Pre-reduction of Titanium Concentrate with Pulverized Coal and Iron Power Based on Response Surface Methodology Method
-
摘要:
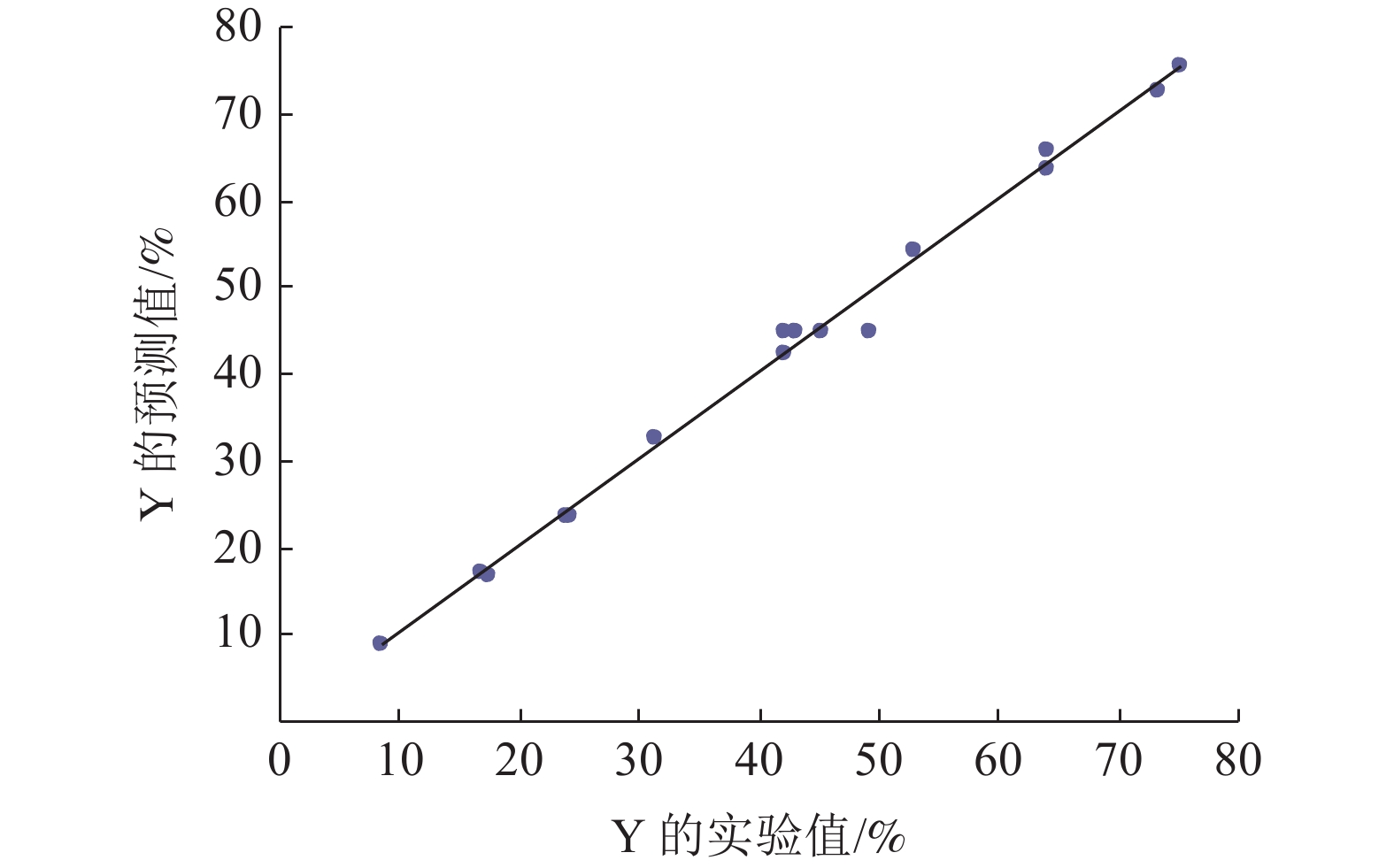
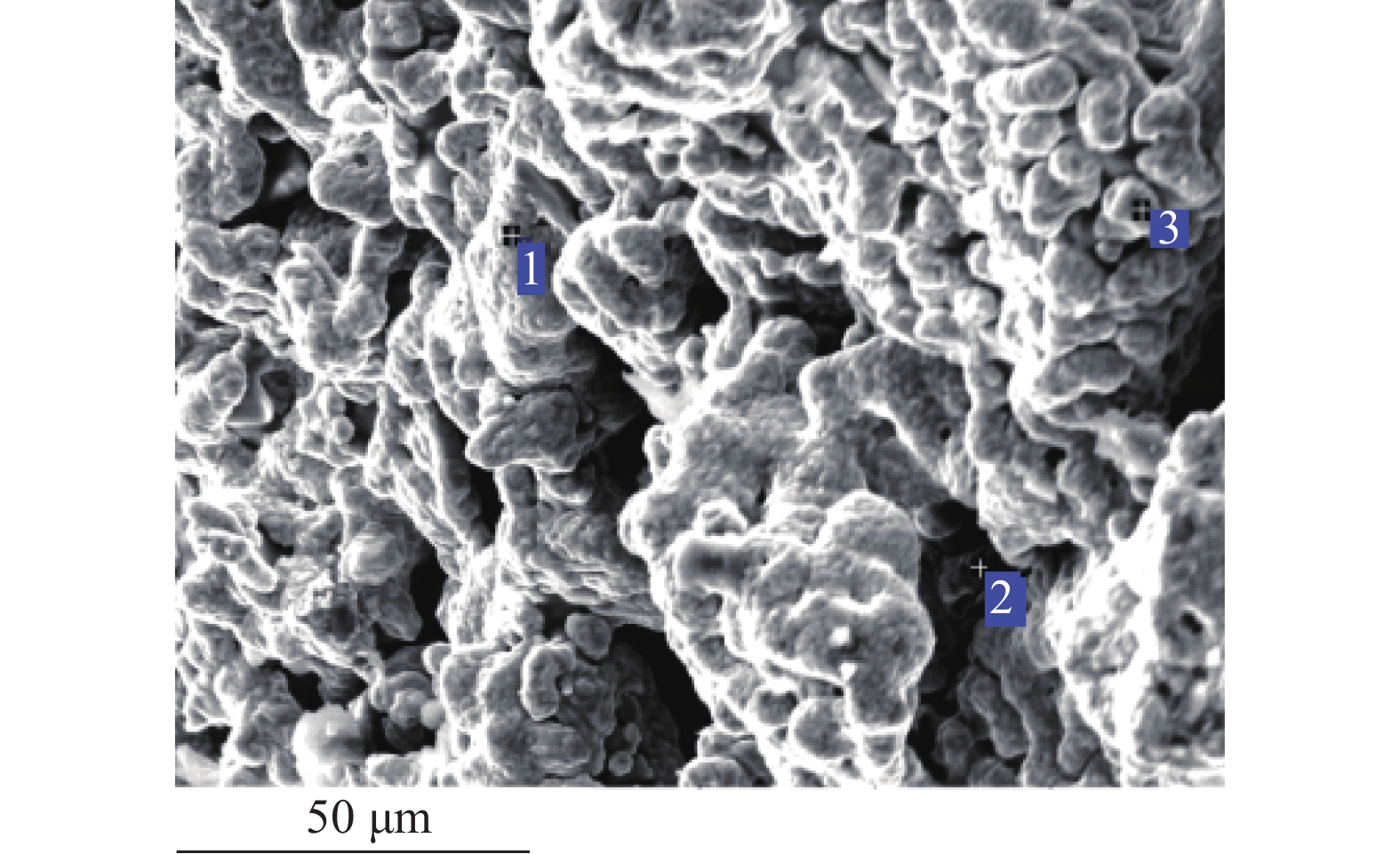
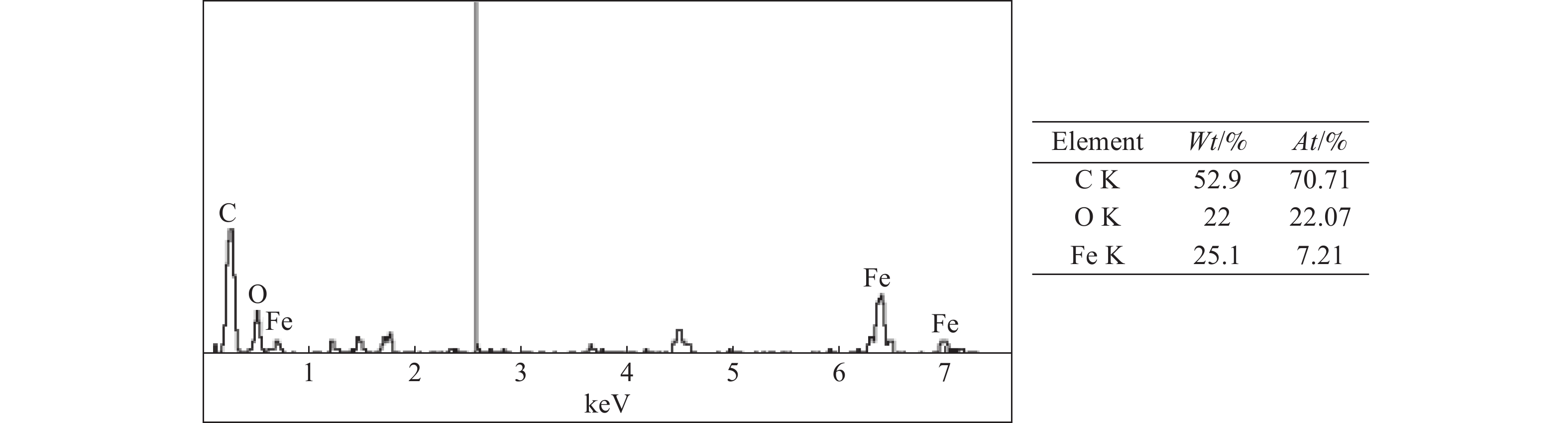
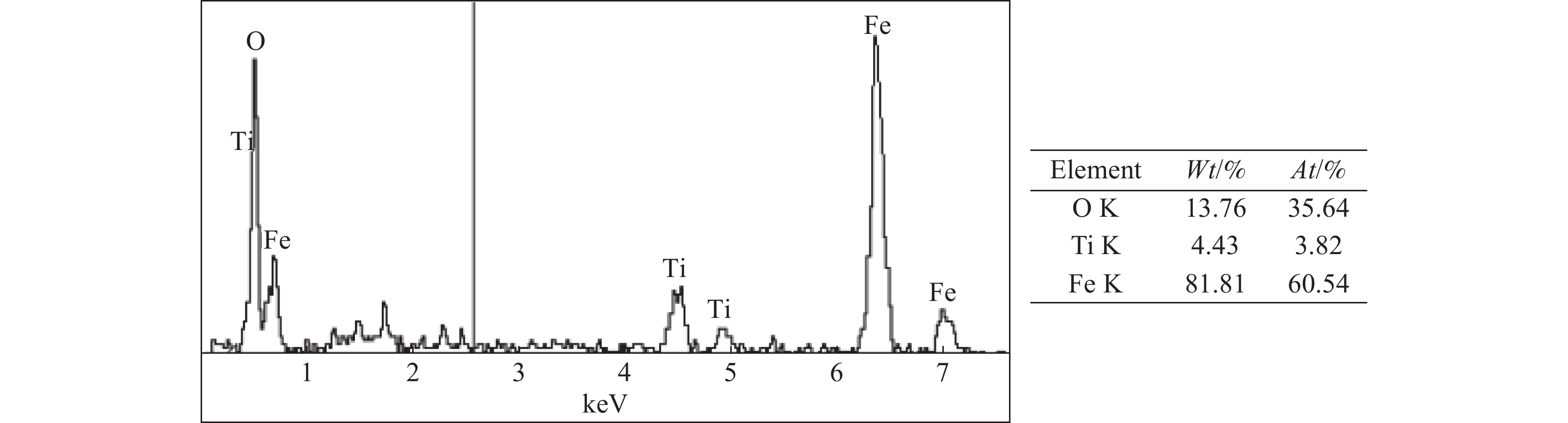
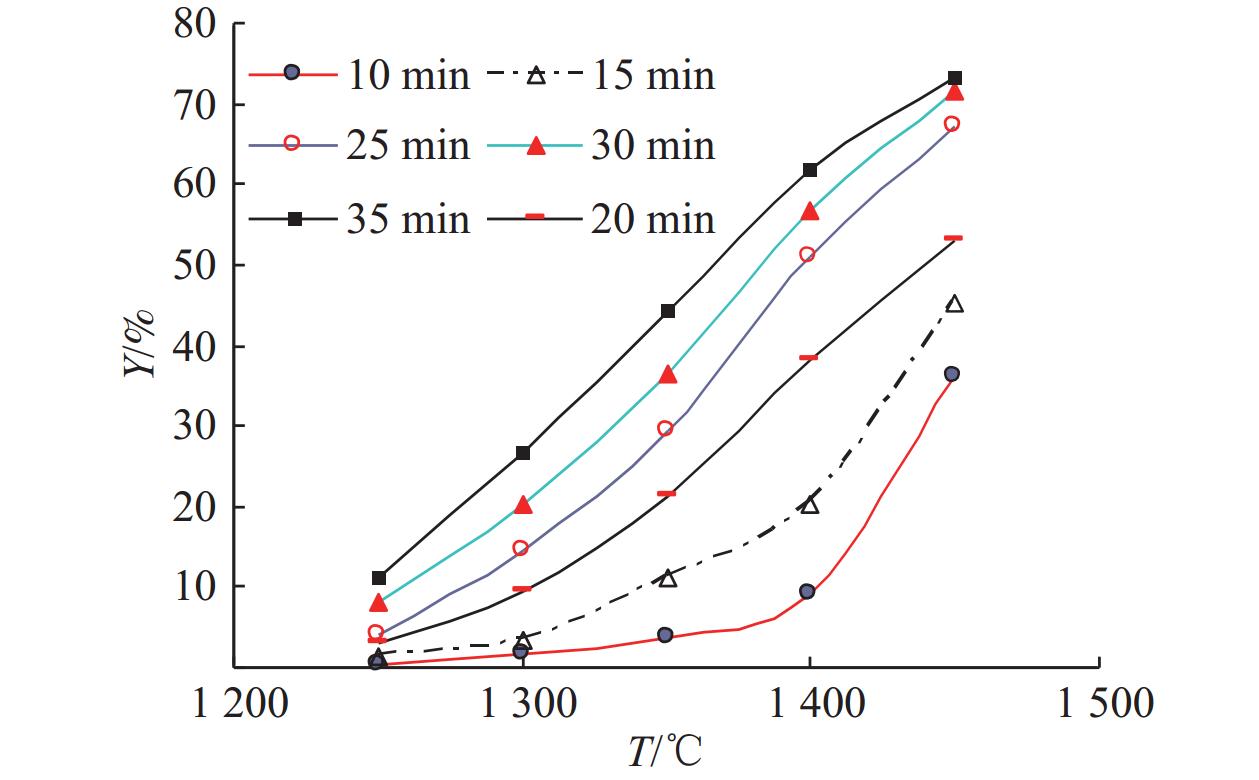
这是一篇冶金工程领域的文章。开展了钛精矿粉共同添加煤粉和铁粉的单因素和响应曲面法加热还原实验,研究了温度、加热时间、铁粉添加量各因素不同水平对钛精矿中铁氧化物还原影响,构建了铁的金属化率3次回归模型,探究了各因素对铁的金属化率影响规律。单因素实验表明:铁粉添加量1.5% ~ 4.0%中,高于2.5%后,铁的金属化率能明显得到提高。响应曲面法实验结果分析发现:在对铁氧化物的还原影响程度中,温度>加热时间>铁粉添加量,温度与时间交互作用>加热时间与铁粉添加量的交互作用;1 450 ℃、33.5 min、4%铁粉添加量优化条件下,铁的金属化率可达86.79%,还原产品中金属铁明显呈现。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of metallurgical engineering. The single factor and response surface experiments of heating reduction of titanium concentrate powder adding pulverized coal and iron powder were carried out, respectively so as to study the effects of temperature, heating time and iron powder addition on iron oxide reduction in titanium concentrate. The three regression model of iron metallization rate was constructed, and the influence law of various influencing factors on iron metallization rate was explored. The single factor test shows that the iron metallization rate can be significantly improved above 2.5% in the range of 1.5% ~ 4.0% of the addition amount of iron powder. The response surface method experiment shows that temperature is the most important factor, followed by time and then amount of iron powder, and the interaction between temperature and time is greater than that between heating time and the amount of iron powder added in the degree of influence on the reduction of iron. The iron metallization rate can reach 86.79%, and metallic iron obviously appears in the reduced product at the optimized conditions of 1 450 ℃, 33.5 min and 4% of iron power addition.
-

-
表 1 钛精矿成分/%
Table 1. Composition of titanium concentrate
TFe TiO2 FeO Fe2O3 CaO MnO MgO SiO2 Al2O3 V2O5 其他 32.2 46.6 35.5 6.5 1.1 0.8 3.2 3.7 1.0 0.5 1.1 表 2 煤粉成分/%
Table 2. Coal composition
固定碳 灰分 挥发分 78.26 11.76 9.98 表 3 单因素实验方案
Table 3. Test program of single factors
温度/℃ 时间/min 钛精矿的铁粉
添加比例 /%温度/℃ 时间/min 钛精矿的铁粉
添加比例 /%温度/℃ 时间/min 钛精矿的铁粉
添加比例 /%1 250 10 0 1 350 20 0 1 450 30 0 1 300 10 0 1 400 20 0 1 250 35 0 1 350 10 0 1 450 20 0 1 300 35 0 1 400 10 0 1 250 25 0 1 350 35 0 1 450 10 0 1 300 25 0 1 400 35 0 1 250 15 0 1 350 25 0 1 450 35 0 1 300 15 0 1 400 25 0 1 400 30 1.5 1 350 15 0 1 450 25 0 1400 30 2 1 400 15 0 1 250 30 0 1 400 30 2.5 1 450 15 0 1 300 30 0 1 400 30 3 1 250 20 0 1 350 30 0 1 400 30 3.5 1 300 20 0 1 400 30 0 1 400 30 4 表 4 实验因数选取水平与编码值
Table 4. Actual and code value of the variables
水平 温度 时间 钛精矿的铁粉添加比例 实际/℃ 编号 实际/min 编号 实际/% 编号 T A t B M C 1 1 450 1 35 1 4 1 0 1 375 0 22.5 0 2 0 -1 1 300 -1 10 -1 0 -1 表 5 响应面法实验结果
Table 5. Program and results of RSM test
A B C Y /% A B C Y /% A B C Y /% A B C Y /% A B C Y /% 1 -1 0 17.1 0 1 -1 53.2 1 0 -1 64.4 -1 0 1 22.4 1 1 0 75.3 0 1 1 64.3 0 0 0 43.3 -1 1 0 42.2 0 0 0 49.3 - - - - -1 -1 0 8.8 0 0 0 43.2 1 0 1 73.4 0 0 0 42.2 - - - - -1 0 -1 17.5 0 -1 -1 31.5 0 0 0 45.5 0 -1 1 24.5 - - - - 表 6 未手动处理的方差分析
Table 6. ANOVA without manual operation
来源 平方和 df 均方 F 值 P 值 显著程度 模型 6 378 12 531.5 65.9 0.000 5 * A 2 396.1 1 2 396.1 297.1 < 0.000 1 ** B 945.56 1 945.56 117.24 0.000 4 * C 4.2 1 4.2 0.52 0.510 3 AB 153.76 1 153.76 19.07 0.012 * AC 4.2 1 4.2 0.52 0.510 3 BC 81.9 1 81.9 10.16 0.033 3 * A2 64.04 1 64.04 7.94 0.047 9 * B2 103.17 1 103.17 12.79 0.023 2 * C2 55.33 1 55.33 6.86 0.058 8 A2B 113.25 1 113.25 14.04 0.02 * A2C 12.01 1 12.01 1.49 0.289 5 AB2 399.03 1 399.03 49.48 0.002 2 * Pure Error 32.26 4 8.06 Cor Total 6 410.26 16 注:P≤0.000 1,为非常显著,用**表示;P≤0.05,为显著,用*表示;P>0.05,为不显著。 表 7 手动处理的方差分析
Table 7. ANOVA analysis with manual operation
来源 平方和 df 均方 F 值 P 值 显著程度 模型 6 369.6 10 636.96 93.98 < 0.000 1 ** A 2 396.1 1 2 396.1 353.54 < 0.000 1 ** B 945.56 1 945.56 139.51 < 0.000 1 ** AB 153.76 1 153.76 22.69 0.003 1 * BC 81.9 1 81.9 12.08 0.013 2 * A2 64.04 1 64.04 9.45 0.021 8 * B2 103.17 1 103.17 15.22 0.008 * C2 55.33 1 55.33 8.16 0.028 9 * A2B 113.25 1 113.25 16.71 0.006 4 * A2C 48.3 1 48.3 7.13 0.037 * AB2 399.03 1 399.03 58.88 0.000 3 * Residual 40.66 6 6.78 Lack of Fit 8.41 2 4.2 0.52 0.629 3 not significant Pure Error 32.26 4 8.06 Cor Total 6 410.26 16 注:P≤0.000 1,为非常显著,用**表示;P≤0.05,为显著,用*表示;P>0.05,为不显著。 -
[1] 刘立伟, 赵礼兵, 李国峰, 等. 某钒钛磁铁精矿深度还原-磁选试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6): 56-63.LIU L W , ZHAO L B , LI G F, et al. Study on coal-based reduction followed by magnetic separation of a vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2020(6): 56-63.
LIU L W , ZHAO L B , LI G F, et al. Study on coal-based reduction followed by magnetic separation of a vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2020(6): 56-63.
[2] 范兴祥, 余宇楠, 袁威, 等. 利用云南钛铁精矿制备还原铁粉及富钛料的试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(2):52-56.FAN X X, YU Y N, YUAN W, et al. Experimental research on preparation of reduced iron powder and rich titanium materials from Yunnan titanium ore concentrate[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2018(2):52-56.
FAN X X, YU Y N, YUAN W, et al. Experimental research on preparation of reduced iron powder and rich titanium materials from Yunnan titanium ore concentrate[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2018(2):52-56.
[3] 付贵勤, 薛逊, 汪锋, 等. 钒钛酸性渣还原过程中钒钛赋存状态的研究[J]. 矿产资源综合利用, 2009(2):40-44.FU G Q, XUE X, WANG F, et al. Study on the occurrence of Ti during reduction process of the acidic vanadium -titanium[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2009(2):40-44.
FU G Q, XUE X, WANG F, et al. Study on the occurrence of Ti during reduction process of the acidic vanadium -titanium[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2009(2):40-44.
[4] 张世敏, 黄孟阳, 彭金辉, 等. 微波还原越南钛精矿制备初级富钛料新工艺研究[J]. 矿产资源综合利用, 2007(3):17-20.ZHANG S M, HUANG M Y, PENG J H, et al. Study on preparing primary titanium materials from self-reduced pellet 0f vietnam ilmenite concentrate by microwave reduction[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2007(3):17-20.
ZHANG S M, HUANG M Y, PENG J H, et al. Study on preparing primary titanium materials from self-reduced pellet 0f vietnam ilmenite concentrate by microwave reduction[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2007(3):17-20.
[5] 刘云龙, 郭培民, 庞建明, 等. 高杂质钛铁矿固态催化还原动力学研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2013, 34(6):1-5.LIU Y L, GUO P M, PANG J M, et al. Kinetics study on solid-phase catalytic reduction of highly impure ilmenite by thermal analysis[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(6):1-5.
LIU Y L, GUO P M, PANG J M, et al. Kinetics study on solid-phase catalytic reduction of highly impure ilmenite by thermal analysis[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(6):1-5.
[6] Y. Zhao, F. Shadman. Kinetics and mechanism of ilmenite reduction with carbon monoxide[J]. AICHE Journal, 1990, 36(9):1433-1438. doi: 10.1002/aic.690360917
[7] J. Pesl, R. H. Eric. High temperature carbothermic reduction of Fe2O3-TiO2-MxOy oxide mixtures[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2002(15):971-984.
[8] WANG Yu-ming, YUAN Zhang-fu, GUO Zhan-cheng, et al. Reduction mechanism of natural ilmenite with graphite[J]. Tansaction. Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 180:962-968.
[9] C. S. Kucukkaragoz, R. H. Eric. Solid state reduction of a nature ilmenite[J]. Miners Engineering, 2006, 19:334-337. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005.09.015
[10] Hai-peng GOU, Guo-hua ZHANG, Xiao-jun HU, et al. Kinetic study on carbothermicreduction of ilmenite with activated carbon[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(8):1856-1861. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60209-7
[11] 韩可喜. 钛精矿预还原球团冶炼钛渣的电耗水平分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014, 35(2):51-55.HAN K X. Analysis on electricity consumption for titanium slag smelting with pre-reduced concentrate pellets[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(2):51-55.
HAN K X. Analysis on electricity consumption for titanium slag smelting with pre-reduced concentrate pellets[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(2):51-55.
[12] 信晓飞, 张晋霞, 冯洪均. 响应曲面法优化含锌尘泥选择性浸出工艺[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):146-151.XIN X F, ZHANG J X, FENG H J. Optimization of selective leaching technology from zinc-bearing dust using response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2021(2):146-151.
XIN X F, ZHANG J X, FENG H J. Optimization of selective leaching technology from zinc-bearing dust using response surface methodology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral, 2021(2):146-151.
[13] 吕学伟, 张凯, 黄润, 等. 添加剂对钛精矿固相碳热还原强化作用的比较[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 34(11):1601-1605.LU X W, ZHANG K, HUANG R. Comparison of the effects of different additives on the solid phase carbon thermal reduction of ilmenite[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2013, 34(11):1601-1605.
LU X W, ZHANG K, HUANG R. Comparison of the effects of different additives on the solid phase carbon thermal reduction of ilmenite[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2013, 34(11):1601-1605.
[14] 郭兴敏, 唐洪福, 张圣弼. Li2CO3在含碳球团中催化机理的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2000, 36(6):638-641.GUO X M, TANG H F, ZHANG S B. Study on the catalysis mechanism of Li2CO3 for reduction of iron ore pellet with carbon[J]. Acta Metellurgical Sinica, 2000, 36(6):638-641.
GUO X M, TANG H F, ZHANG S B. Study on the catalysis mechanism of Li2CO3 for reduction of iron ore pellet with carbon[J]. Acta Metellurgical Sinica, 2000, 36(6):638-641.
[15] 刘牡丹, 姜涛, 李光辉. 硫酸钠和碳酸钠对高铝铁矿钠化还原动力学规律的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(1):220-226.LIU M D, JIANG T, LI G H. Effects of Na2SO4 and Na2CO3 on sodium-reduction dynamics law of high aluminum iron ores[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(1):220-226.
LIU M D, JIANG T, LI G H. Effects of Na2SO4 and Na2CO3 on sodium-reduction dynamics law of high aluminum iron ores[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(1):220-226.
[16] 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013.HUANG X G. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013.
HUANG X G. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013.
-



 下载:
下载: