Experimental Study on Deashing of High Ash and Refractory Coal Slime by Classification Flotation
-
摘要:
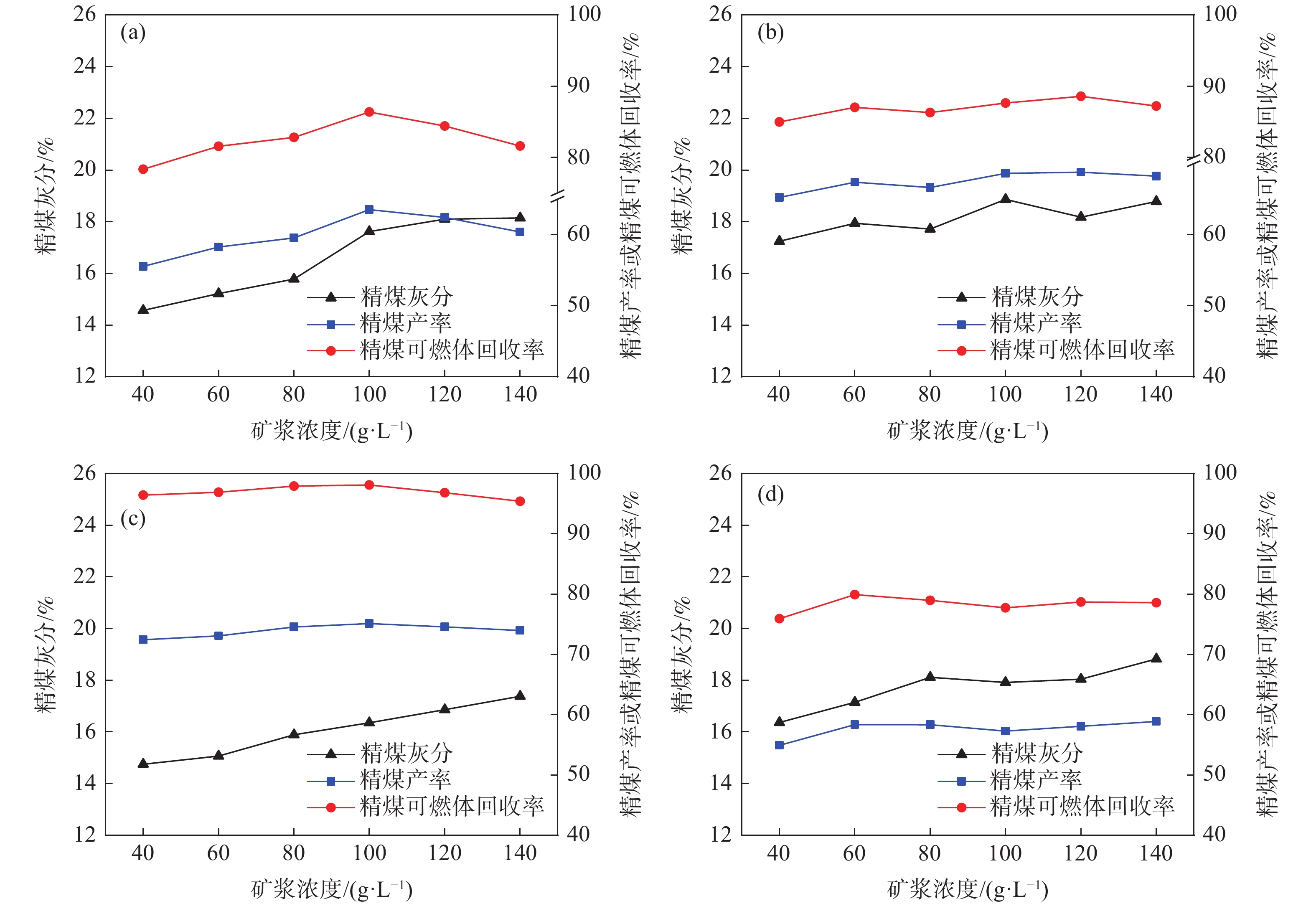
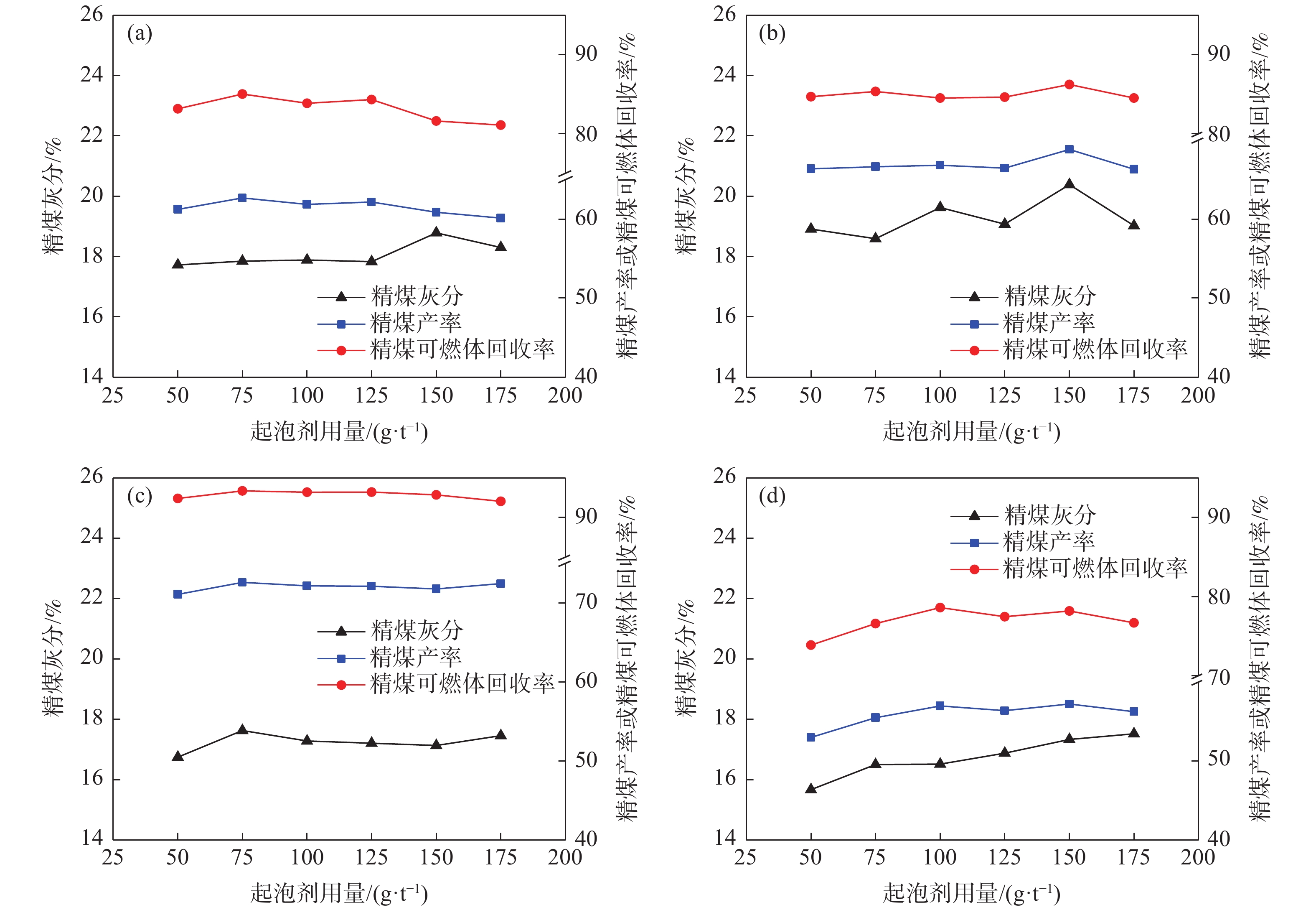
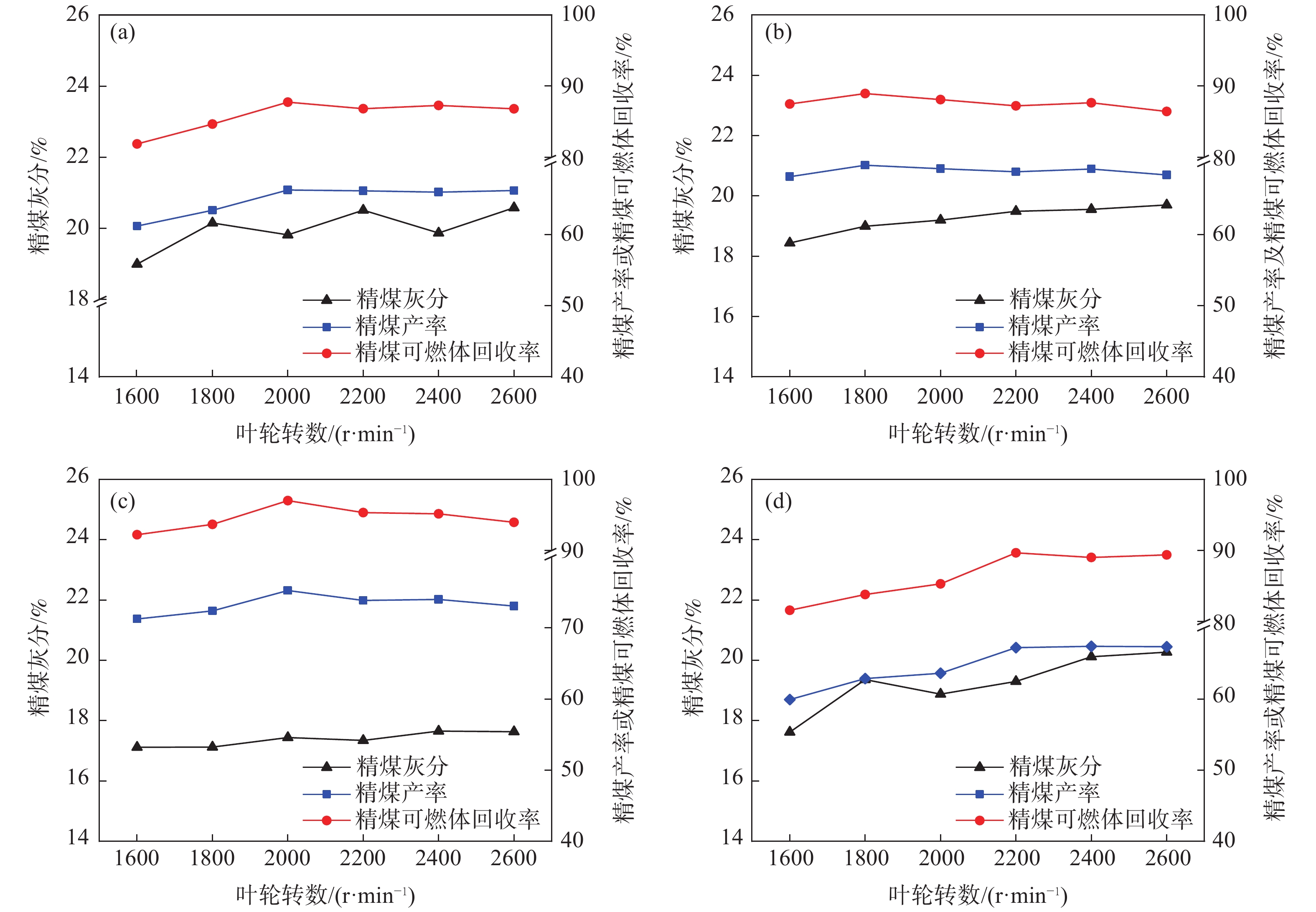
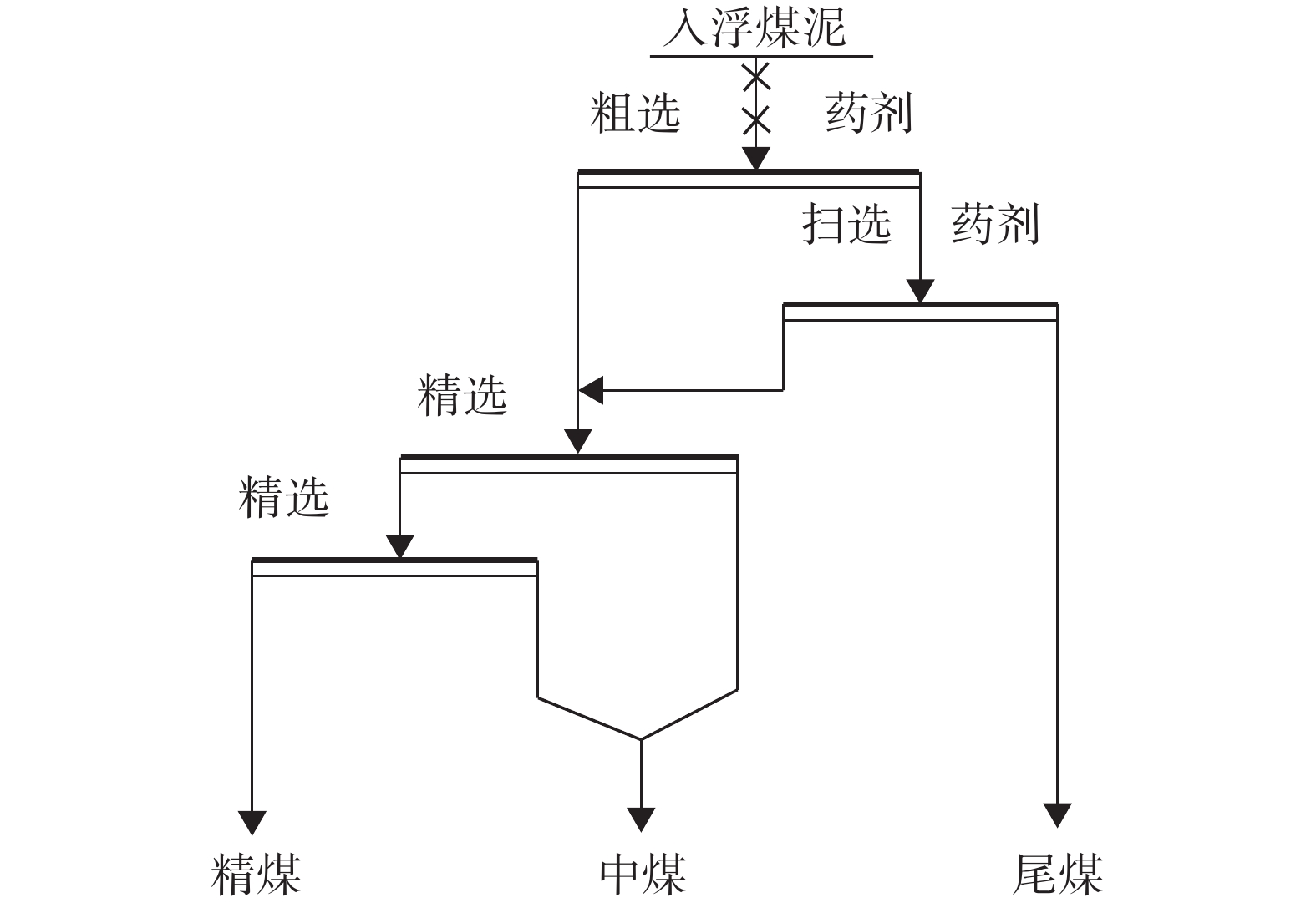
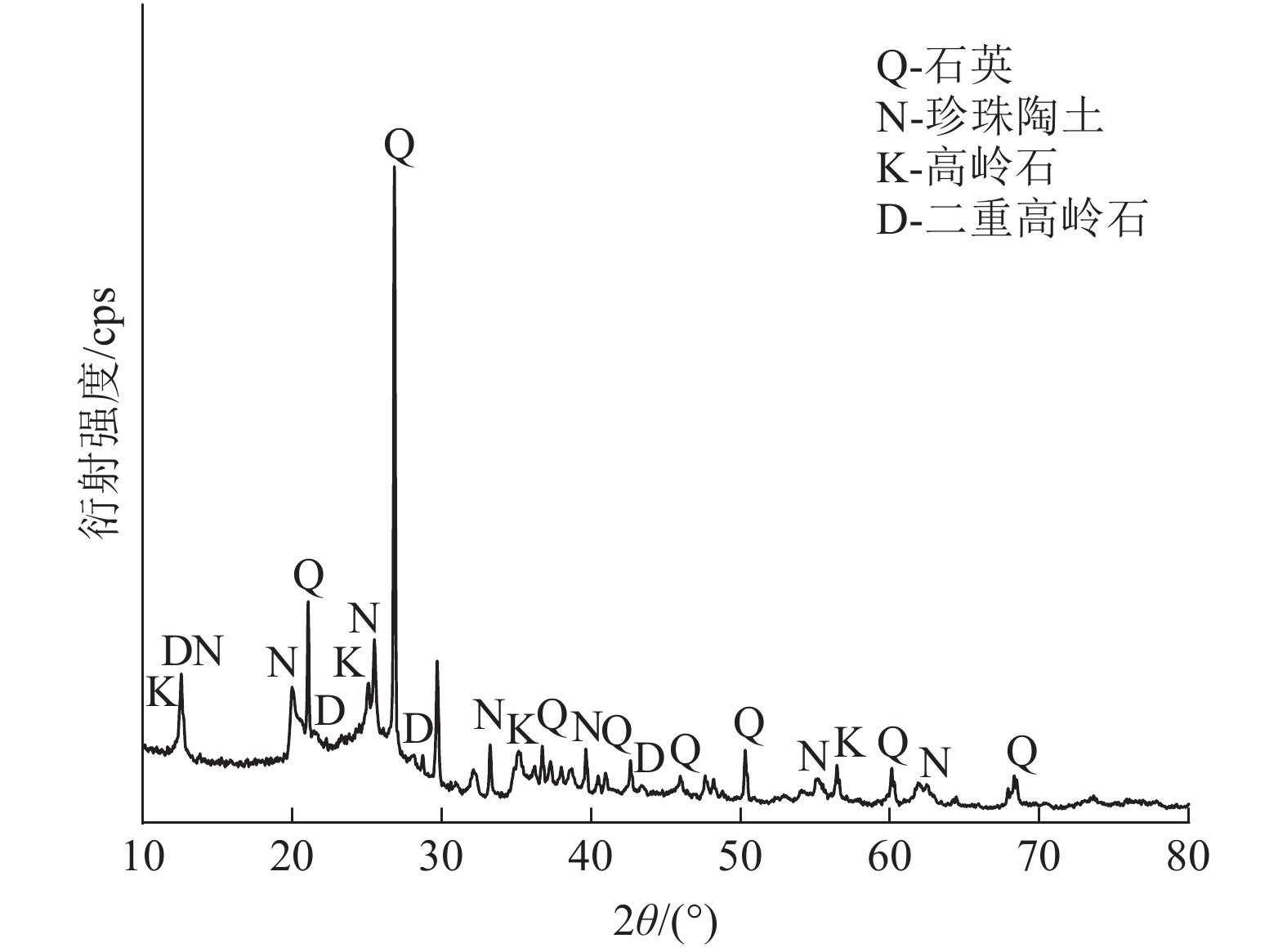
针对贵州某煤泥中-0.074 mm粒级的产率为54.19%,灰分为40.55%,并含有大量的珍珠陶土、高岭石和二重高岭石等黏土矿物,极易泥化的高灰难选煤泥。采用分级浮选方式,分别确认了-0.5+0.25 mm、-0.25+0.074 mm、-0.074 mm粒级浮选的矿浆浓度、捕收剂用量、起泡剂用量、叶轮转速及工艺流程等较优浮选条件并和-0.5 mm全粒级进行对比;结果表明:各粒级的较优药剂用量和工艺参数均不同,在较优浮选条件下,分粒级的精煤产率高于全粒级,灰分低于全粒级;分粒级的尾煤产率低于全粒级,灰分高于全粒级,即分粒级浮选对该煤泥有显著的意义。
Abstract:Aiming at a certain coal slime in Guizhou, the yield rate of -0.074mm class is 54.19%, the ash content is 40.55%, the yield rate of -0.045 mm class is 40.38%, the ash content is 40.79%, and contains a lot of pearl clay, Clay minerals such as kaolinite and double kaolinite, difficlut floated and high-ash coal slime that are easy sliming. The optimal flotation conditions of -0.5+0.25 mm, -0.25+0.074 mm and -0.074 mm classes (slurry concentration, collector dosage, frother dosage and mixing speed)were confirmed by the method of classification flotation. The optimal flotation conditions of -0.5+0.25 mm, -0.25+0.074 mm and -0.074 mm classes were compared with the whole flotation of -0.5mm class. The results show that the optimal dosage of reagents and process parameters for each size classes are different. Under the optimal flotation conditions, the yield of clean coal of classification flotation is higher than that of the full size flotation, and the ash content is lower than that of the full size flotation. The yield of tailings is lower than that of the full size flotation, and the ash content is higher than that of the full size flotation. That is, the flotation of the classification flotation is significant for the slime.
-
Key words:
- High ash /
- Difficult to separate slime /
- Classification flotation /
- Size class
-

-
表 1 煤泥的工业分析结果
Table 1. Industrial analysis results of coal slime
名称 水分 灰分 挥发分 固定碳 含量/% 1.85 39.75 16.62 41.78 表 2 原煤泥筛析结果
Table 2. Sieve analysis results of coal slime
粒级/mm 产率/% 灰分/% 筛上累积 筛下累计 产率/% 灰分/% 产率/% 灰分/% -0.5+0.25 15.45 36.79 15.45 36.79 100.00 39.17 -0.25+0.125 17.10 38.30 32.55 37.58 84.55 39.60 -0.125+0.074 13.27 38.47 45.82 37.84 67.45 39.94 -0.074+0.045 13.81 38.85 59.63 38.08 54.18 40.30 -0.045 40.37 40.79 100.00 39.17 40.37 40.79 总计 100.00 39.17 表 3 各粒级煤泥给料浮选获得的精煤、中煤和尾煤实验结果
Table 3. Test results of various grades of slime clean coal, middling coal and tailings
给料粒级/mm 精煤 中煤 尾煤 产率/% 灰分/% 产率/% 灰分/% 产率/% 灰分/% -0.5 32.64 10.06 35.77 35.42 31.59 80.78 -0. 5+0. 25 35.42 9.72 37.15 25.97 27.43 84.59 -0. 25+0.074 36.25 8.76 42.36 32.57 21.39 85.60 -0.074 35.45 9.22 40.09 36.00 24.46 87.47 -
[1] 程万里, 邓政斌, 刘志红, 等. 煤泥浮选中矿物颗粒间相互作用力的研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(3):48-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.03.008
CHENG W L, DENG Z B, LIU Z H, et al. Research progress of interaction force between mineral particles in coal slurry flotation[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(3):48-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.03.008
[2] 宋帅, 樊玉萍, 马晓敏, 等. 煤泥水中煤与不同矿物相互作用的模拟研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):168-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.034
SONG S, FAN Y P, MA X M, et al. Simulation study on interaction between coal and different minerals in coal slurry[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):168-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.034
[3] 于跃先, 马力强, 张仲玲, 等. 煤泥浮选过程中的细泥夹带与罩盖机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(3):625-658.
YU Y X, MA L Q, ZHANG Z L, et al. Mechanism of entrainment and slime coating on coal flotation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(3):625-658.
[4] 谢才秀, 张永菊, 龙涛, 等. 不同实验设计方法在高灰分煤泥浮选优化实验中的应用[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):72-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.011
XIE C X, ZHANG Y J, LONG T, et al. Application of different experimental design method in the flotation optimization experiments of high ash coal slime[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):72-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.011
[5] 王成勇, 陈鹏, 潘东, 等. 18 疏水引力在煤泥浮选过程中的作用机理及应用[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(3):105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.03.017
WANG C Y, CHEN P, PAN D, et al. Mechanism and application of hydrophobic attraction in coal flotation process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(3):105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.03.017
[6] 崔广文, 张继柱, 扶祥通, 等. 煤泥粒度组成对浮选影响的研究[J]. 选煤技术, 2007(4):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3571.2007.04.006
CUI G W, ZHANG J Z, FU X T, et al. Research on the influence of coal slime particle size composition on flotation[J]. Coal Preparation Technology, 2007(4):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3571.2007.04.006
[7] 周开洪, 程敢, 王永田. 粒度和密度组成对煤泥浮选的影响[J]矿山机械, 2012, 40(11): 84-89.40(11): 84-89.
ZHOU K H, CHENG G, WANG Y T. Influence of granularity and density composition on flotation of coal slime [J]. Mining Machinery, 2012,
[8] 曹钊, 张弘强, 袁治国, 等. 煤泥入料粒度对其浮选动力学特性的影响[J]. 煤炭技术, 2015, 34(7):310-312.
CAO Z, ZHANG H Q, YUAN Z G, et al. Effect of coal particle size on its flotation kinetics characteristics[J]. Coal Technology, 2015, 34(7):310-312.
[9] 谢广元, 吴玲, 欧泽深, 等. 煤泥分级浮选工艺的研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2005(6):78-82.
XIE G Y, WU L, OU Z S, et al. Research on fine coal classified flotation flowsheet[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2005(6):78-82.
[10] 张晓鹏. 高灰细泥对浮选精煤质量的影响分析[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2017(3):30-34.
ZHANG X P. Analysis of the influence of high ash fine sludge on the quality of flotation clean coal[J]. Coal Processing& Comperhensive Utilization, 2017(3):30-34.
[11] 石开仪, 孔德顺, 龙剑, 等. 贵州高灰细粒煤泥浮选研究[J]. 煤炭工程, 2016, 48(10):120-123. doi: 10.11799/ce201610037
SHI K Y, KONG D S, LONG J, et al. Study on flotation on Guizhou high ash fine coal slime[J]. Coal Engineering, 2016, 48(10):120-123. doi: 10.11799/ce201610037
[12] 王婷霞. 捕收剂与煤表面分子间作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2016.
WANG T X. Study on effect between collectors and moleculars on coal [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016.
[13] 卢智强, 刁海瑞, 李彩霞, 等. 难浮煤泥浮选试验研究[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2018, 24(4):50-53.
LU Z Q, DIAO H R, LI C X, et al. Experimental study on floatation test of difficult floated coal[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2018, 24(4):50-53.
-



 下载:
下载: