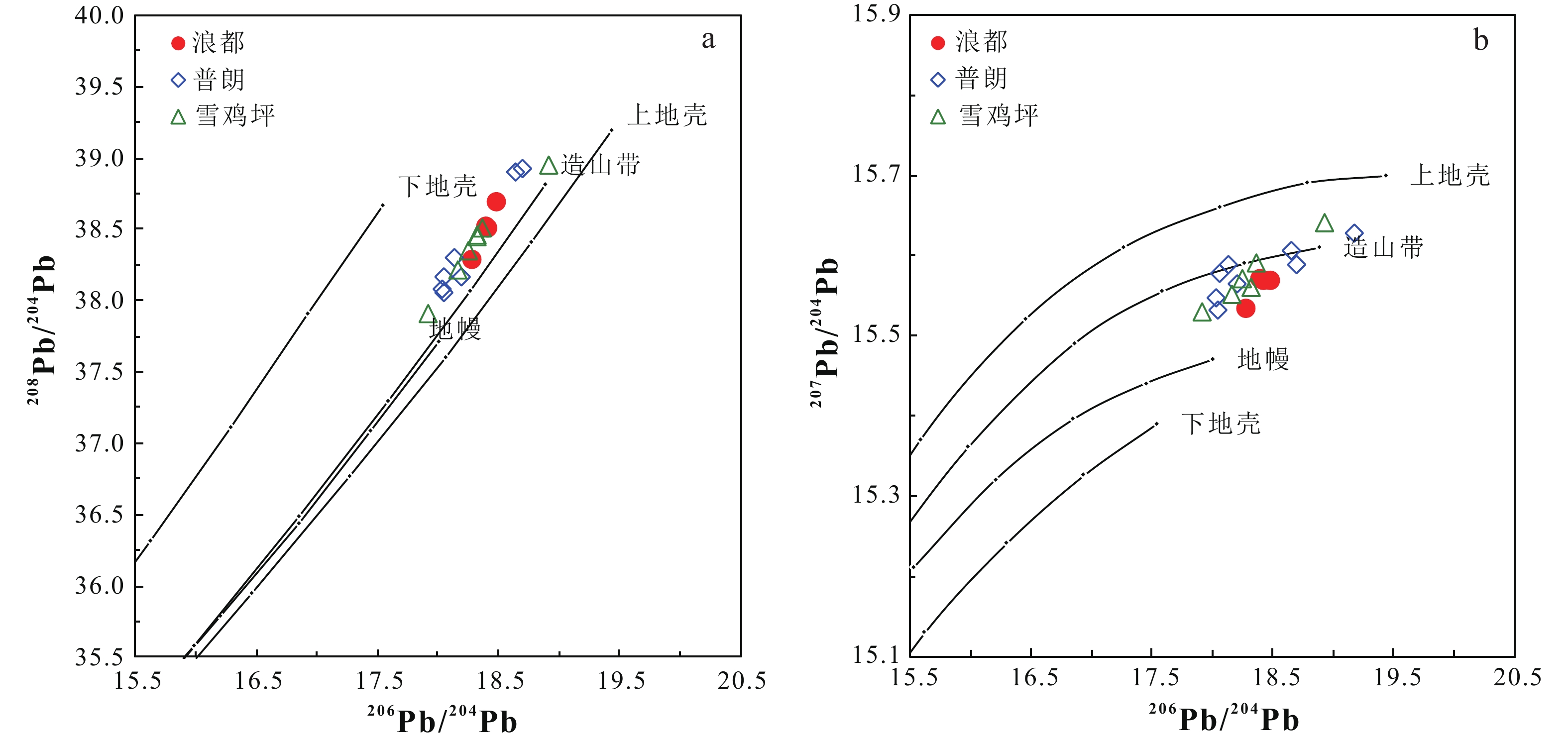
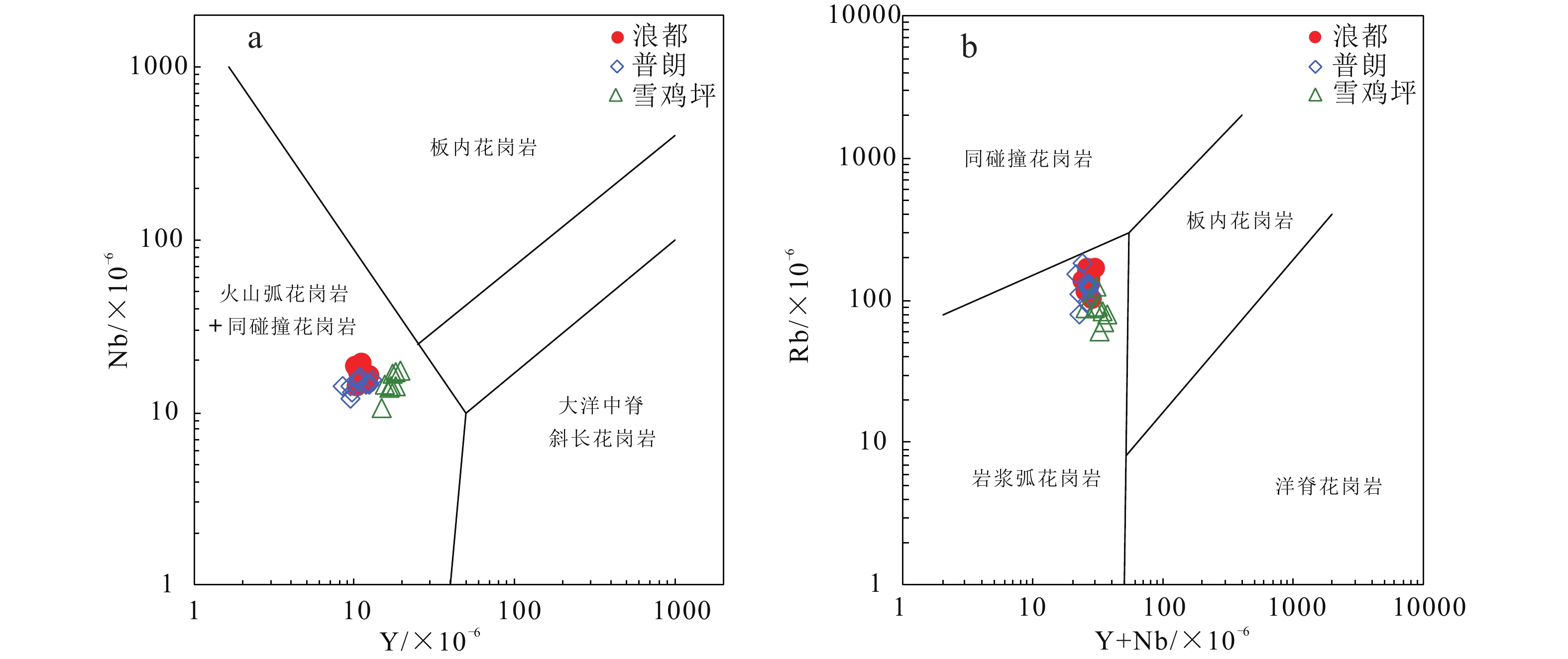
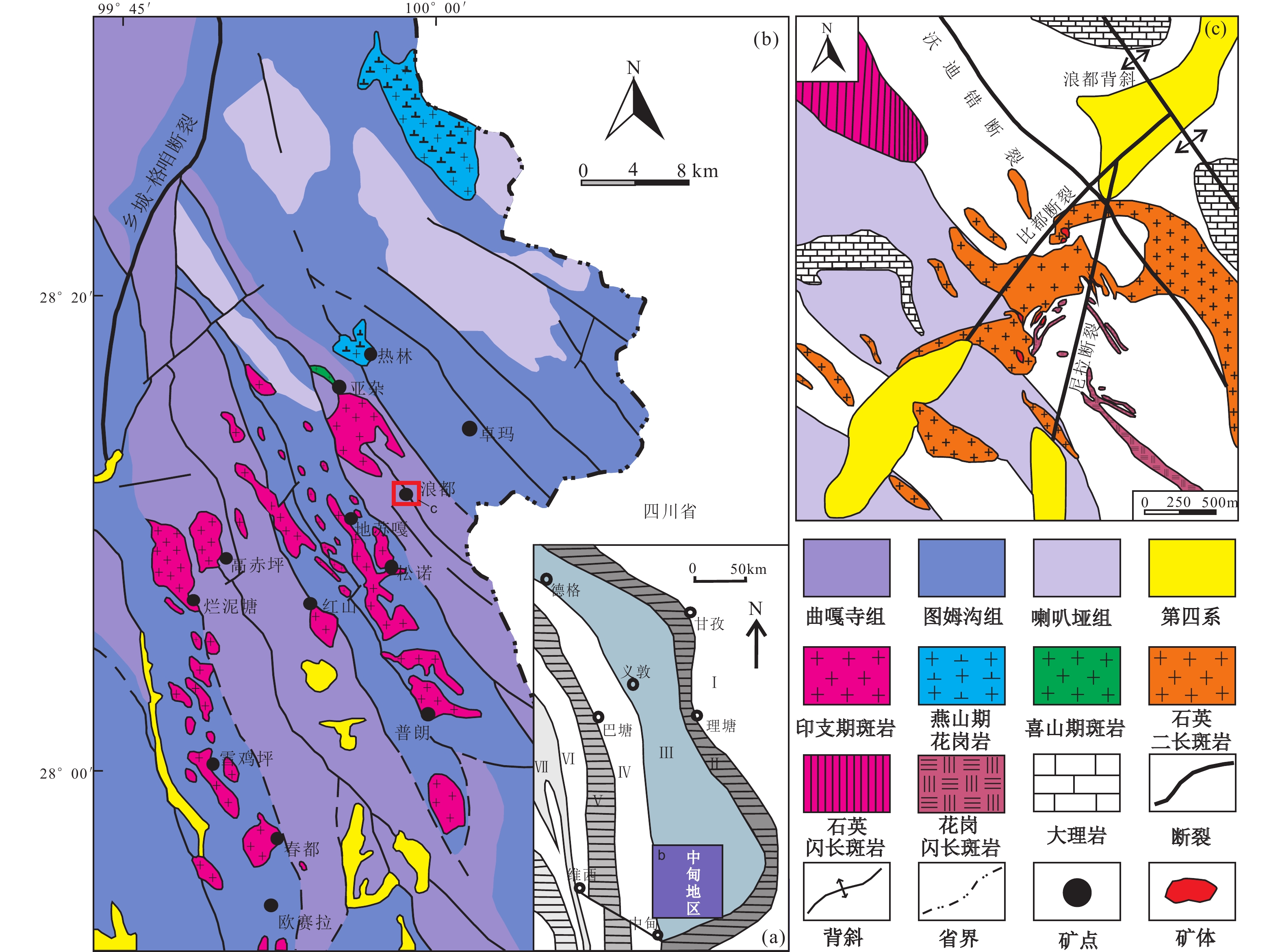
滇西北浪都侵入岩体位于义敦岛弧南段的中甸弧,在空间上属浪都夕卡岩型铜矿床的致矿岩体。本文以浪都致矿岩体中石英二长斑岩为对象,对其开展了锆石SIMS(二次离子质谱)U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素研究。锆石U-Pb定年结果显示浪都石英二长斑岩的成岩年龄为219.2±1.8 Ma(2σ,MSWD=1.3,n = 13),与中甸弧中晚三叠世侵入岩体成岩年龄基本一致。浪都石英二长斑岩具有中等SiO2含量(w(SiO2) 为 60.42%~66.44%),高Al2O3(w(Al2O3)为14.56%~16%)和高K2O(w(K2O)为3.49%~4.49%)含量,以富集LREE和Rb、Ba、Sr等大离子亲石元素,相对亏损HREE和Ta、Nb、Ti等高场强元素为特征,在化学成分上属于高钾钙碱性系列。此外,浪都石英二长斑岩的87Sr/86Sr初始值为0.7054~0.7061,εNd(t)值为-3.5~-2.5,且所有样品在Pb同位素构造模式图上均落在造山带演化线附近。结合浪都石英二长斑岩的成岩时代、岩石化学和同位素特征,本文认为浪都致矿岩体形成于晚三叠世甘孜−理塘洋壳西向俯冲增生的构造背景,是交代地幔部分熔融形成的熔体在上升过程中受到下地壳物质混染,并经历分离结晶作用形成的产物。浪都石英二长斑岩的高Sr/Y比值和高V/Sc比值,指示岩浆具有高含量H2O和较高的氧逸度,是该区斑岩−夕卡岩铜矿床形成的关键。
-
关键词:
- 浪都 /
- 致矿岩体 /
- 岩石地球化学 /
- 锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- Sr-Nd-Pb同位素
Abstract:The Langdu intrusion in northwestern Yunnan is located in the Zhongdian arc of the southern Yidun terrane and it belongs to the ore-causative intrusion of Langdu skarn-type copper deposit, spatially. This study focuses on the quartz-diorite porphyry within the Langdu ore-bearing intrusion and investigates its zircon SIMS U-Pb dating, rock geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic composition. The zircon U-Pb dating results reveal a crystallization age of 219.2±1.8 Ma (2σ, MSWD=1.3, n=13) for the Langdu quartz-diorite porphyry, which is consistent with the late Triassic intrusive rocks in the Zhongdian arc. The Langdu quartz-diorite porphyry exhibits medium SiO2 (60.42%–66.44%), high Al2O3 (14.56%–16%), and high K2O (3.49%–4.49%) contents. It is characterized by enrichment of LREE and large ion lithophile elements such as Rb, Ba, and Sr, and relative depletion of HREE and high field strength elements such as Ta, Nb, and Ti, belonging to the high-K calc-alkaline series. Additionally, the initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of the Langdu quartz-diorite porphyry range from
0.7054 to0.7061 , and εNd(t) values range from -3.5 to -2.5. All samples are plotted near the orogenic evolution line on the Pb isotope evolutionary diagram. Combining the petrological, geochemical, and isotopic characteristics of the Langdu quartz-diorite porphyry, this study suggests that the Langdu ore-bearing intrusion formed in relation to the westward subduction and accretion of late Triassic Garez-Litang oceanic crust. It was a product of partial melting of the metasomatized mantle, mixed with lower crustal material during its ascent, and experienced intense fractional crystallization. The high Sr/Y and high V/Sc ratios of the Langdu quartz-diorite porphyry indicate the characteristics of high-water content and relatively high oxygen fugacity in the magma, which are probably key factors controlling the formation of the porphyry-skarn copper deposit in this region.-
Key words:
- Langdu /
- ore-bearing intrusion /
- rock geochemistry /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes
-

-
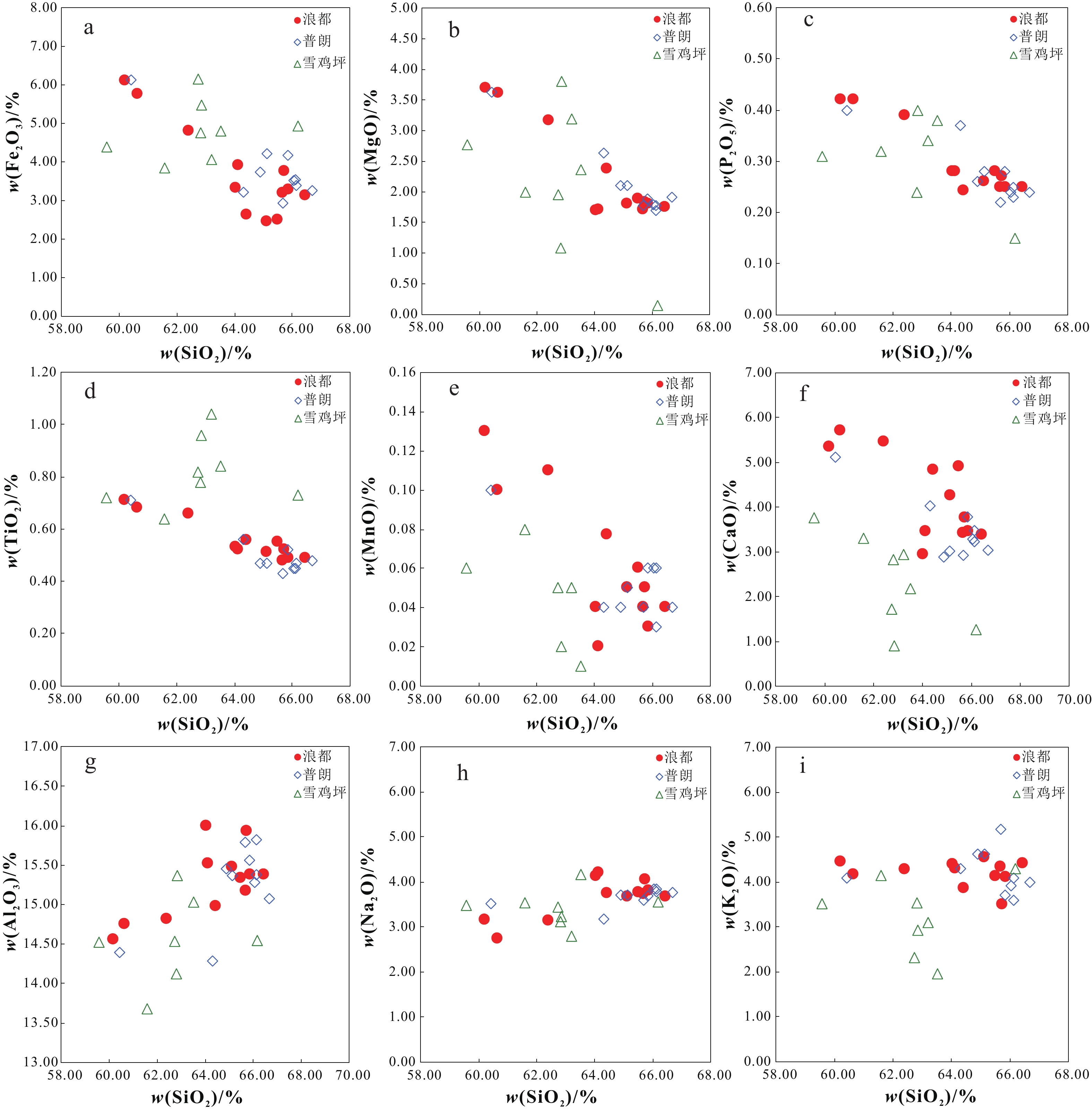
图 2 浪都致矿岩体及普朗雪鸡坪斑岩TAS图解(a)(底图据Middlemost, 1994; 碱度分界线据Irvine et al., 1971),K2O-Na2O图解(b)(底图据Middlemost, 1972),K2O-SiO2图解(c)(实线据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976; 虚线据Middlemost, 1985)和A/NK-A/CNK图解(d)(底图据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989)
Figure 2.
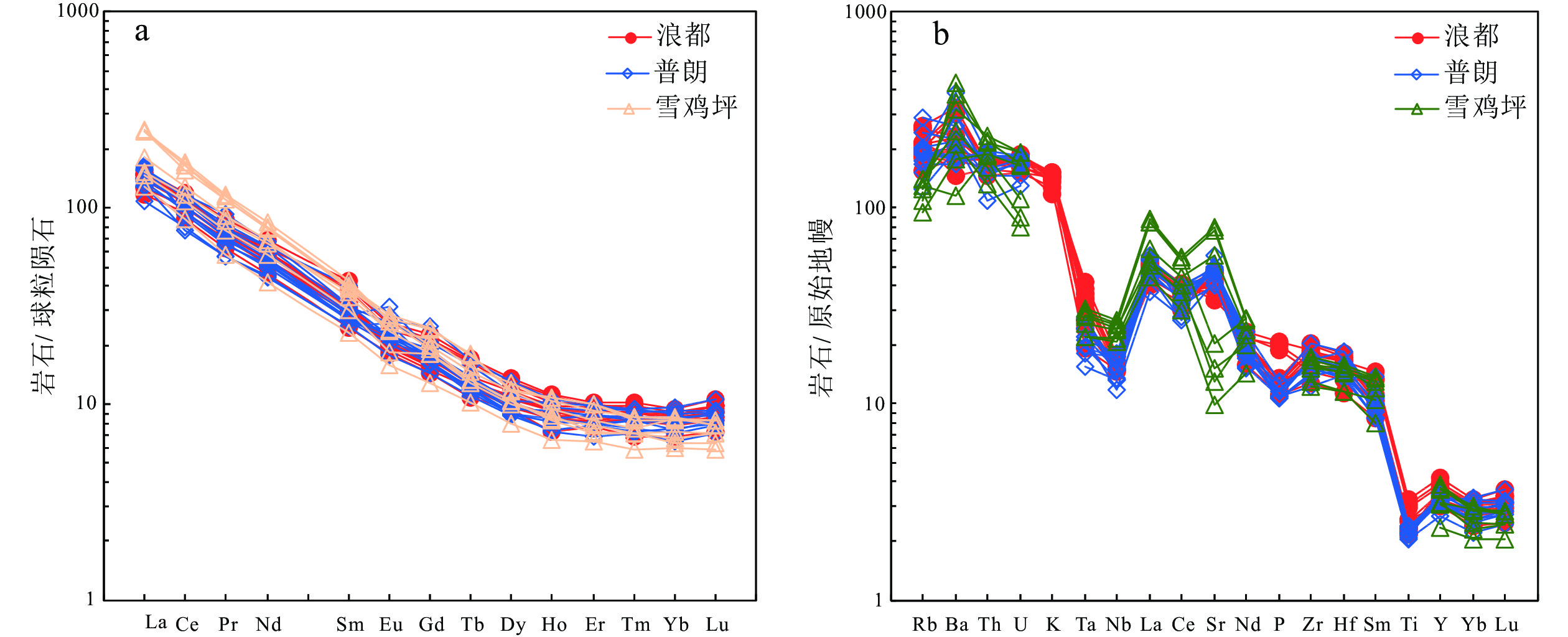
图 4 浪都致矿岩体及普朗雪鸡坪斑岩稀土元素配分模式图(球粒陨石标准化数据来自Sun and McDonough, 1989)(a)和浪都致矿岩体及普朗雪鸡坪斑岩微量元素蛛网图(b)(原始地幔标准化数据来自Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Figure 4.
-
[1] Ariadni A Georgatou,Massimo C,2020. Magmatic sulfides in high-potassium calc-alkaline to shoshonitic and alkaline rocks[J]. Solid Earth,11:1 − 21. doi: 10.5194/se-11-1-2020
[2] Cao K,Yang Z M,Noel C,et al.,2022. Generation of the giant porphyry Cu-Au deposit by repeated recharge of mafic magmas at Pulang in eastern Tibet[J]. Economic Geology,117:57 − 90. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4860
[3] 曹康,许继峰,陈建林,等,2014. 云南普朗超大型斑岩铜矿床含矿斑岩成因及其成矿意义[J]. 矿床地质,33(2):307 − 322.
Cao K,Xu J F,Chen J L,et al.,2014. Origin of porphyry intrusions hosting superlarge Pulang porphyry copper deposit in Yunnan Province:Implications for metallogenesis[J]. Mineral Deposits,33(2): 307 − 322 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] 曹晓民,董涛,余海军,等,2022. 滇西北香格里拉市格咱铜多金属矿集区地质演化与成矿作用[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,42(1):50 − 61.
Cao X M,Dong T,Yu H J,2022. Geological evolution and metallogenesis of the Geza copper polymetallic mineral concentration district,Shangri-La,Southwest Yunnan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,42(1):50 − 61 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Chen B,He J B,Chen C J,et al.,2013. Nd-Sr-Os isotopic data of the Baishiquan mafic-ultramafic complex from east Tianshan,and implications for petrogenesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29:294 − 302.
[6] Chen B,Jahn B W,Wilde S,et al.,2000. Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia,China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics,328(1-2):157 − 187. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00182-7
[7] Chen J L,Xu J F,Wang B D,et al.,2015. Geochemical differences between subduction-and collision-related copper-bearing porphyries and implications for metallogenesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,70:424 − 437. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.01.011
[8] 陈建林,许继峰,任江波,等,2011. 俯冲型和碰撞型含矿斑岩地球化学组成的差异[J]. 岩石学报,27(9):2733 − 2742.
Chen J L,Xu J F,Ren J B,et al.,2011. Geochemical differences between the subduction- and coilisionaitype ore-bearing porphyric rocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(9):2733 − 2742 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Chen Q,Wang C M,Du B,et al.,2021. Petrogenesis of the Late Triassic Biluoxueshan granitic pluton,SW China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Sanjiang Orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,211:104700.
[10] Chen X L,Leng C B,Zou S H,et al.,2021. Geochemical compositions of apatites from the Xuejiping and Disuga porphyries in Zhongdian arc:Implications for porphyry Cu mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,130:103954. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103954
[11] 陈振武,丁昕,于慧敏,等,2019. 中国东部新生代玄武岩指示地幔部分熔融过程中铁−钒同位素分馏[C]//中国矿物岩石地球化学学会. 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第17届学术年会论文摘要集(pp. 400).
Chen Z W,Ding X,Yu H M,et al.,2019. Fe-vanadium isotope fractionation during Cenozoic indicative mantle partial melting in eastern China [C]// China Mineralogical, Petrogeochemical Society. Abstracts of the 17th Annual Conference of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry Society of China (pp. 400) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Core D P,Kesler S E,Essene E J,2006. Unusually Cu-rich magmas associated with giant porphyry copper deposits:Evidence from Bingham,Utah[J]. Geology,34:41 − 44.
[13] 代堰锫,李同柱,张惠华,2021. 扬子陆块西缘江浪穹窿超基性岩的成因:锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,41(4):573 − 584.
Dai Y P,Li T Z,Zhang H H,2021. Petrogenesis of the ultramafic pluton in the Jianglang dome, western margin of the Yangtze block: Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,41(4):573 − 584 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Deng C,Frances E J,Wan B,et al.,2022. The influence of ridge subduction on the geochemistry of Vanuatu arc magmas[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth(1):127.
[15] Deng J,Wang Q F,Li G J,et al.,2014. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region,SW China[J]. Gondwana Research,26:419 − 437. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002
[16] 董涛,余海军,段召艳,等,2020. 云南香格里拉盖吉夏含矿石英二长闪长玢岩年代学、地球化学、锆石Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,36(5):1369 − 1388. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.04
Dong T,Yu H J,Duan Z Y,et al.,2020. Geochronology,geochemistry,and zircon Hf isotope characteristics and their geological significances of the Gaijixia ore-bearing intrusive rocks in the Shangri-La region,NW Yunnan,SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,36(5):1369 − 1388 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.04
[17] Ducea M N,Saleeby J B,Bergantz G,2015. The architecture,chemistry,and evolution of continental magmatic arcs[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,43(1):299 − 331. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105049
[18] Evans K A,2012. The redox budget of subduction zones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,113(1-2):11 − 32. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.03.003
[19] Eyal M,Litvinovsky B A,Katzir Y,et al.,2005. The Pan-African high-K calc-alkaline peraluminous Elat granite from southern Israel:geology,geochemistry and petrogenesis[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,40:115 − 136.
[20] Gao X,Yang L Q,Orovan E A,2018. The lithospheric architecture of two subterranes in the eastern Yidun Terrane,East Tethys:Insights from Hf-Nd isotopic mapping[J]. Gondwana Research,62:127 − 143. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.02.010
[21] Hollings P,Cooke D R,Clark A,2005. Regional geochemistry of Tertiary igneous rocks in Central Chile:implications for the geodynamic environment of giant porphyry copper and epithermal gold mineralization[J]. Economic Geology,100:887 − 904. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.100.5.887
[22] Hou Z Q,Yang Y Q,Lü Y J,et al.,2015. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones[J]. Geology,43(3):643 − 650.
[23] 侯增谦,杨岳清,曲晓明,等,2004. 三江地区义敦岛弧造山带演化和成矿系统[J]. 地质学报,78(1):109 − 120.
Hou Z Q,Yang Y Q,Qu X M,et al.,2004. Tectonic evolution and mineralization systems of the Yidun arc orogen in Sanjiang region,China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,78(1):109 − 120 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 黄肖潇,许继峰,陈建林,等,2012. 中甸岛弧红山地区两期中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 岩石学报,28(5):1493 − 1506.
Huang X X,Xu J F,Chen J L,et al.,2012. Geochronology,geochemistry and petrogenesis of two periods of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks from Hongshan area in Zhongdian arc[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(5):1493 − 1506 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Irvine T N,Baragar W R A,1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences,8(5):523 − 548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
[26] Jahn B M,Windley B,Natalin B,et al.,2004. Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,23(5):599 − 603. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00124-X
[27] 王忠强,李超,江小均,等,2020. 滇西北休瓦促钼钨矿床白钨矿原位微量和Sr同位素特征及其对成矿作用的指示[J]. 岩矿测试,39(5):762 − 776.
Wang Z Q,Li C,Jiang X J,et al.,2020. In situ trace element and Sr isotope composition of scheelite in the Xiuwacu molybdenum-tungsten deposit,northwest Yunnan:Constraints on mineralization[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis,39(5):762 − 776 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] 金灿海,范文玉,张玙,等,2013. 中甸浪都铜矿区二长斑岩中锆石的微量元素组成、U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,37(2):262 − 272.
Jin C H,Fan W Y,Zhang Y,et al.,2013. Trace element composition and U-Pb chronology of zircons in monzonite porphyry from the Langdu copper deposit in Zhongdian and Their Geological Significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,37(2):262 − 272 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Kovalenko V L,Yarmolyuk V V,Kovach V P,et al.,2004. Isotope provinces,mechanisms of generation and sources of the continental crust in the Central Asian mobile belt:Geological and isotopic evidence[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,23(5):605 − 627. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00130-5
[30] Leng C B,Gao J F,Chen W T,et al.,2018. Quantifying exhumation at the giant Pulang porphyry Cu-Au deposit using U-Pb-He dating[J]. Economic Geology,113(0):1077 − 1092.
[31] Leng C B,Huang Q Y,Zhang X C,et al.,2014. Petrogenesis of the Late Triassic volcanic rocks in the southern Yidun arc,SW China:Constraints from the geochronology,geochemistry,and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes[J]. Lithos 190-191,363 − 382.
[32] Leng C B,Zhang X C,Hu R Z,et al.,2012. Zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic constraints on the genesis of the Xuejiping porphyry copper deposit in Zhongdian,Northwest Yunnan,China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,60:31 − 48. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.07.019
[33] 冷成彪,2009. 滇西北雪鸡坪斑岩铜矿地质背景及矿床地球化学特征研究[D]. 中国科学院研究生院.
Leng C B,2009. Ore deposit geochemistry and regional geological setting of the Xuejiping porphyry copper deposit,northwest Yunnan,China[D]. Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] 冷成彪,张兴春,王守旭,等,2007. 云南中甸地区两个斑岩铜矿容矿斑岩的地球化学特征——以雪鸡坪和普朗斑岩铜矿床为例[J]. 矿物学报,27(3-4):414 − 422.
Leng C B,Zhang X C,Wang S X,et al.,2007. Geochemical characteristics of porphyry copper deposits in the Zhongdian area,Yunnan as exemplified by the Xuejiping and Pulang porphyry copper deposits[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,27(3-4):414 − 422 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 冷成彪,张兴春,王守旭,等,2008a. 滇西北雪鸡坪斑岩铜矿S、Pb同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的示踪[J]. 矿物岩石,28(4):80 − 88.
Leng C B,Zhang X C,Wang S X,et al.,2008a. Sulfur and lead isotope compositions of the Xuejiping porphyry copper deposit in northwest Yunnan, China: tracing for the source of metals[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology,28(4):80 − 88 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] 冷成彪,张兴春,王守旭,等,2008b. 滇西北中甸松诺含矿斑岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,32(1):124 − 130.
Leng C B,Zhang X C,Wang S X,et al.,2008b. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the Songnuo ore-hosted porphyry,Zhongdian,northwest Yunnan,Chian and its geological implication[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,32(1):124 − 130 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] 冷成彪,张兴春,王新松,等,2015. 云南中甸地区印支期和燕山晚期斑岩成矿作用研究[J]. 矿物学报,35(S1):401.
Leng C B,Zhang X C,Wang X S,et al.,2015. Metallogenesis of porphyry of Indochinese and Late Yanshanian in the Zhongdian area,Yunnan,China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,35(S1):401 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] 李文昌,2007. 义敦岛弧构造演化与普朗超大型斑岩铜矿成矿模型[D]. 中国地质大学(北京).
Li W C,2007. The tectonic evolution of Yidun island arc and metallogenic model of Pulang porphyry copper deposit,Yunnan,SW Chain[D]. China University of Geosciences(Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] 李文昌,曾普胜. 云南普朗超大型斑岩铜矿特征及成矿模型[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2007(4):436 − 446.
Li W C,Zeng P S. Characteristics and metallogenic model of the Pulang superlarge porphyry copper deposit in Yunnan,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2007(4):436 − 446 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Li W K,Yang Z M,Cao K,et al.,2019. Redox-controlled generation of the giant porphyry Cu-Au deposit at Pulang, southwest China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 174(2):12.
[41] Li X F,Dong G C,He W Y,et al.,2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of the porphyries in Xuejiping deposit in northwestern Yunnan:Petrogenesis and implication for mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition),88:563 − 564. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12374_31
[42] 李雪峰,2016. 滇西北中甸弧印支期斑岩地球化学特征及含矿性研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京).
Li X F,2016. Geochemistry and ore-bearing potential research of the Indo-porphyries in Zhongdian arc,SN Yunnan[D]. China University of Geosciences(Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Li X H,Liu Y,Li Q L,et al,2009. Precise determination of phanerozoic zircon U-Pb age by multicollector SIMS without ex-ternal standardization[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems,doi:10.1029 /2009GC002400.
[44] 李玉荣,范玉华,孟青,2009. 滇西北浪都矽卡岩型铜矿[J]. 云南地质,28(2):137 − 142.
Li Y R,Fan Y H,Meng Q,2009. The Langdu skarn Cu deposit in northwest Yunan[J]. Yunnan Geology,28(2):137 − 142 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] 林清茶,夏斌,张玉泉,2006. 云南中甸地区雪鸡坪同碰撞石英闪长玢岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其意义[J]. 地质通报,25(Z1):133 − 137.
Lin Q C,Xia B,Zhang Y Q,2006. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the syn-collisional Xuejiping quartz diorite porphyrite in Zhongdian,Yunnan,China,and its geological implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,25(Z1):133 − 137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Liu H,Li Y G,Li W C,et al.,2022. Petrogenesis of an early cretaceous Xiabie Co I‐type granite in southern Qiangtang,Tibet:Evidence from geochemistry,geochronology,Rb‐Sr,Sm‐Nd,Lu‐Hf and Pb isotopes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition),96(3):919 − 937. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14777
[47] 刘军,武广,李铁刚,等,2014. 内蒙古镶黄旗哈达庙地区晚古生代中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学、Sr-Nd同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,30(1):95 − 108.
Liu J,Wu G,Li T G,et al.,2014. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating,geochemistry,Sr-Nd isotopic analysis of the Late Paleozoic intermediate-acidic intrusive rocks in the Hadamiao area,Xianghuang Banner,Inner Mongolia and its geological significances[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(1):95 − 108 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] 刘旭东,2018. 滇西北普朗斑岩型铜多金属矿床成矿流体演化[D]. 中国地质大学(北京).
Liu X D,2018. The evolution of ore-forming fluid of the Pulang porphyry copper polymetallic deposit in the northwest Yunnan Province,China[D]. China University of Geosciences(Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Liu X L,Zhang N,Kang J,2015. The lead isotope characteristics and tracing significance of ore metallogenic material in the Geza arc,Yunnan[J]. Advanced Materials Research,1073-1076:2054 − 2057.
[50] 刘学龙,李文昌,张娜,等,2014. 云南格咱岛弧地苏嘎成矿岩体I型花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质论评,60(1):103 − 114.
Liu X L,Li W C,Zhang N,et al.,2014. Geochronological,geochemical characteristics of Disuga ore-forming I-type granitic porphyries in the Geza arc,Yunnan Province,and their geological significance[J]. Geological Review,60(1):103 − 114 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[51] Ludwig K R,2003. ISOPLOT,Version 3.00. A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication,1 − 70.
[52] Luo B J,Zhang H F,Zhang L Q,et al.,2020. The magma plumbing system of Mesozoic Shanyang porphyry groups,South Qinling and implications for porphyry copper mineralization[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,543:116346. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2020.116346
[53] 罗伟,彭静,金廷福,等,2023. 川西李家沟锂多金属矿区晚三叠世花岗细晶岩脉的成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素的证据[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,43(1):36 − 47.
Luo W,Peng J,Jin T F,et al.,2023. Petrogenesis of granite aplite in the Lijiagou lithium polymetallic ore district in western Sichuan:constraints from geochemistry,zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotope[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,43(1):36 − 47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[54] 马星华,王志强,王超,等,2014. 壳幔岩浆混合作用与陆内环境高Sr/Y斑岩的形成及成矿:实例与探讨[J]. 岩石学报,30(7):2020 − 2030.
Ma X H,Wang Z Q,Wang C,et al.,2014. Crust-mantle magma mixing and implications for the formation of high Sr/Y ore-bearing porphyries in non-arc environments:A case study and discussion[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(7):2020 − 2030 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[55] Maniar P D,Piccoli P M,1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,101(5):635 − 643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[56] Middlemost EAK,1972. A simple classification of volcanic rocks[J]. Bulletin of Volcanology, 36:382 − 397.
[57] Middlemost E A K,1985. Magmas and magmatic rocks[M]. London:Longman,1 − 266.
[58] Middlemost E A K,1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Review,37:215 − 224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
[59] Mungall J E,2002. Roasting the mantle:Slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Au-rich Cu deposits[J]. Geology,30:915 − 918.
[60] 潘桂棠,王立全,尹福光,等,2022. 青藏高原形成演化研究回顾、进展与展望[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2022,42(2):151 − 175.
Pan G T,Wang L Q,Yin F G,et al.,2022. Researches on geological-tectonic evolution of Tibetan Plateau:A review,recent advances,and directions in the future[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,42(2):151 − 175 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[61] Pan L C,Hu R Z,Wang X S,et al.,2016. Apatite trace element and halogen compositions as petrogenetic-metallogenic indicators:examples from four granite plutons in the Sanjiang region,SW China[J]. Lithos,254:118 − 130.
[62] Pearce J A,Harris N B W,Tindle A G,1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology,25(4):956 − 983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[63] Peccerillo R,Taylor S R,1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area,Northern Turkey[J]. Contrib. Mineral Petrol,58:63 − 81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
[64] Reich M,Parada M A,Palacios C,et al.,2003. Adakite-like signature of Late Miocene intrusions at the Los Pelambres giant porphyry copper deposit in the Andes of central Chile:metallogenic implications[J]. Mineralium Deposita,38:876 − 885. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0369-9
[65] 任江波,许继峰,陈建林,等,2011. “三江”地区中甸弧普朗成矿斑岩地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,30(4):581 − 592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.04.003
Ren J B,Xu J F,Chen J L,et al.,2011. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Pulang porphyries in Sanjiang region[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,30(4):581 − 592 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.04.003
[66] 任涛,钟宏,陈金法,等,2011. 云南中甸地区浪都高钾中酸性侵入岩的地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报,31(1):43 − 54.
Ren T,Zhong H,Chen J F,et al.,2011. Geochemical characteristics of the Langdu high-K intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in the Zhongdian area,northwest Yunnan province,P. R. China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,31(1):43 − 54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[67] Richards J P,2003. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu(Mo-Au) deposit formation[J]. Economic Geology,98(8):1515 − 1533. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.8.1515
[68] Richards J P,2009. Postsubduction porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposits:Products of remelting of subduction-modified lithosphere[J]. Geology,37:247 − 250.
[69] Richards J P,2011. High Sr/Y arc magmas and porphyry Cu±Mo±Au deposits:Just add water[J]. Economic Geology,106(7):1075 − 1081. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.106.7.1075
[70] Richards J P,Spell T,Rameh E,et al.,2012. High Sr/Y magmas reflect arc maturity,high magmatic water content,and porphyry Cu±Mo±Au potential:examples from the Tethyan arcs of central and eastern Iran and western Pakistan[J]. Econ Geol,107:295 − 332. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.2.295
[71] Schütte P,Chiaradia M,Barra F,et al.,2012. Metallogenic features of Miocene porphyry Cu and porphyry related mineral deposits in Ecuador revealed by Re-Os,40Ar/39Ar,and U-Pb geochronology,Miner[J]. Deposita,47,383 − 410.
[72] 沙建泽,罗朝德,王朋. 滇西北雪鸡坪铜矿区岩浆岩大地构造环境及成矿意义[J]. 矿产与地质,2016,30(5):703 − 711.
Sha J Z,Luo C D,Wang P. Tectonic environment and metallogenic significance of magmatite in Xuejiping copper mine,northwest Yunnan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology,2016,30(5):703 − 711 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[73] Sillitoe R H,2010. Porphyry copper systems[J]. Economic Geology,105(1):3 − 41. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.1.3
[74] Stern R J,2002. Subduction zones[J]. Reviews of Geophysics,40:1012.
[75] Sun S S,McDonough W F,1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,42:313 − 345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[76] Tian Z D,Leng C B,Zhang X C,et al.,2019. Recognition of Late Triassic Cu-Mo mineralization in the northern Yidun arc (S. E. Tibetan Plateau):Implications for regional exploration[J]. Minerals,9:765.
[77] 万多,王可勇,李文昌,等,2012. 滇西北热林Cu-Mo矿床流体包裹体特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),42(S3):54 − 63.
Wan D,Wang K Y,Li W C,et al.,2012. Characteristics of fluid inclusions of Relin Cu-Mo deposit in northwestern Yunnan province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),42(S3):54 − 63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[78] Wang B Q,Zhou M F,Li J W,et al.,2011. Late Triassic porphyritic intrusions and associated volcanic rocks from the Shangri-La region,Yidun Terrane,eastern Tibetan Plateau:adakitic magmatism and porphyry copper mineralization[J]. Lithos,127(1):24 − 38.
[79] Wang J T,Xiong X L,Takaha E,et al.,2019. Oxidation state of arc mantle revealed by partitioning of V,Sc and Ti between mantle minerals and basaltic melts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,124(5):4617 − 4638. doi: 10.1029/2018JB016731
[80] Wang Q,Zhao Z H,Bao Z W,et al.,2004. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Tongshankou and Yinzu adakitic intrusive rocks and the associated porphyry copper-molybdenum mineralization in southeast Hubei,East China[J]. Resource Geology,54:137 − 152. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2004.tb00195.x
[81] 王守旭,2008b. 云南中甸普朗斑岩铜矿矿床地球化学[D]. 中国科学院地球化学研究所.
Wang S X,2008b. Geochemistry of Pulang porphyry copper deposit in the Zhongdian area,Yunnan Province[D]. Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
[82] 王守旭,张兴春,冷成彪,等,2008a. 中甸红山矽卡岩铜矿稳定同位素特征及其对成矿过程的指示[J]. 岩石学报,24(3):480 − 488.
Wang S X,Zhang X C,Leng C B,et al.,2008a. Stable isotopic compositions of the Hongshan skarn copper deposit in the Zhongdian area and its implication for the copper mineralization process[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,24(3):480 − 488 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[83] Wang Y J,Fan W M,Guo F,2003. Geochemistry of early Mesozoic potassium-rich diorites-granodiorites in southeastern Hunan Province,South China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Geochemical Journal,37:427 − 448. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.37.427
[84] Wiedenbeck M,Alle P,Corfu F,et al.,1995. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb,Lu-Hf,trace element and REE ana-lyses[J]. Geostandards Newsletter,19(1):1 − 23. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.1995.tb00147.x
[85] Wu T,Xiao L,Wilde S A,et al.,2017. A mixed source for the Late Triassic Garze-Daocheng granitic belt and its implications for the tectonic evolution of the Yidun arc belt,eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos,288-289:214 − 230. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.07.002
[86] Xiao B,Qin K Z,Li G M,et al.,2012. Highly oxidized magma and fluid evolution of Miocene Qulong giant porphyry Cu-Mo deposit,southern Tibet,China[J]. Resource Geology,62(1):4 − 18. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2011.00177.x
[87] Xie B,Song H,Song S W,et al.,2022. Geochemical,zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotopic evidence and molybdenite Re-Os dating from the Cuojiaoma batholith,eastern Tibetan Plateau:Implications for molybdenum potential and tectonic evolution[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,144.
[88] Xiong X L,Xia B,Xu J F,et al.,2006. Na depletion in modern adakites via melt/rock reaction within the sub-arc mantle[J]. Chemical Geology,229:273 − 292. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.008
[89] Yang L Q,He W Y,Gao X,et al.,2018. Mesozoic multiple magmatism and porphyry-skarn Cu-polymetallic systems of the Yidun Terrane,Eastern Tethys:Implications for subduction-and transtension-related metallogeny[J]. Gondwana Research,62:144 − 162. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.02.009
[90] Yang Z,Fu Y,Fang S J,et al.,2020. Mineralization of the Xuejiping porphyry Cu deposit,Western Yunnan,China:Constraints from magmatic oxidization and source[J]. Geological Journal,9:6412 − 6426.
[91] 尹观,倪师军,等,2009. 同位素地球化学[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
Yin G,Ni S J,et al.,2009. Isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
[92] Zartman R E,Doe B R,1981. Plumbotectonics-the model[J]. Tectonophysics,75(1):135 − 162.
[93] 曾普胜,李文昌,王海平,等,2006. 云南普朗印支期超大型斑岩铜矿床:岩石学及年代学特征[J]. 岩石学报,22(4):989 − 1000.
Zeng P S,Li W C,Wang H P,et al.,2006. The Indosinian Pulang superlarge porphyry copper deposit in Yunnan,China:Petrology and chronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,22(4):989 − 1000 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[94] Zhang C C,Sun W D,Wang J T,et al.,2017. Oxygen fugacity and porphyry mineralization:a zircon perspective of Dexing porphyry Cu deposit,China[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta,206:343 − 363. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.03.013
[95] 张昌振,2020. 滇西北普朗斑岩型铜矿外围矿体流体特征及成矿物质来源研究[D]. 昆明理工大学.
Zhang C Z,2020. Study on the fluid characteristics and ore forming material sources of the peripheral ore bodies of Pulang porphyry copper deposit in northwest Yunnan[D]. Kunming University of Science and Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
[96] 张德会,赵仑山,张本仁,等,2013. 地球化学[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
Zhang D H,Zhao L S,Zhang B R,et al.,2013. Geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract).
[97] 张兴春,冷成彪,杨朝志,等,2009. 滇西北中甸春都斑岩铜矿含矿斑岩的锆石SIMS U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 矿物学报,29(S1):359 − 360.
Zhang X C,Leng C B,Yang C Z,et al.,2009. SIMS zircon U-Pb dating of the Chundu ore-hosted porphyry,Zhongdian,northwest Yunnan,Chian and its geological implication[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,29(S1):359 − 360 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[98] 张向飞,李文昌,杨镇,等,2022. 青藏高原东缘休瓦促钨钼矿区复式岩体时空分布及演化意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,42(1):105 − 121.
Zhang X F,Li W C,Yang Z,et al.,2022. Temporal-spatial distribution and evolution implication of the composite intrusion in the Xiuwacu W-Mo deposit,SE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,42(1):105 − 121 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[99] 周放,王保弟,刘函,等,2018. 中甸弧阿热岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学,43(8):2614 − 2627.
Zhou F,Wang B D,Liu H,et al.,2018. Zircon U-Pb dating,geochemistry and petrogenesis of intrusive rocks from A're area,Zhongdian arc[J]. Earth Sciences,43(8):2614 − 2627 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[100] 周晓丹,杨帆,吴静,等,2018. 云南普朗斑岩型铜矿床外围斑岩体成因探讨[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(4):39 − 50.
Zhou X D,Yang F,Wu J,et al.,2018. Petrogenesis of porohyry body in the periphery of Pulang porphyry copper deposit,Yunnan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(4):39 − 50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[101] Zhu D C,Wang Q,Zhao Z D,et al.,2015. Magmatic record of India-Asia collision[J]. Scientific Reports,5:14289. doi: 10.1038/srep14289
[102] Zi J W,Peter A C,Fan W M,et al.,2012. Generation of early indosinian enriched mantle-derived granitoid pluton in the Sanjiang Orogen (SW China) in response to closure of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos,140-141:166 − 182. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.006
-



 下载:
下载: