Present Situation and Research Progress of Comprehensive Utilization of Low Grade Zinc Oxide Ore
-
摘要:
最新的十四五计划提出,我国鼓励对伴生矿、低品位矿和尾矿等矿山资源的综合利用,加强资源综合利用是改变粗放型经济增长,实现循环经济与绿色发展的重要手段。随着锌、铅等有价金属需求量的增加以及有限高品位锌矿资源的日益枯竭,综合回收利用中低品位氧化锌矿中的有价组分迫在眉睫。首先,本文从焙烧法和浸出法两个方面对低品位氧化锌矿资源综合利用的现有工艺技术原理、工艺流程及成效进行了综述性分析,提出了各项工艺在应用中存在的问题。其次,对微生物湿法冶金技术综合利用低品位氧化锌矿及含锌废料的研究现状进行简要分析。最后,对低品位氧化锌矿综合利用的前景进行了展望:微生物湿法冶金技术尤其是微生物-化学联合工艺技术,因其具有既能实现有价组分的高效回收,又能实现经济效益、绿色环保双赢的特点,将是未来研究的重点方向。
Abstract:According to the latest 14th Five-Year Plan, China encourages the comprehensive utilization of mining resources such as associated ore, low-grade ore and tailings. Strengthening the comprehensive utilization of resources is an important means to change the extensive economic growth and realize the circular economy and green development. With the increasing demand for valuable metals such as zinc and lead and the depletion of limited high-grade zinc ore resources, it is urgent to comprehensively recover and utilize the valuable components of middle and low grade zinc oxide ore. In this paper, the existing technology principle, process flow and effect of the comprehensive utilization of low grade zinc oxide ore resources are summarized and analyzed from two aspects of roasting method and leaching method, and the problems existing in the application of each process are put forward. Secondly, the research status of comprehensive utilization of low grade zinc oxide ore and zinc containing waste by microbial hydrometallurgical technology is briefly analyzed. Finally, the prospect of the comprehensive utilization of low grade zinc oxide ore is prospected: the microbial hydrometallurgy technology, especially the microbial and chemical combined process technology, will be the focus of future research because of its characteristics of not only realizing the efficient recovery of valuable components, but also realizing the win-win of economic benefits and environmental protection.
-
Key words:
- Low-grade zinc oxide ores /
- Roasting method /
- Bio-metallurgy /
- Comprehensive utilization
-

-
表 2 微生物-化学联合浸出实验与其中单独实验的对比
Table 2. Comparison of microbial - chemical leaching experiments with individual experiments
实验类型 实验条件 铜浸出率 酸浸试验 矿样粒度-0.080 mm,矿浆浓度20%,搅拌浸出60~90 min 17.13% 单独的化学浸出实验 一定浓度的Fe3+,浸出48 h 53.82% 单独的微生物浸出实验 Fe2+浓度9 g/L,矿浆浓度10%,温度30℃,接种量10%、粒度-0.080 mm 40% 微生物-化学联合浸出实验 在单独生物浸出(较优浸出条件下)的初期添加浓度为80 g/L的Fe3+,浸出时间为8 d 84.36% -
[1] 洪磊. 云南某氧化铅锌矿可选性试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(4):68-72. HONG L. Study on the separability of lead and zinc oxide ores from Yunnan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):68-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.014
[2] 许晓阳, 李黎婷, 谢洪珍, 等. 低品位氧化锌矿新工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(5):52-54+62. XU X Y, LI L T, XIE H Z, et al. Study on new technology of low grade zinc oxide ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(5):52-54+62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.05.011
[3] 申亚芳, 张馨圆, 王乐, 等. 氧化锌矿处理方法现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2):23-28. SHEN Y F, ZHANG X Y, WANG L, et al. Preparation of zinc and its compounds from zinc oxide ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.004
[4] 许大洪, 刘小妹, 崔伟勇, 等. 缅甸某难选锌氧化矿浮选工艺[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):17-22. XU D H, LIU X M, CUI W Y, et al. Flotation technology of a refractory zinc oxide ore in Burma[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.004
[5] 李文超, 王海军, 王雪峰, 等. 法规政策标准精准支撑, 开发利用水平稳步提升[N]. 中国自然资源报, 2020-12-17(003).
LI W C, WANG H J, WANG X F, et al. Steady progress has been made in the precise support of regulations, policies and standards for development and utilization[N]. China Natural Resources Journal, 2020-12-17(3).
[6] 安久长. 浅析低碳经济模式下开展有色金属矿产资源综合利用的价值[J]. 信息记录材料, 2021, 22(1):243-244. AN J C. Analysis on the value of comprehensive utilization of nonferrous metal mineral resources under the low carbon economic model[J]. Information Recording Material, 2021, 22(1):243-244. doi: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2021.01.168
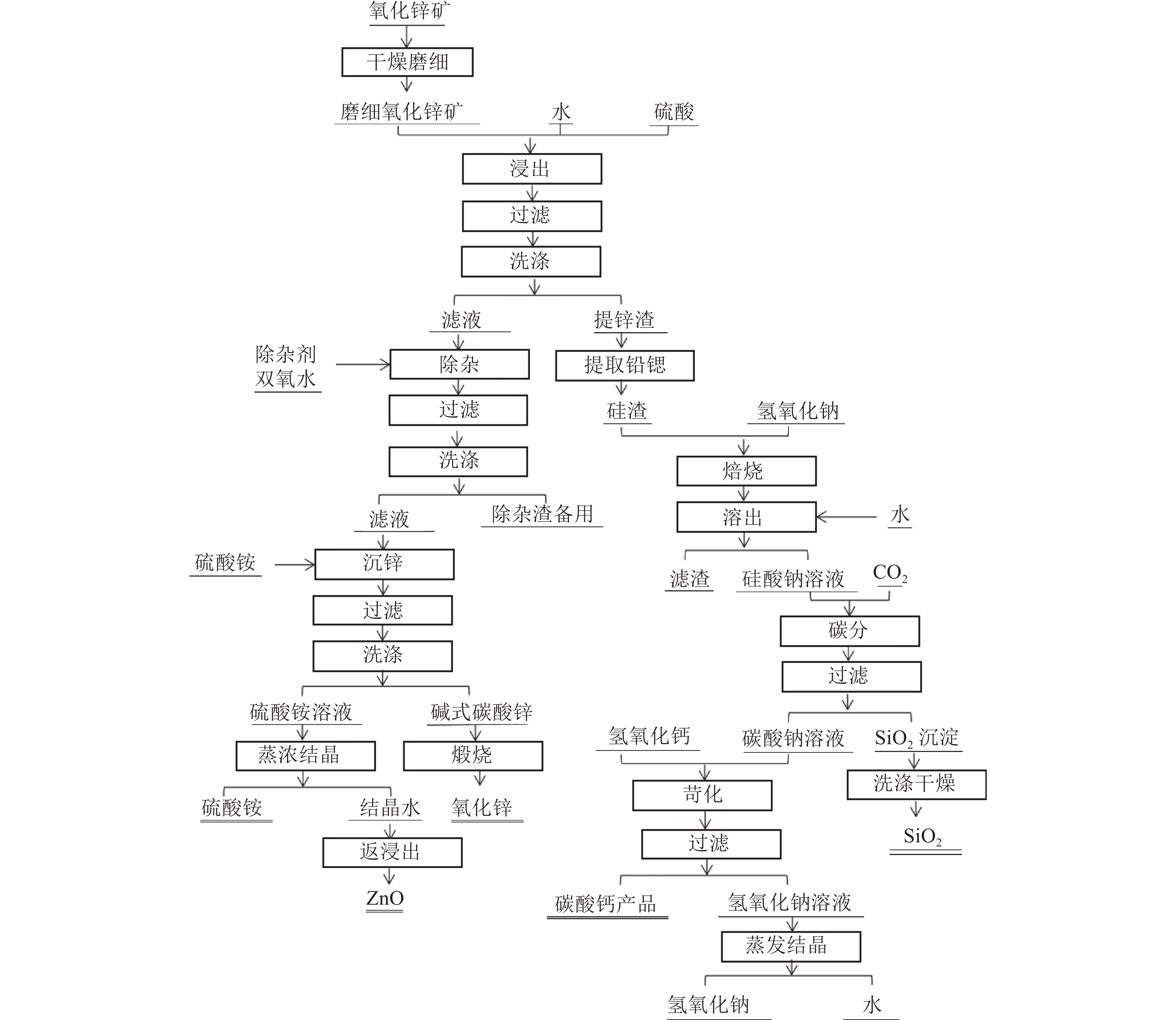
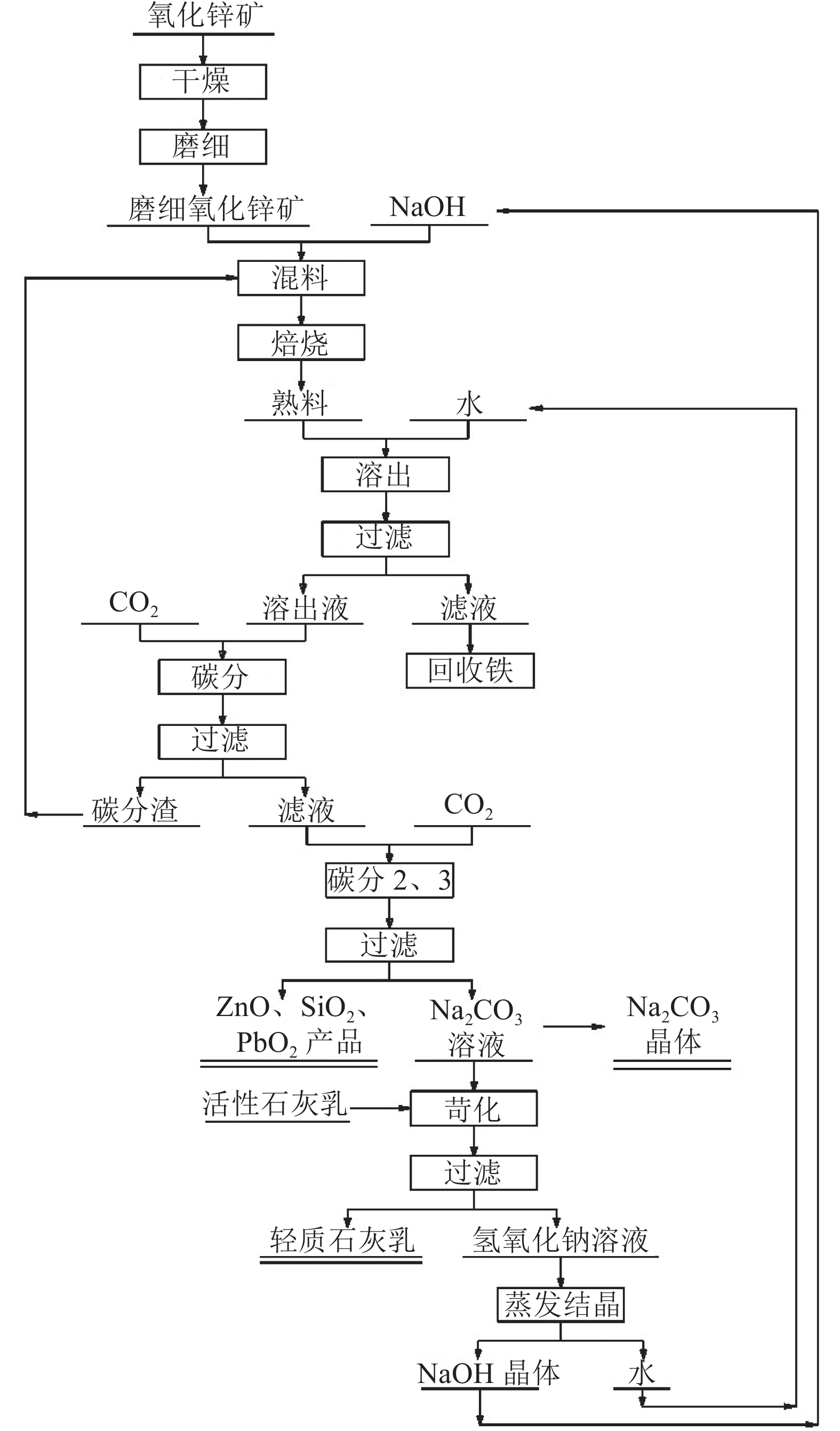
[7] 陈兵, 申晓毅, 顾惠敏, 等. 碱焙烧法综合利用低品位氧化锌矿[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2016(5):30-33. CHEN B, SHEN X Y, GU H M, et al. Comprehensive utilization of low grade zinc oxide ore by alkaline roasting[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016(5):30-33.
[8] 邵鸿媚, 申晓毅, 孙毅, 等. 硫酸铵焙烧法综合利用低品位氧化锌矿[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2016(2):70-73. SHAO H M, SHEN X Y, SUN Y, et al. Comprehensive utilization of low grade zinc oxide ore by ammonium sulfate roasting[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016(2):70-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.02.016
[9] 申晓毅, 邵鸿媚, 顾惠敏, 等. NaOH焙烧Zn2SiO4反应机理(英文)[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(9):1878-1886. SHEN X Y, SHAO H M, GU H M, et al. Reaction mechanism of NaOH roasting Zn2SiO4[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(9):1878-1886. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64833-2
[10] 王乐. 低品位氧化锌矿提取铅锌的研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2017.
WANG L. Study on extraction of lead and zinc from low grade zinc oxide ore[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2017.
[11] 杨斌. 对湿法炼锌中热酸浸出-黄钾铁矾工艺的探讨[J]. 甘肃冶金, 2010, 32(3):56-58. YANG B. Discussion on hot acid leaching-jarosite process in hydrometallurgical zinc smelting[J]. Gansu Metallurgy, 2010, 32(3):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2010.03.016
[12] 王磊, 徐智达, 申晓毅. 中低品位氧化锌矿综合利用试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(2):37-41. WANG L, XU Z D, SHEN X Y. Experimental study on comprehensive utilization of middle and low grade zinc oxide ore[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(2):37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.02.007
[13] 王振银, 高文成, 温建康, 等. 锌浸出渣有价金属回收及全质化利用研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(11):1400-1410. WANG Z Y, GAO W C, WEN J K, et al. Research progress in recovery and utilization of valuable metals from zinc leaching residue[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(11):1400-1410.
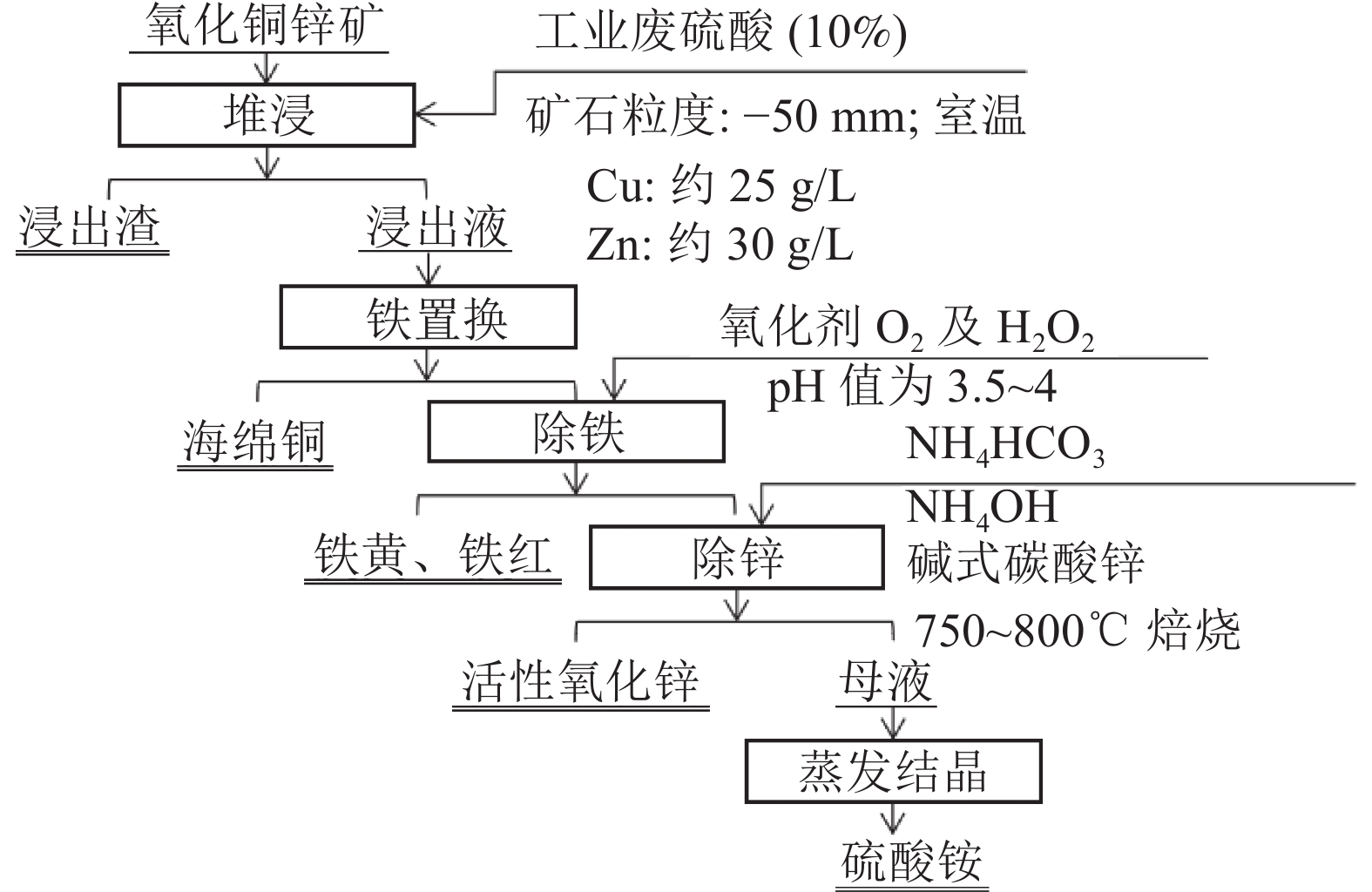
[14] 水浩东. 废酸堆浸氧化铜锌矿工艺[J]. 有色矿冶, 2003(1):29-30+36. SHUI H D. Process of waste acid heap leaching copper-zinc oxide ore[J]. Nonferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2003(1):29-30+36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2003.01.008
[15] Yang Z H, Zhang Z, Chai L Y, et al. Bioleaching remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils using Burkholderia sp. Z-90[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 3(1):145-152.
[16] Diaz M A, De Ranson I U, Dorta B, et al. Metal removal from contaminated soils through bioleaching with oxidizing bacteria and rhamnolipid biosurfactants. Soil Sediment Contamin Int[J]. Soil and Sediment Contamination:An International Journal, 2015, 24(1):16-29. doi: 10.1080/15320383.2014.907239
[17] 牛志睿. 高固液比下废旧锌锰电池生物淋沥的特性、机理和资源化利用[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016.
NIU Z R. Characteristics, mechanism and resource utilization of bioleaching of Waste Zn Mn batteries at high solid-liquid ratio[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2016.
[18] 叶茂友. 铅锌硫化尾矿中金属的生物浸出行为及浸出机理的研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2017.
YE M Y. Bioleaching behavior and leaching mechanism of metals from lead zinc sulfide tailings[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2017.
[19] Sethurajan M, Lens P, Rene E R, et al. Bioleaching and selective biorecovery of zinc from zinc metallurgical leach residues from the Três Marias zinc plant (Minas Gerais, Brazil)[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2017.
[20] Sajjad, Wasim, Zheng, et al. Bioleaching of copper- and zinc-bearing ore using consortia of indigenous iron-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Extremophiles Life Under Extreme Conditions, 2018.
[21] Zhang M, Guo X, Tian B, et al. Improved bioleaching of copper and zinc from brake pad waste by low-temperature thermal pretreatment and its mechanisms[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 87:629-635. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.02.047
[22] Haschke M, Ahmadian J, Zeidler L, et al. In-situ recovery of critical technology elements[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 138:248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.02.082
[23] Pakostova E, Grail B M, Johnson D B. Indirect oxidative bioleaching of a polymetallic black schist sulfide ore[J]. Miner Eng, 2017, 106:102. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.08.028
[24] 陈志红. 低品位氧化锌矿资源化利用的工业生产研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017.
CHEN Z H. Study on industrial production of resource utilization of low grade zinc oxide ore[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2017.
[25] Dong S H, Yun C, Ping X, et al. Study on the pre-treatment of oxidized zinc ore prior to flotation[J]. Int J Miner Metall Mater 2018, 25(2): 117-122.
[26] Frenay J. Leaching of oxidized zinc ores in various media[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1985, 15(2):243-253. doi: 10.1016/0304-386X(85)90057-X
[27] 王振银, 高文成, 温建康, 等. 锌浸出渣有价金属回收及全质化利用研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, v.42(319):14-24. WANG Z Y, GAO W C, WEN J K, et al. Research progress in recovery and utilization of valuable metals from zinc leaching residue[J]. Journal of Engineering Sciences, 2020, v.42(319):14-24.
[28] 张婧. 化学—生物联合浸出次生硫化铜精矿的研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2015.
ZHANG J. Study on the combined chemical-biological leaching of secondary copper sulfide concentrate[D]. Kunming: Yunnan university, 2015.
[29] 黄玉霞. 生物—化学法回收电解锰废渣中锰的工艺及机理探讨[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2011.
HUANG Y X. Study on the process and mechanism of recovery of manganese from electrolytic manganese waste residue by bio-chemical metho[D]. Changsha: Hunan university, 2011.
-



 下载:
下载: