Extraction of Carbon from Fine Coal Gasification Slag by Hydrophobic-hydrophilic Separation
-
摘要:
这是一篇矿业工程领域的论文。煤气化细渣是煤气化过程中产生的一种固体废物,其中残炭严重制约了其资源化利用,从煤气化细渣中提取残炭是一个紧迫的问题。本研究应用疏水-亲水双液分离技术来提取煤气化细渣中残碳,其主要的影响因素有搅拌速度、搅拌时间、疏水液体用量、矿浆浓度、矿浆温度和疏水液体种类。疏水-亲水双液分离技术对煤气化细渣有优异的提碳降灰效果,其碳产品的灰分可达30%以下,灰质产品的灰分可达95%以上。通过表征分析揭示了分离机理,结果表明残炭对煤油的吸附强度远超灰质,使得煤油处理过的残炭疏水性大幅度增加,容易被油相捕获。本研究可为煤气化细渣的高效提碳降灰提供重要指导,有助于实现煤气化固废的综合利用。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of mining engineering. Coal gasification slag is a type of solid waste generated during the coal gasification process. The presence of residual carbon significantly limits its potential for reuse and recycling. Therefore, the extraction of residual carbon from coal gasification slag is a pressing concern. In this research, the separation of residual carbon and inorganic minerals from gasification fine slag was studied by hydrophobic-hydrophilic separation technology. The effects of stirring speed, stirring time, hydrophobic liquid dosage, pulp concentration, pulp temperature, and hydrophobic liquid type on the separation effect of carbon/ ash were investigated. The hydrophobic-hydrophilic separation technology has excellent carbon extraction and ash reduction effect on coal gasification slag, and the ash content of its carbon product can be up to 30% or less, while that of the ash product can be up to 95% or more. The separation mechanism was revealed by the characterisation analysis, which showed that the adsorption strength of residual carbon on paraffin was much higher than that of ash, which made the kerosene-treated residual carbon hydrophobicity greatly increased and easy to be captured by the oil phase. This study can provide important guidance for the efficient carbon extraction and ash reduction of coal gasification fine residue, which can help to achieve the comprehensive utilisation of coal gasification solid waste.
-

-
表 1 神宁炉煤气化细渣筛分实验结果
Table 1. Particle size composition of the samples
粒度/mm +0.5 -0.5+0.25 -0.25+0.125 -0.125+0.074 -0.074+0.045 -0.045 总计 产率/% 3.56 7.43 10.98 12.82 11.47 53.74 100.00 灰分/% 90.00 86.40 64.77 61.65 72.16 84.61 78.39 表 2 神宁炉煤气化细渣的工业分析和元素分析
Table 2. Proximate and ultimate analysis of coal samples
工业分析/% 元素分析/% 水分Mad 灰分Aad 挥发分Vad 固定碳FCad C H N O S 0.46 79.80 2.40 12.16 19.18 0.18 0.12 0.41 0.31 表 3 实验方案
Table 3. Test schemes
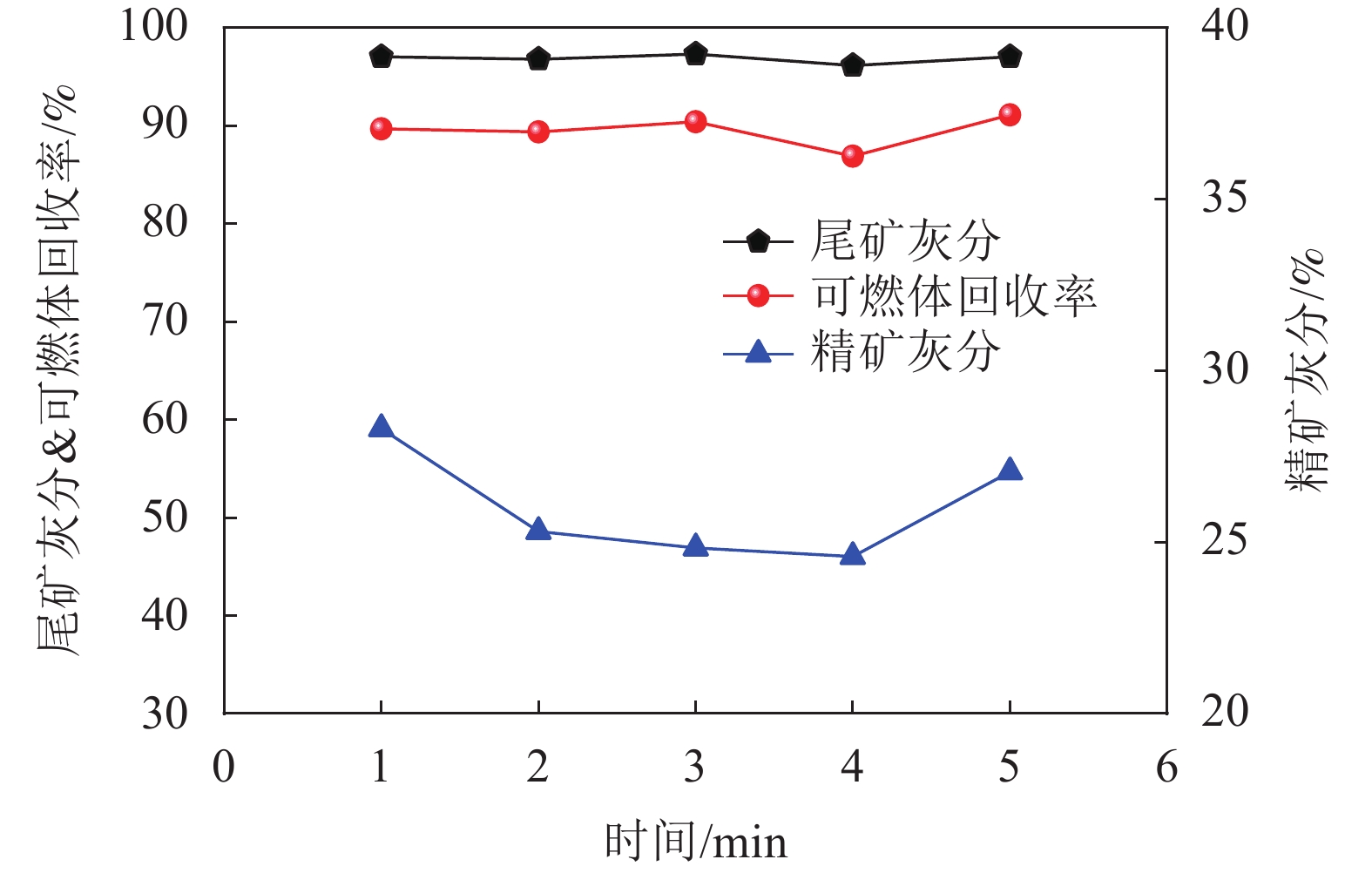
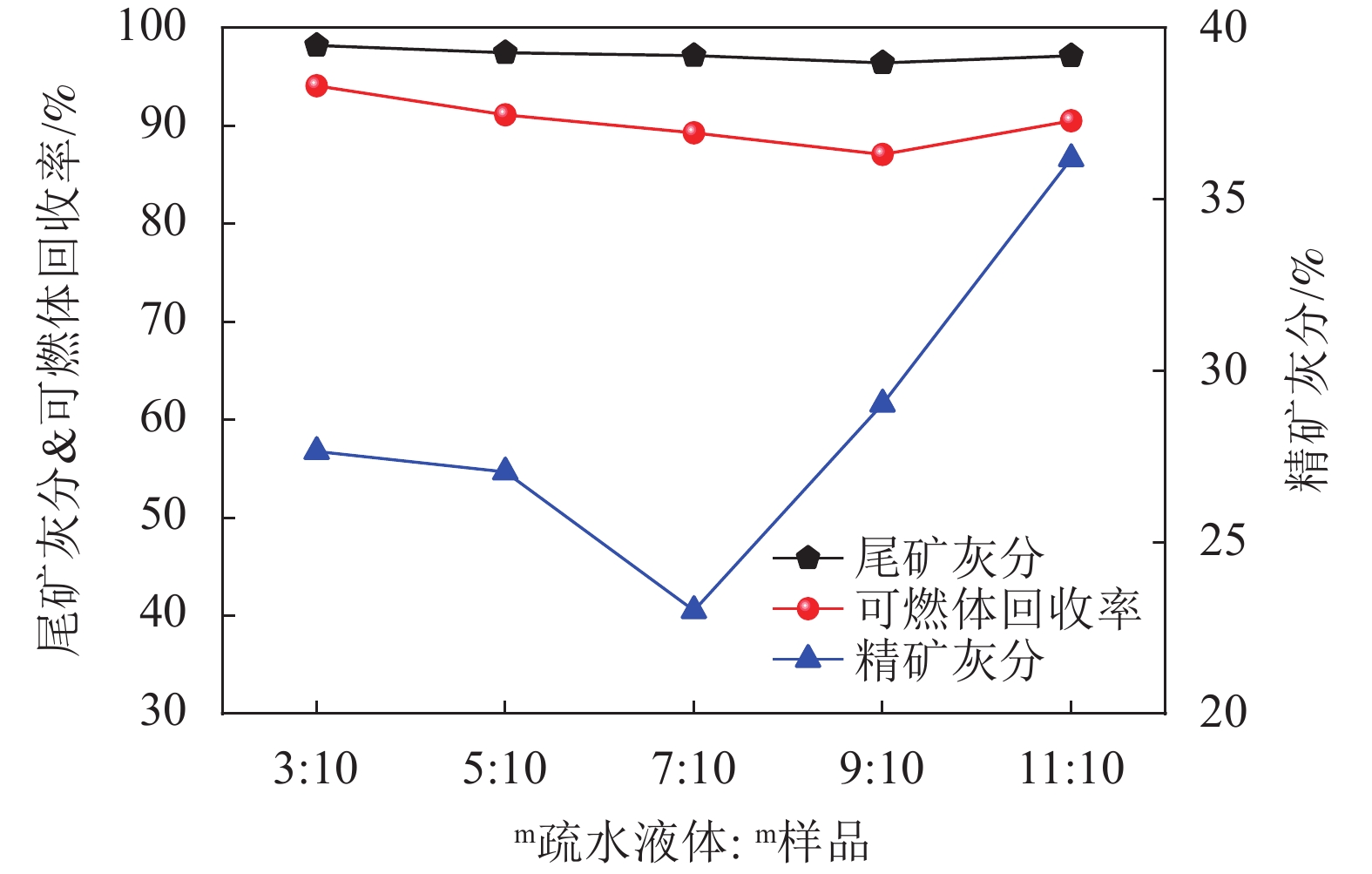
编号 搅拌速度/
(r/min)搅拌时间/
minm疏水液体∶m样品 矿浆浓度/
(g/L)温度/
℃试剂 1 变量 5 1:2 50 10 煤油 2 1800 变量 1:2 50 10 煤油 3 1800 5 变量 50 10 煤油 4 1800 5 1:2 变量 10 煤油 5 1800 5 1:2 50 变量 煤油 6 1800 5 1:2 50 10 变量 表 4 疏水液体种类对炭/灰分离效果的影响
Table 4. Effects of various hydrophobic liquids on the HHS separation
试剂 黏度
(20 ℃/cp)精矿
灰分/%尾矿
灰分/%可燃体
回收率/%正戊烷 0.23 25.74 97.79 92.00 石油醚 0.30 24.59 97.96 92.42 正庚烷 0.40 23.12 97.49 89.46 煤油 2.50 27.05 97.44 91.10 表 5 神宁炉气化细渣原样及炭/灰分离产品的XRF分析结果/%
Table 5. XRF results of the samples and separation products
名称 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 TiO2 K2O Na2O P2O5 合计 原样 53.78 15.02 10.08 9.01 3.11 2.79 1.94 1.87 1.14 0.42 99.16 精矿 50.19 15.39 12.15 9.36 3.11 2.61 1.29 2.21 1.65 1.11 99.07 尾矿 51.71 15.57 10.25 8.84 3.23 2.70 1.99 2.70 1.99 0.35 99.33 折合灰分的原样 42.15 11.77 7.90 7.06 2.44 2.19 1.52 1.47 0.89 0.33 77.72 折合灰分的精矿 11.08 3.40 2.68 2.07 0.69 0.58 0.28 0.49 0.36 0.24 21.86 折合灰分的尾矿 50.31 15.15 9.97 8.60 3.14 2.63 1.94 2.63 1.94 0.34 96.65 表 6 神宁炉煤气化炉气化细渣密度组成
Table 6. Density composition of the sample
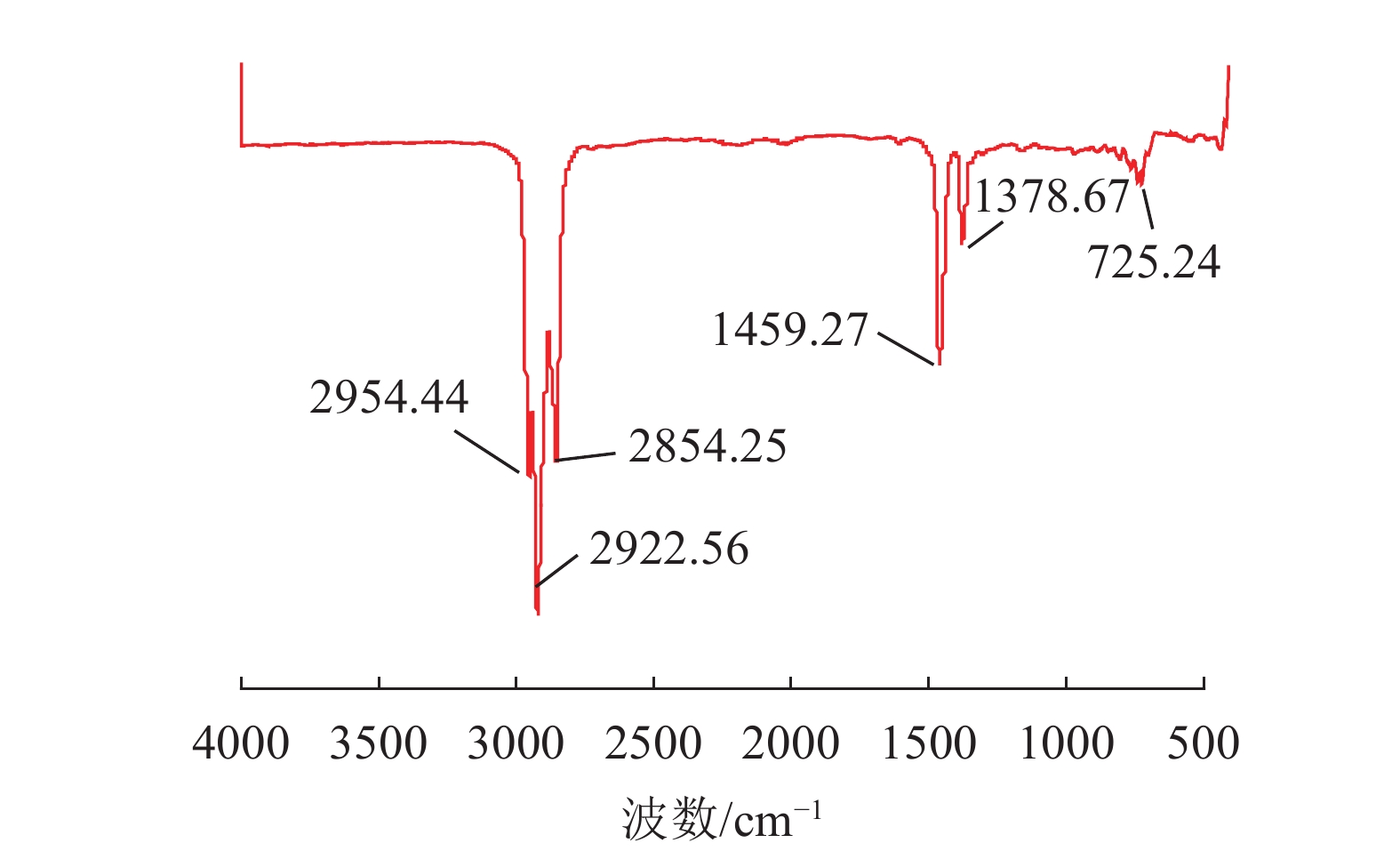
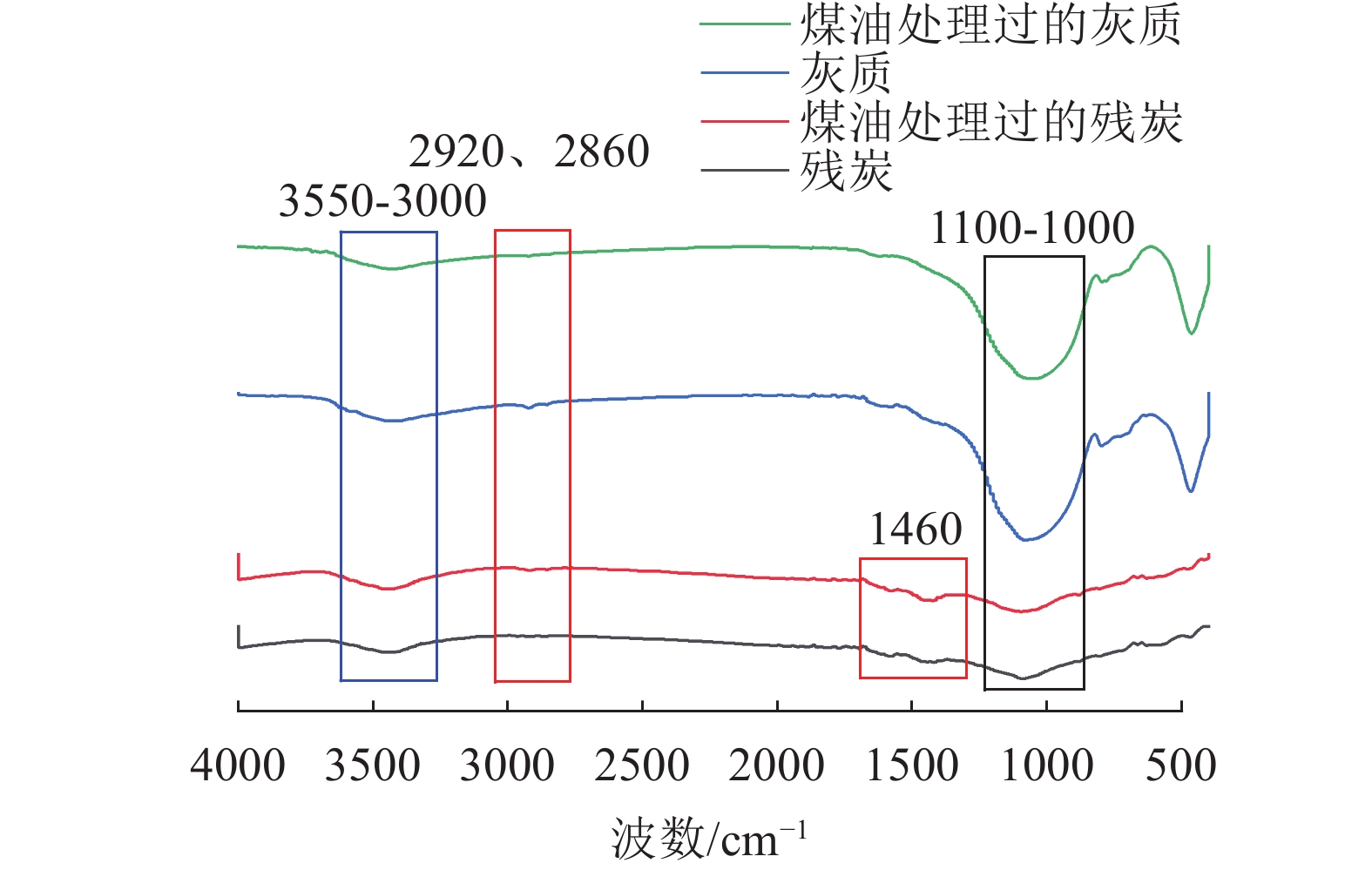
密度/(g/cm) 产率/% 灰分/% 累计产率/% 累计灰分/% -2.1 14.34 30.72 14.34 30.72 2.1-2.2 5.13 54.85 19.47 37.07 2.2-2.3 10.53 60.30 30.00 45.23 2.3-2.4 20.87 83.17 50.87 60.79 +2.4 49.13 96.39 100.00 78.28 表 7 官能团种类及其对应吸收峰范围
Table 7. Type of functional groups and their corresponding absorption peak range
吸收峰范围/cm-1 官能团种类 3750~3000 -OH与N-H特征峰 3100~2750 C-H脂肪族振动区 3550~3450 分子间氢键-二分子缔合 3500~3200 分子间氢键-多分子缔合 2954.44、2922.56、2854.25 饱和烷烃氢的C-H伸缩振动 1470~1450 -CH(CH3)2的C-H伸缩振动 725.24 碳原子个数大于4的-C(CH2)n- 1100~1000 Si-O-Si伸缩振动 表 8 接触角测试结果
Table 8. Test results of the contact angle
残炭 煤油处理后的残炭 灰质 煤油处理后的灰质 36.11 107.82 28.08 80.19 -
[1] 杨丹, 王海锋, 黄志刚, 等. 纳米煤制备及其改善煤泥浮选的机理研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):70-76.YANG D, WANG H F, HUANG Z G, et al. Preparation of nano coal and its mechanism of improvement on coal flotation[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):70-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.014
YANG D, WANG H F, HUANG Z G, et al. Preparation of nano coal and its mechanism of improvement on coal flotation[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):70-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.014
[2] 史达, 张建波, 杨晨年, 等. 煤气化灰渣脱碳技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2020, 26(6):1-10.SHI D, ZHANG J B, YANG C N, et al. Progress of coal gasification ash decarbonization technology[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2020, 26(6):1-10.
SHI D, ZHANG J B, YANG C N, et al. Progress of coal gasification ash decarbonization technology[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2020, 26(6):1-10.
[3] 史兆臣, 戴高峰, 王学斌, 等. 煤气化细渣的资源化综合利用技术研究进展[J]. 华电技术, 2020, 42(7):63-73.SHI Z C, DAI G F, WANG X B, et al. Research progress on resource utilization technology of coal gasification fine slag[J]. Huadian Technology, 2020, 42(7):63-73.
SHI Z C, DAI G F, WANG X B, et al. Research progress on resource utilization technology of coal gasification fine slag[J]. Huadian Technology, 2020, 42(7):63-73.
[4] 刘淑琴, 牛茂斐, 齐凯丽, 等. 煤炭地下气化特征污染物迁移行为探测[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(9):2618-2624.LIU S Q, NIU M F, QI K L, et al. Detection of characteristic pollutant migration behavior in underground coal gasification[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(9):2618-2624.
LIU S Q, NIU M F, QI K L, et al. Detection of characteristic pollutant migration behavior in underground coal gasification[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(9):2618-2624.
[5] 晁岳建, 王洪记. 循环流化床锅炉掺烧气化渣和煤泥的可行性研究[J]. 化肥工业, 2015(3):48-50.CHAO Y J, WANG H J. The feasibility study of mixing gasification slag and coal slime in a circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. Chemical Fertilizer Industry, 2015(3):48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7779.2015.03.015
CHAO Y J, WANG H J. The feasibility study of mixing gasification slag and coal slime in a circulating fluidized bed boiler[J]. Chemical Fertilizer Industry, 2015(3):48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7779.2015.03.015
[6] 董永波. 水煤浆气化细渣碳资源回收及循环利用[J]. 氮肥技术, 2018, 39(3):25-26.DONG Y B. Recovery and recycling of carbon resources from coal-water slurry gasification fine slag[J]. Nitrogenous Fertilizer Technology, 2018, 39(3):25-26.
DONG Y B. Recovery and recycling of carbon resources from coal-water slurry gasification fine slag[J]. Nitrogenous Fertilizer Technology, 2018, 39(3):25-26.
[7] 宁永安, 段一航, 高宁博, 等. 煤气化渣组分回收与利用技术研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2020(S1): 14-19.NING Y A, DUAN Y H , GAO N B, et al. Research progress in the recovery and utilization of coal gasification slag components[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2020(S1): 14-19.
NING Y A, DUAN Y H , GAO N B, et al. Research progress in the recovery and utilization of coal gasification slag components[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2020(S1): 14-19.
[8] 曲江山, 张建波, 孙志刚, 等. 煤气化渣综合利用研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2020, 26(1): 184-193.QU J S, ZHANG J B, SUN Z G , et al. Research progress in comprehensive utilization of coal gasification slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2020, 26(1): 184-193.
QU J S, ZHANG J B, SUN Z G , et al. Research progress in comprehensive utilization of coal gasification slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2020, 26(1): 184-193.
[9] 胡文豪. 煤气化渣铝硅组分活化分离与资源化利用基础研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019.HU W H. Basic research on activation separation and resource utilization of aluminum and silicon components of coal gasification slag[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019.
HU W H. Basic research on activation separation and resource utilization of aluminum and silicon components of coal gasification slag[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019.
[10] 汤云. 利用气化炉渣和煤矸石制备Sialon基复相陶瓷[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2011.TANG Y. Preparation of Sialon-based multiphase ceramics using gasification slag and coal gangue[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011.
TANG Y. Preparation of Sialon-based multiphase ceramics using gasification slag and coal gangue[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2011.
-




 下载:
下载: