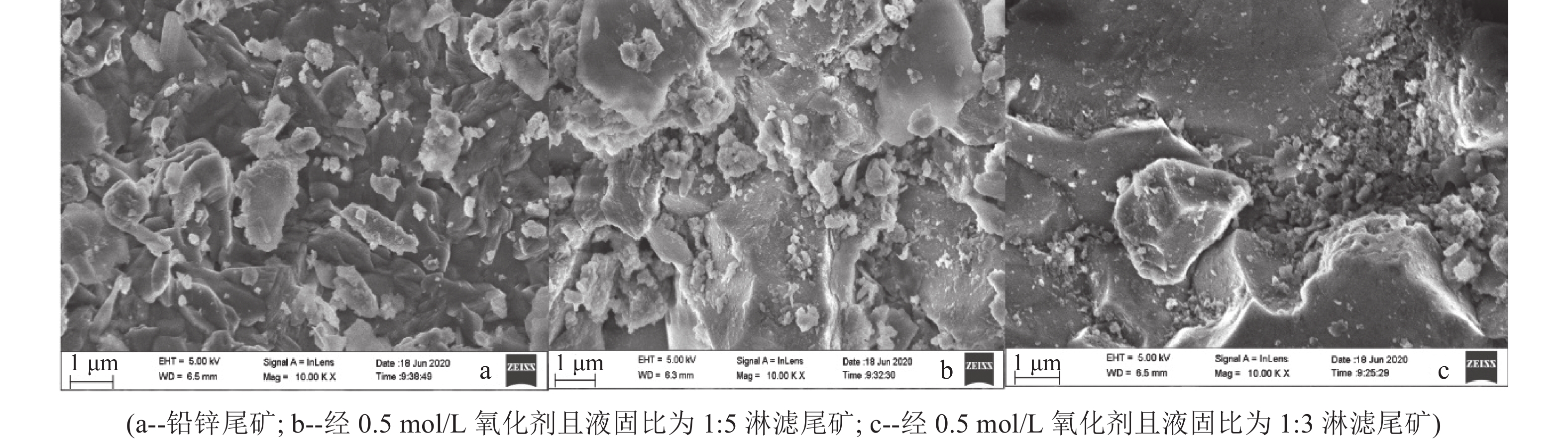
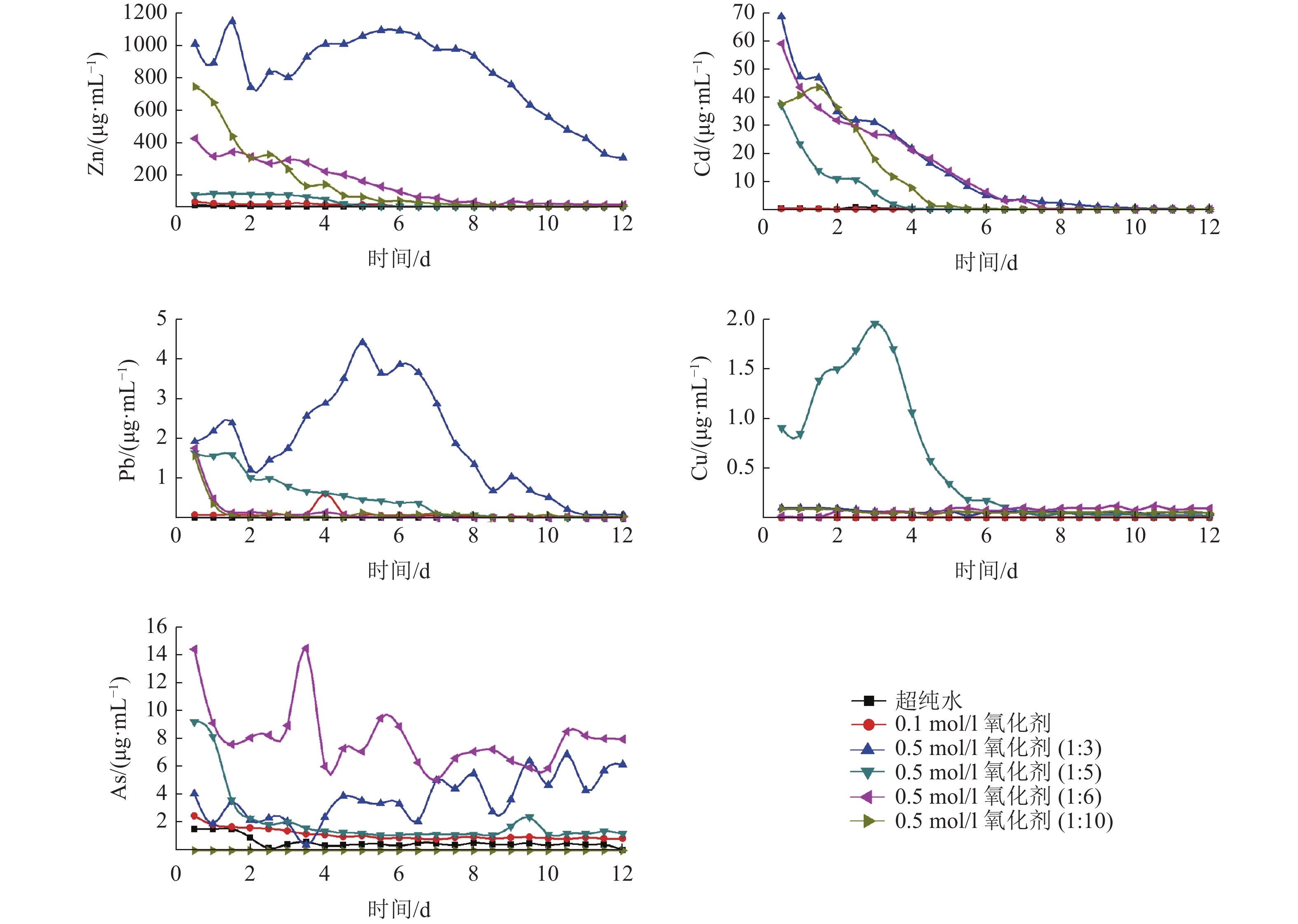
Dynamic Study on the Release and Migration of Heavy Metals during the Oxidation of Lead-Zinc Tailings
-
摘要:
铅锌尾矿堆放造成矿山周边环境严重污染,为研究尾矿安全堆放并在堆放过程中去除一定量重金属,以广西大厂鲁塘铅锌尾矿为研究对象,研究在不同氧化剂浓度和不同液固比条件下Zn、Cd、Pb、Cu和As的释放迁移能力。结果表明:氧化环境可以有效促进各元素的释放迁移能力,氧化剂浓度越高各元素迁移出的量也越多;各元素较佳释放迁移的液固比不同,Zn元素的最适合固液比为1∶10,Cd元素的最适合固液比为1∶6,Pb元素的较适合固液比为1∶6,Cu元素的较适合固液比为1∶5,As元素的较适合固液比为1∶6。
Abstract:The dumping of lead-zinc tailings causes serious environmental pollution around the mine. In order to study the safe dumping of tailings and the removal of a certain amount of heavy metals during the dumping process, the release and migration of Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu and As under different oxidant concentrations and different liquid to solid ratios were investigated in lead-zinc tailings of Lutang, Dachang, Guangxi. The results show that the oxidizing environment can effectively promote the release and migration of the elements. The higher the oxidant concentration, the more the elements can be migrated out. The optimum liquid-solid ratio for release and migration varies among the elements, with the most suitable solid to liquid ratio being 1∶10 for Zn and 1∶6 for Cd, 1∶6 for Pb, 1∶5 for Cu and 1∶6 for As.
-
Key words:
- Lead-zinc mine /
- Heavy metals /
- Release migration /
- Tailings
-

-
[1] Shweta Singh, Saswati Chakraborty. Performance of organic substrate amended constructed wetland treating acid mine drainage (AMD) of North-Eastern India [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 397: 1-12.
[2] 杨进忠, 毛益林, 陈晓青, 等. 某尾矿资源化处置与综合利用研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(6):117-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.025
YANG J Z, MAO Y L, CHEN X Q, et al. Study on resource treatment and comprehensive utilization of a tailing[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(6):117-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.025
[3] 王宝, 董兴玲, 葛碧洲. 尾矿库酸性矿山废水的源头控制方法[J]. 中国矿业, 2015, 24(10):88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.10.018
WANG B, DONG X L, GE B Z. Source control method of acid mine wastewater from tailings pond[J]. China Mining, 2015, 24(10):88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.10.018
[4] 万选志, 刘明实, 刘子龙, 等. 重金属酸性废水回用选矿厂的实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):120-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.025
WAN X Z, LIU M S, LIU Z L, et al. Experimental study on heavy metal acidic wastewater recycling the concentrator[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):120-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.025
[5] 于童, 徐绍辉, 林青. 不同初始氧化还原条件下土壤中重金属的运移研究. 单一的土柱实验[J]. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(4):688-697. doi: 10.11766/trxb201107070254
YU T, XU S H, LIN Q. Research on migration of heavy metals in soil at different redox conditions. Soil column test of Cd, Cu and Zn[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 2012, 49(4):688-697. doi: 10.11766/trxb201107070254
[6] 张密, 文波, 黄凌霞, 等. 氧化还原条件对城市水体沉积物重金属迁移转化的影响[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2016(2):160-170.
ZHANG M, WEN B, HUANG L X, et al. Effects of redox conditions on heavy metal migration and transformation in urban water sediments[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2016(2):160-170.
[7] 刘昌庚, 张盼月, 蒋娇娇, 等. 生物沥浸耦合类 Fenton 氧化调理城市污泥[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1):333-337.
LIU C G, ZHANG P Y, JIANG J J, et al. Oxidation conditioning of urban sludge by bio-leaching coupling Fenton[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1):333-337.
[8] 王媛, 魏忠义, 张卫, 等. 柴河铅锌尾矿中重金属铅、锌、镉的迁移特征[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2015, 37(10):58-62+69. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2015.10.012
WANG Y, WEI Z Y, ZHANG W, et al. Migration characteristics of heavy metals lead, zinc and cadmium in chaihe lead-zinc tailings[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2015, 37(10):58-62+69. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2015.10.012
[9] 于童. 土壤氧化还原条件的改变对镉吸附解吸的影响[J]. 科技信息, 2010, 33:59-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2010.36.048
YU T. Effects of changes in soil redox conditions on cadmium adsorption and desorption[J]. Science and Technology Information, 2010, 33:59-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2010.36.048
[10] 方楠, 吴健, 何强, 等. 响应面法优化铁尾矿砂对铜(Ⅱ)的吸附条件[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020, 1(1):140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.029
FANG N, WU J, HE Q, et al. Optimization of adsorption conditions of copper (Ⅱ)on ferrous mill tailings by response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 1(1):140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.029
[11] 李玲, 张国平, 刘虹. 广西大厂多金属矿区河流中Sb和As的迁移及环境影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2009, 22(6):682-687. doi: 10.13198/j.res.2009.06.60.lil.010
LI L, ZHANG G P, LIU H. The migration and environmental impact of Sb and As in the rivers of Guangxi Dachang polymetallic mining area[J]. Environmental Science Research, 2009, 22(6):682-687. doi: 10.13198/j.res.2009.06.60.lil.010
[12] 陈兆鑫, 李达明, 罗锡明. 不同浸提工艺的金矿尾矿中砷的存在形态研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(3):363-368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.03.014
CHEN Z X, LI D M, LUO X M. Study on the existence of arsenic in gold tailings with different extraction processes[J]. Rock and Mineral Testing, 2014, 33(3):363-368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.03.014
[13] 陈明, 杨涛, 徐慧, 等. 赣南某钨矿区土壤中Cd、Pb的形态特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(12):2257-2262. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015070201
CHEN M, YANG T, XU H, et al. Morphological characteristics and ecological risk assessment of Cd and Pb in the soil of a tungsten mining area in southern Jiangxi[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(12):2257-2262. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015070201
[14] 郭平, 宋杨, 谢忠雷. 冻融作用对黑土和棕壤中Pb、Cd吸附/解吸特征的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(1):226-232.
GUO P, SONG Y, XIE Z L. The effect of freezing and thawing on the adsorption/desorption characteristics of Pb and Cd in black soil and brown soil[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(1):226-232.
[15] 胡延彪, 李忠武, 黄金权. 湘江长沙段洲滩菜园土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2016, 16(1):354-358. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2016.01.073
HU Y B, LI Z W, HUANG J Q. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in vegetable garden soils in the Changsha section of the Xiangjiang River[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2016, 16(1):354-358. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2016.01.073
-



 下载:
下载: