Experiment on Production of Silicon Fertilizer from Polyaluminum Chloride Industrial Waste Residue
-
摘要:
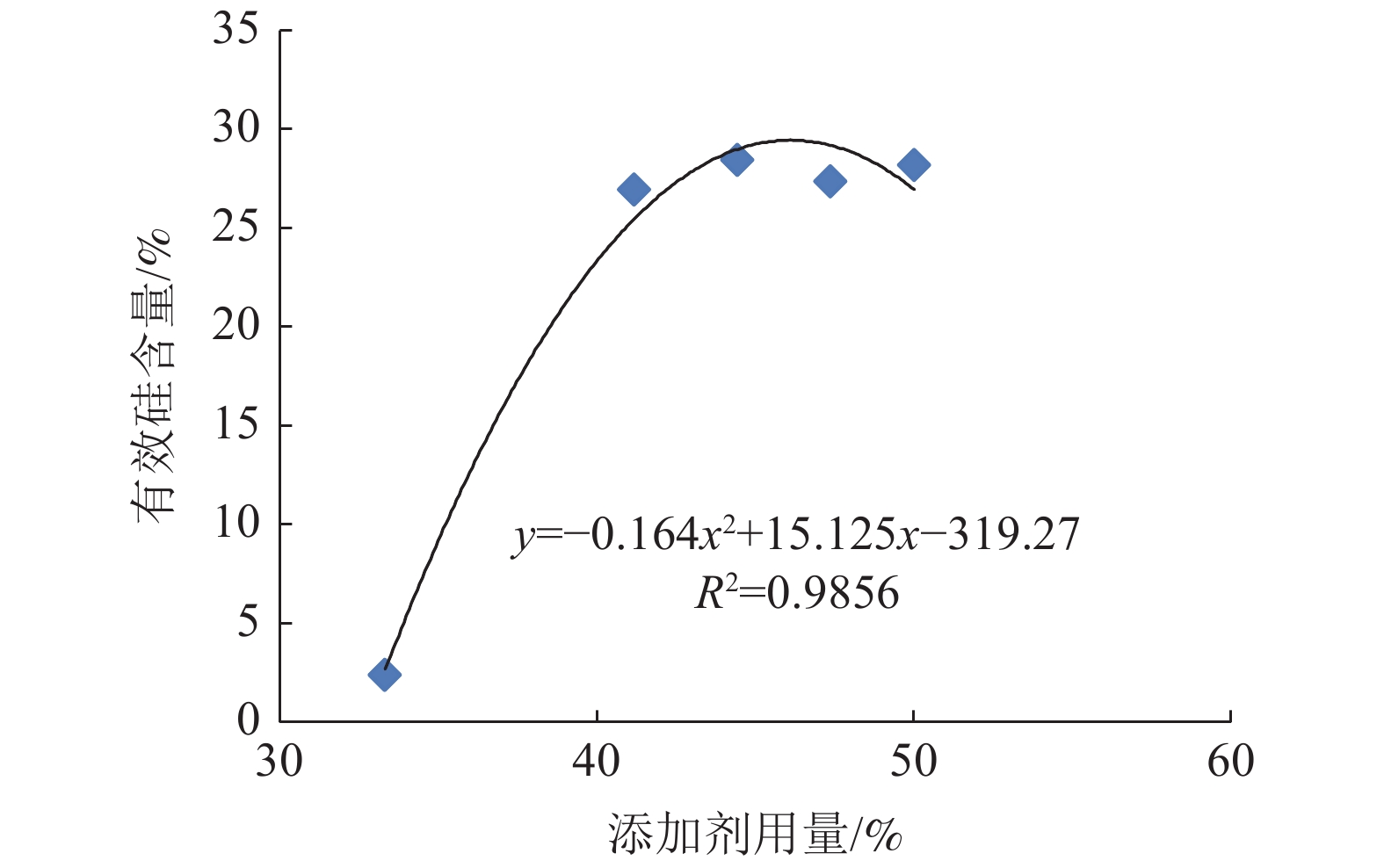
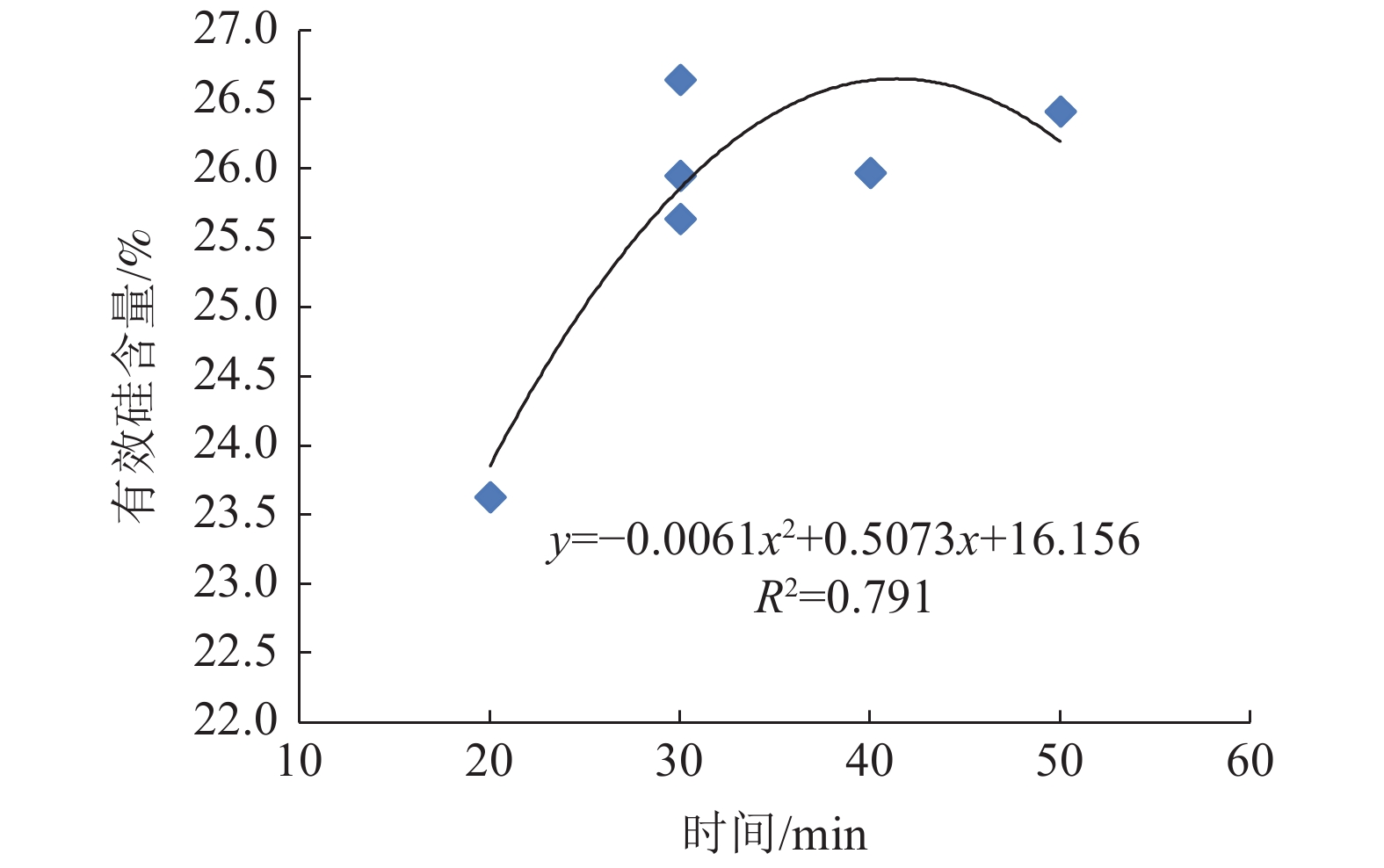
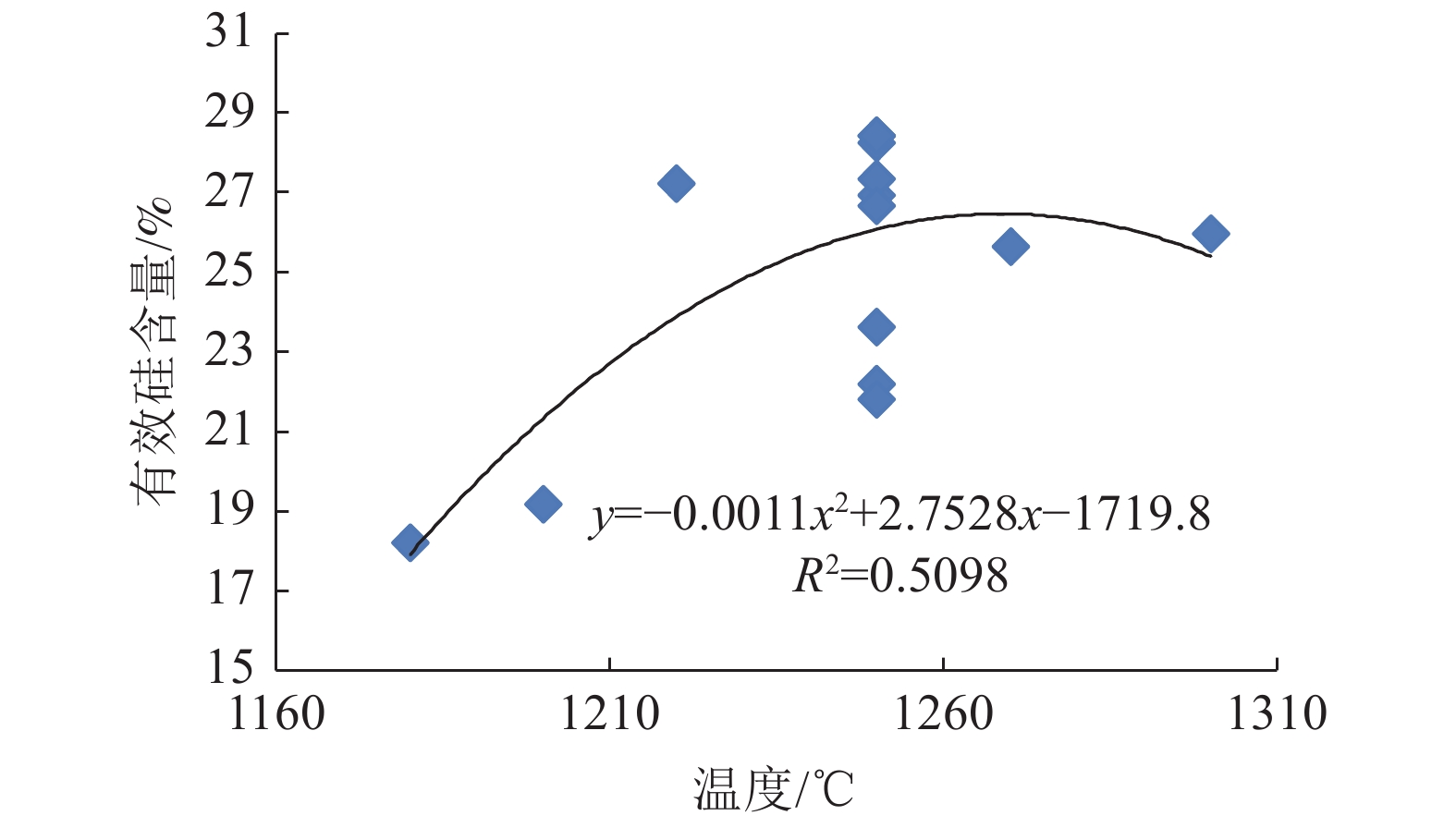
以聚合氯化铝废渣为原料,采用单因素实验和正交设计研究了焙烧温度、焙烧时间、添加剂配比等因素对聚合氯化铝废渣中二氧化硅活化效果的影响,确定了利用聚合氯化铝废渣生产硅肥的工艺技术条件。结果表明,3个因素对聚合氯化铝废渣焙烧产品的有效硅含量和废渣中硅活化率影响显著性大小为:活化剂用量 > 焙烧温度 > 焙烧时间。其中活化剂用量和焙烧温度对聚合氯化铝废渣焙烧产品中的有效硅含量有明显影响,而焙烧时间对聚合氯化铝废渣焙烧产品中的有效硅含量没有明显影响。随着活化剂用量的增加,所得产品中有效硅含量增加,活化剂用量达到41%以后,有效硅含量趋于稳定,活化剂用量与有效硅含量的相关系数达到0.9829;随着焙烧温度的升高,所得产品中有效硅含量增加,达到1250℃以后,有效硅含量达到峰值;焙烧时间对废渣中有效硅含量和硅活化率的影响不显著。温度为1240 ~ 1270℃、时间为30 ~ 40 min、活化剂用量为41% ~ 45%时,所得产品中有效硅含量较高,达到30%左右。
Abstract:Using polyaluminum chloride residue as raw material, the effects of roasting temperature, roasting time, additive ratio and other factors on the activation effect of silicon dioxide in polyaluminum chloride residue were studied by single factor experiment and orthogonal design, and the technological conditions for producing silicon fertilizer from polyaluminum chloride residue were determined. The results show that the significant influence of three factors effective silicon content and the activation rate of silicon in polyaluminum chloride waste residue is as follows: activator dosage > calcination temperature > calcination time. The amount of activator and calcination temperature have obvious influence on the content of effective silicon in the calcined product, while the calcination time has no obvious influence on the content of effective silicon in the calcined product. With the increase of the amount of activator, the effective silicon content in the product increases. When the amount of activator reaches 41%, the effective silicon content tends to be stable, and the correlation coefficient between the amount of activator and the effective silicon content reaches 0.9829; with the increase of calcination temperature, the effective silicon content in the product increases, and reaches the peak after 1250℃, when the temperature is 1240~1270℃, the time is 30~40 min and the dosage of activator is 41%~45%, the content of effective silicon in the product is the highest, reaching about 30%.
-

-
表 1 废渣主要成分和重金属含量以及相关标准
Table 1. Main components and heavy metal content of waste residue and relevant standards
含量 聚合氯化铝废渣 粉煤灰 硅肥
(NY/T 797-2004)(≥)硅钙钾镁肥
(GB/T 36207-2018)肥料中砷、镉、铅、铬、汞
生态指标GB/T 23349-2009(≤)SiO2/% 43.5~61.1 47.8~53.6 20.0(以SiO2计) ≥9.0(以硅计) CaO/% 1.45~1.54 2.43~7.13 ≥20.0(以钙计) MgO/% 0.79~0.90 0.72~0.97 ≥2.0(以镁计) Al2O3/% 11.5~15.9 28.1~30.5 Fe2O3/% 3.05~3.15 3.37~5.32 K2O/% 1.04~1.55 ≥3.0(以K2O计) Na2O/% 0.60~0.72 Pb/(mg·kg−1) 5.19~6.02 ≤ 200 ≤ 200 200 Cd/(mg·kg−1) 未检出 ≤ 10 ≤ 10 10 Cr/(mg·kg−1) 20.1~30.5 ≤ 500 ≤ 500 500 Hg/(mg·kg−1) 未检出 ≤ 5 ≤ 5 5 As/(mg·kg−1) 未检出 ≤ 50 ≤ 50 50 Cu/(mg·kg−1) 1.38~2.70 Ni/(mg·kg−1) 6.43~8.69 表 2 正交实验因素水平L27 (313)
Table 2. Orthogonal experimental factor level L27(313)
水平 因素A
焙烧温度/℃因素B
焙烧时间/min因素C
活化剂用量/%1 1180 20 50.0 2 1240 35 41.2 3 1300 50 33.3 表 3 正交实验结果
Table 3. Orthogonal experimental results
实验号 A/℃ B/min C/% 有效硅/% 硅活化率/% 1 1 1 1 16.6 54.4 2 1 1 2 17.7 49.8 3 1 1 3 9.3 22.8 4 1 2 1 17.1 56.1 5 1 2 2 19.7 55.2 6 1 2 3 9.4 23.0 7 1 3 1 19.0 62.2 8 1 3 2 20.5 57.5 9 1 3 3 10.6 26.0 10 2 1 1 22.4 73.4 11 2 1 2 24.2 68.0 12 2 1 3 9.7 23.9 13 2 2 1 28.3 92.6 14 2 2 2 30.5 85.4 15 2 2 3 10.9 26.6 16 2 3 1 29.0 95.0 17 2 3 2 31.1 87.2 18 2 3 3 11.2 27.4 19 3 1 1 26.7 87.2 20 3 1 2 30.0 84.0 21 3 1 3 11.6 28.4 22 3 2 1 28.8 94.3 23 3 2 2 30.9 86.8 24 3 2 3 12.4 30.3 25 3 3 1 27.7 90.6 26 3 3 2 31.0 86.9 27 3 3 3 11.6 28.4 ka1 15.6 18.7 24.0 ka2 21.9 20.9 26.2 ka3 23.4 21.3 10.7 Ra1) 7.5 2.6 15..5 kb1 45.2 54.7 78.4 kb2 64.4 61.1 73.4 kb3 68.5 62.4 26.3 Rb2) 23.3 7.7 52.1 1)ka1,ka2,ka3,Ra以有效硅含量为考查指标。2)kb1,kb2,kb3,Rb以硅活化率为考查指标。 表 4 正交实验模型统计分析结果
Table 4. ANOVA for orthogonal experimental
因素 设计条件 有效硅 /% F P 硅活化率/% F P
焙烧温度/ ℃平均值 标准差 平均值 标准差 1180 15.6 b 4.5 2.659 0.091 45.2 16.3 2.033 0.153 1240 21.9 a 9.0 64.4 30.0 1300 23.4 a 8.8 68.5 29.8 焙烧时间/min 20 18.7 a 7.6 0.251 0.780 54.7 25.3 0.196 0.824 35 20.9 a 8.9 61.1 29.6 50 21.3 a 8.7 62.4 29.2 活化剂用量/% 50.0 24.0 a 5.2 31.3 0.000 78.4 17.0 41.0 0.000 41.2 26.2 a 5.6 73.4 15.7 33.3 10.7 b 1.1 26.3 2.6 -
[1] 李柏林, 梁亚楠, 张程琛, 等. 粉煤灰-铝土矿改性制备铝铁复合混凝剂的除磷性能及混凝机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36( 7): 2503-2511.
LI B L, LIANG Y N, ZHANG C C, et al. Preparation of monohydrallite-coal ash composite flocculant: phosphorus removal performance and flocculation mechanism[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(7): 2503-2511.
[2] 杨茹霞, 孙慧芳, 张国栋, 等. 聚合氯化铝靶向混凝去除焦化废水难降解有机物的研究[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2017, 48(6):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2017.06.004
YANG R X, SUN H F, ZHANG G D, et al. Removal of hard-degradable organic matters from coking wastewater by polyaluminum chloride targeted coagulation[J]. Industrial Water & Wastewater, 2017, 48(6):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2017.06.004
[3] 李沛伦, 胡真, 王成行, 等. 酸改性粉煤灰的制备及其降解选矿废水COD研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(2):103-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.02.021
LI P L, HU Z, WANG C X, et al. Experimental study on preparation of acid modified fly ash and its degradation of COD in mineral processing wastewater[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(2):103-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.02.021
[4] 刘三军, 刘永, 李向阳, 等. 用铝土矿选矿尾矿制备聚合氯化铝及污水处理实验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2020, 39(6):539-542.
LIU S J, LIU Y, LI X Y, et al. Preparation of polyaluminum chloride using bauxite tailings and its application in wastewater treatment[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2020, 39(6):539-542.
[5] 李凡修, 陈武. 聚合氯化铝制备技术的研究现状和进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2003, 23(3):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2003.03.002
LI F X, CHEN W. Recent development in preparation of polyaluminium chloride[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2003, 23(3):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2003.03.002
[6] 闫玉兵. 改性粉煤灰对含磷废水的处理研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):34-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.004
YAN Y B. Research on modified fly ash treats for phosphorus wastewater[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):34-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.004
[7] 郭庆, 陈书文, 张军红, 等. 微波强化赤泥制备Fe-Al基絮凝剂工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(4):117-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.025
GUO Q, CHEN S W, ZHANG J H, et al. Study on preparation of Fe/Al-base flocculant from red mud by microwave[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):117-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.025
[8] 李晴淘, 张淳之, 周吉峙, 等. 改性聚铝废渣对污泥脱水性能的影响[J]. 工业水处理, 2019, 39(12):79-81. doi: 10.11894/iwt.2018-0999
LI Q T, ZHANG C Z, ZHOU J Z, et al. Improvement of sludge dewatering capability with modified polyaluminium chloride residue[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2019, 39(12):79-81. doi: 10.11894/iwt.2018-0999
[9] 高红莉, 李洪涛, 张硌, 等. 不同前处理方法对粉煤灰有效成分提取率的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(S1):205-209.
GAO H L, LI H T, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of different pretreatment methods on extraction rate of effective components of fly ash[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(S1):205-209.
[10] 高红莉, 李洪涛, 郭雷, 等. 粉煤灰聚硅酸铝铁絮凝剂对含磷废水处理效果的研究[J]. 河南科学, 2017, 35(6):985-989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2017.06.025
GAO H L, LI H T, GUO L, et al. Treatment effect of fly ash based polysilicate-aluminum-ferric flocculant on phosphorus wastewater[J]. Henan Science, 2017, 35(6):985-989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2017.06.025
-



 下载:
下载: