Reservoir formation mechanism of the microbialite in the Fengjiawan Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Jixian System, southern Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
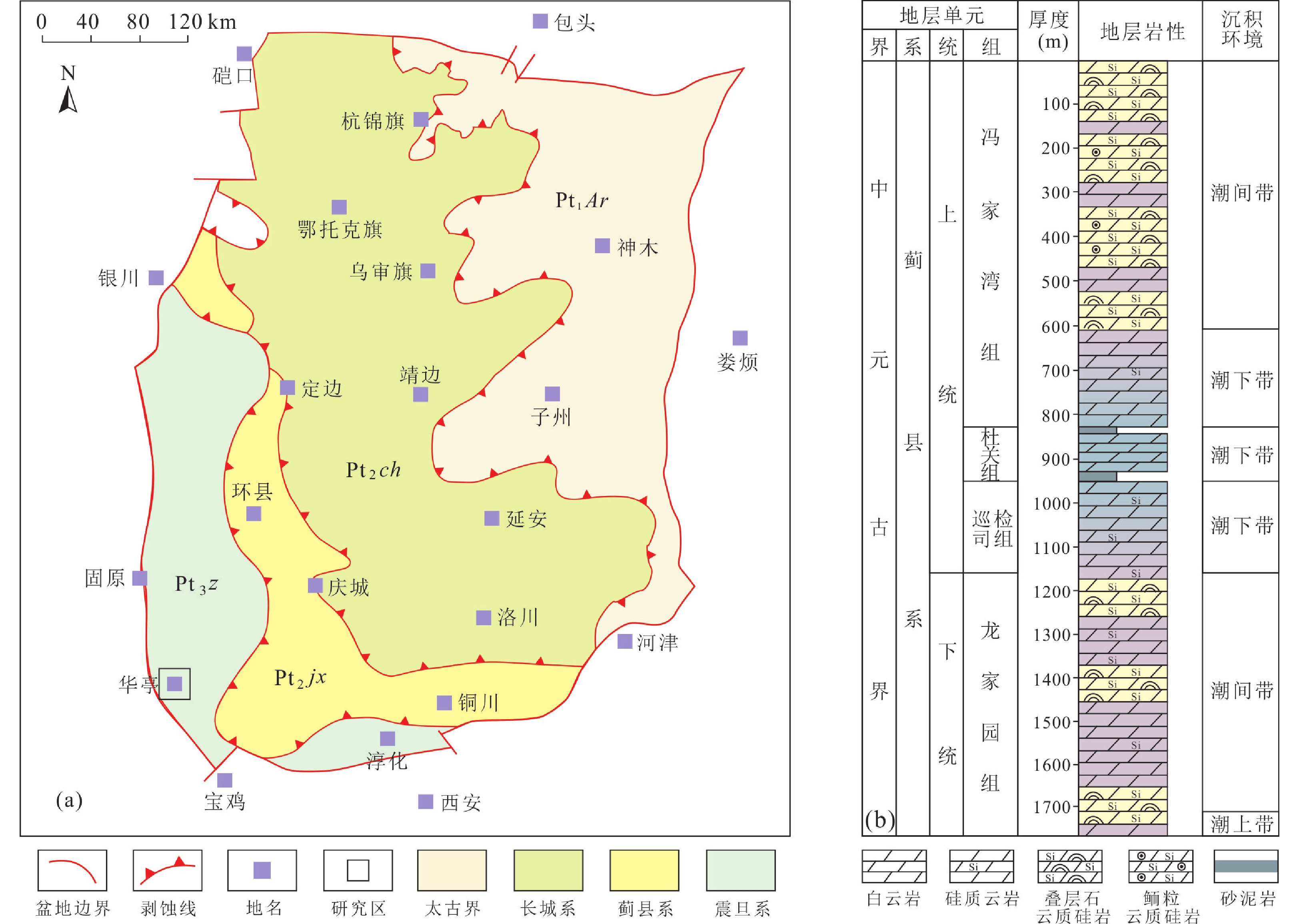
在鄂尔多斯盆地南缘中元古界蓟县系冯家湾组硅质叠层石和鲕粒岩中,存在白云石及其溶蚀形成的孔洞。分布特征与发育规模明显受富有机质组构控制的白云石和溶蚀孔洞是基质孔隙发育的关键。显微薄片、扫描电镜、阴极发光、大面积拼接成像及微量元素原位成像等分析显示,大量自形白云石晶体分布于叠层石的暗色纹层与鲕粒的暗色圈层中,且晶体周缘普见缝隙的存在。部分白云石发生了溶蚀,形成晶体铸模孔并成为暗色组构中孔洞的基本构成单元。白云石的形成与随后的溶蚀均发生在富有机质组构内部。组构内受微生物因素影响的成岩物质的富集,以及随之产生的环境酸碱度变化,共同促进了白云石的发育与溶解过程。上述现象和认识可以为前寒武系部分白云岩的成因和可能与微生物因素有关的成岩、成储研究提供一些参考借鉴。
Abstract:Dolomite crystals and related pores and vugs, evidently controlled by organic-rich fabrics, can be found in the siliceous stromatolites and oolites in the Fengjiawan Formation of the Mesoproterozoic Jixian System, located in the southern Ordos Basin. With the application of microscope, scanning electron microscope (SEM), cathodoluminescence, large-area SEM image acquisition, and in-situ trace element imaging, it can be observed that many euhedral dolomite crystals are concentrated within the dark laminae of the stromatolites and the dark spheres of the ooids, with gaps present on the crystal peripheries. A considerable number of these dolomite crystals have undergone dissolution, leading to the formation of moldic pores and vugs, which are the dominant matrix pores in the stromatolites and oolites in the study area. Dolomite formation and dissolution were confined to the organic-rich fabrics. The microenvironment within these fabrics was influenced by microbial factors, with the enrichment of necessary diagenetic substances and changes in pH. These phenomena and scientific understandings may have some referential value for the genesis of some Precambrian dolomites and microbial-related diagenesis, which are of great significance for petroleum geology.
-
Key words:
- Ordos Basin /
- Fengjiawan Formation /
- microbialite /
- dolomite /
- dissolution
-

-
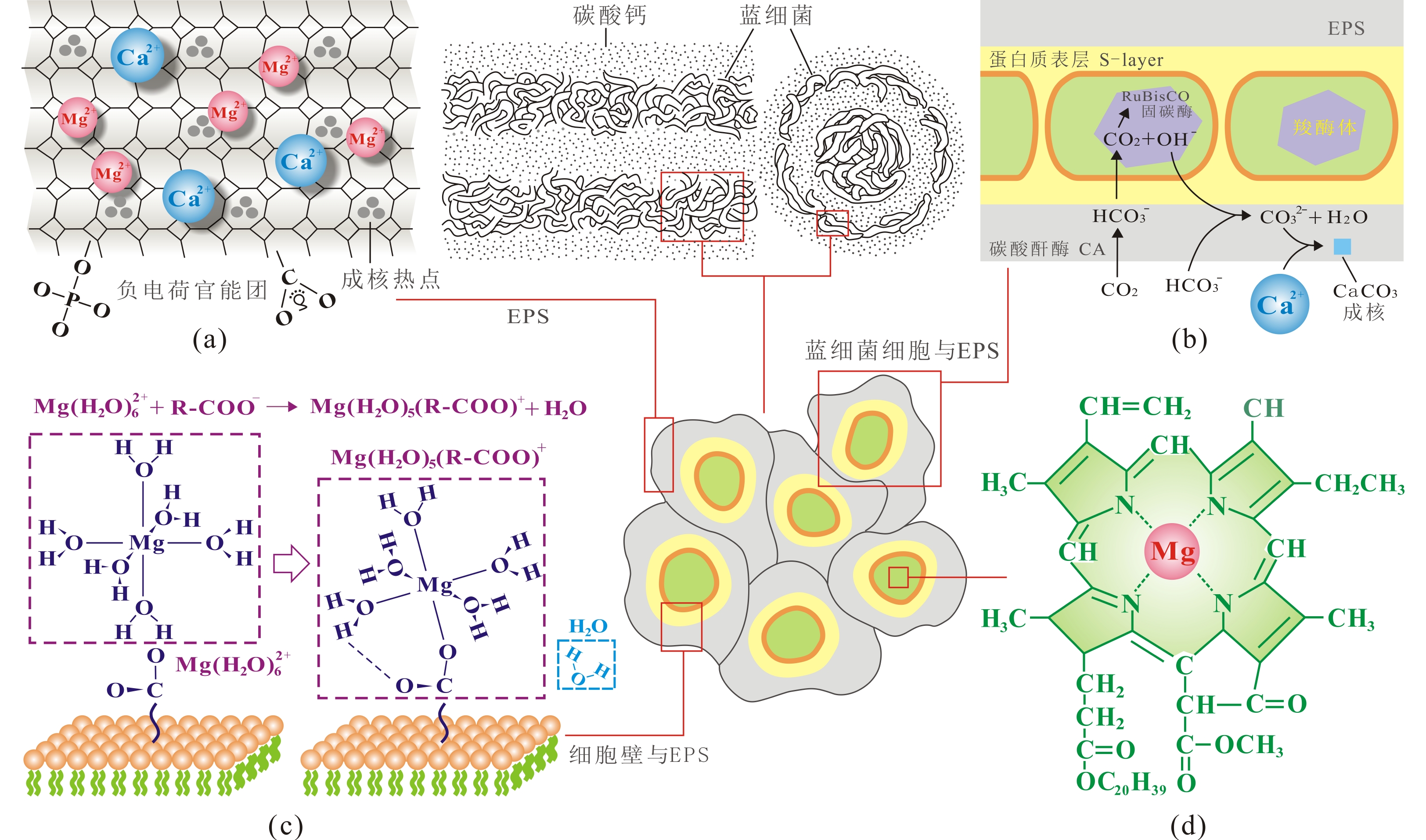
图 5 受微生物因素影响的白云石成因综合模式图(据Riding,2006;张喜洋,2016;董陈松,2020;李飞等,2022;赵东方等,2022修编)
Figure 5.
-
[1] Batchelor M T,Burne R V,Henry B I,et al.,2018. A biofilm and organomineralisation model for the growth and limiting size of ooids[J]. Scientific Reports,8(1):559. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18908-4
[2] Bengtsson S,Hallquist J,Werker A,et al.,2008. Acidogenic fermentation of industrial wastewaters:Effects of chemostat retention time and pH on volatile fatty acids production[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal,40(3):492 − 499. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2008.02.004
[3] Bosence D,Gibbons K,Le Heron D P,et al.,2015. Microbial carbonates in space and time:introduction[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,418(1):1 − 15. doi: 10.1144/SP418.14
[4] Diaz M R,Eberli G P,2019. Decoding the mechanism of formation in marine ooids:A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,190:536 − 556. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.016
[5] Diaz M R,Eberli G P,Blackwelder P,et al.,2017. Microbially mediated organomineralization in the formation of ooids[J]. Geology,45(9):771 − 774. doi: 10.1130/G39159.1
[6] 董陈松,2020. 蓝细菌中光依赖性原叶绿素酸酯氧化还原酶的结构和分子机理[D]. 合肥:安徽大学.
Dong C S,2020. Structural and functional studies of cyanobacteria light-dependent protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase[D]. Hefei:Anhui University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Dupraz C,Reid R P,Braissant O,et al.,2009. Processes of carbonate precipitation in modern microbial mats[J]. Earth Science Reviews,96:141 − 162. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.10.005
[8] Frankel R B,Bazylinski D A,2003. Biologically induced mineralization by bacteria[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry,54(1):95 − 114.
[9] 胡安平,沈安江,郑剑锋,等,2021. 微生物碳酸盐岩分类、沉积环境与沉积模式[J]. 海相油气地质,26(1):1 − 15.
Hu A P,Shen A J,Zheng J F,et al.,2021. The classification,facies and sedimentary models of microbialites[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,26(1):1 − 15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Johnston D T,Wolfe-Simon F,Pearson A,2009. Anoxygenic photosynthesis modulated Proterozoic oxygen and sustained Earth's middle age[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,106(40):16925 − 16929.
[11] Kenward P A,Fowle D A,Goldstein R H,et al.,2013. Ordered low-temperature dolomite mediated by carboxyl-group density of microbial cell walls[J]. AAPG Bulletin,97(11):2113 − 2125. doi: 10.1306/05171312168
[12] 李飞,易楚恒,李红,等,2022. 微生物成因鲕粒研究进展[J]. 沉积学报,40(2):319 − 334.
Li F,Yi C H,Li H,et al.,2022. Recent advances in ooid microbial origin:A review[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,40(2):319 − 334 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] 李怀坤,苏文博,周红英,等,2014. 中−新元古界标准剖面蓟县系首获高精度年龄制约——蓟县剖面雾迷山组和铁岭组斑脱岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb同位素定年研究[J]. 岩石学报,30(10):2999 − 3012.
Li H K,Su W B,Zhou H Y,et al.,2014. The first precise age constraints on the Jixian System of the Meso-to Neoproterozoic Standard Section of China:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of bentonites from the Wumishan and Tieling formations in the Jixian Section,North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,30(10):2999 − 3012 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] 李延河,侯可军,万德芳,等,2010. 前寒武纪条带状硅铁建造的形成机制与地球早期的大气和海洋[J]. 地质学报,84(9):1359 − 1373.
Li Y H,Hou K J,Wan D F,et al.,2010. Formation mechanism of Precambrian banded iron formation and atmosphere and ocean during early stage of the earth[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,84(9):1359 − 1373 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] 李子阳,2020. 蓝藻厌氧发酵产酸及发酵液作为反硝化外加碳源研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学.
Li Z Y,2020. Acid production from cyanobacteria by anaerobic fermentation and its application as additional carbon source for denitrification[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] 林孝先,彭军,侯中健,等,2018. 四川汉源−峨边地区上震旦统灯影组藻白云岩特征及成因研究[J]. 沉积学报,36(1):57 − 71.
Lin X X,Peng J,Hou Z J,et al.,2018. Study on characteristics and geneses of algal dolostone of the Upper Sinian Dengying Formation in the Hanyuan-Ebian area of Sichuan Province,China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,36(1):57 − 71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] 马赛,2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘构造演化与中上元古界成藏条件[D]. 西安:西北大学.
Ma S,2020. Tectonic evolution and Middle-Upper Proterozoic petroleum geological setting in south-western Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an:Northwest University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] 梅冥相,2021. 光合作用生物膜诱发的放射鲕粒:以江苏徐州贾旺剖面寒武系苗岭统张夏组为例[J]. 古地理学报,23(3):461 − 488.
Mei M X,2021. Radial ooids induced by photosynthetic biofilms:An example from the Cambrian Miaolingian Zhangxia Formation at Jiawang section in Xuzhou city of Jiangsu Province,North-China Platform[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,23(3):461 − 488 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Pace A,Bourillot R,Bouton A,et al.,2018. Formation of stromatolite lamina at the interface of oxygenic-anoxygenic photosynthesis[J]. Geobiology,16(4):378 − 398. doi: 10.1111/gbi.12281
[20] Peters S E,Husson J M,Wilcots J,2017. The rise and fall of stromatolites in shallow marine environments[J]. Geology,45:487 − 490.
[21] Petrash D A,Bialik O M,Bontognali T R R,et al.,2017. Microbially catalyzed dolomite formation:From near-surface to burial[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,171:558 − 582. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.06.015
[22] 钱一雄,冯菊芳,何治亮,等,2017. 从岩石学及微区同位素探讨四川盆地灯影组皮壳−葡萄状白云石成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质,38(4):665 − 676.
Qian Y X,Feng J F,He Z L,et al.,2017. Applications of petrography and isotope analysis of micro-drill samples to the study of genesis of grape-like dolomite of the Dengying Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,38(4):665 − 676 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Reid R P,Visscher P T,Decho A W,et al.,2000. The role of microbes in accretion,lamination and early lithification of modern marine stromatolites[J]. Nature,406:989 − 992. doi: 10.1038/35023158
[24] 任冠雄,2018. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组葡萄状构造精细研究[D]. 成都:西南石油大学.
Ren G X,2018. Study on the botryoidal structure of the Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Petroleum University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Riding R,1991. Calcareous algae and stromatolites[M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag:21 − 51.
[26] Riding R,2000. Microbial carbonates:The geological record of calcified bacterial-algal mats and biofilms[J]. Sedimentology,47(1):179 − 214.
[27] Riding R,2006. Cyanobacterial calcification,carbon dioxide concentrating mechanisms,and Proterozoic-Cambrian changes in atmospheric composition[J]. Geobiology,4(4):299 − 316. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-4669.2006.00087.x
[28] Riding R,2008. Abiogenic,microbial and hybrid authigenic carbonate crusts:Components of Precambrian stromatolites[J]. Geologia Croatica,61(2 − 3):73 − 103.
[29] 沈安江,胡安平,张杰,等,2022. 微生物碳酸盐岩“三因素”控储地质认识和分布规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质,43(3):582 − 596.
Shen A J,Hu A P,Zhang J,et al.,2022. "Three-factor" driven microbial carbonate reservoirs and their distribution[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,43(3):582 − 596 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] 谭聪,卢远征,宋昊南,等,2019. 华北克拉通西南缘高山河组凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报,93(5):1113 − 1124.
Tan C,Lu Y Z,Song H N,et al.,2019. Zircon U-Pb dating of the Gaoshanhe Formation tuff in the southwestern margin of the North China craton,and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geological Sinica,93(5):1113 − 1124 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] 王璇,梅朝佳,李忠日,2024. 寒武系张夏组树形石中的钙化蓝细菌——以山东淄博峨庄镇后紫峪剖面为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,44(2):339 − 350.
Wang X,Mei C J,Li Z R,2024. Calcifying cyanobacteria in dendrolites of the Cambrian Zhangxia Formation: A case study of the Houziyu section in Ezhuang Town,Zibo City,Shandong Province[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,44(2):339 − 350 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] 肖恩照,隋明园,Latif K,等,2017. 微生物白云岩形成机制研究进展与存在问题[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,36(2):26 − 32.
Xiao E Z,Sui M Y,Latif K,et al.,2017. Study advances and existed problem for the forming mechanism of the microbial dolomite[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,36(2):26 − 32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] 许杨阳,刘邓,于娜,等,2018. 微生物(有机)白云石成因模式研究进展与思考[J]. 地球科学,43(Suppl1):63 − 70.
Xu Y Y,Liu D,Yu N,et al.,2018. Advance and review on microbial/organogenic dolomite model[J]. Earth Science,43(Suppl1):63 − 70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] 游杰,胡广,张玺华,等,2020. 微生物碳酸盐岩同生−早成岩阶段有机质降解示踪:以四川盆地灯影组四段为例[J]. 南京大学学报:自然科学版,56(3):308 − 321.
You J,Hu G,Zhang X H,et al.,2020. Geochemical tracing of organic matter degradation in microbial carbonates during syngenetic-early diagenesis:A case study from the Member IV of Dengying Formation,Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences),56(3):308 − 321 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] 张喜洋. 2016. 豫西寒武纪微生物碳酸盐岩中蓝细菌的钙化作用[D]. 焦作:河南理工大学.
Zhang X Y,2016. The calcification of cyanobacteria from microbial carbonates in the Cambrian,western Henan[D]. Jiaozuo:Henan Polytechnic University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] 张亦凡,马怡飞,姚奇志,等,2015. “白云石问题”及其实验研究[J]. 高校地质学报,21(3):395 − 406.
Zhang Y F,Ma Y F,Yao Q Z,et al.,2015. "Dolomite problem" and experimental studies of dolomite formation[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,21(3):395 − 406 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] 赵东方,谭秀成,罗冰,等,2022. 微生物诱导白云石沉淀研究进展及面临的挑战[J]. 沉积学报,40(2):335 − 349.
Zhao D F,Tan X C,Luo B,et al.,2022. A review of microbial dolomite:Advances and challenges[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,40(2):335 − 349 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] 钟怡江,文华国,陈洪德,等,2022. 胞外聚合物在蓝细菌钙化过程中的作用及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报,40(1):88 − 105.
Zhong Y J,Wen H G,Chen H D,et al.,2022. The role of extracellular polymeric substances in cyanobacterial calcification and its geological significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,40(1):88 − 105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
-



 下载:
下载: