Evolution of in-situ geochemical records in hydrothermal recrystallization of dolomite: A case study from Upper Cambrian dolostones in the Bachu area, Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
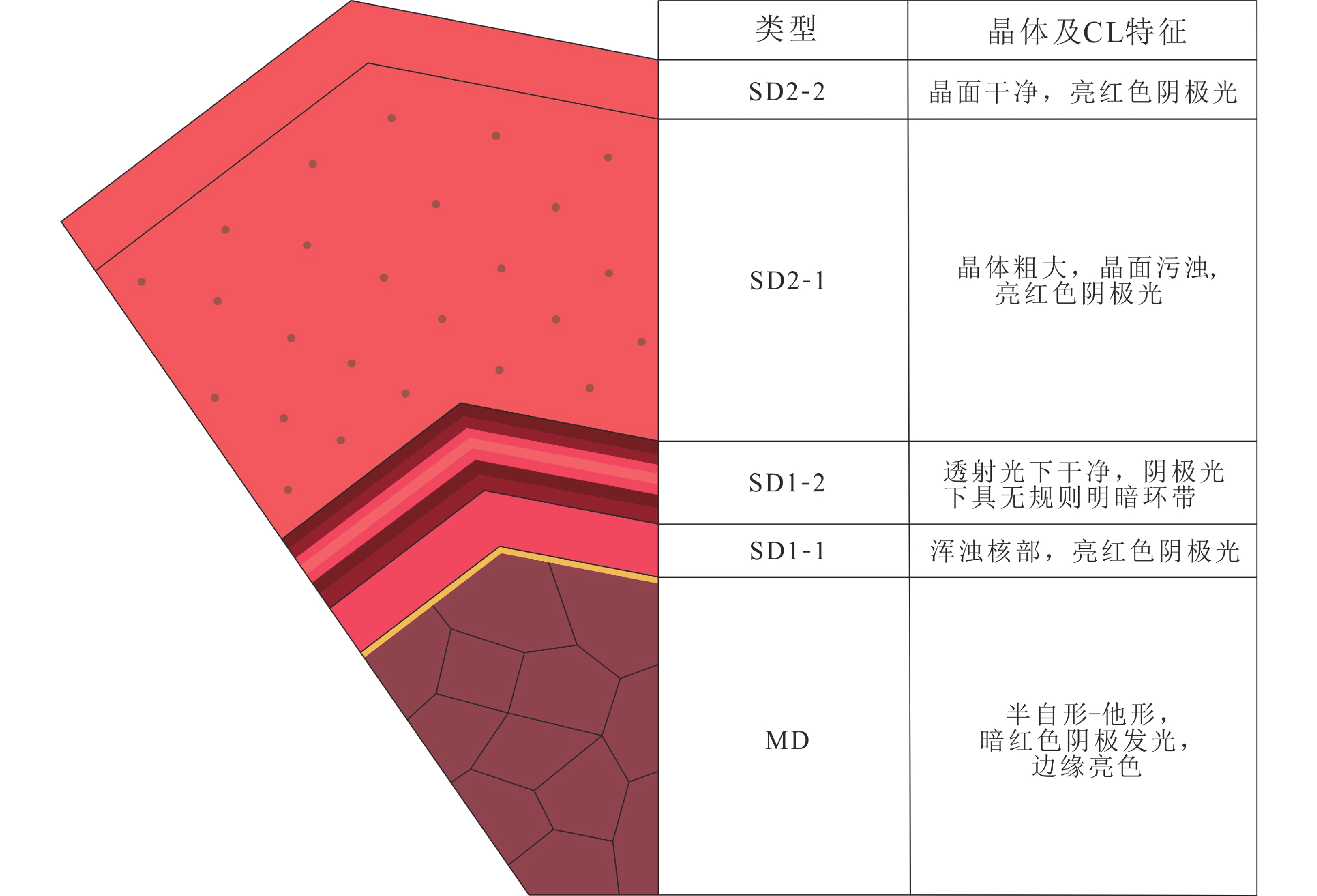
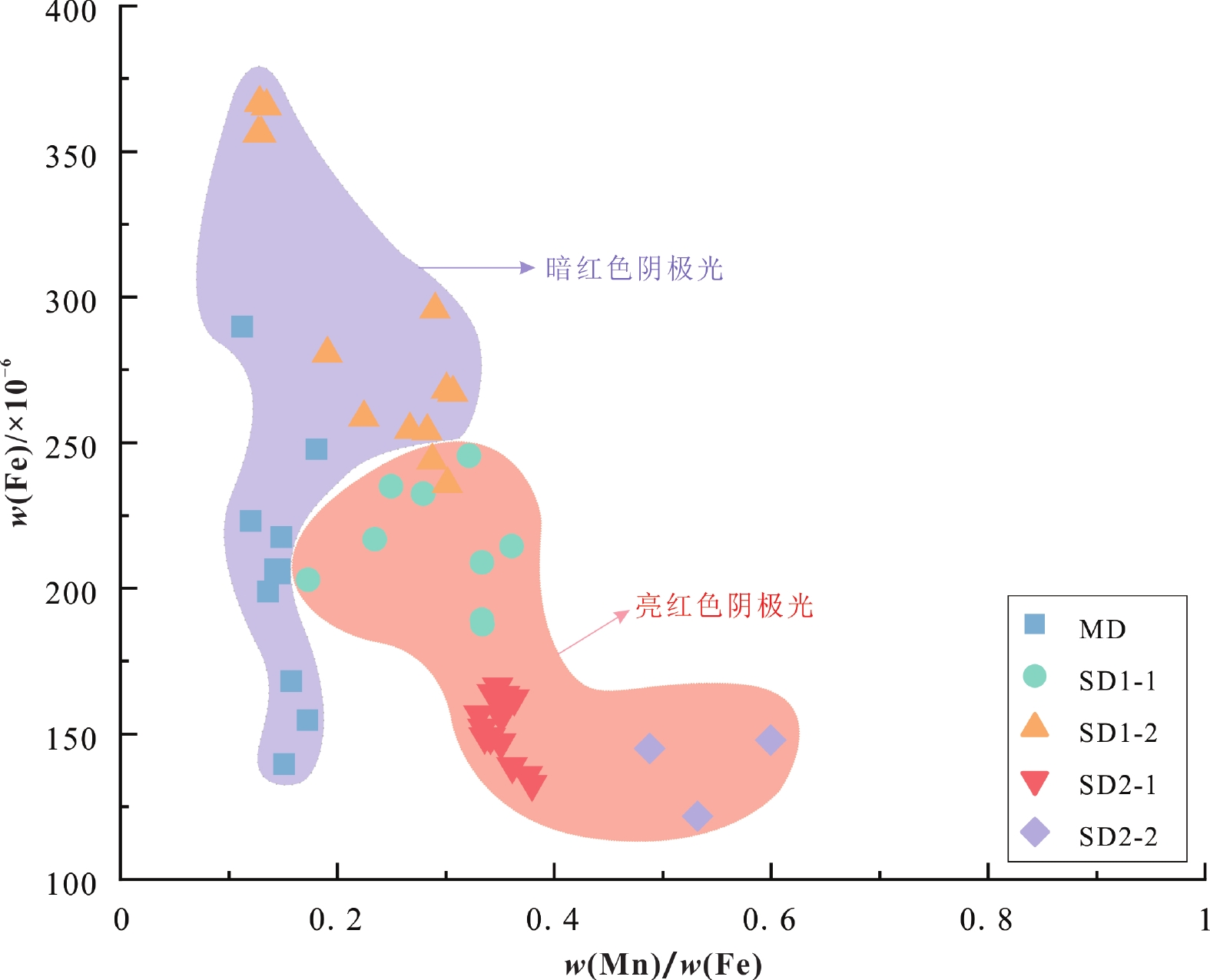
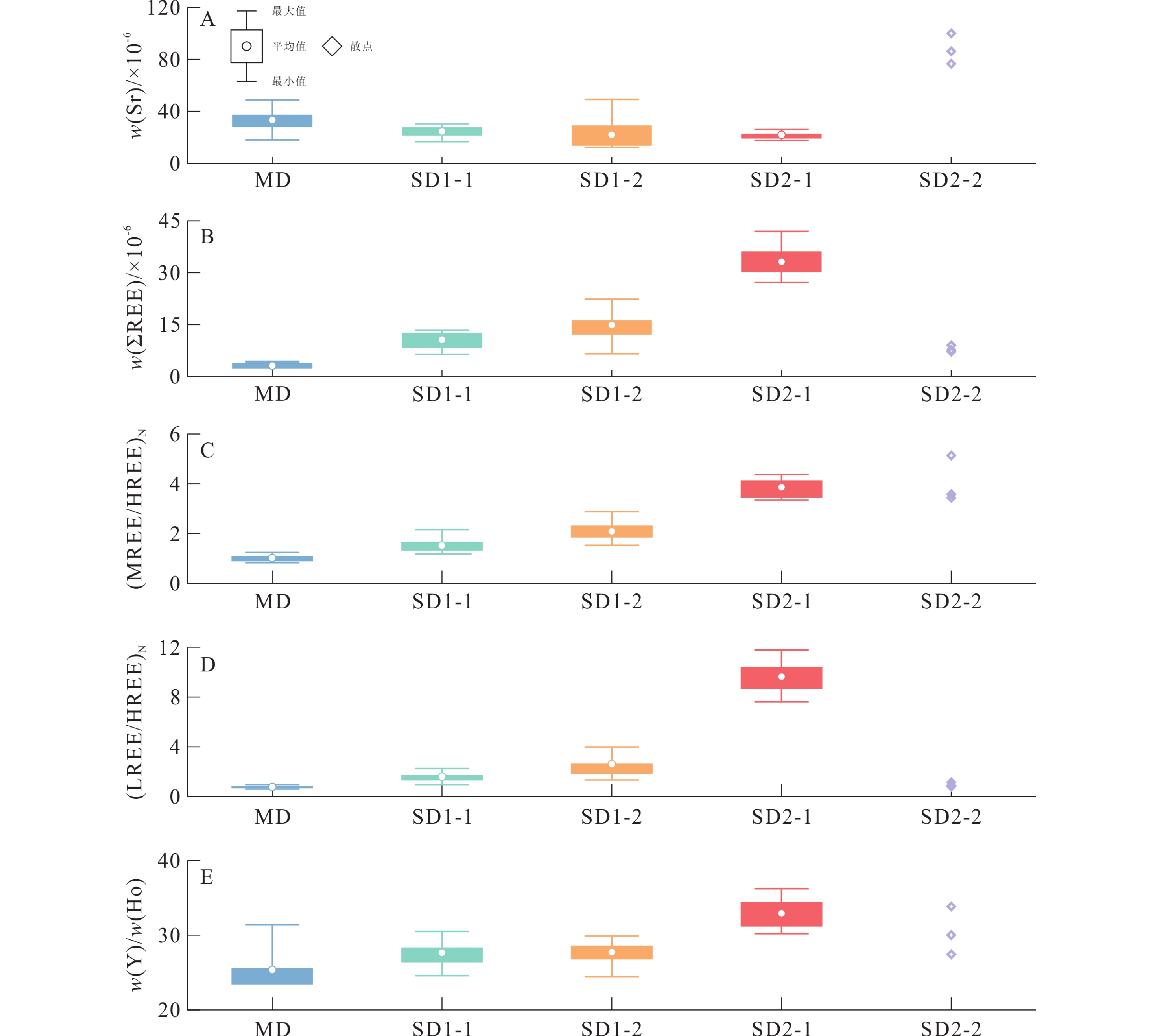
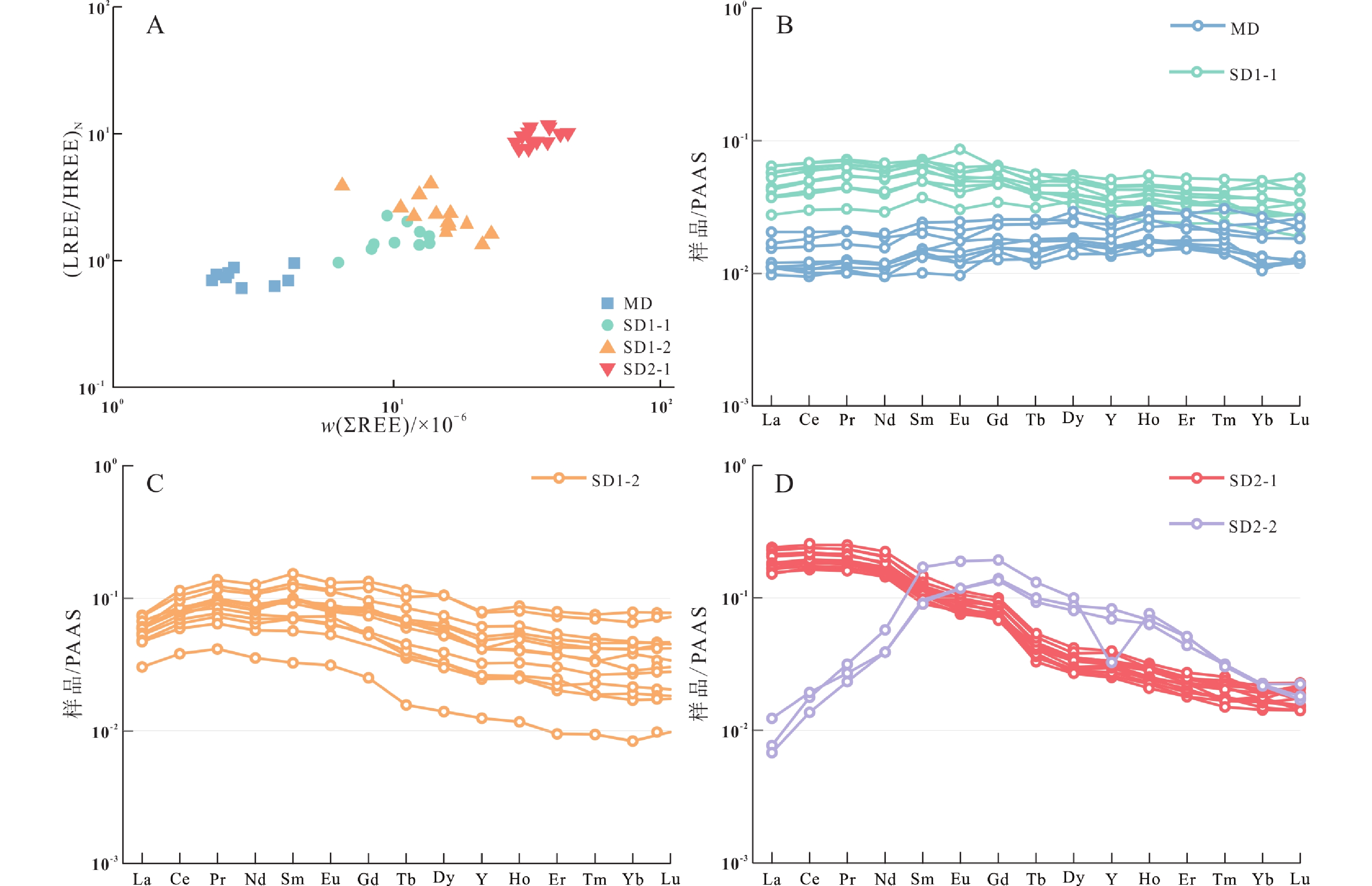
塔里木盆地巴楚地区上寒武统白云岩遭受了大量的热液改造。基于岩石学、原位微量元素特征分析及前人的研究成果,本研究从BT5井上寒武统白云岩中识别出了3种组构的白云石:基质白云石(MD)、环带状鞍形白云石(SD1)和巨晶鞍形白云石(SD2)。其中,SD1自形程度较好,其核部(SD1-1)具有污浊的晶面和亮红色阴极光,边缘(SD1-2)具有明亮的晶面并在阴极光下显示无规则明暗环带;SD2具有波状消光和亮红色阴极光。原位微量元素分析显示,从MD到SD1和SD2核部(SD2-1),样品呈现Sr元素含量逐渐下降、稀土元素总含量逐渐增加且轻稀土元素的富集程度逐渐增加的规律。综合上述研究,推测SD2-1是从热液中沉淀的白云石充填物,而SD1与热液导致的MD重结晶改造有关。本研究显示热液导致的重结晶形成的白云石具过渡性质稀土元素构成(介于MD和SD2之间),这种特征可以用来识别热液导致的重结晶过程。
Abstract:The Upper Cambrian dolostones in the Tarim Basin have undergone widely alteration by hydrothermal fluids. In this study, based on petrological and trace element analyses, three types of dolomites were identified in the Upper Cambrian dolostones of Well BT5 in the Bachu area: matrix dolomites (MD), dolomite cements with cathodoluminescence zonation (SD1), and blocky dolomite cements (SD2). SD1 occurs as euhedral crystals, consisting of a core (SD1-1) and a rim (SD1-2). SD1-1 is characterized by cloudy crystal surfaces and bright red luminescence under cathodoluminescence (CL), while SD1-2 displays bright crystal surfaces with irregular bright-dark zoning under CL. And SD2 exhibits wavy extinction and shows bright red under CL. From the host dolostone (MD) to the last generation of dolomite cements (SD1, and SD2's core SD2-1), the Sr concentrations decreased, and the total rare earth element concentrations (ƩREE) as well as light rare earth element enrichment increased. Consequently, SD2-1 is interpreted to be dolomite fillings precipitated from hydrothermal fluids, while SD1 results from hydrothermal recrystallization of MD. This study suggests that the dolomites formed from hydrothermal recrystallization show transitional REE characteristics, which can serve as a useful tool to identify recrystallization process in dolomites.
-

-
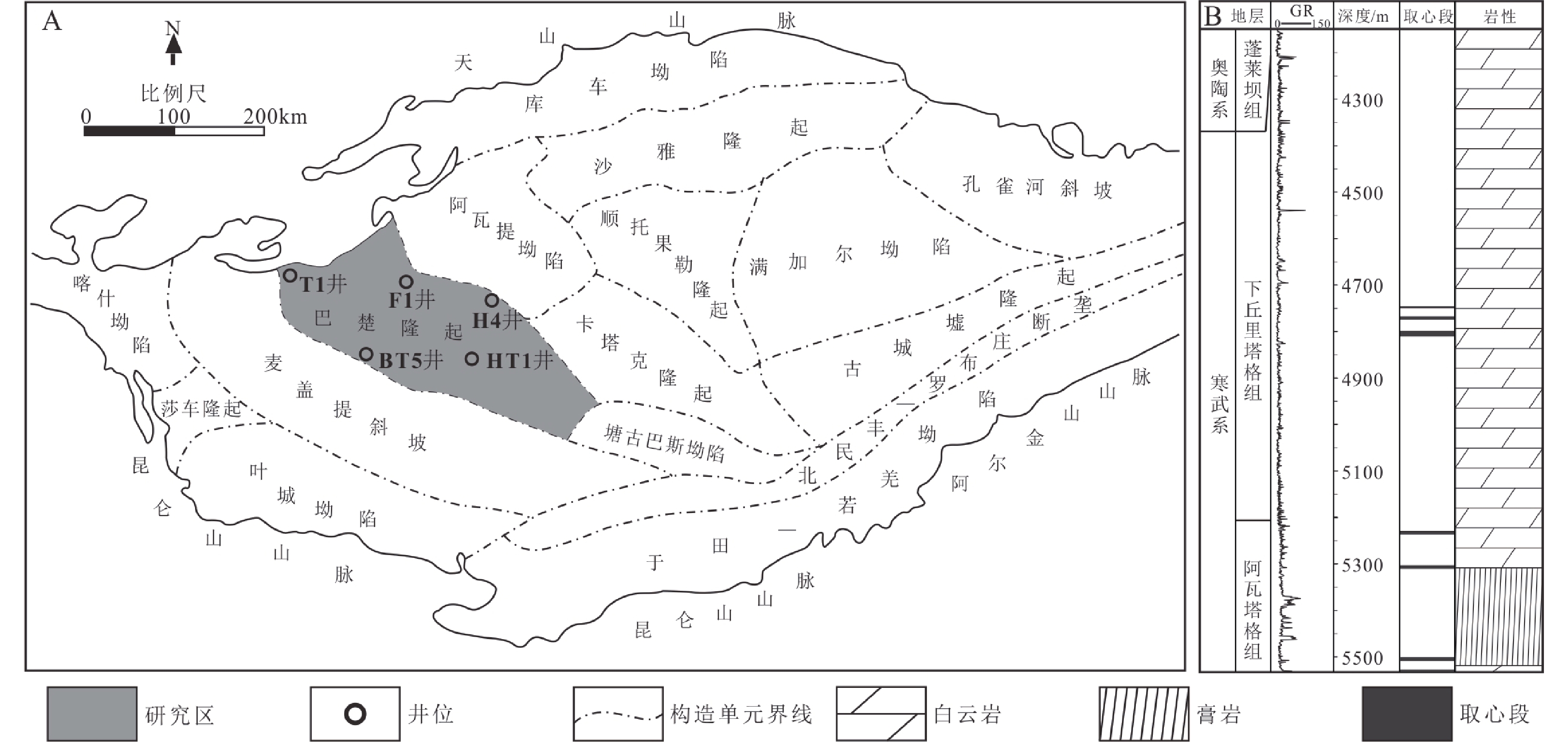
图 1 塔里木盆地构造图(据王家豪,2012修编)和BT5井上寒武统综合柱状图
Figure 1.
-
[1] Bau M,1991. Rare − earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid − rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium[J]. Chemical Geology,93(3 − 4):219 − 230. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(91)90115-8
[2] Bau M,Balan S,Schmidt K,Koschinsky A,2010. Rare earth elements in mussel shells of the Mytilidae family as tracers for hidden and fossil high-temperature hydrothermal systems[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters,299(3–4):310 − 316.
[3] Bau M,Romer R L,Lüders V,Dulski P,2003. Tracing element sources of hydrothermal mineral deposits:REE and Y distribution and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes in fluorite from MVT deposits in the Pennine Orefield,England[J]. Mineralium Deposita,38:992 − 1008. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0376-x
[4] 白璇,钟怡江,黄可可,等,2022. 白云石重结晶作用及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,41(4):804 − 817. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2022.04.009
Bai X,Zhong Y J,Huang K K,et al.,2022. Recrystallization of dolomite and its geological signification[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,41(4):804 − 817 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2022.04.009
[5] Davies G,Smith L,2006. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies:An overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin,90(11):1641 − 1690. doi: 10.1306/05220605164
[6] Debruyne D,Hulsbosch N,Philippe M,2016. Unraveling rare earth element signatures in hydrothermal carbonate minerals using a source-sink system[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,72(1):232 − 252.
[7] 丁文龙,林畅松,漆立新,等,2008. 塔里木盆地巴楚隆起构造格架及形成演化[J]. 地学前缘,15(2):242 − 252. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.02.027
Ding W L,Lin S C,Qi L X,et al.,2008. Structural framework and evolution of Bachu Uplift in Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,15(2):242 − 252 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.02.027
[8] Dong S F,Chen D Z,Qing H R,et al.,2013a. In situ stable isotopic constraints on dolomitizing fluids for the hydrothermally-originated saddle dolomites at Keping,Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,58(23):2877 − 2882. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5801-7
[9] Dong S F,Chen D Z,Qing H R,et al.,2013b. Hydrothermal alteration of dolostones in the Lower Ordovician,Tarim Basin,NW China:Multiple constraints from petrology,isotope geochemistry and fluid inclusion microthermometry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,46:270 − 286. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.06.013
[10] Duggan J P,Mountjoy E W,Stasiuk L D,2001. Fault controlled dolomitization at Swan Hills Simonette oil field (Devonian),deep basin west-central Alberta,Canada[J]. Sedimentology,48(2):301 − 323. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2001.00364.x
[11] Fantle M S,2015. Calcium isotopic evidence for rapid recrystallization of bulk marine carbonates and implications for geochemical proxies[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,148(1):378 − 401.
[12] Fantle M S,DePaolo D J,2006. Sr isotopes and pore fluid chemistry in carbonate sediment of the Ontong Java Plateau:Calcite recrystallization rates and evidence for a rapid rise in seawater Mg over the last 10 million years[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,70(15):3883 − 3904. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.06.009
[13] Flügel E,Depaolo D J,2010. Microfacies of carbonate rock:Analysis,interpretation and application[M]. Berlin:Springer.
[14] Goldstein R,2012. Fluid inclusion geothermometry in sedimentary systems:From paleoclimate to hydrothermal[J]. SEPM special publication,Thermal History Analysis of Sedimentary Basins,103:45 − 63.
[15] Gong Q L,Li F,Lu C J,et al.,2021. Tracing seawater- and terrestrial-sourced REE signatures in detritally contaminated,diagenetically altered carbonate rocks[J]. Chemical Geology,570:120169.
[16] Gregg J M,Sibley D F,1984. Epigenetic dolomitization and the origin of xenotopic dolomite texture[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,54(3):908 − 931.
[17] Hood A v S,Wallace M W,2015. Extreme ocean anoxia during the Late Cryogenian recorded in reefal carbonates of Southern Australia[J]. Precambrian Research,261:96 − 111. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.02.008
[18] 胡九珍,刘树根,冉启贵,等,2009. 塔东地区寒武系—下奥陶统成岩作用特征及对优质储层形成的影响[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版,36(2):138 − 146.
Hu J Z,Liu S G,Ran Q G,et al.,2009. Diagenetic characteristics and their effect on the formation of good-quality reservoirs of the Cambrian System to Lower Ordovician in the east of Tarim Basin,Xinjiang,China[J]. Journal of Chendu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),36(2):138 − 146 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Huang B W,Zhang S N,Lu Z Y,et al.,2021. Origin of dolomites in Lower-Middle Ordovician carbonate rocks in the Yingshan Formation,Gucheng Area,Tarim Basin:Evidence from petrography and geochemical data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,134:105322. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105322
[20] 黄擎宇,刘伟,石书缘,等,2016. 塔中—巴麦地区下古生界不同结构类型白云岩元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学,45(2):199 − 212. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2016.02.008
Huang Q Y,Liu W,Shi S Y,et al.,2016. Trace-element geochemical characteristics of different textural types of Lower Paleozoic dolomites in the Tazhong-Bamai area[J]. Geochimica,45(2):199 − 212 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2016.02.008
[21] Jiang L,Cai C F,Richard H W,et al.,2016. Multiphase dolomitization of deeply buried Cambrian petroleum reservoirs,Tarim Basin,north-west China[J]. Sedimentology,63(7):2130 − 2157. doi: 10.1111/sed.12300
[22] 金之钧,朱东亚,胡文瑄,等,2006. 塔里木盆地热液活动地质地球化学特征及其对储层影响[J]. 地质学报,80(2):245 − 253. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.02.009
Jin Z J,Zhu D Y,Hu W X,et al.,2006. Geological and geochemical signatures of hydrothermal activity and their influence on carbonate reservoir beds in the Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica sinica,80(2):245 − 253 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.02.009
[23] 金之钧,朱东亚,孟庆强,等,2013. 塔里木盆地热液流体活动及其对油气运移的影响[J]. 岩石学报,29(3):1048 − 1058.
Jin Z J,Zhu D Y,Meng Q Q,et al.,2013. Hydrothermal activities and influences on migration of oil and gas in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(3):1048 − 1058 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] 景帅,2020. 塔里木盆地巴楚隆起带寒武系白云岩岩相与地球化学特征[D]. 西安石油大学.
Jing S,2020. Lithic facies and geochemical characteristics of Cambrian dolomite in the Bachu Uplift belt,Tarim Basin[D]. Xi'an Shiyou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Li F,Webb G E,Algeo T J,et al.,2019. Modern carbonate ooids preserve ambient aqueous REE signatures[J]. Chemical Geology,509:163 − 177. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.01.015
[26] 李映涛,叶宁,袁晓宇,等,2015. 塔里木盆地顺南4井中硅化热液的地质与地球化学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质,36(6):934 − 944. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150608
Li Y T,Ye N,Yuan X Y,et al.,2015. Geological and geochemical characteristics of silicified hydrothermal fluids in Well Shunnan 4,Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,36(6):934 − 944 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11743/ogg20150608
[27] 刘红,冯子辉,邵红梅,等,2022. U-Pb同位素定年分析在热液对白云岩储层改造研究中的应用—以塔里木盆地古城地区下奥陶统鹰三段为例[J]. 岩石学报,38(3):765 − 776. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.03.10
Liu H,Feng Z H,Shao H M,et al.,2022. Application of U-Pb dating technique in the study of hydrothermal activities of dolomite reservoir:A case study on 3rd member of Yingshan Formation in Gucheng area,Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,38(3):765 − 776 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.03.10
[28] Liu L H,Ma Y S,Liu B,et al.,2017. Hydrothermal dissolution of Ordovician carbonates rocks and its dissolution mechanism in Tarim Basin,China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites,32(4):525 − 537. doi: 10.1007/s13146-016-0309-2
[29] Liu P X,Deng S B,Guan P,et al.,2020. The nature,type,and origin of diagenetic fluids and their control on the evolving porosity of the Lower Cambrian Xiaoerbulak Formation dolostone,northwestern Tarim Basin,China[J]. Petroleum Science,17(4):873 − 895. doi: 10.1007/s12182-020-00434-0
[30] 刘伟,黄擎宇,王坤,等,2016. 深埋藏阶段白云岩化作用及其对储层的影响—以塔里木盆地下古生界白云岩为例[J]. 天然气地球科学,27(5):772 − 779. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.05.0772
Liu W,Huang Q Y,Wang K,et al.,2016. Dolomization and influence on reservoir development in deep-burial stage:A case study of Lower Paleozoic in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,27(5):772 − 779 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.05.0772
[31] Lonnee J,Machel H,2006. Pervasive dolomitization with subsequent hydrothermal alteration in the Clarke Lake gas field,Middle Devonian Slave Point Formation,British Columbia,Canada[J]. AAPG Bulletin,90(11):1739 − 1761. doi: 10.1306/03060605069
[32] Louvel M,Etschmann B,Guan Q,et al.,2022. Carbonate complexation enhances hydrothermal transport of rare earth elements in alkaline fluids[J]. Nature Communications,13(1),1723.
[33] Lu Z Y,Chen H H,Qing H R,et al.,2017. Petrography,fluid inclusion and isotope studies in Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in the Shunnan area,Tarim basin,NW China:Implications for the nature and timing of silicification[J]. Sedimentary Geology,359:29 − 43. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.08.002
[34] Lu Z Y,Li Y T,Liu M M,et al.,2022. Non-hydrothermal saddle dolomite in Upper Cambrian dolostones of Tarim Basin:Evidence from C-O-Sr isotopic and in-situ trace elemental studies[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites,37(3):1 − 17.
[35] Lukoczki G,Haas J,Gregg J,et al.,2019. Multi-phase dolomitization and recrystallization of Middle Triassic shallow marine-peritidal carbonates from the Mecsek Mts. (SW Hungary),as inferred from petrography,carbon,oxygen,strontium and clumped isotope data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,101:440 − 458. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.004
[36] 马庆佑,吕海涛,蒋华山,等,2015. 塔里木盆地台盆区构造单元划分方案[J]. 海相油气地质,20(1):1 − 9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.01.001
Ma Q Y,Lü H T,Jiang H S,et al.,2015. A division program of structural units in the Paleozoic platform-basin region,Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,20(1):1 − 9 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.01.001
[37] Machel H G,1997. Recrystallization versus neomorphism,and the concept of ‘significant recrystallization’ in dolomite research[J]. Sedimentary Geology,113(3):161 − 168.
[38] Machel H G,Cavell P A,Patey K S,et al.,1996. Isotopic evidence for carbonate cementation and recrystallization,and for tectonic expulsion of fluids into the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,108(9):1108 − 1108. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1996)108<1108:IEFCCA>2.3.CO;2
[39] Machel H G,Lonnee J,2002. Hydrothermal dolomite − a product of poor definition and imagination[J]. Sedimentary Geology,152(3 − 4):163 − 171. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00259-2
[40] McLennan S M,1989. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks:Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Rev. Miner. Geochem.,21(1):169 − 200.
[41] Migdisov A,Williams-Jones A E,Brugger J,et al.,2016. Hydrothermal transport,deposition,and fractionation of the REE:Experimental data and thermodynamic calculations[J]. Chemical Geology,439:13 − 42. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.005
[42] 宁飞,云金表,李建交,等,2021. 塔里木盆地巴楚隆起西南缘构造特征与勘探前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质,42(2):299 − 308.
Ning F,Yun J B,Li J J,et al.,2021. Structural characteristics and exploration prospects of the southwestern margin of Bachu Uplift,Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,42(2):299 − 308 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Qing H R,Mountjoy E,1992. Large-scale fluid-flow in the Middle Devonian Presqu'ile Barrier,Western Canada Sedimentary Basin[J]. Geology,20(10):903 − 906. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0903:LSFFIT>2.3.CO;2
[44] Taylor S R,McLennan S M,1985. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Blackwell Scientific Publications.
[45] Tostevin R,Shields G A,Tarbuck GM,et al.,2016. Effective use of cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings[J]. Chem. Geol.,438:146 − 162. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.027
[46] Veizer J,Ala D,Azmy K,et al.,1999. 87Sr/86Sr,δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater[J]. Chem. Geol.,161(1 − 3):59 − 88. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00081-9
[47] 万友利,王剑,付修根,等,2020. 羌塘盆地南坳陷中侏罗统布曲组白云岩储层成因流体同位素地球化学示踪[J]. 石油与天然气地质,41(1):189 − 200.
Wan Y L,Wang J,Fu X G,et al.,2020. Geochemical tracing of isotopic fluid of dolomite reservoir in the Middle Jurassic Buqu Formation in southern depression of Qiangtang Basin[J]. 41(1):189 − 200 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] 万友利,王剑,万方,等,2017. 羌塘盆地南部古油藏带布曲组碳酸盐岩稀土元素特征及意义[J]. 石油实验地质,39(5):655 − 665. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201705655
Wan Y L,Wang J,Wang F,et al.,2017. Characteristics and indications of rare earth elements in carbonates in the Buqu Formation,southern Qiangtang Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,39(5):655 − 665(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11781/sysydz201705655
[49] 王家豪,陈红汉,云露,等,2012. 塔里木盆地台盆区三叠纪大型挤压坳陷湖盆层序地层及构造响应[J]. 地球科学,37(4):735 − 742.
Wang J H,Chen H H,Yun L,et al.,2012. Tectonic responses of Triassic sequence stratigraphy in the large-scale compressional down-warped Lacustrine basin of Inner Tarim basin[J]. Earth Science,37(4):735 − 742(in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] Wang L C,Hu W X,Wang X L,et al.,2014. Seawater normalized REE patterns of dolomites in Geshan and Panlongdong sections,China:Implications for tracing dolomitization and diagenetic fluids[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,56:63 − 67. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.02.018
[51] Wang Z Y,Zhang Y F,Tao X Y,et al.,2015. Genesis of the Ordovician fluorite and its geological significance in central uplift of the Tarim basin,China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology,109(3):339 − 348. doi: 10.1007/s00710-014-0341-7
[52] Webb G E,Kamber B S,2000. Rare earth elements in Holocene reefal microbialites:A new shallow seawater proxy[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,64(9):1557 − 1565. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00400-7
[53] 谢世文,张东辉,竹合林,等,2013. 从岩石结构和地化特征看巴楚隆起上寒武统白云岩的成因及演化[J]. 海相油气地质,18(2):41 − 50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.02.006
Xie S W,Zhang D H,Zhu H L,et al.,2013. Lithological and geochemical characteristics indicating genetic mechanism and evolution of Upper Cambrian dolostone in Bachu Uplift,Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,18(2):41 − 50 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.02.006
[54] Ye N,Li Y T,Huang B W,et al.,2022. Hydrothermal silicification and its impact on Lower–Middle Ordovician carbonates in Shunnan area,Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Geological Journal,57(9):3538 − 3557. doi: 10.1002/gj.4482
[55] Ye N,Zhang S N,Qing H R,et al.,2019. Dolomitization and its impact on porosity development and preservation in the deeply burial Lower Ordovician carbonate rocks of Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,182:106303. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106303
[56] Zhang J T,Hu W X,Qian Y X,et al.,2009. Formation of saddle dolomites in Upper Cambrian carbonates,western Tarim Basin (northwest China):Implications for fault–related fluid flow[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology (8):1428 − 1440.
[57] Zhang W,Guan P,Jian X,et al.,2014. In situ geochemistry of Lower Paleozoic dolomites in the northwestern Tarim basin:implications for the nature,origin,and evolution of diagenetic fluids[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems,15(7):2744 − 2764. doi: 10.1002/2013GC005194
[58] Zhang Y,He D F,Liu C L,et al.,2019. Three-dimensional geological structure and genetic mechanism of the Bachu Uplift in the Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,26(1):134 − 148 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[59] 赵文智,沈安江,乔占峰,等,2018. 白云岩成因类型、识别特征及储集空间成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发,45(6):923 − 935. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.06.01
Zhao W Z,Shen A J,Qiao Z F,et al.,2018. Genetic types and distinguished characteristics of dolomite and the origin of dolomite reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,45(6):923 − 935 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.06.01
[60] 周波,李明,段书府,等,2012. 巴楚地区寒武系碳酸盐岩白云石化机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发,39(2):198 − 202.
Zhou B,Li M,Duan S F,et al.,2012. Dolomitization mechanism of Cambrian carbonates in the Bachu area,Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,39(2):198 − 202 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[61] 朱东亚,金之钧,胡文瑄,等,2008. 塔里木盆地深部流体对碳酸盐岩储层影响[J]. 地质论评,54(3):348 − 354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.03.008
Zhu D Y,Jin Z J,Hu W X,et al.,2008. Effects of deep fluid on carbonates reservoir in Tarim Basin[J]. Geological Review,54(3):348 − 354 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.03.008
[62] 朱东亚,金之钧,胡文瑄,2010. 塔北地区下奥陶统白云岩热液重结晶作用及其油气储集意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,40(2):156 − 170.
Zhu D Y,Jin Z J,Hu W X,2010. Hydrothermal recrystallization of the Lower Ordovician dolomite and its significance to reservoir in northern Tarim Basin[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,40(2):156 − 170 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[63] Zhu D Y,Meng Q,Jin Z J,et al.,2015. Formation mechanism of deep Cambrian dolomite reservoirs in the Tarim basin,northwestern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,59:232 − 244. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.08.022
-



 下载:
下载: