Research on the Process Mineralogy of Phosphogypsum Using Mineral Liberation Analysis System
-
摘要:
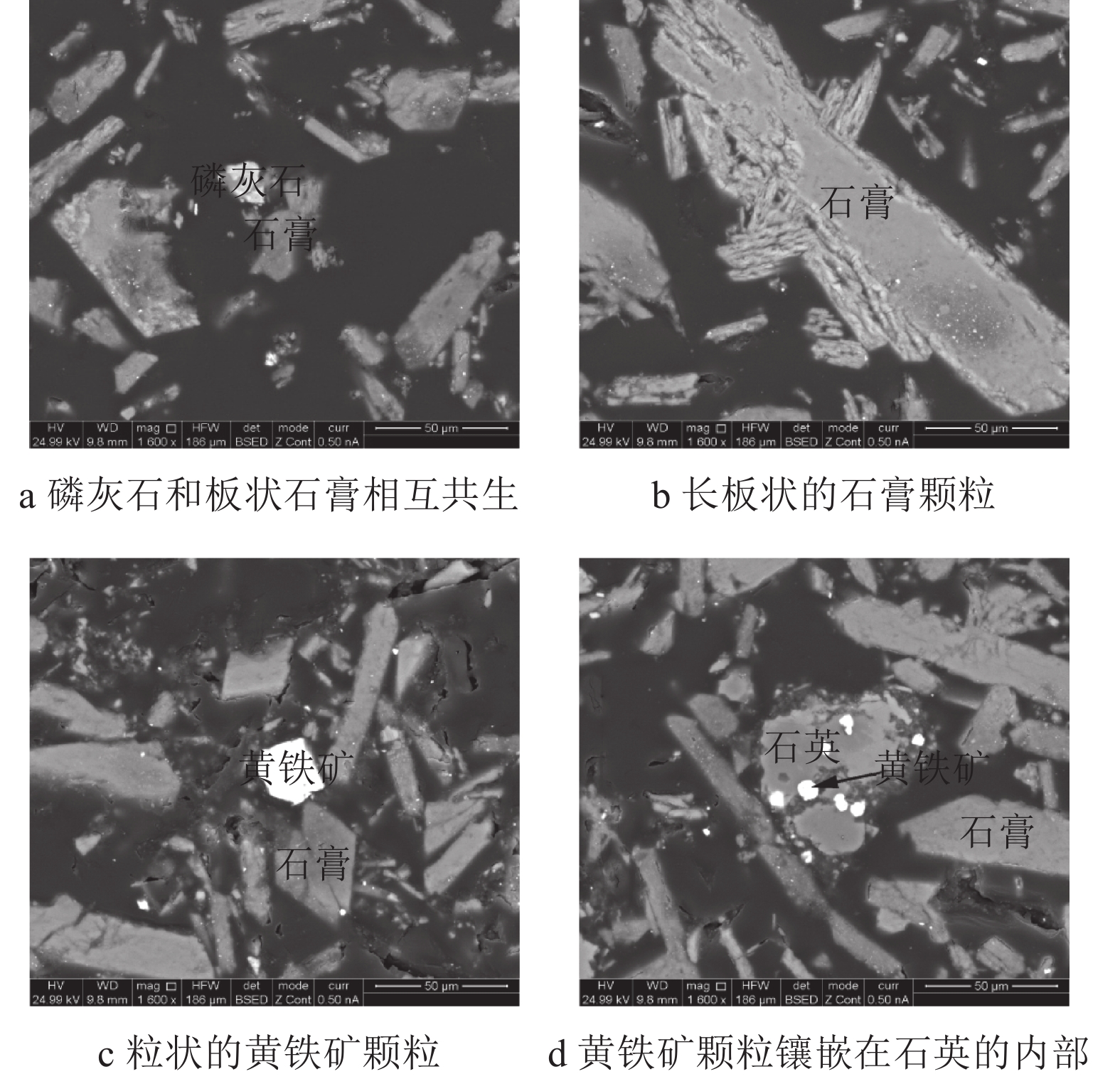
首次采用矿物解离分析系统(MLA),对湖北某工业磷石膏的化学组成、矿物组成、主要矿物颗粒形貌与嵌部特征、矿物解离度、有害元素赋存状态等方面进行了系统的工艺矿物学的探索研究,为磷石膏的资源化利用提供参考。研究表明:该磷石膏中,含量最高的为氧、钙、硫和硅元素,若要提高样品的白度,需要去除磷石膏中的致色杂质元素铁、钛。该磷石膏中矿物组成比较简单,石膏矿物含量满足GB/T 23456-2009 《磷石膏》中一级磷石膏的标准(≥85%),其次含有少量的石英、钾长石、绿泥石、含铁铝硅酸盐、褐铁矿和黄铁矿等矿物。该磷石膏中的杂质磷主要分布在磷灰石和五氧化二磷中,深度脱磷需要水洗与酸洗相结合。
Abstract:For the first time, process mineralogy including the chemical composition, mineral composition, main mineral particle morphology and embedded features, mineral dissociation analysis, and the occurrence status of harmful elements of an industrial phosphogypsum from Hubei provence was conducted using the mineral liberation analysis (MLA). The results provides a theoretical basis for the purification of phosphogypsum and impurity removal. It shows that the industrial phosphogypsum is mainly consist of oxygen, calcium, sulfur, and silicon. To improve the whiteness of the phosphogypsum, the coloring impurities elementsincluding iron, titaniumneed to be removed. The mineral composition of this phosphogypsum is relatively simple, and the content of gypsum mineral meets the standard of first-level phosphogypsum (≥85%) in GB/T 23456-2009 "Phosphogypsum", followed by a small amount of quartz, potassium feldspar, chlorite, iron-containing aluminosilicate, limonite and pyrite, etc. The impurity phosphorus in the phosphogypsum is mainly distributed in apatite and phosphorus pentoxide, and deep dephosphorization process requires water washing combined with pickling.
-
Key words:
- Phosphogypsum /
- Process mineralogy /
- MLA
-

-
表 1 磷石膏中主要化学成分/%
Table 1. Main chemical compositions in phosphogypsum
P2O5 MgO CaO Fe2O3 Al2O3 SiO2 Na2O SO3 K2O TiO2 Loss Y2O3 BaO SrO 0.662 0.066 30.985 0.252 0.56 5.433 0.139 45.062 0.275 0.099 16.355 0.003 0.061 0.048 表 2 磷石膏的矿物组成
Table 2. Mineral composition of phosphogypsum
矿物名称 硅灰石 石膏 石膏+石英(1:4) 黄铁矿 褐铁矿 金红石 含量 /% 0.01 88.34 2.86 0.23 0.24 0.07 矿物名称 含铁铝硅酸盐 钾长石 绿泥石 磷灰石 石英 钠长石 含量 /% 0.72 1.76 0.2 0.02 4.14 0.28 矿物名称 石膏+高岭石 氧化铁 铝酸钙 白云母 透辉石 高岭石 含量 /% 0.08 0.02 0.04 0.05 0.02 0.05 矿物名称 含铁五氧化二磷 方解石 Unknown 氧化铝 磷灰石+石英(1:1) 含量 /% 0.003 0.03 0.71 0.11 0.01 表 3 含磷石膏中磷的赋存状态定量测定/%
Table 3. Quantitative determination of the occurrence state of phosphorus in phosphogypsum
测试方法 总磷 磷灰石中的磷 五氧化二磷中的磷 MLA+XRF 0.66 0.57 0.11 化学分析 0.72 0.55 0.17 表 4 磷灰石嵌布特征定量测定/%
Table 4. Quantitative determination of apatite distribution characteristics
矿物名称 石膏 石膏+石英 钾长石 石英 磷灰石+石英 其他 单体解离 33.22 共生状态 42.59 4.09 0.62 2.94 0.30 0.61 包裹关系 6.45 9.29 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.36 表 5 磷灰石单矿物单体解离度测定
Table 5. Determination of apatite monomer dissociation degree
磷灰石复合颗粒 20%<x≤30% 30%<x≤40% 40%<x≤50% 50%<x≤60% 60%<x≤70% 矿物的累积分布/% 65.99 64.22 61.50 57.79 55.96 磷灰石复合颗粒 70%<x≤80% 80%<x≤90% 90%<x<100% 100% 矿物的累积分布/% 49.62 49.62 33.22 33.22 表 6 五氧化二磷嵌布特征定量测定
Table 6. Quantitative determination of distribution characteristics of phosphorus pentoxide
矿物名称 石膏 石膏+石英 含铁铝硅酸盐 石英 单体解离 81.38 共生状态 1.69 6.92 0.00 0.00 包裹关系 4.41 4.14 0.28 1.18 表 7 五氧化二磷单体解离度测定
Table 7. Determination of dissociation degree of phosphorus pentoxide monomer
P2O5复合颗粒 20%<x≤30% 30%<x≤40% 40%<x≤ 50% 50%<x≤60% 60%<x≤70% 矿物的累积分布/% 89.54 89.54 89.54 81.38 81.38 P2O5复合颗粒 70%<x≤80% 80%<x≤90% 90%<x<100% 100% 矿物的累积分布/% 81.38 81.38 81.38 81.38 -
[1] 赵红涛, 包炜军, 孙振华, 等. 磷石膏中杂质深度脱除技术[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(4):1240-1246.
ZHAO H T, BAO W J, SUN Z H, et al. Removal of impurities from phosphogypsum[J]. Progress in Chemical Industry, 2017, 36(4):1240-1246.
[2] 叶学东. 2018年我国磷石膏利用现状、问题及建议[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2019, 34(7):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2019.07.002
YE X D. Current situation, problems and suggestions of phosphogypsum utilization in China in 2018[J]. Phosphate Fertilizer & Compound Fertilizer, 2019, 34(7):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2019.07.002
[3] 王圳, 张均, 陈芳, 等. 贵州省磷矿固体废弃物治理现状与建议[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(1):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.003
WANG Z, ZHANG J, CHEN F, et al. Present situation and suggestion of management of phosphate rock solid waste[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(1):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.01.003
[4] 唐湘平, 李超, 黄云阶, 等. 四川某地磷石膏开发利用试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(5):28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.05.006
TANG X P, LI C, HUANG Y J, et al. Experimental study on development and utilization of phosphogypsum in Sichuan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(5):28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.05.006
[5] 张浩, 李辉. 用磷石膏制备贝利特-硫铝酸盐水泥[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2014, 33(6):1567-1571.
ZHANG H, LI H. Preparation of belite - sulphoaluminate cement by phosphogypsum[J]. Chinese Journal of Ceramics, 2014, 33(6):1567-1571.
[6] 朱志伟, 何东升, 陈飞, 等. 磷石膏预处理与综合利用研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(4):19-25.
ZHU Z W, HE D S, CHEN F, et al. Research progress on pretreatment and comprehensive utilization of phosphogypsum[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 39(4):19-25.
[7] 杨斌. 水热法处理磷石膏过程研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2006.
YANG B. Study on the process of hydrothermal treatment of phosphogypsum [D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2006.
[8] 白有仙. 磷石膏组成及脱磷脱硫方法的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2009.
BAI Y X. Study on the composition of phosphogypsum and the method of dephosphorization and desulfurization [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2009.
[9] 陈嘉懿. 预处理工艺对磷石膏性能的影响及作用机理研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2012.
CHEN J Y. Study on the effect of pretreatment process on the properties of phosphogypsum and the mechanism of action [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2012.
[10] 庞建涛, 肖喆, 王灿霞, 周建一. MLA系统在磷块岩工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2015, 44(10):19-21.
PANG J T, XIAO Z, WANG C X, et al. Application of MLA system in process mineralogy research of phosphorite block[J]. Chemical Minerals and Processing, 2015, 44(10):19-21.
[11] 苏庆东, 刘会忠, 刘会友, 等. NY/T1060-2006《水泥生产用磷石膏》[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006.
SU Q D, LIU H Z, LIU H Y, et al. NY/T1060-2006 Phosphogypsum for cement production [S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2006.
[12] 郑建国, 王德伦, 袁运法, 等. GB/T 23456-2009《磷石膏》[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010.
ZHENG J G, WANG D L, YUAN Y F, et al. GB/T 23456-2009 Phosphogypsum [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2010.
[13] 张欢. 磷石膏的质量影响因素及质量评价指标体系研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2013.
ZHANG H. Study on quality influencing factors and quality evaluation index system of phosphogypsum [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2013.
[14] 胡敏, 彭丽, 郭娜, 等. 磷石膏- 炭化污泥胶凝材料力学性能试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4):196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.034
HU M, PENG L, GUO N, et al. Study on mechanical properties of phosphogypsum-carbonized sludge composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):196-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.034
[15] 李美. 磷石膏品质的影响因素及其建材资源化研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2012.
LI M. Study on the influencing factors of phosphogypsum quality and the resource utilization of building materials [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012.
[16] Ölmez H, Yilmaz V T. Infrared study on the refinement of phosphogypsum for cements[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1988, 18(3):449-454. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(88)90079-8
[17] 彭家惠, 万体智, 汤玲, 等. 磷石膏中有机物、共晶磷及其对性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2003, 6(3):221-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2003.03.001
PENG J H, WAN T Z, TANG L, et al. Organic matter and eutectic phosphorus in phosphogypsum and their effects on properties[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2003, 6(3):221-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2003.03.001
-




 下载:
下载: