Milankovitch cycle identification of Denglouku Formation in Songliao Basin and its paleoclimate significance
-
摘要:
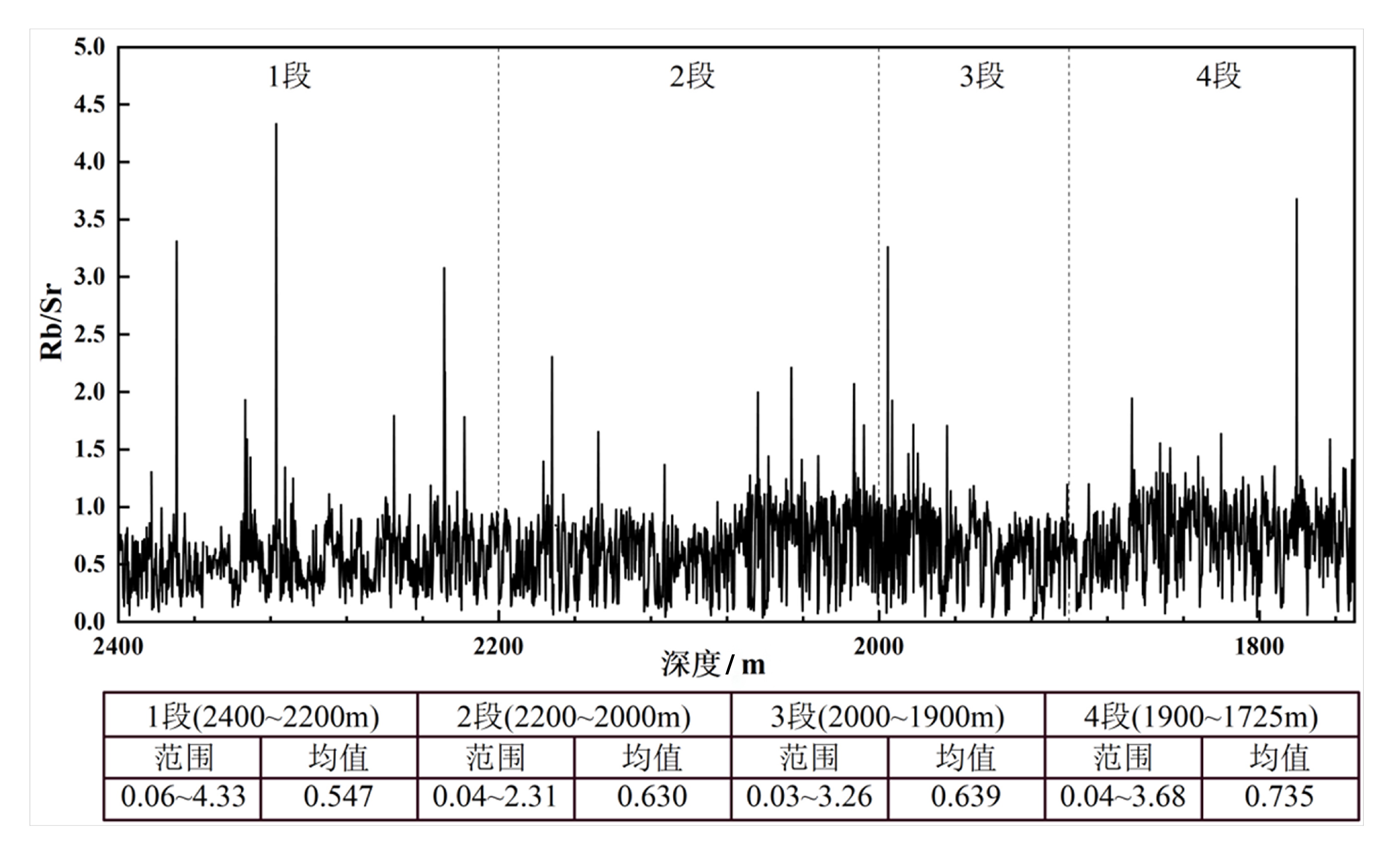
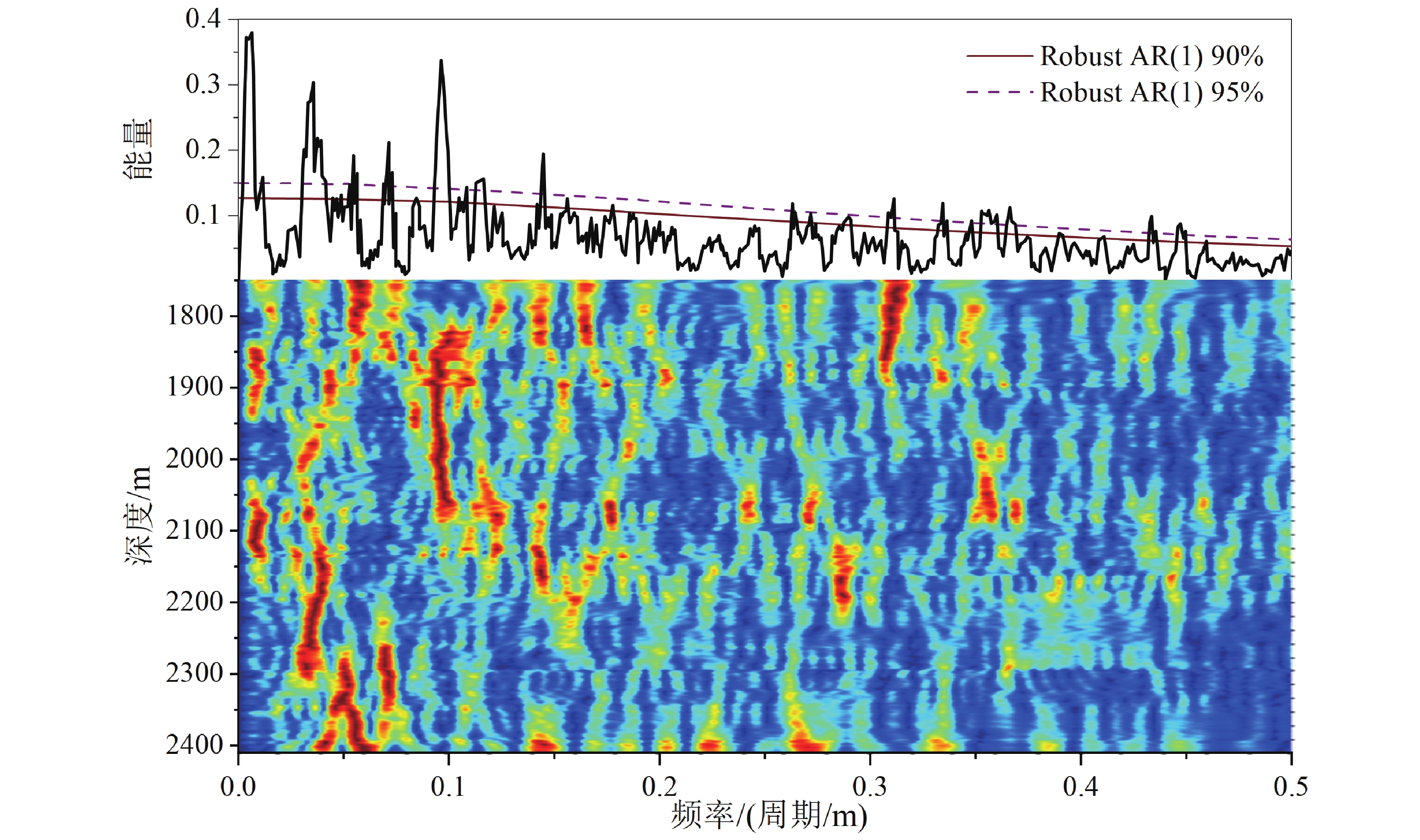
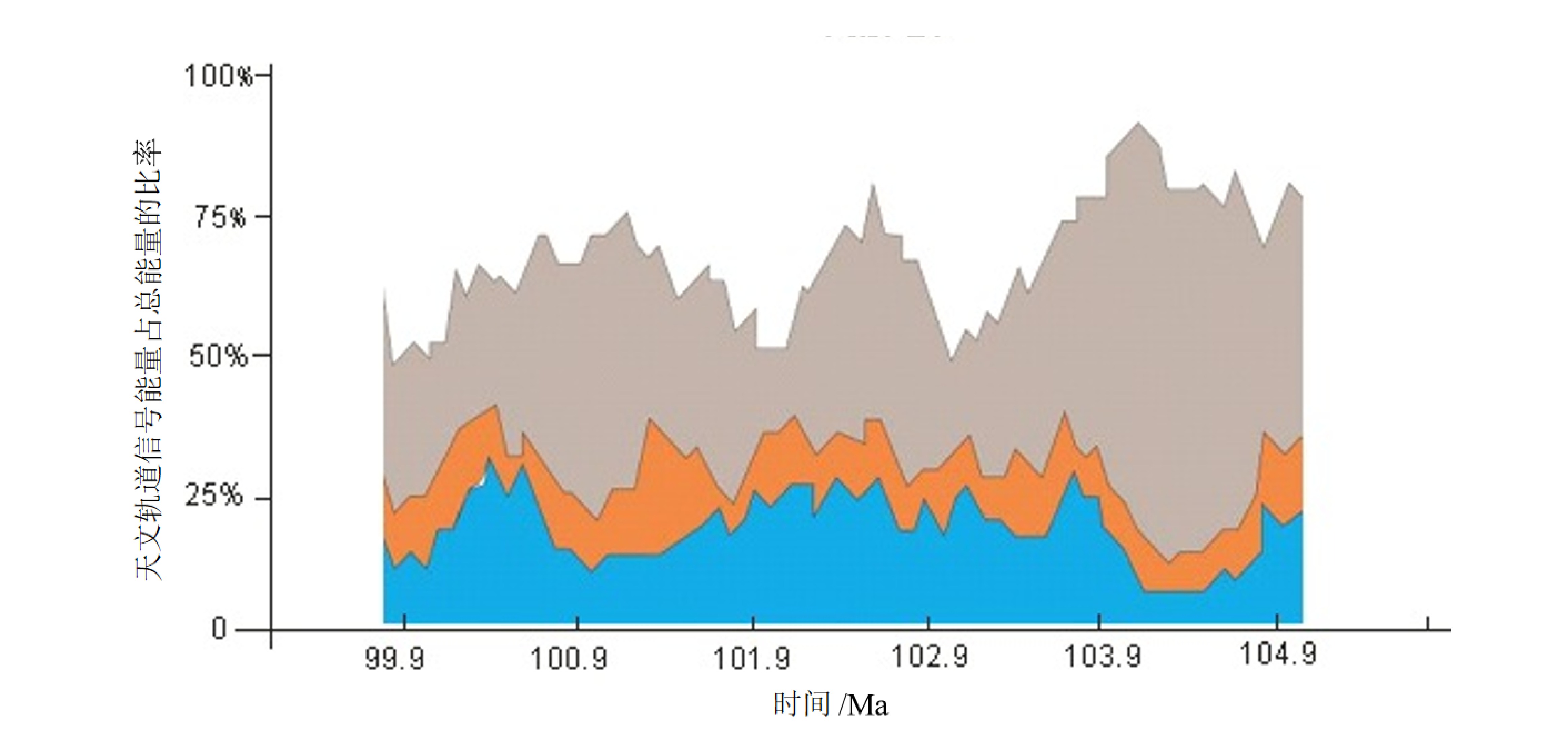
在白垩纪大陆科学钻探工程的推动下,松辽盆地成为白垩纪陆相古气候研究的热点地区之一,其中松辽盆地古气候变化与全球气候变化的一致性和差异性是目前关注的重点。本文选择松辽盆地松科3井获得的登娄库组岩心,通过X射线荧光(XRF)扫描获得化学风化指标Rb/Sr比值,应用时间序列分析方法开展旋回地层学研究。分析结果表明:(1)松科 3 井登娄库组 XRF 扫描曲线中化学风化指标Rb/Sr的变化,指示了登娄库组沉积期间气候由湿润逐渐变得干旱的过程;(2)松科 3 井登娄库组最优沉积速率约为14.43 cm/ka,结合地层深度域的气候旋回波长,利用比值法识别出登娄库组地层中记录了白垩纪中期岁差(20~19 ka)、斜率(45~39 ka)、短偏心率(130~100 ka)和长偏心率(450~390 ka)等气候旋回周期信号,判定登娄库组记录了米兰科维奇旋回信息;(3)应用功率能量分解方法,结果表现为,早白垩世登娄库组以偏心率和岁差信号为主,斜率信号非常弱,这与全球气候变化记录具有一致性。
Abstract:Under the promotion of the Cretaceous continental scientific drilling project, the Songliao Basin has become one of the hotspots for the Cretaceous terrestrial paleoclimate research. Among these studies, the consistency and differences between the paleoclimate change of the Songliao Basin and coeval global climate change are currently the focus of attention. In this paper, the cores of the Denglouku Formation obtained from the continental scientific drilling of Well Songke-3 in the Songliao Basin were selected. The chemical weathering index Rb/Sr ratio was obtained through XRF scanning, and the time series analysis method was applied to study the cyclostratigraphy. The analysis results show that: (1) The variation in the chemical weathering index Rb/Sr ratio, as shown in the XRF scanning curve, indicates the process of the climate from humid to arid during the deposition of the Denglouku Formation. (2) The optimal deposition rate of the Denglouku Formation is about 14.43 cm/ka, which can be combined with the wavelength of the depth domain to identify the Milankovitch cycles preserved in the Denglouku Formation, including precession (20-19 ka), obliquity (45-39 ka), short eccentricity (130-100 ka), and long eccentricity (450-390 ka) signals of the climate cycle. (3) With the application of power decomposition analysis (PDA), it is shown that eccentricity and precession signals are dominant, while the obliquity signal is very weak in the Early Cretaceous Denglouku Formation. This is consistent with the global climate change record.
-
Key words:
- Songliao Basin /
- Denglouku Formation /
- Milankovitch cycle /
- paleoclimate
-

-
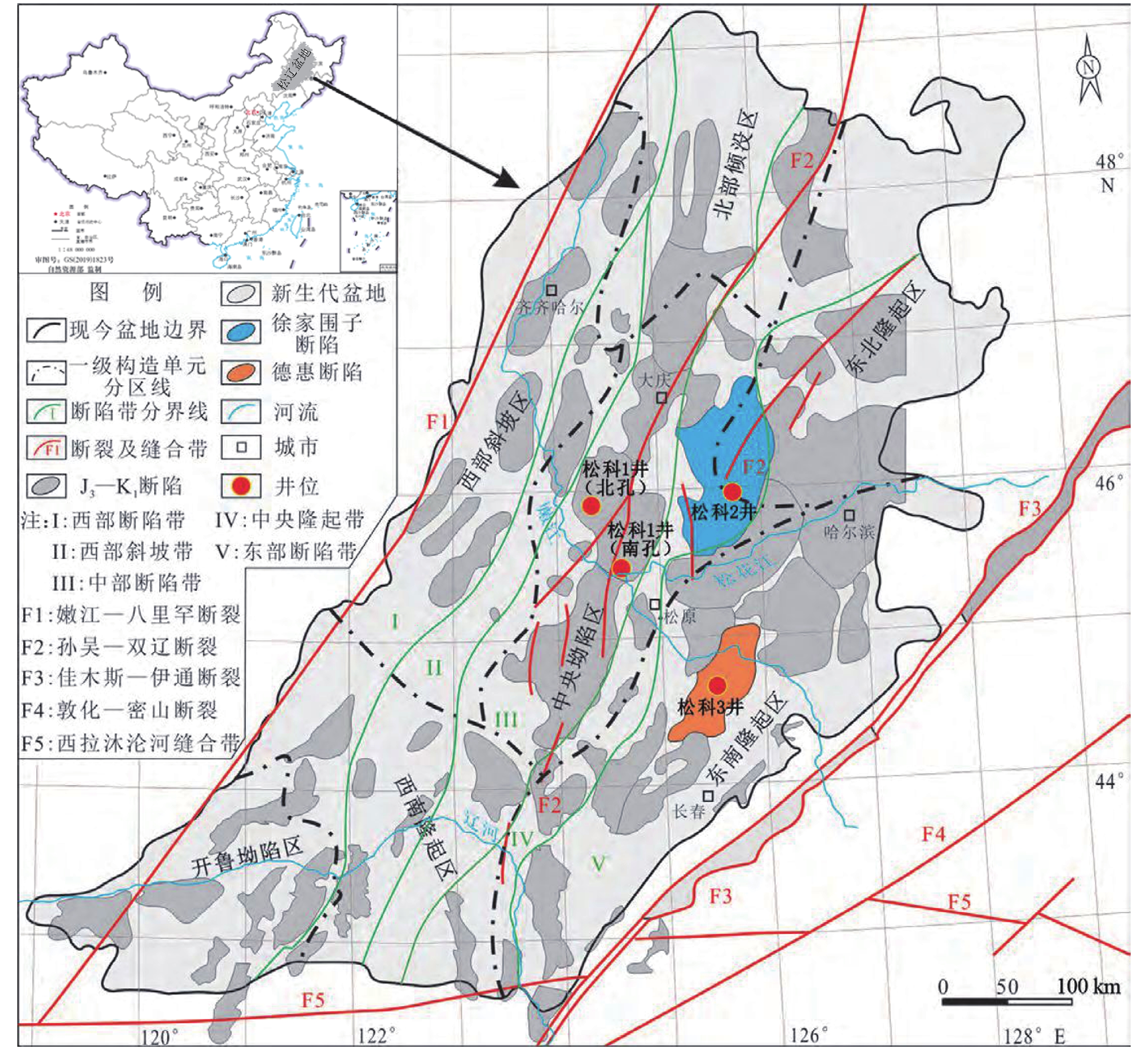
图 1 松辽盆地构造图(据Feng et al.,2010; Wang et al.,2013b)
Figure 1.
-
[1] Arnaud F,Révillon S,Debret M,et al.,2012. Lake Bourget regional erosion patterns reconstruction reveals Holocene NW European Alps soil evolution and paleohydrology[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,51:81 − 92. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.07.025
[2] Boulila S,Galbrun B,Kenneth G,et al.,2011. On the origin of Cenozoic and Mesozoic “third-order” eustatic sequences[J]. Earth Science Reviews,109:94 − 112. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.09.003
[3] Chen PJ,1987. Cretaceous paleogeography of China[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,59:49 − 56.
[4] Croudace I W,Rothwell R G,2015. Micro-XRF Studies of Sediment Cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences[M]. Netherlands:Springer:455.
[5] Feng Z Q,Jia C Z,Xie X N,et al.,2010. Tectonostratigraphic units and stratigraphic sequences of the nonmarine Songliao basin,northeast China[J]. Basin Research,22(1):79 − 95.
[6] Fernandez M,Björck S,Wohlfarth B,et al.,2013. Diatom assemblage changes in lacustrine sediments from Isla de los Estados,southernmost South America,in response to shifts in the southwesterly wind belt during the last deglaciation[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology,50(4):433 − 446. doi: 10.1007/s10933-013-9736-4
[7] Foster G L,Royer D L,Lunt D J,2017. Future climate forcing potentially without precedent in the last 420 million years[J]. Nature Communications,8:14845. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14845
[8] Hays J D,Imbrie J,Shackleton N J,1976. Variations in the Earth's orbit:Pacemaker of the Ice Ages[J]. Science,194:1121 − 1132.
[9] Huang H,Gao Y,Ma C,et al.,2021. Organic carbon burial is paced by a ∼173-ka obliquity cycle in the middle to high latitudes[J]. Science advances, 7 (28):eabf9489.
[10] Jin Z D,Zhang E L,2002. Paleoclimate implication of Rb/Sr ratios from lake sediments[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2:20 − 22.
[11] Kodama K P,Hinnov L A,2014. Rock magnetic cyclostratigraphy[M]. Sussex:John Wiley & Sons,Ltd.
[12] Larson R L,1991. Latest pulse of Earth:Evidence for a mid Cretaceous superplume[J]. Geology,19(6):547 − 550. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0547:LPOEEF>2.3.CO;2
[13] Laskar J,Robutel P,Joutel F,et al.,2004. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Astronomy &. Astrophysics,428:261 − 285.
[14] Laurin J,Meyers S R,Uličný D,et al.,2015. Axial obliquity control on the greenhouse carbon budget through middle- to high-latitude reservoirs[J]. Paleoceanography,30:133 − 149 . doi: 10.1002/2014PA002736
[15] Li M S,Hinnov L A,Kump L R,2019a. Acycle:Time-series analysis software for paleoclimate research and education[J]. Computers & Geosciences,127:12 − 22.
[16] Li M S,Huang C J,Ogg J,et al.,2019b. Paleoclimate proxies for cyclostratigraphy:Comparative analysis using a Lower Triassic marine section in South China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,189:125 − 146. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.01.011
[17] Li M S,Huang C J,Hinnov L,et al.,2016. Obliquity-forced climate during the Early Triassic hothouse in China[J]. Geology,44(8):623 − 626. doi: 10.1130/G37970.1
[18] Li X,Huang Y J,Zhang Z F,et al.,2022a. Chemical weathering characteristics of the Late Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation from the Songliao Basin (Northeastern China) reveal prominent Milankovitch band variations[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology ,601:111130.
[19] Li X,Huang Y J,Zhang Z F,et al.,2022b. Orbitally forced chemical weathering in the Late Cretaceous northeastern China:Implications for paleoclimate change[J]. Global and Planetary Change,218:103982. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2022.103982.
[20] 马坤元,李若琛,龚一鸣,2016. 秦皇岛石门寨亮甲山奥陶系剖面化学地层和旋回地层研究[J]. 地学前缘,23(6):268−286.
Ma K Y,Li R C,Gong Y M,2016. Chemostratigraphy and cyclostratigraphy of the Ordovician Liangjiashan section from Shimenzhai of Qinhuangdao in North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,23(6):268−286 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Muhs D R,Bettis E A,Been J,et al.,2001. Impact of climate and parentmaterial on chemical weathering in loess-derived soils of the Mississippi River valley[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,65(6):1761 − 1777. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2001.1761
[22] Pang J L ,Huang C C ,Zhang Z P ,2001. Rb,Sr elements and high resolution climatic records in the loess-paleosol profifile at Qishan,Shannxi[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,19:637 − 641.
[23] 高航,王璞珺,高有峰,等,2023. 松辽盆地南部上、下白垩统界线研究:以松辽盆地国际大陆科学钻探松科3井为例[J]. 地学前缘,30(3):425 − 440.
Gao H,Wang P J,Gao Y F,et al.,2023. The Upper-Lower Cretaceous boundary in the southern Songliao Basin:A case study of ICDP borehole SK-3[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,30(3):425 − 440 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 瞿雪姣,高有峰,林志成,等,2021. 松辽盆地及周缘地区侏罗系/白垩系界线区域对比特征探讨[J]. 地学前缘,28(4):299 − 315. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.7.3.
Qu X J,Gao Y F,Lin Z C,et al.,2021. Comparative characteristics of Jurassic/Cretaceous boundary in Songliao Basin and its surrounding areas[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,28(4):299 − 315 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.7.3.
[25] Thomson D J,1982. Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE,70(9):1055 − 1096.
[26] Unkel I,Fernandez M,Bjrck S,et al.,2010. Records of environmental changes during the Holocene from Isla de los Estados (54.4°S),southeastern Tierra del Fuego[J]. Global and Planetary Change,74(3):99 − 113.
[27] Wang C S,Scott R W,Wan X Q,2013a. Late Cretaceous climate changes recorded in Eastern Asian lacustrine deposits and North American Epieric sea strata[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,126:275 − 299.
[28] Wang C S,Feng Z Q,Zhang L M,et al.,2013b. Cretaceous paleogeography and paleoclimate and the setting of SKI borehole sites in Songliao Basin,northeast China[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,385:17 − 30.
[29] Wang P J,Mattern F,Frank D,et al.,2016. Tectonics and cycle system of the Cretaceous Songliao Basin:An inverted active continental margin basin[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,159(1):82 − 102.
[30] Wang P J,Chen S M,2015. Cretaceous volcanic reservoirs and their exploration in the Songliao Basin,northeast China[J]. AAPG Bulletin,99(3):499 − 523.
[31] Wendler J E,Wendler I,Vogt C,et al.,2016. Link between cyclic eustatic sea-level change and continental weathering: Evidence for aquifer-eustasy in the Cretaceous[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,441:430 − 437.
[32] Ruddiman W F,Earth's climate:Past and future[M]. 3rd ed. Macmillan:1−464.
[33] Wu H C,Zhang S H,Hinnov L A,et al.,2014. Cyclostratigraphy and orbital tuning of the terrestrial upper Santonian–Lower Danian in Songliao Basin,northeastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,407:82 − 95. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.09.038
[34] Wu H C,Zhang S H,Jiang G Q,et al.,2013. Astrochronology of the Early Turonian–Early Campanian terrestrial succession in the Songliao Basin,northeastern China and its implication for long−period behavior of the Solar System[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,385:55 − 70.
[35] 席党鹏,孙立新,覃祚焕,等,2021. 中国白垩纪岩石地层划分和对比[J]. 地层学杂志,45(3):375 − 401.
Xi D P,Sun L X,Qin Z H,et al.,2021. Lithostratigraphic subdivision and correlation of the cretaceous in China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,45(3):375 − 401 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] 许志琴,杨文采,杨经绥,等,2016. 中国大陆科学钻探的过去、现在和未来——纪念中国大陆科学钻探实施 15 周年、国际大陆科学钻探委员会成立 20 周年[J]. 地质学报,90(9):2109−2122.
Xu Z Q,Yang W C,Yang J S,et al.,2016. 15 Years of hardship and struggle history and the prospects for the future of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling program (CCSD) : In memory of the 15 year anniversary of CCSD and 20 year anniversary of ICDP[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,90(9):2109−2122 (in Chinese with English abstract).
-



 下载:
下载: