Effect of Crushing Particle Size for Leaching of Lithium and Cobalt with Citric Acid from Spend Lithium Ion Battery
-
摘要:
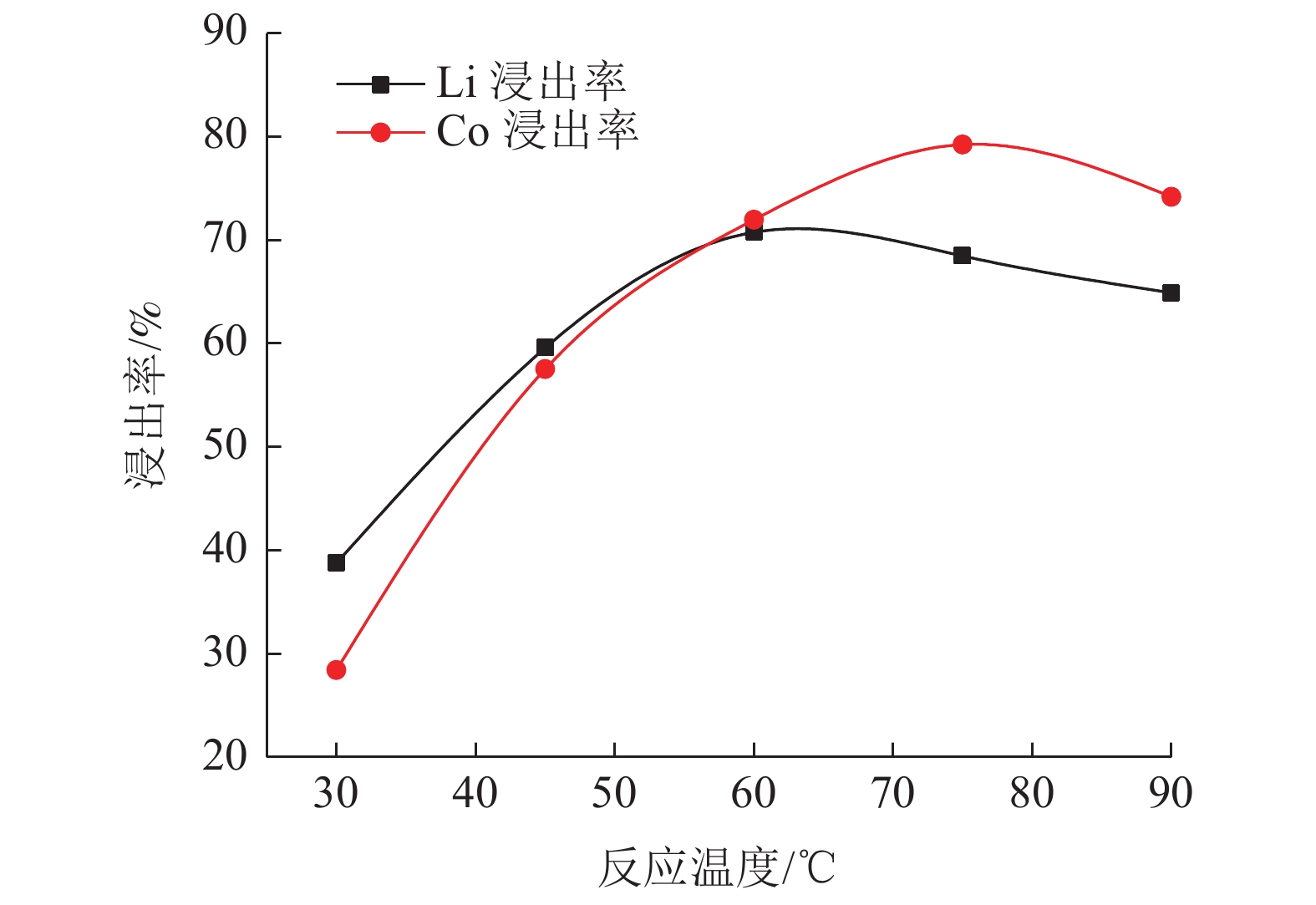
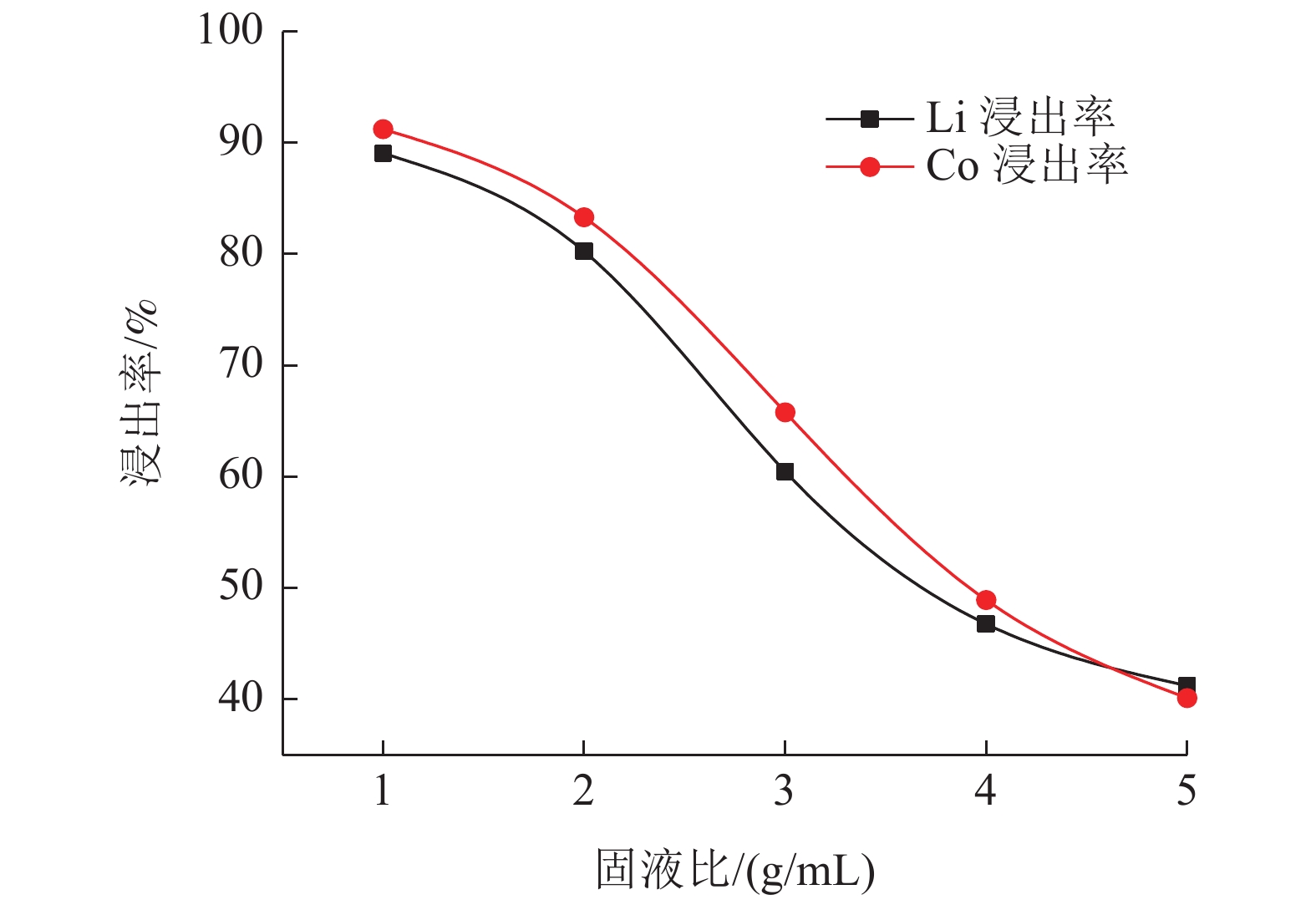
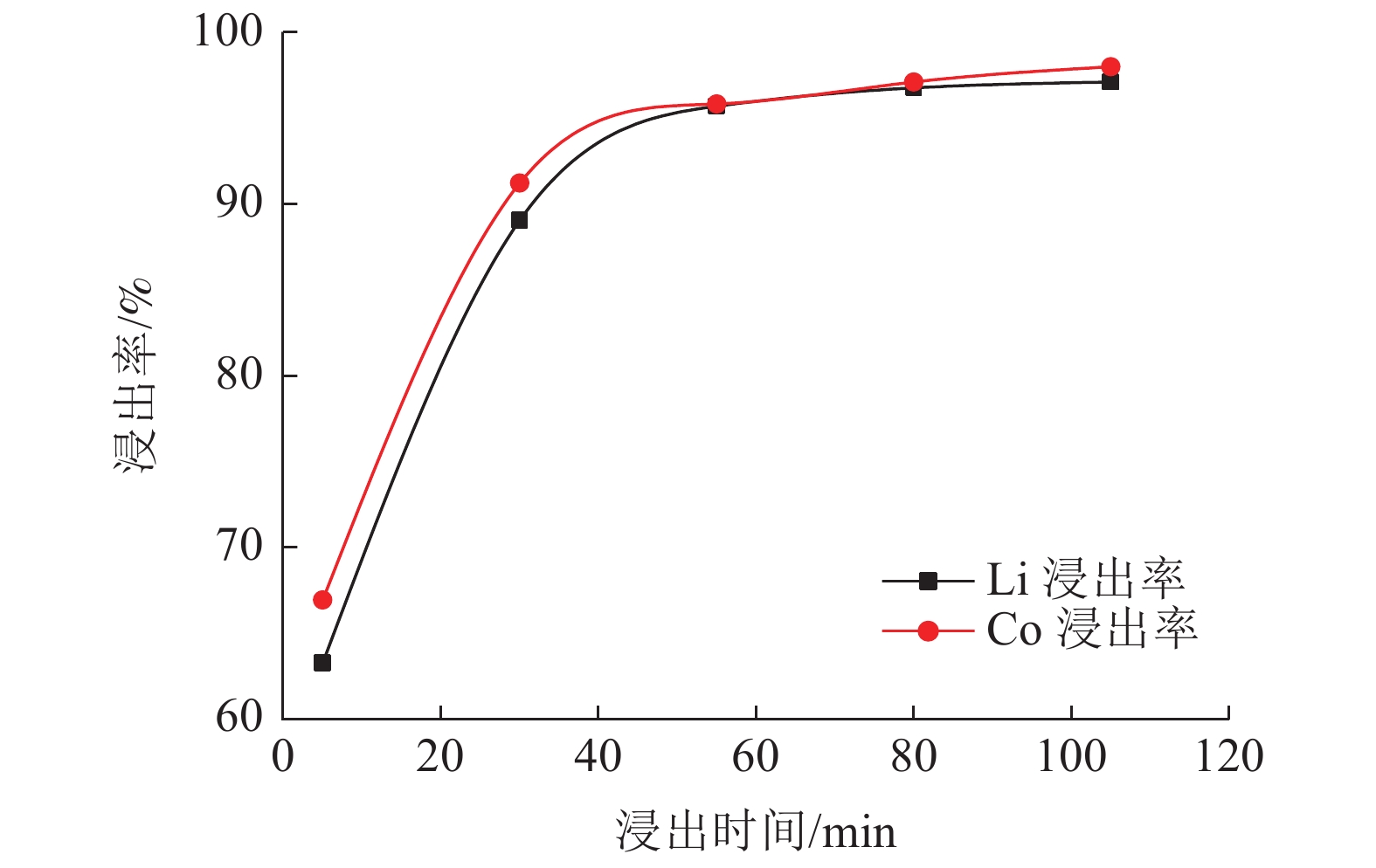
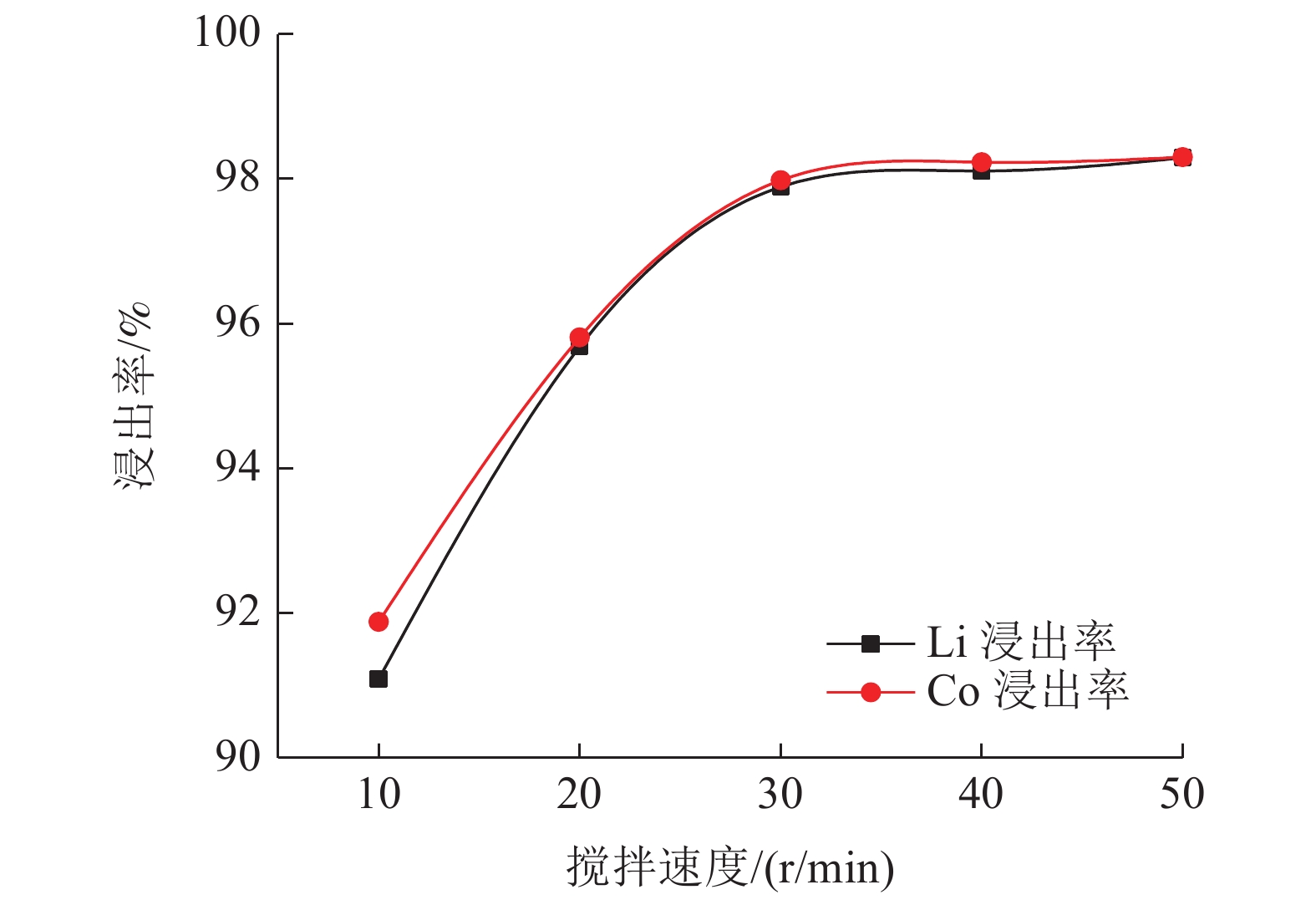
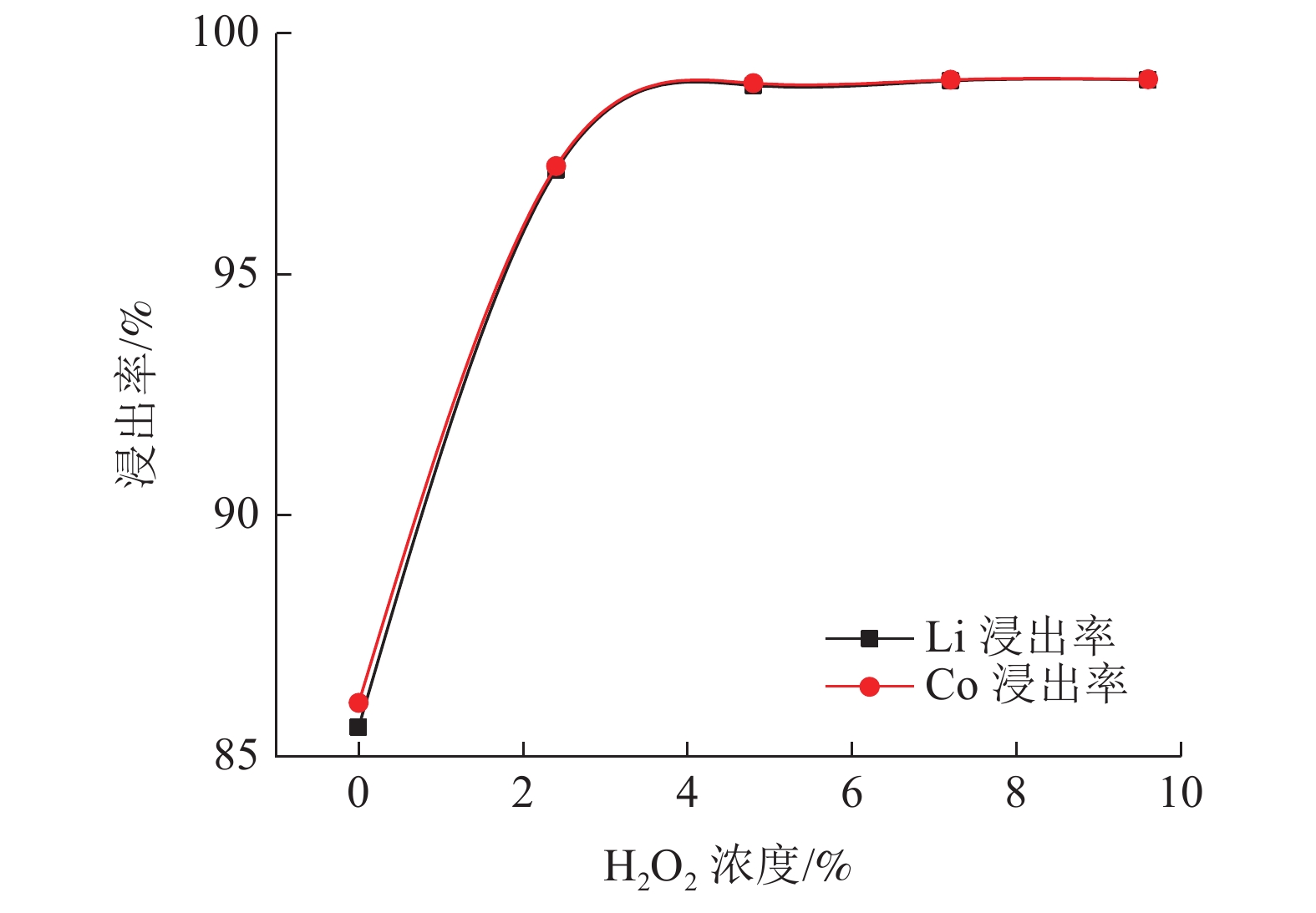
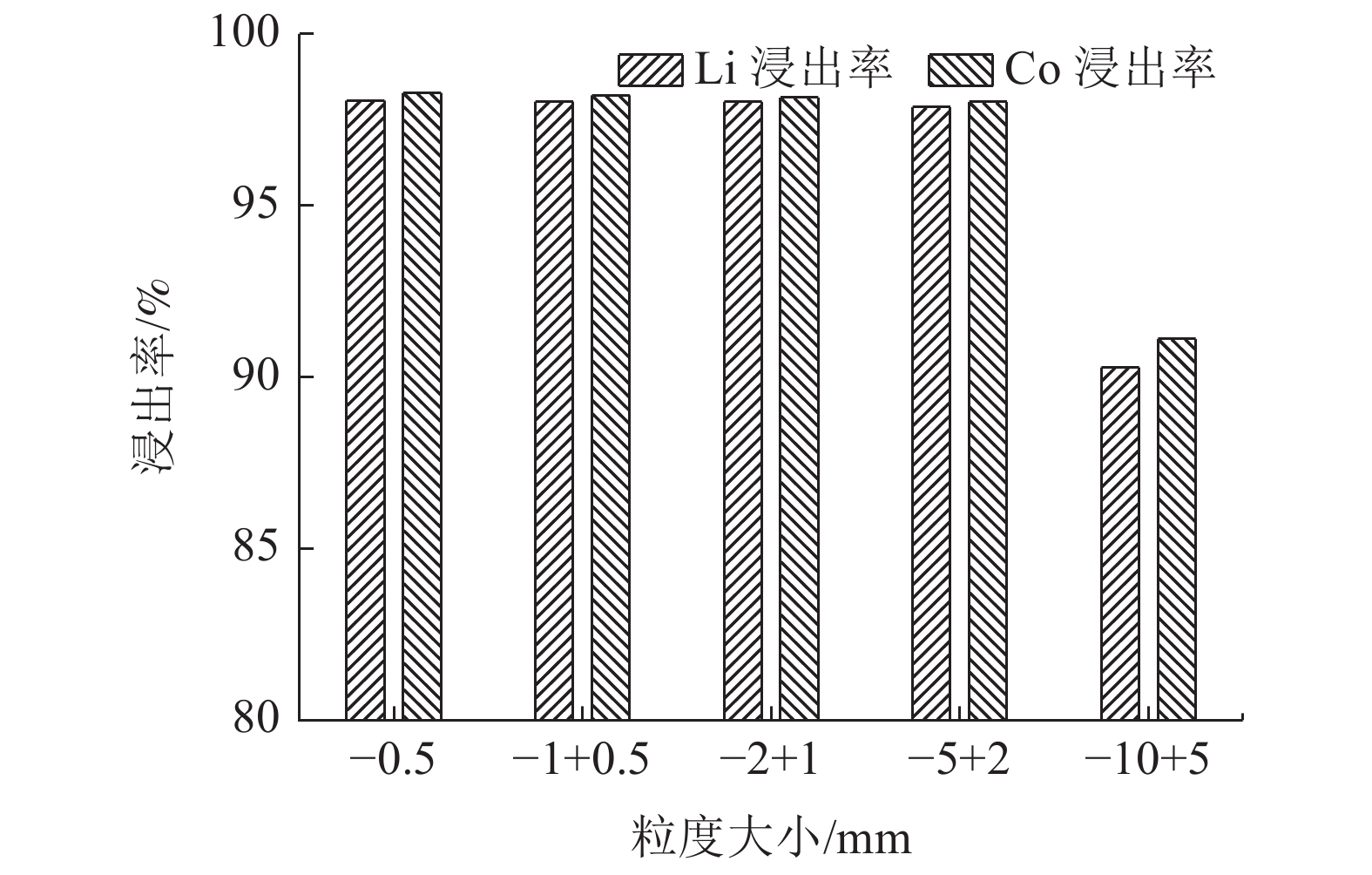
这是一篇冶金工程领域的论文。研究了柠檬酸环境下破碎粒度和浸出条件对失效锂离子电池锂钴的浸出,为不同类型混合失效锂离子电池回收提供一定参考。结果表明:混合了不同类型的失效锂离子电池中金属含量占比较大的有Mn,Al,Ni,Co,Li,为简化回收工艺及Co、Li的回收价值较大,可只回收Co、Li。破碎粒度在-5 mm范围内对锂钴浸出率的影响较小,而较大破碎粒度浸出率不高可能是因为锂钴包裹在了颗粒中间而不能与浸出液接触而降低了浸出效果。针对混合了不同类型的失效锂离子电池而言,在-5 mm粒级下,柠檬酸浓度1.0 mol/L,浸出温度65 ℃,固液比1 g/100 mL,H2O2 浓度3%,浸出时间55 min,搅拌速度30 r/min条件下进行浸出实验,获得锂浸出率97.86%,钴浸出率98.01%的较好浸出效果。
Abstract:This is an essay in the field of metallurgical engineering. The effects of crushing particle size and leaching conditions on the leaching of lithium cobalt from spend lithium-ion batteries in the citric acid environment were studied, which provided some reference for the recovery of different types of mixed spend lithium-ion batteries. The results showed that Mn, Al, Ni, Co and Li accounted for a large proportion of the contents in mixed different types of spend lithium-ion batteries. Due to the larger recovery value of Co and Li and simplify the recovery process, only Co and Li be recovered. The crushing particle size has little influence on the leaching rate of lithium cobalt in the range of -5 mm, while the leaching rate of lithium cobalt in the larger crushing particle size is not high, which may be lithium and cobalt wrapped in the middle of particles and cannot contact with the leaching solution, thus reducing the leaching effect. For mixed different types of spend lithium-ion batteries, under the conditions of -5 mm particle size, citric acid concentration 1.0 mol/L, leaching temperature 65 ℃, solid-liquid ratio 1 g/100 mL, H2O2 concentration 3%, leaching time 55 min, stirring speed 30 r/min, the lithium leaching rate of 97.86% and cobalt leaching rate of 98.01% are obtained.
-
Key words:
- Metallurgical engineering /
- Spend lithium ion battery /
- Crushing size /
- Citric acid /
- Recycling /
- Leaching
-

-
表 1 混合样品元素含量/%
Table 1. Element content of mixed samples
Al Co Cr Cu Fe Li Mn Ni 11.92 6.55 0.02 0.06 0.23 3.70 18.71 7.90 表 2 各粒级样品中锂钴含量
Table 2. Content of lithium and cobalt in each particle size sample
粒级/mm Co/% Li/% -0.25 6.65 3.87 -0.5+0.25 5.94 3.42 -1+0.5 5.78 3.42 -2+1 6.95 3.39 -4+2 6.25 3.23 混合粒级 6.55 3.70 -
[1] 张晓虎, 孙现众, 张熊, 等. 锂离子电容器在新能源领域应用展望[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2020, 39(11):48-58. ZHANG X H, SUN X Z, ZHANG X, et al. Prospect of lithium-ion capacitor application in new energy field[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2020, 39(11):48-58.
ZHANG X H, SUN X Z, ZHANG X, et al. Prospect of lithium-ion capacitor application in new energy field[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2020, 39(11): 48-58.
[2] 王萌萌, 张付申. 废旧锂电池的机械化学处理方法与机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(2):1069-1074. WANG M M, ZHANG F S. Mechanochemical recycling of spent lithium-ion battery and reaction mechanisms clarification[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(2):1069-1074.
WANG M M, ZHANG F S. Mechanochemical recycling of spent lithium-ion battery and reaction mechanisms clarification[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(2): 1069-1074.
[3] 李金龙, 何亚群, 付元鹏, 等. 废弃锂离子电池正极材料酸浸出实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2):128-134. LI J L, HE Y Q, FU Y P, et al. Study on leaching cathode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):128-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.023
LI J L, HE Y Q, FU Y P, et al. Study on leaching cathode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2): 128-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.023
[4] 吴西顺, 孙艳, 王登红, 等. 国际锂矿开发技术现状、革新及展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6):110-120. WU X S, SUN Y, WANG D H, et al. International lithium mine utilization technology: current status, innovation and prospects[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):110-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.019
WU X S, SUN Y, WANG D H, et al. International lithium mine utilization technology: current status, innovation and prospects[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6): 110-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.019
[5] 吴西顺, 王登红, 黄文斌, 等. 全球锂矿及伴生铍铌钽的采选冶技术发展趋势[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):1-9. WU X S, WANG D H, HUANG W B, et al. Global technical development trends of litihium minerals and associated beryllium-niobium-tantalum exploitation[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):1-9.
WU X S, WANG D H, HUANG W B, et al. Global technical development trends of litihium minerals and associated beryllium-niobium-tantalum exploitation[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1): 1-9.
[6] 朱华炳, 卫道柱, 葛晓倩, 等. 废旧动力电池回收的机械拆解系统[J]. 机械工程师, 2017(12):69-72. ZHU H B, WEI D Z, GE X Q, et al. Mechanical dismantling system for recycling waste power battery[J]. Mechanical Engineer, 2017(12):69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2333.2017.12.024
ZHU H B, WEI D Z, GE X Q, et al. Mechanical dismantling system for recycling waste power battery[J]. Mechanical Engineer, 2017(12): 69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2333.2017.12.024
[7] 邓孝荣, 曾桂生, 李卓, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌浸出废旧锂离子电池的工艺条件[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(9):1381-1386. DENG X R, ZENG G S, LI Z, et al. Optimization conditions of bioleaching spent lithium-ion batteries by thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(9):1381-1386.
DENG X R, ZENG G S, LI Z, et al. Optimization conditions of bioleaching spent lithium-ion batteries by thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(9): 1381-1386.
[8] 刘星, 李成秀, 程仁举, 等. 国外某锂多金属矿选矿实验[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(2):65-69. LIU X, LI C X, CHENG R J, et al. Test of the beneficiation of one lithium polymetallic ore overseas[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(2):65-69.
LIU X, LI C X, CHENG R J, et al. Test of the beneficiation of one lithium polymetallic ore overseas[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(2): 65-69.
[9] 魏锦雯, 杜英, 谢丽娟, 等. 电动汽车废旧电池回收工艺研究[J]. 内燃机与配件, 2020(1):23-24. WEI J W, DU Y, XIE L J, et al. Research on recycling process of electric vehicle waste battery[J]. Internal Combustion Engine & Parts, 2020(1):23-24.
WEI J W, DU Y, XIE L J, et al. Research on recycling process of electric vehicle waste battery[J]. Internal Combustion Engine & Parts, 2020(1): 23-24.
[10] 张飞, 陆颖舟. 一步法回收和再生废旧钴酸锂电池中的钴酸锂[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(8):3874-3880. ZHANG F, LU Y Z. One-step recovery and regeneration of LiCoO2 from the spent lithiumcobalt oxide battery[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(8):3874-3880.
ZHANG F, LU Y Z. One-step recovery and regeneration of LiCoO2 from the spent lithiumcobalt oxide battery[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(8): 3874-3880.
[11] 陈超, 张裕书, 张少翔, 等. 川西九龙地区低品位锂辉石浮选实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(4):55-58. CHEN C, ZHANG Y S, ZHANG S X, et al. Flotation test of low-grade spodumene in the Jiulong area of west Sichuan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.011
CHEN C, ZHANG Y S, ZHANG S X, et al. Flotation test of low-grade spodumene in the Jiulong area of west Sichuan[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.04.011
[12] 席国喜, 高修艳, 姚路. 柠檬酸溶解废锂离子电池正极材料的研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2013, 25(8):1114-1119. XI G X, GAO X Y, YAO L. Study on the dissolution conditions of waste lithium-ionbattery anode material in the citric acid[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2013, 25(8):1114-1119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2013.08.008
XI G X, GAO X Y, YAO L. Study on the dissolution conditions of waste lithium-ionbattery anode material in the citric acid[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2013, 25(8): 1114-1119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2013.08.008
-




 下载:
下载: