Permeability and Microstructure of Phosphate Slag Modified Cement-Based Filling Material
-
摘要:
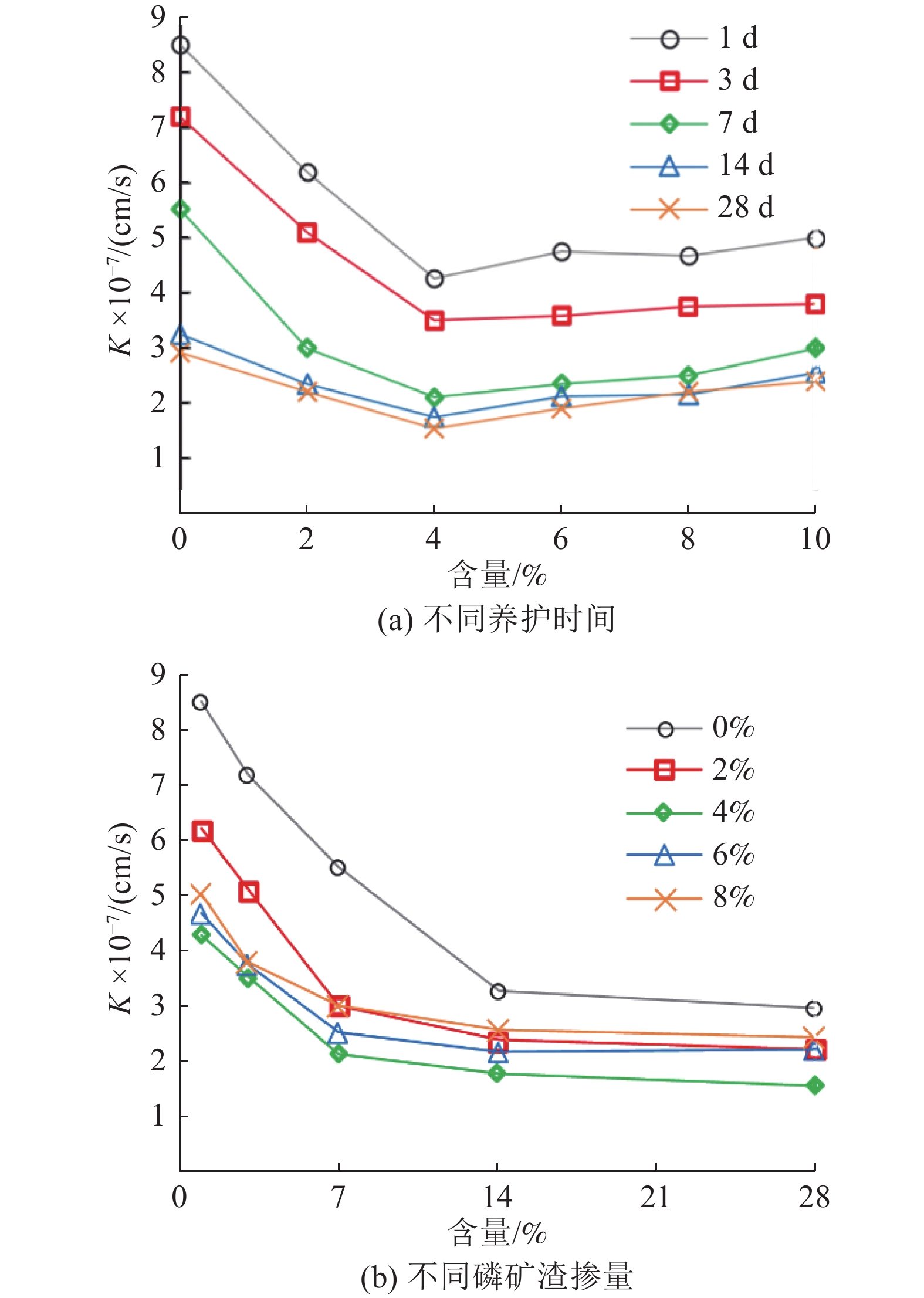
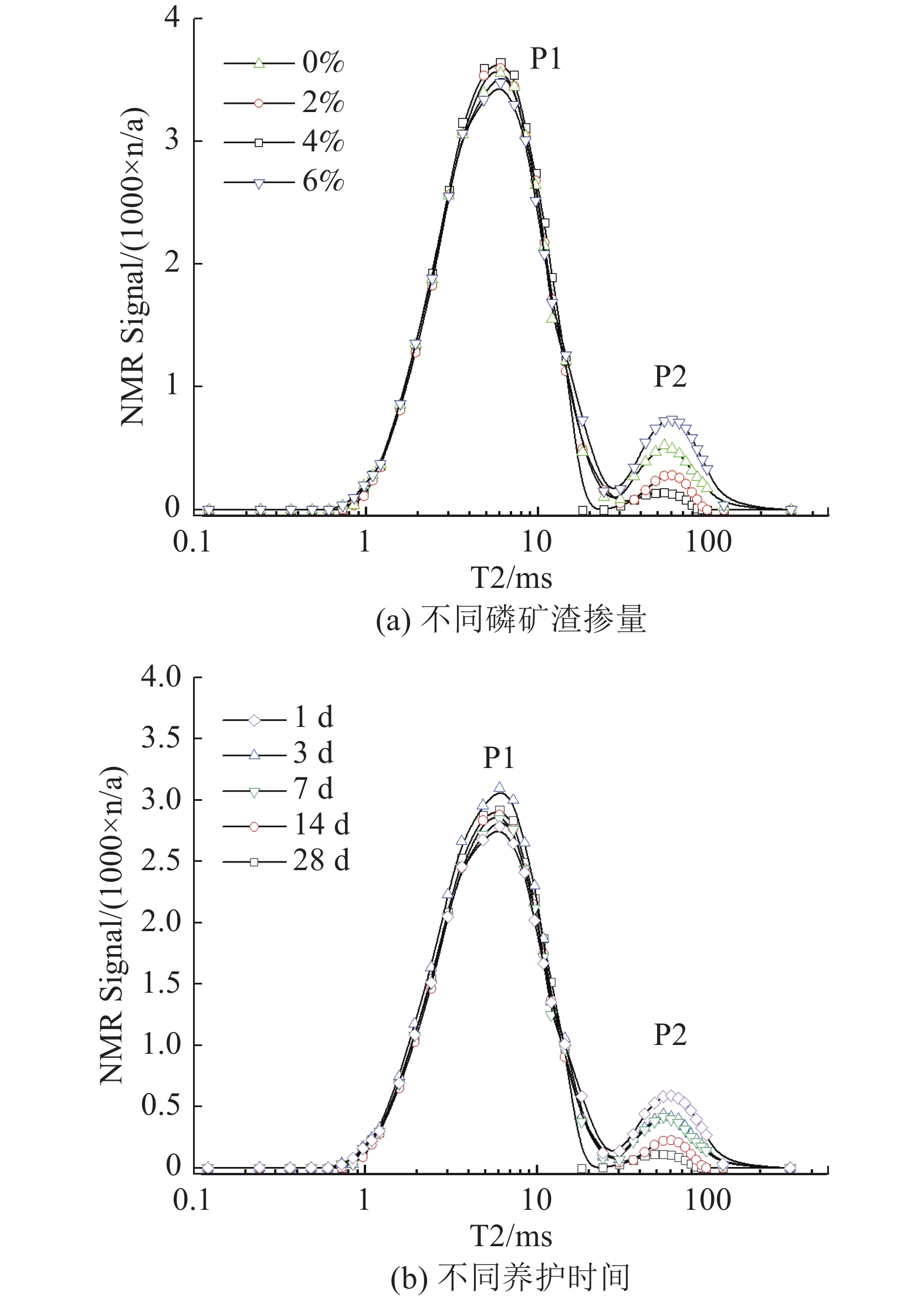
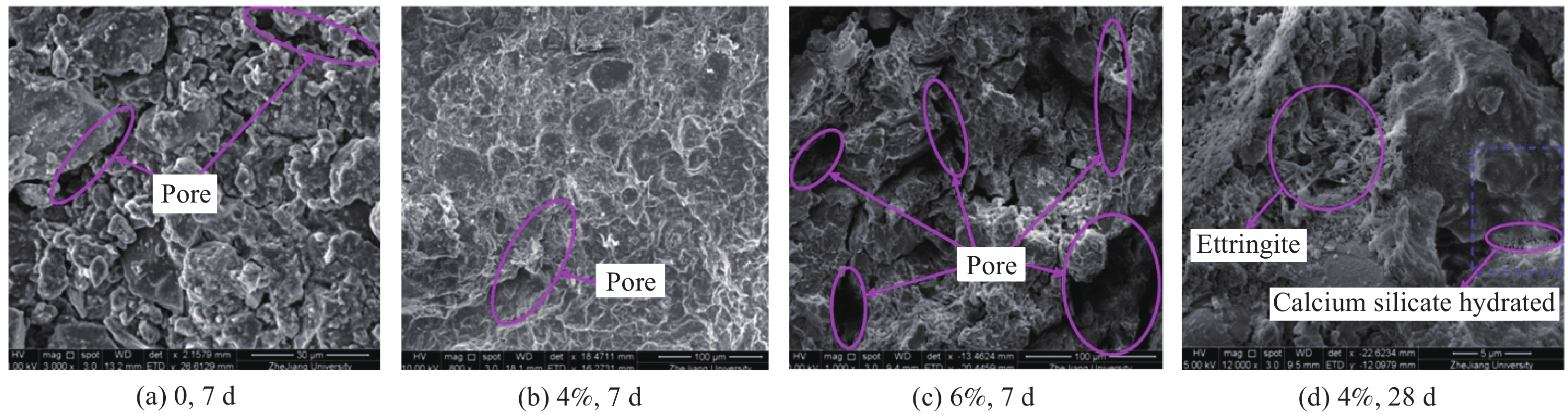
这是一篇陶瓷及复合材料领域的论文。采用碱激发混合法制备了4种不同磷矿渣掺量的水泥基充填料,对养护过程中的改性充填料开展渗透率、核磁共振(NMR)与电子显微镜扫描(SEM)实验。结果表明:随磷矿渣掺量增加,水泥基充填料试件的抗压强度呈现先增后减的变化趋势,渗透率呈现先减后增的非线性变化趋势,且两者均在4%时达到极值;经过养护1~28 d的充填料试件弛豫时间(T2)分布曲线均为双峰分布,代表小孔隙的峰占比超过80%,代表大孔隙的峰占比随养护时间增加而逐渐降低;根据SEM图像可以看出一定掺量的磷矿渣能够促进水化反应的发生,使得材料的孔隙显著减少;磷矿渣为4%时,水泥基充填料的密实度较好,抗渗性能和强度达到较佳,据此可以确定磷矿渣改性水泥基充填料的较佳掺量是4%。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of ceramics and composites. In order to improve the impermeability and microstructure of the impermeable wall materials, four kinds of calcium-based bentonite modified and filling material with different dosages were prepared under the action of alkali excitation reaction. The modified and filling material samples in the curing process were tested by flexible wall penetration (FWPT), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) scanning and electron microscope scanning (SEM). The results show that the permeability coefficient of filling material samples decreases first and then increases with the increase of bentonite content, and reaches a minimum value when the content of bentonite is 4%. The relaxation time (T2) distribution curves of the filled material specimens after curing from 1 to 28 d were all bimodal, with more than 80% of the peaks representing small pores, and the percentage of the peaks representing large pores decreasing with the increase of curing time. According to SEM images, it can be seen that a certain amount of calcium bentonite can promote the occurrence of hydration reaction, and the porosity of the material is significantly reduced. At 4% phosphate slag, the cementitious filler has the best compactness and better impermeability and strength. Accordingly, it can be determined that the better dosage of phosphate slag modified cementitious filler is 4%.
-
Key words:
- Ceramics and composites /
- Filling material /
- Phosphate slag /
- Strength /
- Permeability coefficient /
- Microstructure
-

-
表 1 磷矿渣的基本技术性能指标
Table 1. Basic technical properties of bentonite
比表面积/
( m2/g)含水量/% 密度
(cm3/g)液限/% 塑性
极限/%活性
指数/%525 8.5 1.75 91 48 85 表 2 改性充填料试样的核磁信号分布特征指标
Table 2. NMR signal distribution characteristic index of modified filling material
含量/% 峰值型号 1 d 3 d 7 d 14 d 28 d T2 区域 比例/% T2 区域 比例/% T2 区域 比例 /% T2 区域 比例 /% T2区域 比例 /% 0 P1 25856 87.49 23758 87.78 22040 87.97 21302 88.06 21050 88.12 P2 3693 12.51 3305 12.22 3042 12.03 3014 11.94 2387 11.88 2 P1 23058 88.04 21025 88.09 20894 88.34 20514 88.95 20116 89.05 P2 3140 11.96 2885 11.91 2737 11.66 2622 11.05 2286 10.95 4 P1 26532 89.59 20542 90.55 20410 90.65 20005 90.82 19885 90.95 P2 3069 10.41 2142 9.45 2078 9.35 2024 9.18 1968 9.05 6 P1 28254 89.81 30422 90.06 P2 3259 10.19 3344 9.94 -
[1] 卓庆奉, 巴蕾, 王奇峰. 掺粉煤灰的混合充填骨料配比优化实验[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(3):187-192.ZHUO Q F, BA L, WANG Q F. Optimum experiment of aggregate proportion for mixed filling with fly ash[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3):187-192.
ZHUO Q F, BA L, WANG Q F. Optimum experiment of aggregate proportion for mixed filling with fly ash[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3):187-192.
[2] 杨志强, 王永前, 高谦, 等. 金川镍矿废弃物在充填采矿中利用现状与展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(3):22-28.YANG Z Q, WANG Y Q, GAO Q, et al. Current status and prospect of Jinchuan nickel mine waste utilization in fill mining[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(3):22-28.
YANG Z Q, WANG Y Q, GAO Q, et al. Current status and prospect of Jinchuan nickel mine waste utilization in fill mining[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(3):22-28.
[3] 李文臣. 硫酸盐对胶结充填体早期性能的影响及其机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2016.LI W C. Research on the effect of sulfate on the early performance of cemented filler and its mechanism[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016.
LI W C. Research on the effect of sulfate on the early performance of cemented filler and its mechanism[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016.
[4] 单志伟, 李凤久, 刘立伟, 等. 超细粉磨活化河北某磷矿粉实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2):55-59.SHAN Z W, LI F J, LIU L W, et al. Experimental study on activation of a phosphate rock powder in Hebei by ultrafine grinding[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):55-59.
SHAN Z W, LI F J, LIU L W, et al. Experimental study on activation of a phosphate rock powder in Hebei by ultrafine grinding[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):55-59.
[5] 李欣, 郭利杰, 许文远. 某铁矿全尾砂胶结充填实验研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(S1):211-215.LI X, GUO L J, XU W Y. Experimental study on the collodion filling of the whole tailing sand in an iron ore mine[J]. China Mining Industry, 2018, 27(S1):211-215.
LI X, GUO L J, XU W Y. Experimental study on the collodion filling of the whole tailing sand in an iron ore mine[J]. China Mining Industry, 2018, 27(S1):211-215.
[6] 包明, 吴雄, 杨文, 等. 黄磷渣改性对水泥复合胶凝材料性能的影响[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(4):122-125.BAO M, WU X, YANG W, et al. Influence of the modification phosphorus slag on the properties of cement composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):122-125.
BAO M, WU X, YANG W, et al. Influence of the modification phosphorus slag on the properties of cement composite cementitious materials[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(4):122-125.
[7] 兰文涛, 吴爱祥, 王贻明, 等. 半水磷石膏充填体离子固化与尺寸效应[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(1):210-218.LAN W T, WU A X, WANG Y M, et al. Ionic curing and size effect of semi-aqueous phosphogypsum filler[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(1):210-218.
LAN W T, WU A X, WANG Y M, et al. Ionic curing and size effect of semi-aqueous phosphogypsum filler[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(1):210-218.
[8] Marsh A, Heath A, Patureau P, et al. Alkali activation behaviour of un-calcined montmorillonite and illite clay minerals[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2018, 166(1):250-261.
[9] Mei X P, Zheng H W, Qiu G X, et al. Effects of alkali on one-part alkali-activated cement synthesized by calcining bentonite with dolomite and Na2CO3[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 139.
[10] 王亚洁. 新型膨胀性胶凝充填材料研制与工程特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2020.WANG Y J. Research on the development and engineering characteristics of new expansive collodion filling material[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2020.
WANG Y J. Research on the development and engineering characteristics of new expansive collodion filling material[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2020.
[11] 安然, 孔令伟, 黎澄生, 等. 炎热多雨气候下花岗岩残积土的强度衰减与微结构损伤规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(9):1902-1911.AN R, KONG L W, LI C S, et al. Strength attenuation and microstructural damage pattern of granite residual soil under hot and rainy climate[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(9):1902-1911.
AN R, KONG L W, LI C S, et al. Strength attenuation and microstructural damage pattern of granite residual soil under hot and rainy climate[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(9):1902-1911.
[12] 彭饶, 陈伟, 李秋, 等. 硫酸钠激发尾矿充填材料的性能与微观结构[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(3):685-691.PENG R, CHEN W, LI Q, et al. Properties and microstructure of sodium sulfate-inspired tailings filling materials[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(3):685-691.
PENG R, CHEN W, LI Q, et al. Properties and microstructure of sodium sulfate-inspired tailings filling materials[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(3):685-691.
-



 下载:
下载: