Analysis of the Mechanism of Choline Chloride-oxalate Action on Zinc Oxide Leaching Based on First Principles
-
摘要:
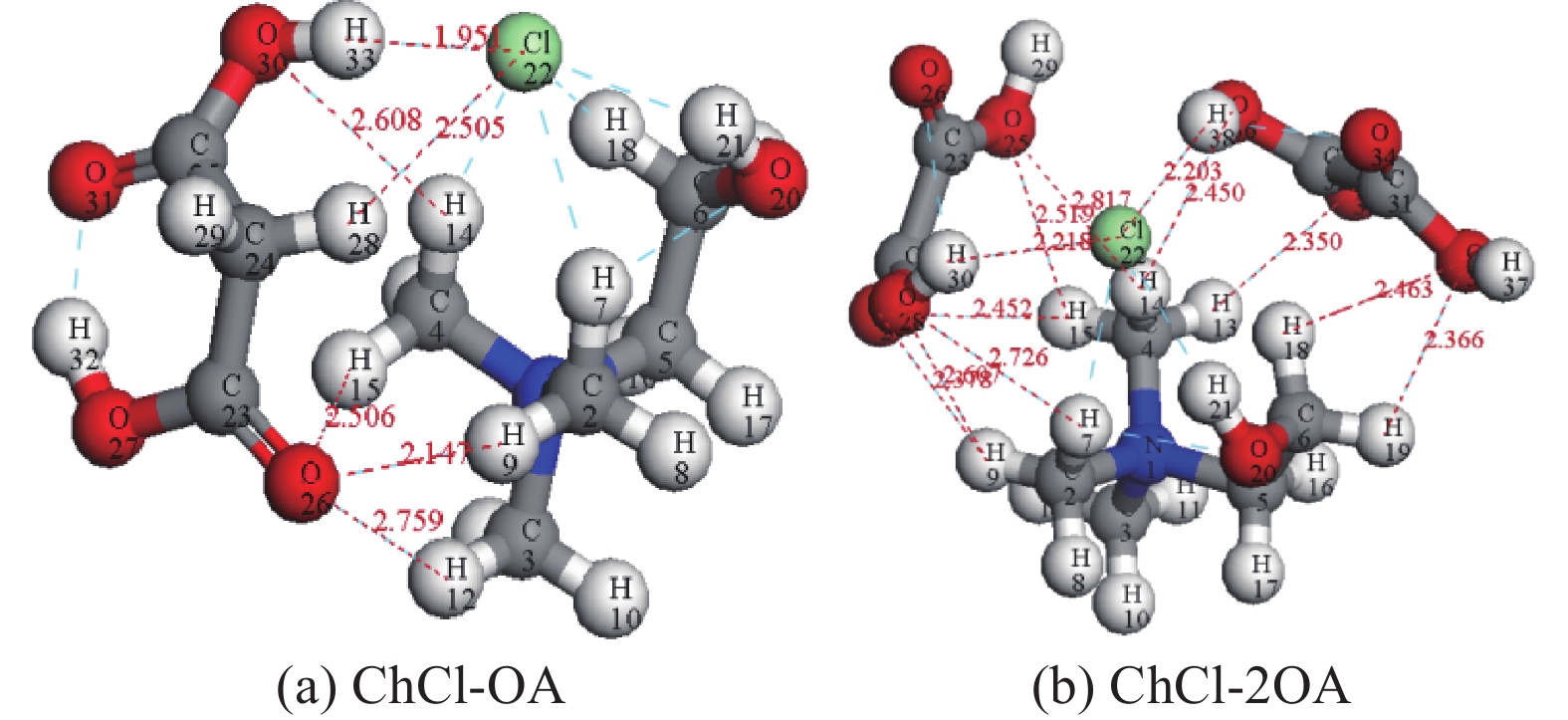
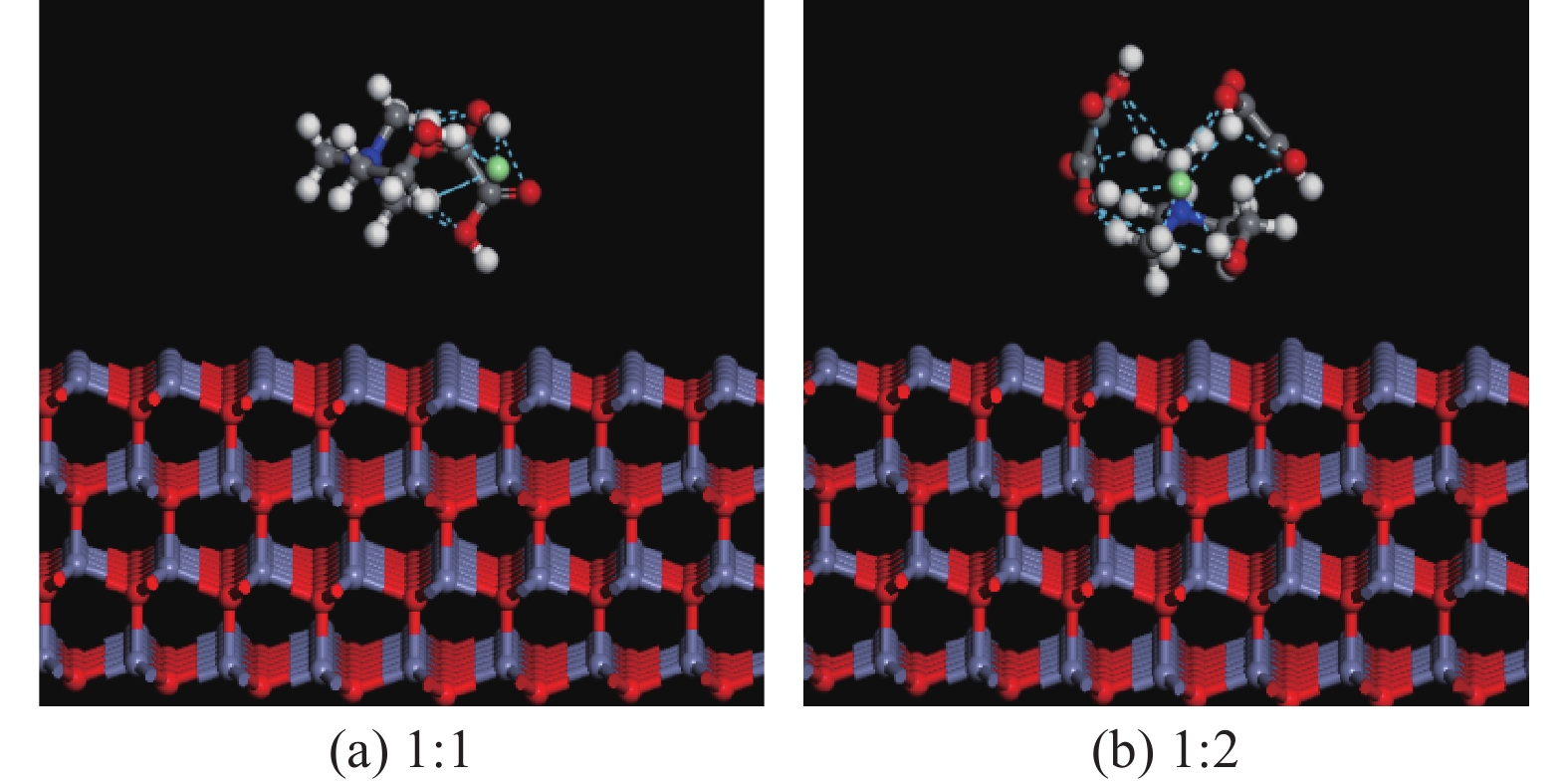
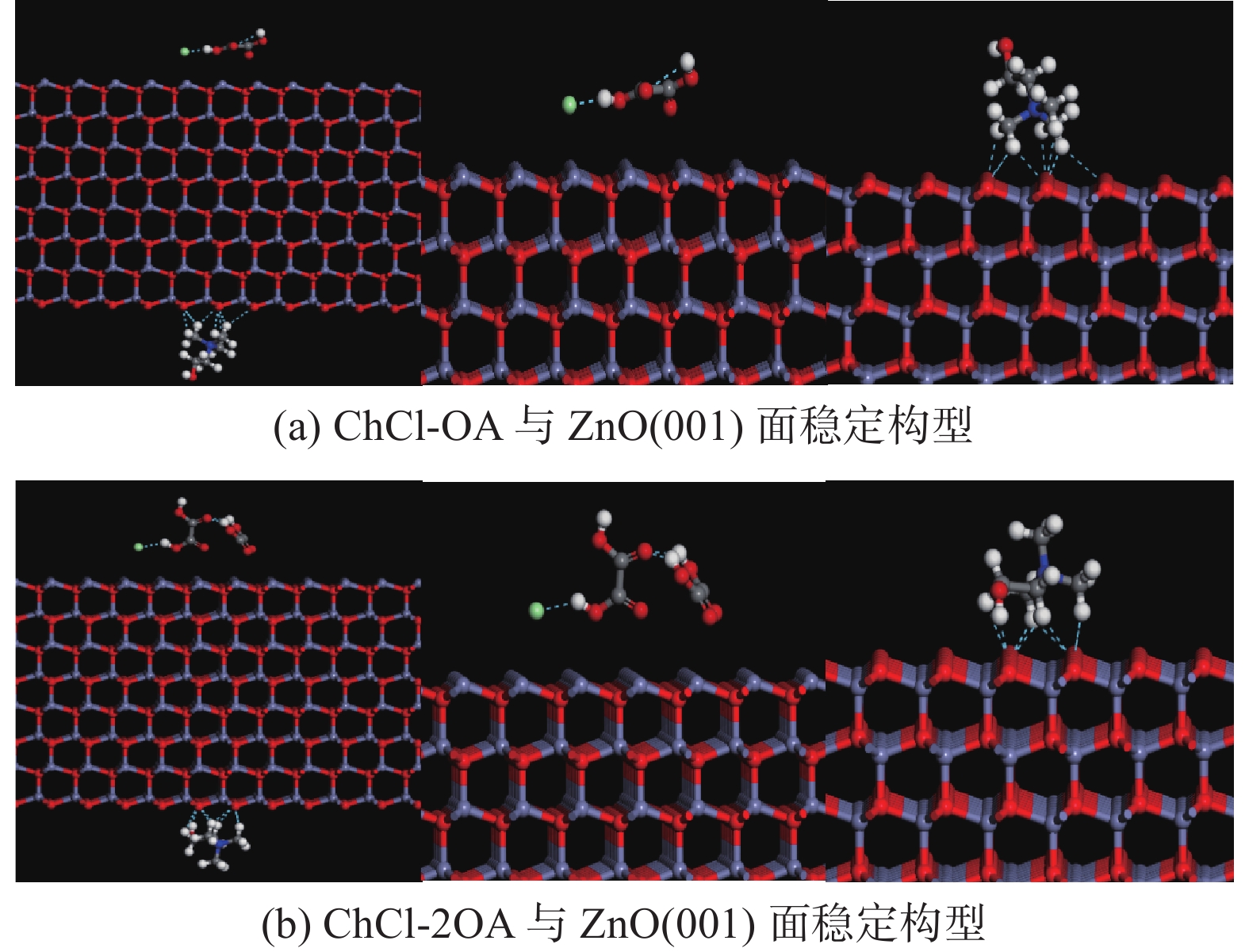
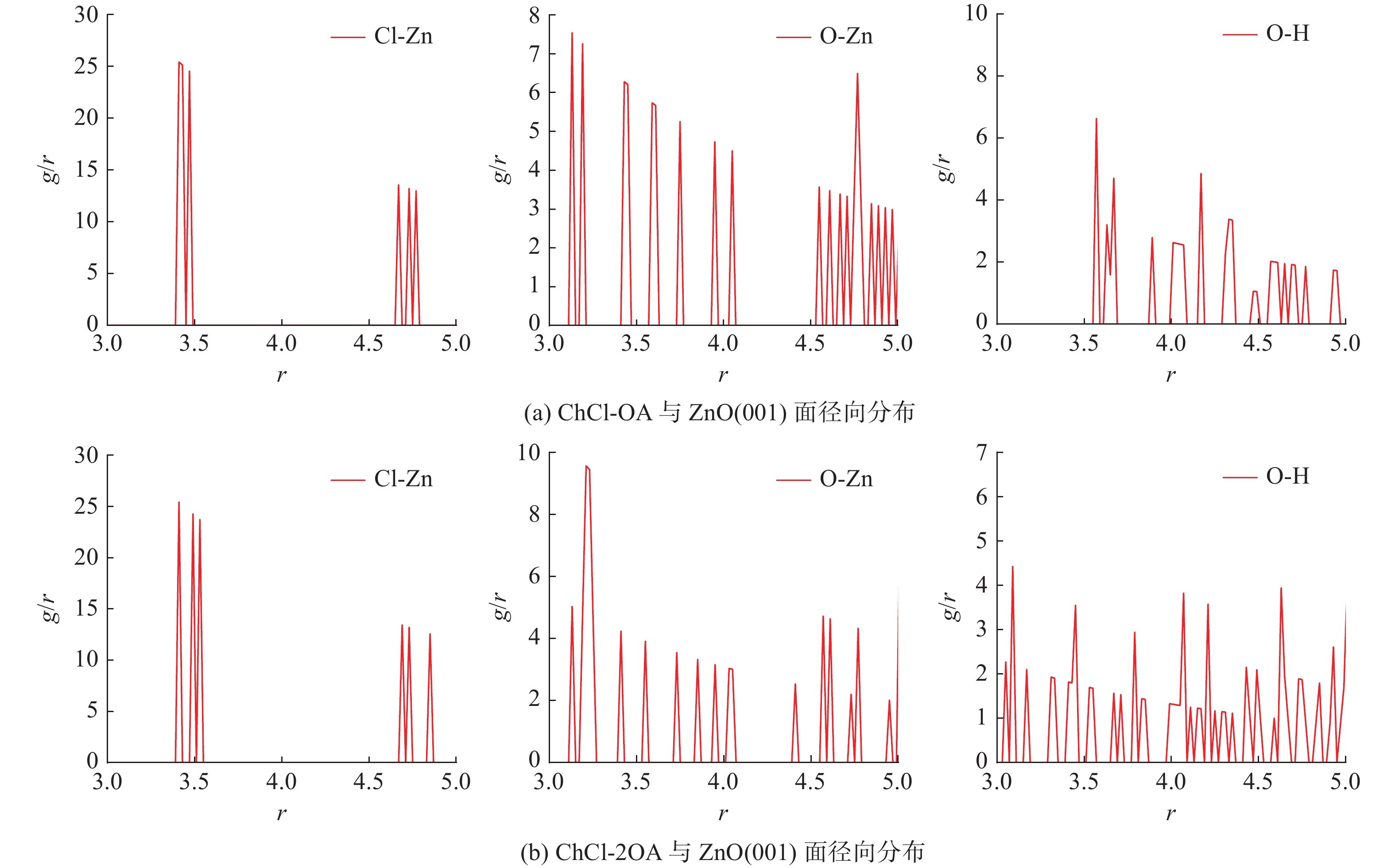
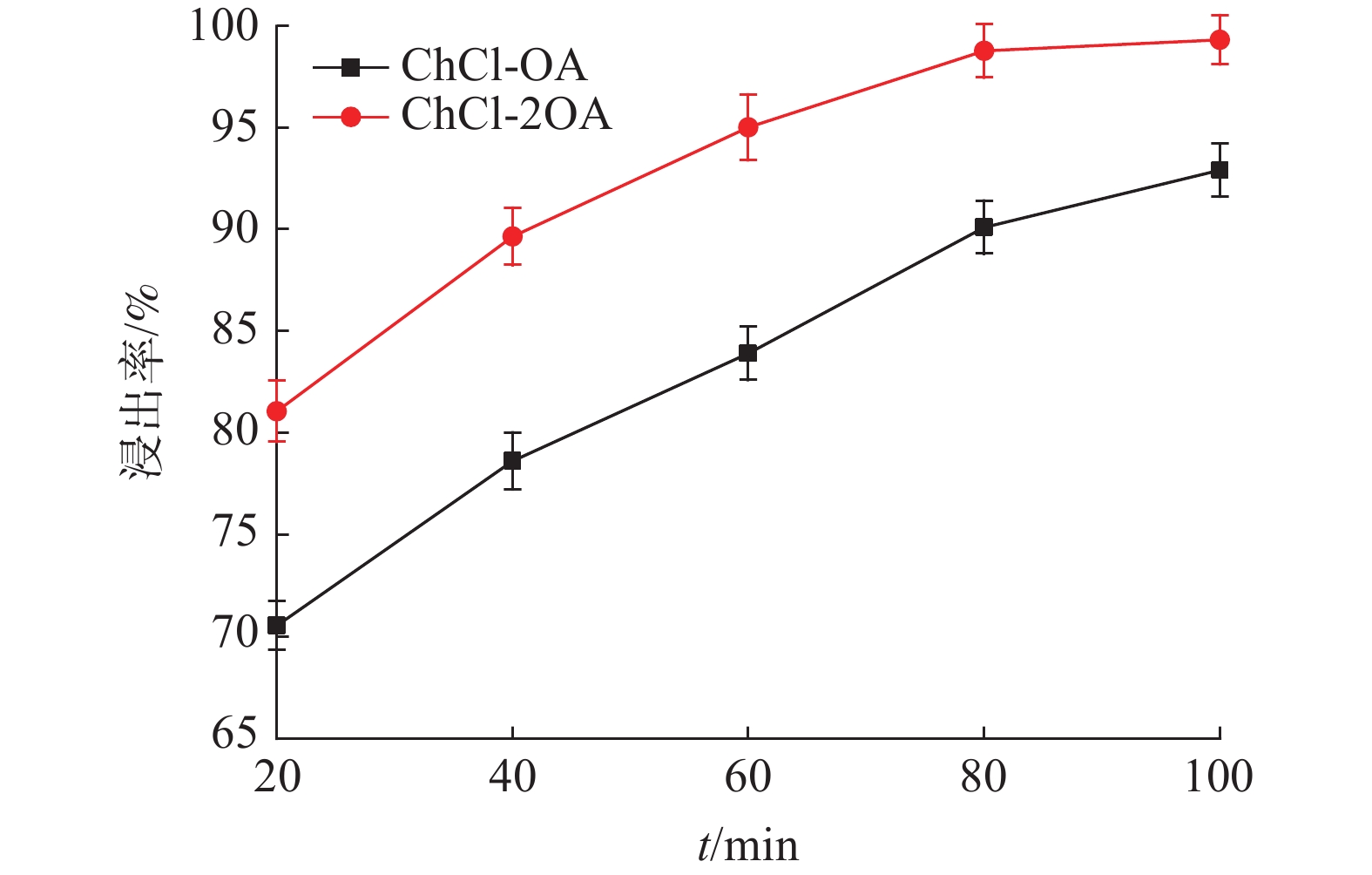
这是一篇冶金工程领域的文章。为探究氯化胆碱-草酸对含锌尘泥中氧化锌的浸出机理,运用量子力学手段,模拟氯化胆碱-草酸1∶1、1∶2低共熔溶剂在氧化锌表面相互作用,通过实验对模拟结果进行验证。结果表明,氯化胆碱-草酸形成的分子间氢键对低共熔溶剂稳定性起到重要作用,电子得失情况为Ch+得到电子,OA、Cl-失去电子。ZnO(001)面为氧化锌完全解理面,氧与锌原子形成四面体结构,在与外界发生反应过程中氧原子容易得电子,锌原子容易失去电子。氯化胆碱-草酸和氧化锌相互作用过程中氧化锌失去电子,氯化胆碱-草酸得到电子。ChCl-2OA和ZnO相互作用能$ \Delta \mathrm{E} $=-819.6896Ha较小,说明氧化锌更容易与ChCl-2OA发生反应。径向分布函数表明氯化胆碱-草酸在与氧化锌相互作用过程中主要以化学吸附为主,物理吸附为辅,化学吸附形成的Cl-Zn比O-Zn贡献较大。通过纯矿物实验验证可知,ChCl-2OA对氧化锌的浸出效果较好,验证了利用分子模拟氯化胆碱-草酸与氧化锌相互作用机理的准确性,为低共熔溶剂浸出含锌尘泥提供理论基础。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of metallurgical engineering. In order to explore the leaching mechanism of zinc oxide from zinc-containing dust by choline chloride and oxalic acid, the interaction of choline chloride and oxalic acid with 1∶1 and 1∶2 eutectic solvent on zinc oxide surface was simulated by means of quantum mechanics, and the simulation results were verified by experiments. The results show that the intermolecular hydrogen bond formed by choline chloride and oxalic acid plays an important role in the stability of eutectic solvent. Ch+ gains electrons, OA and Cl- lose electrons. ZnO(001) surface is the complete cleavage surface of zinc oxide, oxygen and zinc atoms form tetrahedral structure, oxygen atom is easy to gain electrons and zinc atom is easy to lose electrons during the reaction with the outside world. The zinc oxide loses electrons during the interaction between cholinergic chloride-oxalic acid and zinc oxide, and cholinergic chloride-oxalic acid gains electrons. The interaction energy △E=-819.6896Ha between ChCl-2OA and ZnO is small, indicating that zinc oxide is more likely to react with ChCl-2OA. The radial distribution function shows that the chemical adsorption is the main factor in the interaction between choline chloride and oxalic acid and zinc oxide, and the physical adsorption is the secondary factor. The contribution of Cl-Zn formed by chemical adsorption is greater than that of O-Zn. Through the pure mineral test, it can be verified that ChCl-2OA has a better leaching effect on zinc oxide, which verifies the accuracy of molecular simulation of the interaction mechanism between choline chloride and oxalic acid and zinc oxide, and provides a theoretical basis for the leaching of zinc-containing dust with eutectic solvent.
-

-
表 1 两种比例氯化胆碱-草酸电荷布居/e
Table 1. Charge distribution of choline chloride and oxalic acid in two proportions
ChCl-OA ChCl-2OA Ch+ +0.728 +0.752 Cl- -0.569 -0.564 OA -0.159 -0.188 其中+代表得到电子,-代表失去电子 表 2 氧化锌常见解理面表面能/(J/m2)
Table 2. Common surface energy of metal oxides
单矿物 001 011 111 101 110 ZnO 0.8177 3.9275 3.9271 2.0852 2.4053 表 3 原子层数对表面能的影响
Table 3. Influence of atomic layer number on surface energy
完全解理面 原子层数 原子数 表面能J/m2
ZnO(001)2 8 1.5438 3 12 1.5908 4 16 1.6079 5 20 1.6088 6 24 1.6093 表 4 氧化锌各原子电荷布居
Table 4. Atomic charge population of zinc oxide
原子 各轨道布居数 总数 电荷数 s轨道 p轨道 d轨道 O 1.86 4.97 - 6.82 -0.83 Zn 0.48 0.72 9.97 11.18 0.83 表 5 两种比例氯化胆碱-草酸和氧化锌前线分子轨道能量
Table 5. Frontier molecular orbital energy of choline chloride - oxalic acid and zinc oxide in two proportions
HOMO LUMO △E1 △E2 ChCl-OA -0.2023 -0.0679 0.1734 0.0941 ChCl-2OA -0.2118 -0.1154 0.1897 0.0771 ZnO -0.1625 -0.0221 其中ΔE1=|HOMODES−LUMOZnO|、△E2=|HOMOZnO−LUMODES| 表 6 两种比例氯化胆碱-草酸与氧化锌相互作用能/Ha
Table 6. Interaction energy between choline chlorine-oxalic acid and zinc oxide in two proportions
低共熔溶剂 EA EB EAB △E ChCl-OA 101.2460 - 448581.5872 - 449217.2274 - 736.8862 ChCl-2OA 130.9856 - 448581.5872 - 449267.8158 - 817.2142 -
[1] 申亚芳, 张馨圆, 王乐, 等. 氧化锌矿处理方法现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2):23-28.SHEN Y F, ZHANG X Y, WANG L, et al. Preparation of zinc and its compounds from zinc oxide ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.004
SHEN Y F, ZHANG X Y, WANG L, et al. Preparation of zinc and its compounds from zinc oxide ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2):23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.02.004
[2] 马爱元, 郑雪梅, 李松 , 等. 含锌钢铁冶金渣尘处理技术现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4): 1-7.MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Present situation of zinc metallurgical slags and dusts treatment technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4): 1-7.
MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Present situation of zinc metallurgical slags and dusts treatment technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4): 1-7.
[3] 牛福生, 倪文, 张晋霞, 等. 中国钢铁冶金尘泥资源化利用现状及发展方向[J]. 钢铁, 2016, 51(8):1-5+10.NIU F S, NI W, ZHANG J X, et al. Current situation and development direction of resource utilization of metallurgical dust sludge of iron and steel in China[J]. Steel, 2016, 51(8):1-5+10.
NIU F S, NI W, ZHANG J X, et al. Current situation and development direction of resource utilization of metallurgical dust sludge of iron and steel in China[J]. Steel, 2016, 51(8):1-5+10.
[4] 谢泽强, 郭宇峰, 陈凤, 等. 钢铁厂含锌粉尘综合利用现状及展望[J]. 烧结球团, 2016, 41(5):53-56+61.XIE Z Q, GUO Y F, CHEN F, et al. Current status and prospects of comprehensive utilization of zinc-containing dust in steel plants[J]. Sintered Pellets, 2016, 41(5):53-56+61.
XIE Z Q, GUO Y F, CHEN F, et al. Current status and prospects of comprehensive utilization of zinc-containing dust in steel plants[J]. Sintered Pellets, 2016, 41(5):53-56+61.
[5] 信晓飞, 张晋霞, 冯洪均. 响应曲面法优化含锌尘泥选择性浸出工艺[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):146-151.XIN X F, ZHANG J X, FENG H J. Optimization of selective leaching technology from zinc-bearing dust using response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):146-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.025
XIN X F, ZHANG J X, FENG H J. Optimization of selective leaching technology from zinc-bearing dust using response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):146-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.025
[6] Wu Zhaojin, Huang Wei, Cui Keke, et al. Sustainable synthesis of metals-doped ZnO nanoparticles from zinc-bearing dust for photodegradation of phenol[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 278(8):91-99.
[7] 张晋霞, 冯洪均, 王龙, 等. 含锌冶金尘泥氨浸溶蚀实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):124-129.ZHANG J X, FENG H J, WANG L, et al. Study on treating zinc-bearing dust by Ammonia leaching process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.021
ZHANG J X, FENG H J, WANG L, et al. Study on treating zinc-bearing dust by Ammonia leaching process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.021
[8] 王英磊, 陈鹏月, 游咸丰, 等. 低共熔溶剂氯化胆碱-草酸催化合成乙酰水杨酸[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(25):212-215.WANG Y L, CHEN P Y, YOU X F, et al. Low eutectic solvent choline chloride-oxalic acid catalyzed synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(25):212-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.25.033
WANG Y L, CHEN P Y, YOU X F, et al. Low eutectic solvent choline chloride-oxalic acid catalyzed synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(25):212-215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.25.033
[9] 毛春峰, 赵荣祥, 李秀萍. 氯化胆碱/草酸低共熔溶剂高效脱除模拟油中硫[J]. 化学工程, 2017, 45(5):6-10.MAO C F, ZHAO R X, LI X P. Efficient removal of sulfur from simulated oil with choline chloride/oxalic acid low eutectic solvent[J]. Chemical Engineering, 2017, 45(5):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2017.05.002
MAO C F, ZHAO R X, LI X P. Efficient removal of sulfur from simulated oil with choline chloride/oxalic acid low eutectic solvent[J]. Chemical Engineering, 2017, 45(5):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2017.05.002
[10] 许涛, 廖美婷, 衷水平, 等. 紫金山黄铁矿的第一性原理和前线轨道理论分析[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2015, 23(4):57-62.XU T, LIAO M T, ZHONG S P, et al. First principles and frontline orbital theory analysis of Zijinshan Pyrite[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2015, 23(4):57-62. doi: 10.11872/j.issn.1005-2518.2015.04.057
XU T, LIAO M T, ZHONG S P, et al. First principles and frontline orbital theory analysis of Zijinshan Pyrite[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2015, 23(4):57-62. doi: 10.11872/j.issn.1005-2518.2015.04.057
[11] 王邸博, 陈达畅, 皮守苗, 等. 基于密度泛函理论的SF_6分解组分在ZnO(001)吸附及传感性能研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(7):1592-1602.WANG D B, CHEN D C, PI S M, et al. Study on the adsorption and sensing performance of SF_6 decomposition components in ZnO(001) based on density flooding theory[J]. Journal of Electrotechnology, 2020, 35(7):1592-1602.
WANG D B, CHEN D C, PI S M, et al. Study on the adsorption and sensing performance of SF_6 decomposition components in ZnO(001) based on density flooding theory[J]. Journal of Electrotechnology, 2020, 35(7):1592-1602.
[12] 刘亚明, 戴宪起, 姚树文, 等. Sn对O在ZnO(001)面上吸附影响的第一原理研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(理学版), 2008(1):76-79.LIU Y M, DAI X Q, YAO S W, et al. First-principles study of the effect of Sn on O adsorption on the ZnO(001) surface[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Science Edition), 2008(1):76-79.
LIU Y M, DAI X Q, YAO S W, et al. First-principles study of the effect of Sn on O adsorption on the ZnO(001) surface[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Science Edition), 2008(1):76-79.
[13] 李玉琼, 陈建华, 陈晔, 等. 黄铁矿(100)表面性质的密度泛函理论计算及其对浮选的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(4):919-926.LI Y Q, CHEN J H, CHEN Y, et al. Density flood theory calculation of surface properties of pyrite(100) and its effect on flotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(4):919-926.
LI Y Q, CHEN J H, CHEN Y, et al. Density flood theory calculation of surface properties of pyrite(100) and its effect on flotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(4):919-926.
[14] 王根, 李新梅. 第一性原理计算Cu、Co含量对 CoCuFeNi系高熵合金的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2020, 51(3): 3189-3195.WANG G , LI X M. Calculation of the effect of Cu and Co content on the CoCuFeNi system of high-entropy alloys by first-nature principle[J]. Functional Materials, 2020, 51(3): 3189-3195.
WANG G , LI X M. Calculation of the effect of Cu and Co content on the CoCuFeNi system of high-entropy alloys by first-nature principle[J]. Functional Materials, 2020, 51(3): 3189-3195.
[15] GaoZ, SunW, HuY. Mineral cleavage nature and surface energy: Anisotropic surface broken bonds consideration[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(9):2930-2937. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63428-2
[16] 徐尧. 白云母浮选体系的分子动力学模拟研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2015.XU Y. Molecular dynamics simulation study of white mica flotation system[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2015.
XU Y. Molecular dynamics simulation study of white mica flotation system[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[17] Agrawal Ravi, Peng Bei, Espinosa Horacio D. Experimental-computational investigation of ZnO nanowires strength and fracture[J]. Nano letters, 2009, 9(12):
[18] 何伟平, 黄菊, 王德堂, 等. 苯乙烯与苯酚反应的前线轨道理论分析[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2017, 34(2):231-237.HE W P, HUANG J, WANG D T, et al. Front-line orbital theory analysis of the reaction of styrene with phenol[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2017, 34(2):231-237.
HE W P, HUANG J, WANG D T, et al. Front-line orbital theory analysis of the reaction of styrene with phenol[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2017, 34(2):231-237.
[19] 张慧婷. 十二胺和油酸组合捕收剂在锂云母表面吸附的分子动力学模拟[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2017.ZHANG H T. Molecular dynamics simulation of adsorption of combined dodecylamine and oleic acid trap on lithium mica surface[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Technology, 2017.
ZHANG H T. Molecular dynamics simulation of adsorption of combined dodecylamine and oleic acid trap on lithium mica surface[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Technology, 2017.
[20] Fairushin I , Khrapak S A , Mokshin A . Direct evaluation of the physical characteristics of Yukawa fluids based on a simple approximation for the radial distribution function[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 19(12): 103359.
-



 下载:
下载: