Experimental Study on Extraction of Aluminum and Iron from Bayer Red Mud by Deep Reduction Sintering
-
摘要:
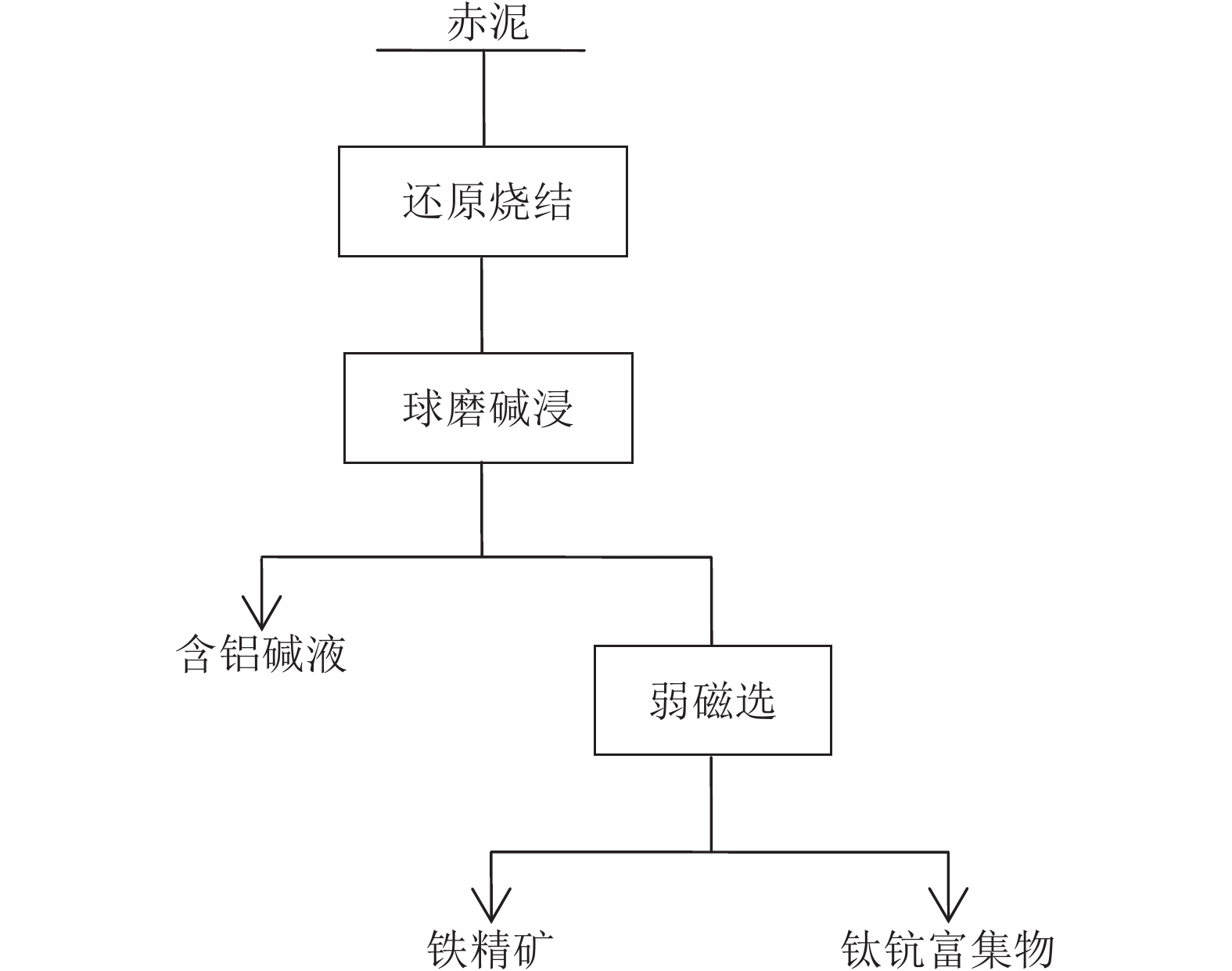
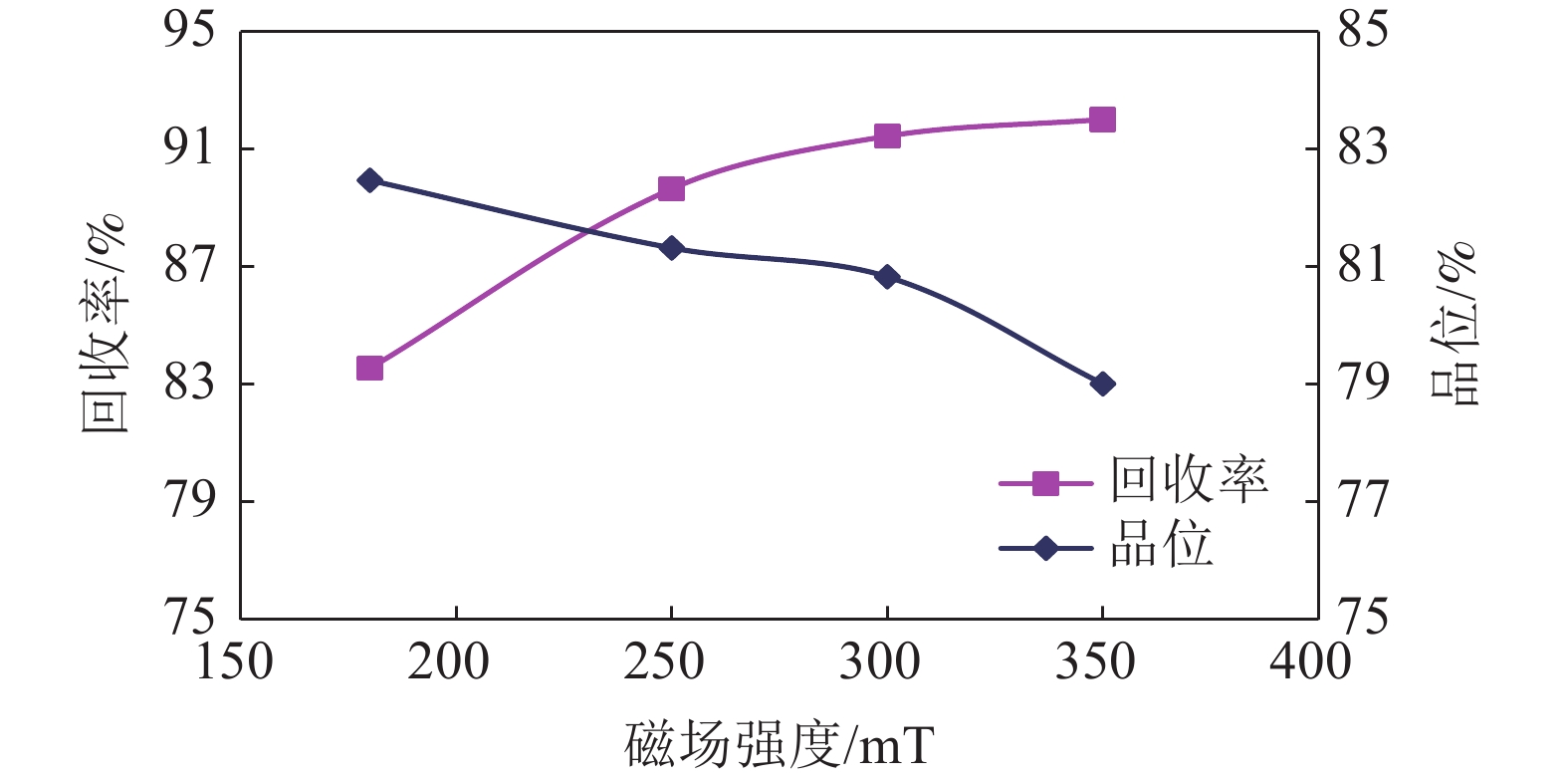
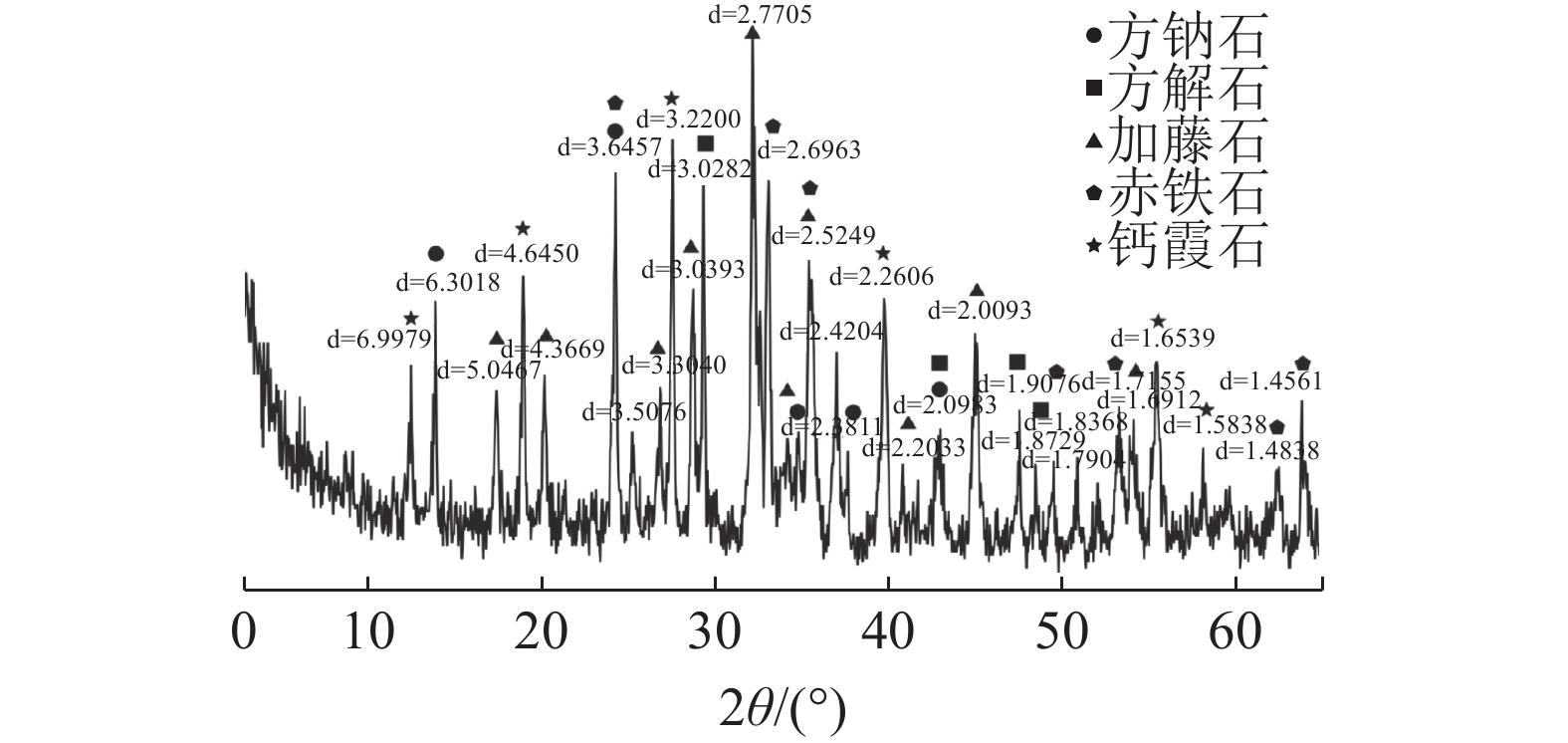
赤泥中铁、铝的存在影响钪和稀土的浸出及萃取。通过对拜耳法赤泥进行分析测试,设计了还原烧结协同回收铝、铁技术方案,系统研究了熔融态深度还原烧结协同提取赤泥中铝、铁的工艺。在较佳条件下,铁精矿品位为73.97%,回收率达到90.27%,铝溶出率达到96.28%,铝硅酸盐矿物转化为铝酸钠,碱浸得到铝酸钠溶液,后续可用于制取聚合氯化铝产品。赤泥中的含铁复杂矿物转化成具有磁性的磁铁矿和单质铁,磁选回收含铁矿物,实现赤泥中铁、铝的协同回收。该工艺不仅减弱了铝、铁矿物对后续酸浸萃取提取钪、钛、稀土的不利影响,且使得钛、钪和稀土在尾渣中得到富集,有利于实现赤泥多元素高值化综合利用。
Abstract:The presence of iron and aluminum in the red mud affect the leaching and extraction of scandium and rare earths. Through the analysis and testing of the Bayer process red mud, a technical plan for the reduction and sintering to recover aluminum and iron was designed, and the process of the molten deep reduction and sintering to extract aluminum and iron from the red mud was systematically studied. Under the optimum conditions, the grade of iron concentrate is 73.97%, the recovery rate is 90.27%, and the dissolution rate of aluminum is 96.28%, the aluminosilicate mineral is converted into sodium aluminate, and the sodium aluminate solution is obtained by alkali leaching, which can be used to prepare polyaluminum chloride products in the subsequent. The iron-containing complex minerals in the red mud are transformed into magnetic magnetite and elemental iron, and the iron-containing minerals are recovered by magnetic separation to realize the coordinated recovery of iron and aluminum in the red mud. The process not only weakens the adverse effect of aluminum and iron ore on the subsequent extraction of scandium, titanium and rare earth by acid leaching, but also enriches titanium, scandium and rare earth in the tailings, which is conducive to the realization of multi-element comprehensive utilization of red mud.
-
Key words:
- Red mud /
- Molten state /
- Reduction sintering
-

-
表 1 赤泥化学多元素分析结果/%
Table 1. Analysis results of multi-elements of red mud
Fe2O3 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO TiO2 K2O Na2O P2O5 LOI 14.62 18.02 20.67 20.68 0.54 3.83 0.39 4.26 0.37 13.16 表 2 赤泥ICP-MS分析结果/(g·t−1)
Table 2. Analysis results of ICP-MS of red mud
Sc REE Li V Ni Nb Ta Ga 74.8 1409 258.49 1357.61 323.88 132.32 16.94 80.97 表 3 赤泥铁物相分析/%
Table 3. Phase analysis of red mud
磁性铁 菱铁矿 赤褐铁矿 硫铁矿 硅酸铁 总量 10.85 12.38 75.31 0.20 1.26 100.00 表 4 主要矿物嵌布粒度分布/%
Table 4. Granularity distribution of main minerals
粒度/mm 钙霞石 加藤石 铝针铁矿 赤铁矿 方解石 石英 −0.15+0.5 8.78 5.97 6.57 0.72 3.83 0 −0.075+0.15 11.31 7.76 17.29 5.34 9.61 5.06 −0.038+0.075 20.58 9.56 19.93 11.34 10.78 3.37 −0.01+0.038 20.48 16.91 33.30 18.18 35.19 51.92 −0.01 38.85 59.81 22.91 64.45 40.57 39.64 表 5 添加剂种类实验效果
Table 5. Test effect of additive type
序号 添加剂种类及组合 铁回收效果 铝溶出效果 1 C+CaF2 好 几乎无溶出 2 C+CaF2+CaO 一般 几乎无溶出 3 C+CaF2+Na2CO3+CaO 较好 好 4 C+CaF2+Na2SO4 较好 几乎无溶出 5 C+Na2CO3+CaO 较差 好 表 6 750℃烧结时间实验
Table 6. Results of 750℃ sintering time
升温方式 铁精矿
品位/%铁精矿
回收率/%铝溶出率/% 直接升温至1200℃ 80.76 88.13 74.40 升温至750℃保持20 min 80.05 87.66 78.19 升温750℃保持40 min 80.80 87.41 71.28 表 7 优化实验设计及实验结果/%
Table 7. Optimized test design and test results
序号 焦炭 CaF2 Na2CO3 CaO 铁精矿
品位铁回
收率铝回
收率1 4 4 15 5 68.65 57.29 14.86 2 4 8 30 15 68.35 19.31 13.65 3 4 12 45 25 23.48 5.91 28.22 4 4 16 60 35 40.82 14.74 64.90 5 8 4 30 25 59.29 75.16 79.84 6 8 8 15 35 59.86 76.65 37.76 7 8 12 60 5 69.84 45.74 69.99 8 8 16 45 15 76.75 65.12 67.77 9 12 4 45 35 55.18 69.89 30.69 10 12 8 60 25 27.23 77.58 86.80 11 12 12 15 15 78.51 88.69 44.87 12 12 16 30 5 81.10 87.51 54.79 13 16 4 60 15 40.10 89.83 85.85 14 16 8 45 5 74.61 87.73 86.54 15 16 12 30 35 71.66 82.39 43.30 16 16 16 15 25 79.02 81.43 49.83 表 8 优化实验结果/%
Table 8. Optimized test results
序号 条件 C CaF2 Na2CO3 CaO 铁精矿
品位铁回
收率铝溶
出率1 验证实验 16 4 60 5 67.25 84.29 96.64 2 CaO为0% 16 4 60 0 73.97 90.27 96.28 3 CaF2为0% 16 0 60 5 54.88 73.77 96.28 表 9 尾渣多元素分析和ICP-MS分析结果/%
Table 9. Analysis results of multi-elements and ICP-MS of the tailings
SiO2 Al2O3 TFe TiO2 Na2O MgO CaO Sc2O3 REO 26.23 2.33 0.73 5.35 15.82 1.38 27.62 0.015 0.22 -
[1] 朱晓波, 李望, 管学茂. 赤泥综合利用研究现状及分析[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2016(1):7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.01.002
ZHU X B, LI W, GUAN X M. Research status and analysis of the comprehensive utilization of red mud[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016(1):7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.01.002
[2] 张成林, 王家伟, 刘华龙, 等. 赤泥脱碱技术研究现状与进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2012( 2) : 11 – 14.
ZHANG C L, WANG J W, LIU H L, et al. Research status and progress of red mud dealkalization technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2012( 2) : 11 – 14.
[3] 庄锦强. 高铁氧化铝赤泥中铁的回收技术对究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
ZHUANG J Q. Research on the recovery technology of iron in high-iron alumina red mud [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
[4] 孙道兴. 赤泥脱碱处理和有价金属钛钪提取的研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2008, 40(10):49-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2008.10.017
SUN D X. Research on dealkalinization of red mud and extraction of valuable metal titanium and scandium[J]. Inorganic Salt Industry, 2008, 40(10):49-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2008.10.017
[5] 李建伟, 马炎, 马挺, 等. 赤泥制备免烧砖的研究现状及技术要点探讨[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(3):7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.03.002
LI J W, MA Y, MA T, et al. Research status and technical points of preparation of unburned brick by the red mud[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(3):7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.03.002
[6] 郭庆, 陈书文, 张军红, 等. 微波强化赤泥制备Fe-Al基絮凝剂工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(4):117-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.025
GUO Q, CHEN S W, ZHANG J H, et al. Study on preparation of Fe/Al-base flocculant from red mud by microwave[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):117-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.025
[7] 李爱民, 何瑞明. 低铁拜耳法赤泥熔融态深度还原除铁试验研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2018, 38(10):101-105. doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2018.10.022
LI A M, HE R M. Experimental study on the deep reduction of iron removal from the molten state of the low-iron Bayer process red mud[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2018, 38(10):101-105. doi: 10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2018.10.022
-



 下载:
下载: