Metallogenesis of Miaoya Nb-REE Deposit with Comparison to Typical Carbonatite-Alkaline Rock-Related Nb-REE Deposits in China
-
摘要:
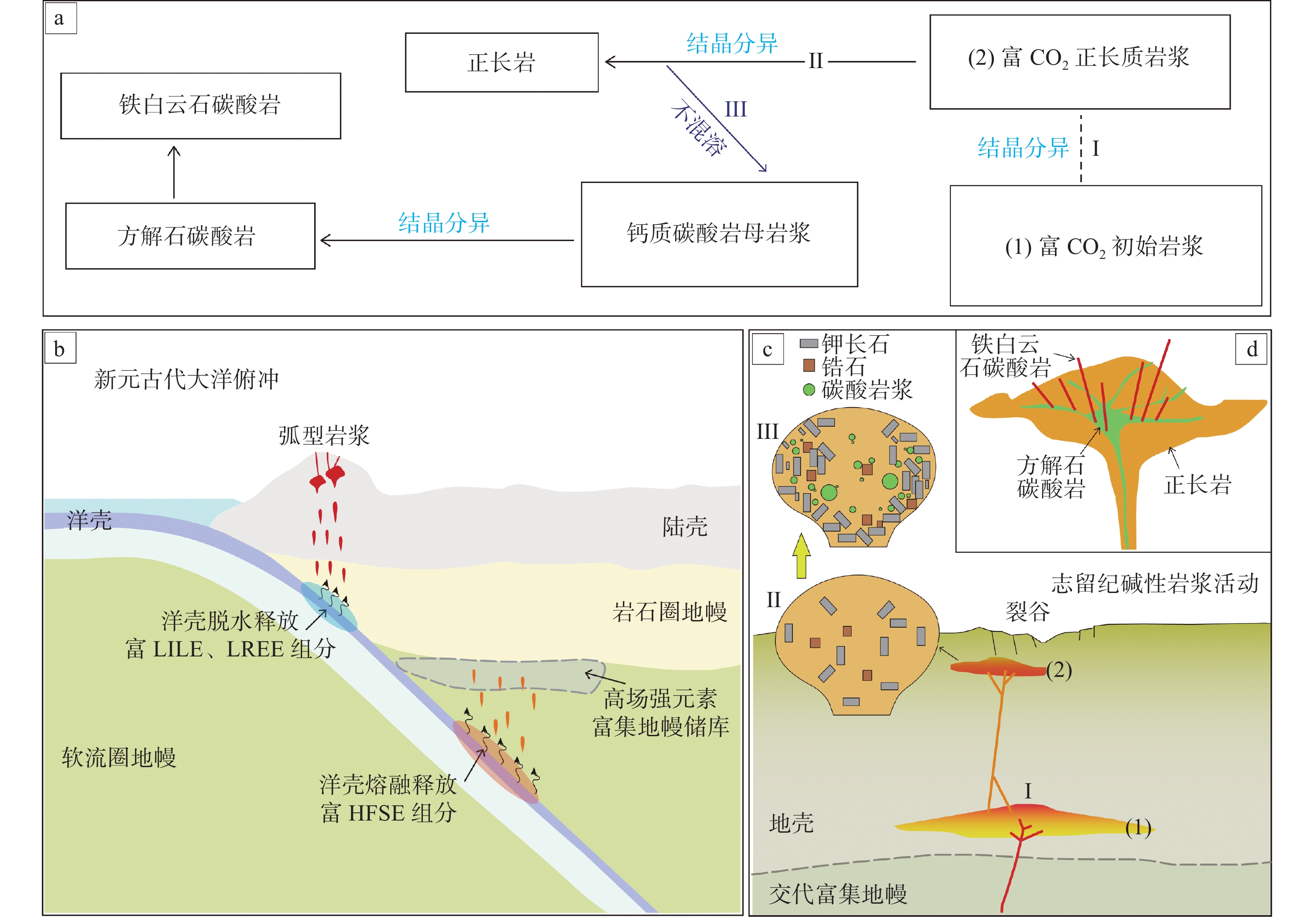
稀土元素(REE)和铌(Nb)等战略性关键金属主要赋存在碳酸岩和(或)碱性岩体中。因此,碳酸岩-碱性岩型铌稀土矿床成矿作用研究具有重要的科学意义和经济价值。本文以湖北庙垭碳酸岩-正长岩型铌稀土矿床为例,详细综述了其矿床地质、成岩成矿年代学及矿床模式等方面的相关研究进展,并以“比较矿床学”的方法,将其与国内其他典型碳酸岩-碱性岩型铌稀土矿床进行了对比。通过系统对比,本文指出地幔源区富集组分、岩浆演化程度以及岩浆期后热液流体作用程度的差异是控制碳酸岩-碱性岩型铌稀土矿床成矿差异性的关键因素。庙垭铌稀土矿床由于相对低的热液流体作用程度,稀土品位相对偏低导致稀土资源的经济性偏低。对庙垭铌稀土矿床的开发利用应以其中丰富的铌资源为重点进行攻关,在当前高的铌对外高依存度形势下有望改善我国的铌矿资源格局。
Abstract:REE and Nb are strategic and critical metals mainly sourced from carbonatite-alkaline rocks. Thus, it is of great scientific and economic significance for the research on metallogenic mechanism of Nb-REE deposits associated with carbonatite-alkaline rocks. In this paper, we have detailedly summarized the recent progress in Miaoya Nb-REE deposit from Hubei which is related with carbonatite-syenite complex, with respect to geological characteristics, chronology, genesis and metallogenic model. Meanwhile, the method of “comparative metallogeny” is used for its comparison with other typical Nb-REE deposits of the same type from China. Through systematic analysis, we point out that the difference in enriched component introduced into mantle source, the degree of magma evolution, and the intensity of post-magmatic hydrothermal fluid activity are the key factors controlling the mineralization differences of carbonatite-alkaline rock-related Nb-REE deposits. Due to the relatively low-intensity hydrothermal fluid activity, the REE grade of the Miaoya deposit is correspondingly low, leading to the low economic value of its rare earth resources. The rich niobium resources should be focused on with the development and utilization of the Miaoya deposit, which is expected to lower down the currently high external dependency on niobium for China and improve China’s niobium resource pattern.
-
Key words:
- Miaoya /
- carbonatite-alkaline rock /
- critical metals /
- Nb-REE /
- comparative metallogeny
-

-
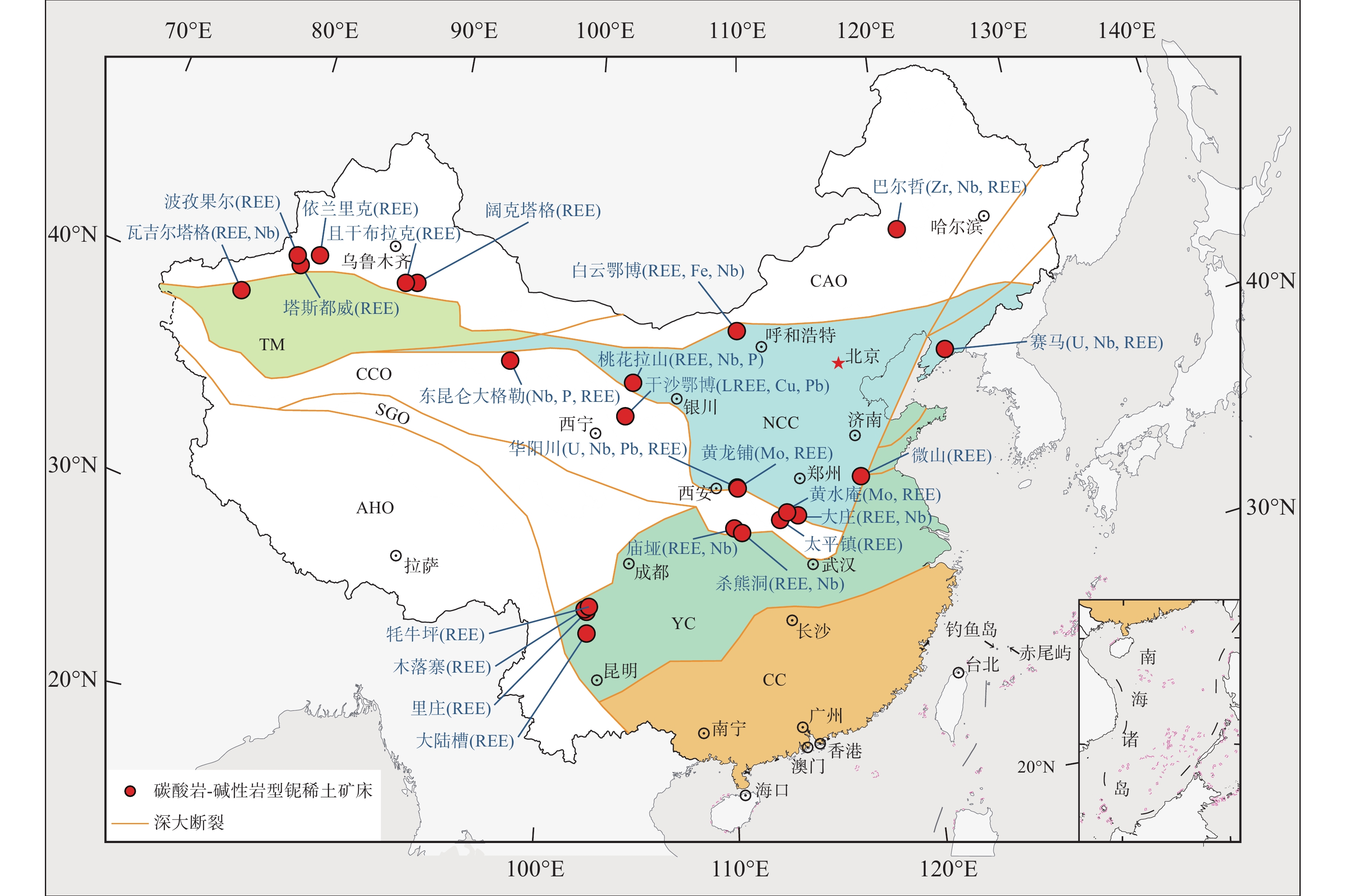
表 1 我国主要碳酸岩-碱性岩型铌稀土矿床岩石类型、矿种组合、矿化品位及储量
Table 1. Ore type, mineralization, grade, and reserves of main Nb-REE deposits related to carbonatite-alkaline complex in China
矿床名称 地理位置 岩石类型 矿种组合 REO
平均品位
(wt.%)REO储量(t) Nb2O5
平均品位
(wt.%)Nb2O5
储量(t)参考文献 白云鄂博 内蒙古包头 白云质火成
碳酸岩REE、Fe、Nb 6 57400000 0.13 2200000 Fan H R et al., 2016 牦牛坪 四川冕宁 碳酸岩‒
碱性杂岩体REE 2.95 3170000 Liu Y and Hou Z Q, 2017 庙垭 湖北竹山 碳酸岩‒
碱性杂岩体REE、Nb 1.73 1210000 0.12 930000 马玉兴等, 1981 巴尔哲 内蒙古哲里木 碱性花岗岩 Zr、Nb、REE ~1 1000000 0.26 > 100000 Yang W B et al., 2020 干沙鄂博 甘肃武威 碱性正长岩 LREE、Cu、Pb 1.39~1.65 ~ 600000 黄增保, 2019 华阳川 陕西华阴 火成碳酸岩脉 U、Nb、Pb、REE 0.085 550000 0.019 110000 高成等, 2017 微山 山东郗山 碱性正长岩 REE 3~10 440000 李建康等, 2008 赛马 辽宁凤城 碱性正长岩 U、Nb、REE 0.3~4.5 0.04 ~0.05 何宏平和杨武斌, 2022;
南哲等,2023太平镇 河南西峡 斜长花岗岩 REE 2.26~2.97 170000 王瑞利, 2022 黄水庵 河南嵩县 火山碳酸岩脉 Mo、REE 王汉辉, 2023 大庄 河南方城 碱性正长岩 REE、Nb 0.076~0.151 30147 0.05~0.1 16245 李山坡, 2022 黄龙铺 陕西华阴 火成碳酸岩脉 Mo、REE > 2000 Zhao X C et al., 2021 木落寨 四川冕宁 碳酸岩‒
碱性杂岩体REE 3.97 100000 Liu Y and Hou Z Q, 2017 大陆槽 四川德昌 碳酸岩‒
碱性杂岩体REE 5.21 82000 Liu Y and Hou Z Q, 2017 里庄 四川冕宁 碳酸岩‒
碱性杂岩体REE 1.47~1.63 5800 Liu Y and Hou Z Q, 2017 东昆仑
大格勒青海格尔木 碳酸岩‒
碱性杂岩体Nb、P、REE 0.12~0.29 0.092 ~
0.156潜在资源> 100000 李五福等, 2024;
金婷婷等,2023;
王涛等, 2024桃花拉山 内蒙古
阿拉善右旗火成碳酸岩 REE、Nb、P 0.3~1.15 0.04~0.2 蒋荣良, 1989 阔克塔格 新疆尉犁 碱性正长岩 REE 0.045~0.099 0.05 邹天人等, 2002 塔斯都威 新疆拜城 火成碳酸岩 REE 0.037~0.111 邹天人等, 2002 且干布拉克 新疆尉犁 火成碳酸岩 REE 0.087~0.163 邹天人等, 2002 瓦吉尔塔格 新疆巴楚 火成碳酸岩 REE、Nb 3.46 5678 0.005~0.29 邹天人等, 2002 波孜果尔 新疆拜城 碱性花岗岩 REE 0.07~0.19 邹天人等, 2002 依兰里克 新疆拜城 碱性岩脉 REE 0.02~1.55 袁忠信等, 2012 表 2 庙垭、白云鄂博、牦牛坪碳酸岩-碱性岩型(铌)稀土矿床对比
Table 2. Comparison of Miaoya, Bayan Obo and Maoniuping carbonatite-alkaline rock-related (Nb)REE deposits
对比项 庙垭 牦牛坪 白云鄂博 含矿岩体
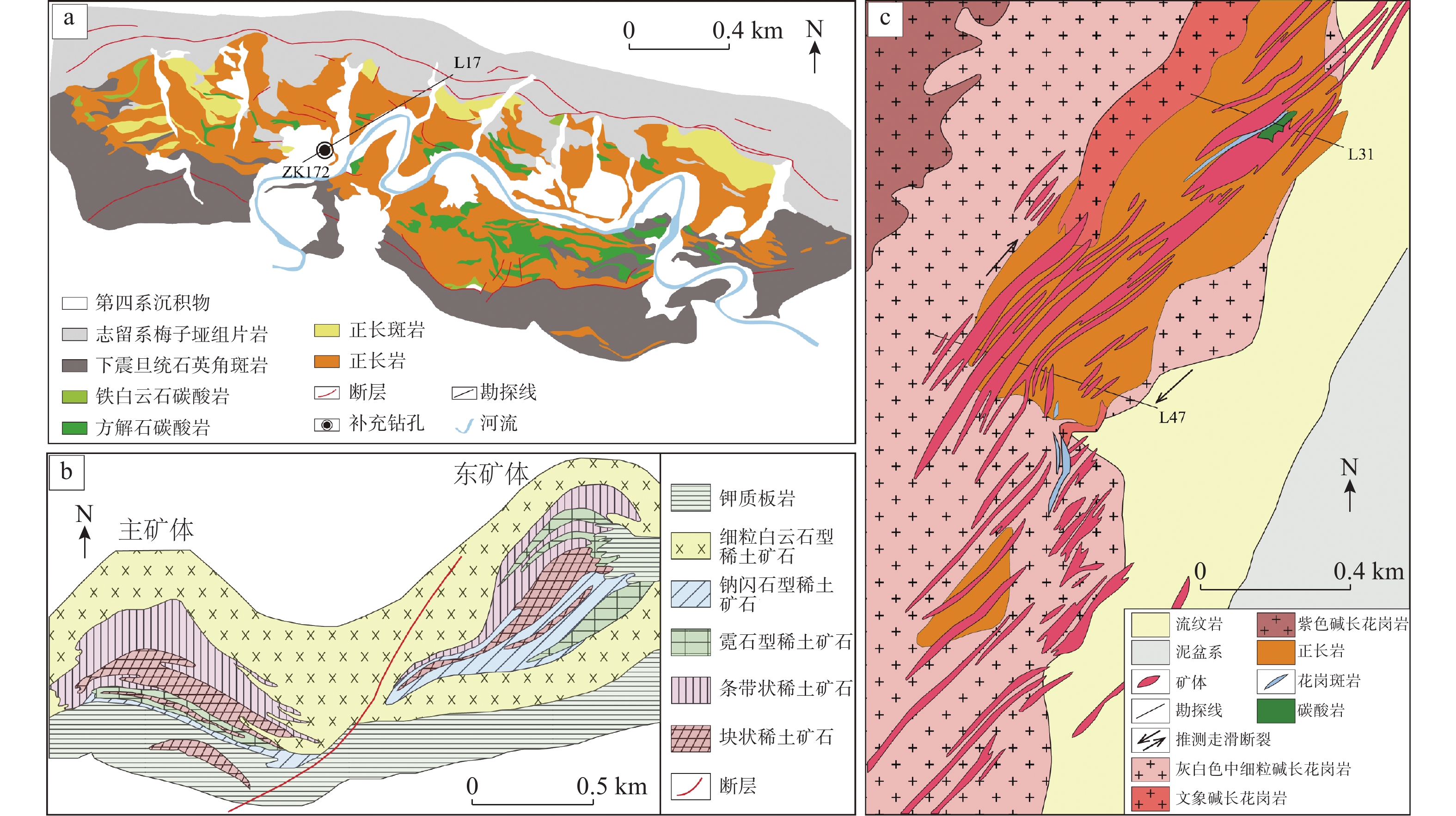
岩石组合正长岩类、(黑云母)方解石碳酸岩、含炭方解石碳酸岩、铁白云石碳酸岩 正长岩、方解石碳酸岩、霓辉重晶伟晶岩、碱性花岗斑岩 以白云质碳酸岩为主,铁白云石碳酸岩墙、方解石-白云石碳酸岩墙、方解石碳酸岩墙穿插 矿石类型 块状、细脉状 脉状、条带状、细脉浸染状 块状、条带状、细脉浸染状 有用矿物
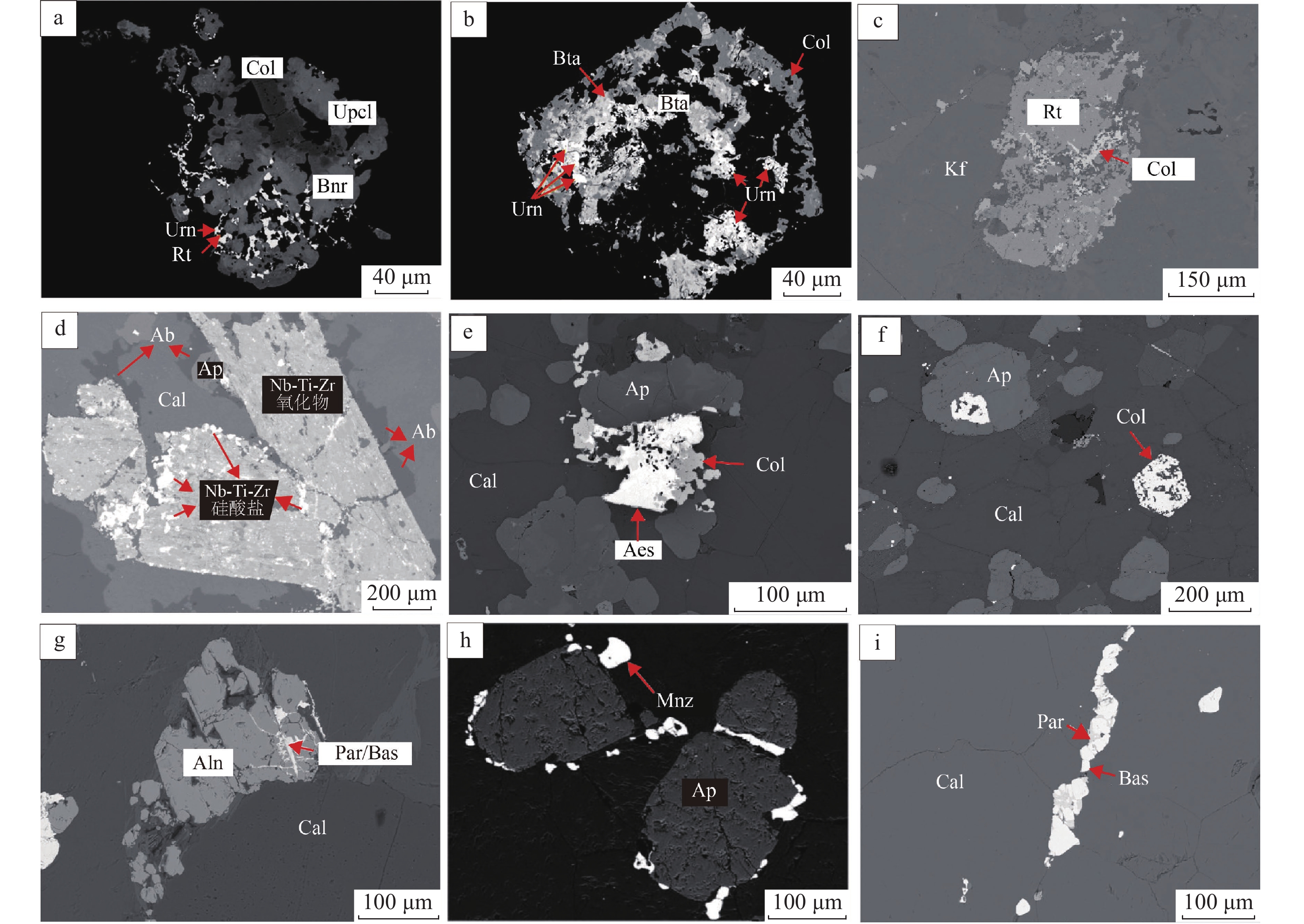
类型铌矿物 正长岩:铌铁矿、铌金红石、铌钛铀矿;方解石碳酸岩:铌铁矿、铌金红石、易解石、烧绿石、铌钙矿 易解石、铌铁矿、烧绿石、铌金红石、褐钇铌矿、包头矿 稀土
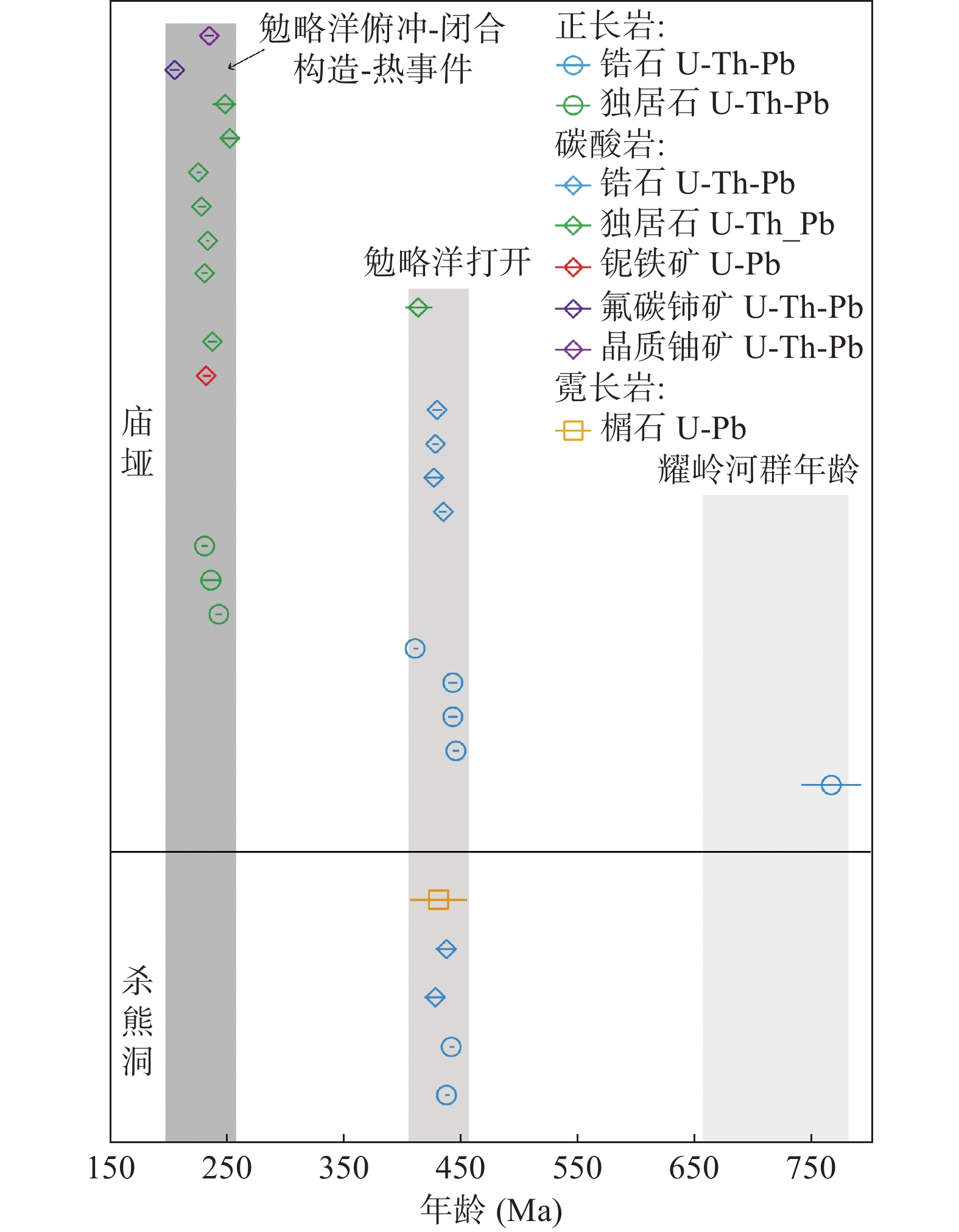
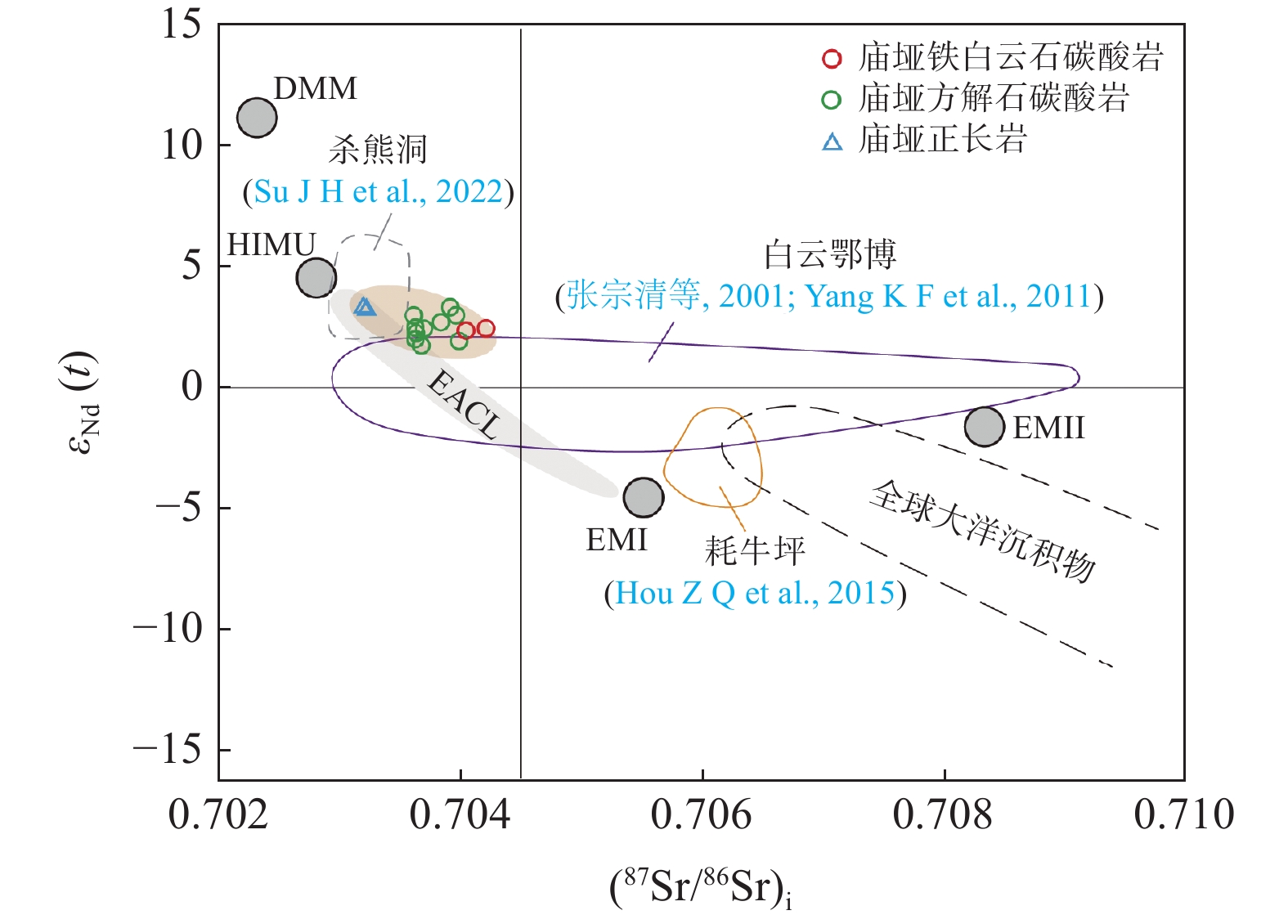
矿物方解石碳酸岩:独居石、褐帘石、氟碳铈矿和氟碳钙铈矿;铁白云石碳酸岩:氟碳铈矿 氟碳铈矿 以独居石和氟碳铈矿为主,其次为氟碳钙铈矿、铈硅石、黄河矿、氟碳铈钡矿 热液蚀变 缺乏典型岩浆热液蚀变霓长岩化,局部发育萤石-石英-方解石脉;黄铁矿、磁黄铁矿等晚期低温热液蚀变普遍 霓长岩化广泛,形成氟碳铈矿-霓辉石-萤石-重晶石、氟碳铈矿-霓辉石-微斜长石、氟碳铈矿-萤石-重晶石-方解石脉型多种矿化蚀变组合 霓长岩化广泛,霓石、钠闪石、镁钠闪石、金云母、透辉石、碱性长石、萤石、重晶石等热液蚀变矿物组合 地幔源区 以HIMU为主,兼具EMI EMI HIMU-EMI-EMⅡ 矿床类型 岩浆型 热液型 热液型 年龄(Ma) 420 ~ 440 12 ~ 40 1300 -
[1] 陈 彪,贾晓琪,魏 威,金海龙.2024.内蒙古白云鄂博矿床年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报,43(1):63-73.
[2] 陈 唯,应元灿,柳加俊,杨 帆,蒋少涌.2024.与碳酸岩-碱性岩有关的铌-稀土矿床成矿作用及成因机制[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,43(1):1-14.
[3] 陈 唯.2015.碳酸岩型铌矿床成矿作用[J]. 矿物学报,35(S1):276.
[4] 邓 淼,韦春婉,许 成,石爱国,李卓骐,范朝熙,匡光喜.2022.白云鄂博超大型稀土矿床成因评述[J]. 地学前缘,29(1):14-28.
[5] 高 成,康清清,江宏君,郑 惠,李 鹏,张熊猫,李 雷,董强强,叶兴超,胡小佳.2017.秦岭造山带发现新型铀多金属矿:华阳川与伟晶岩脉和碳酸岩脉有关的超大型铀-铌-铅-稀土矿床[J]. 地球化学,46(5):446-455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.05.004
[6] 何宏平,杨武斌.2022.我国稀土资源现状和评价[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,46(5):829-841.
[7] 侯增谦,田世洪,谢玉玲,袁忠信,杨竹森,尹淑苹,费红彩,邹天人,李小渝,杨志明.2008.川西冕宁-德昌喜马拉雅期稀土元素成矿带:矿床地质特征与区域成矿模型[J]. 矿床地质,27(2):145-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.02.002
[8] 胡 朋,刘国平,江思宏,莫江平.2023.全球稀土矿床的主要类型和成因研究进展[J]. 矿产勘查,14(5):691-700.
[9] 黄增保,李葆华,董晓燕,傅太宇,许 龙,高昆丽,陈 晨,郑 慧,朱永新.2019.北祁连干沙鄂博稀土元素矿床地质和矿床地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质,38(1):129-143.
[10] 江 拓,邱啸飞,卢山松,张利国,杨红梅,彭练红. 2019. 扬子北缘早志留世大陆裂谷:来自南秦岭天宝铌矿双峰式火山岩的证据[A]. //中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第17届学术年会论文摘要集[C].
[11] 蒋荣良.1989.内蒙阿右旗桃花拉山稀有稀土矿床地质特征及赋存规律[J]. 西北地质,(3):41-48.
[12] 金婷婷,王秉璋,王 涛,李五福,刘建栋,袁博武,付长垒,李玉龙,张新远,韩晓龙,郑 英,曹锦山.2023.东昆仑大格勒富铌碳酸岩矿物学特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,47(6):1-15.
[13] 赖绍聪,杨 航,张方毅.2024.南秦岭早古生代碱性岩地球化学特征及其成因机制:研究进展与展望[J]. 地质学报,98(3):799-828.
[14] 李建康,白 鸽,袁忠信,应立娟,张 建.2008.富氟钡型碳酸岩岩浆的演化机制及其成矿效应[J]. 地质论评,54(6):793-800.
[15] 李山坡,乔欣欣,陈俊魁,郑 凯,潘小娜,吴祥珂,张哨波,张荣臻,高传宝.2022.河南方城大庄铌-稀土矿床碱性正长岩成矿机理研究[J]. 中国地质,49(4):1224-1235.
[16] 李 石.1980.湖北庙垭碳酸岩地球化学特征及岩石成因探讨[J]. 地球化学,(4):345-355.
[17] 李五福,王 涛,王秉璋,张新远,谭运鸿,袁博武,王春涛,韩晓龙,金婷婷,郑 英,曹锦山,王泰山,张 焜,付长垒,陈 健,刘建栋,李 青,张启龙,陈丽娟.2024.东昆仑大格勒地区稀有和稀土矿化碱性杂岩体的发现及意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,48(1):38-49.
[18] 刘 琰,舒小超.2021.碳酸岩型稀土矿床中的霓长岩化作用概述[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,40(5):1025-1033+996-997.
[19] 鲁显松,周 豹,孙 腾,朱 金,冷双梁,熊意林.2021.鄂西北地区碱性岩-碳酸岩及相关铌钽-稀土矿研究与勘查进展[J]. 资源环境与工程,35(3):279-284+312.
[20] 马玉兴,朱惠民,顾同瑚,等. 1981. 湖北省竹山县庙垭铌、稀土矿区详查--初勘地质报告[DS]. 全国地质资料馆,DOI:10.35080/n01.c.67233.
[21] 南 哲,王林世,侯 旭,翟征博,王 杨,刘 洋.2023.赛马碱性岩稀有稀土矿地质化学特征及找矿潜力[J]. 物探与化探,47(3):670-680.
[22] 邱啸飞,蔡应雄,江 拓,卢山松,彭练红,赵小明,彭三国,朱 江.2017.庙垭铌-稀土矿床的热液蚀变作用:来自碳酸岩碳-氧同位素的制约[J]. 华南地质与矿产,33(3):275-281.
[23] 沈莽庭,郭维民,徐 鸣,孙建东.2021.巴西铌钽矿典型矿床特征及其资源分布规律和找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质,40(3):603-624.
[24] 石 林,解广轰,夏 斌.1998.地幔端元组分的微量元素地球化学研究综述[J]. 地质地球化学,(2):77-82.
[25] 宋文磊,许 成,刘 琼,王林均,吴 敏,曾 亮.2012.火成碳酸岩的实验岩石学研究及对地球深部碳循环的意义[J]. 地质论评,58(4):726-744.
[26] 苏建辉. 2023. 南秦岭早古生代碱性岩-碳酸岩岩浆作用及铌-稀土成矿机制[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文.
[27] 王登红,刘善宝,王成辉,于 扬,赵 芝,代鸿章.2023.我国三稀矿产找矿进展述评与新一轮找矿建议[J]. 中国地质调查,10(5):1-8.
[28] 王汉辉,唐 利,杨勃畅,唐吉根,张彦生,郭 俊,冯嘉颖,盛渊明.2023.东秦岭黄水庵碳酸岩型Mo-REE矿床方解石地球化学特征和氟碳铈矿U-Th-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 西北地质,56(1):48-62.
[29] 王 珂,王连训,朱煜翔,马昌前,黄宏业.2024.湖北庙垭碳酸岩杂岩体中铌赋存状态及富集机制:矿物化学制约[J]. 地球科学,49(2):594-611.
[30] 王瑞利.2022.豫西太平镇稀土矿床地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 现代矿业,38(8):41-44+56.
[31] 王 涛,王秉璋,袁博武.2024.东昆仑大格勒地区碱性岩‒碳酸岩型铌矿勘查进展及找矿前景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,48(1):50-60.
[32] 韦春婉,许 成,付 伟,易泽邦,李卓骐,石爱国,范朝熙,匡光喜.2022.稀土元素在岩浆和水热系统的实验岩石学和地球化学研究进展[J]. 岩石学报,38(2):455-471.
[33] 翁 强,牛贺才,杨武斌,李宁波,单 强.2022.川西碱性岩-碳酸岩型稀土矿床成矿模型[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,41(3):465-473+464.
[34] 吴 敏,许 成,王林均,宋文磊.2011.庙垭碳酸岩型稀土矿床成矿过程初探[J]. 矿物学报,31(3):478-484.
[35] 谢玉玲,曲云伟,杨占峰,梁 培,钟日晨,王其伟,夏加明,李必成.2019.白云鄂博铁、铌、稀土矿床:研究进展、存在问题和新认识[J]. 矿床地质,38(5):983-1003.
[36] 谢玉玲,夏加明,崔 凯,曲云伟,梁 培,钟日晨.2020.中国碳酸岩型稀土矿床:时空分布与成矿过程[J]. 科学通报,65(33):3794-3808.
[37] 杨 成,刘成新,刘万亮,万 俊,段先锋,张 众.2017.南秦岭竹溪县天宝乡粗面岩地球化学特征与铌成矿[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,36(5):605-618.
[38] 杨道明,潘荣昊,王 萌,侯 通.2022.成矿碳酸岩的实验岩石学研究现状与展望[J]. 地学前缘,29(1):54-64.
[39] 尹淑苹,谢玉玲,侯增谦,曲云伟.2024.碳酸岩研究进展[J]. 岩石学报,40(3):1003-1022.
[40] 袁忠信,李建康,王登红,郑国栋,娄德波,陈郑辉,赵 芝,于 扬. 2012. 中国稀土矿床成矿规律[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
[41] 张宗清,唐索寒,王进辉,袁忠信,白 鸽.2001.白云鄂博矿床白云岩的Sm-Nd、Rb-Sr同位素体系[J]. 岩石学报,(4):637-642.
[42] 朱 江,程昌红,王连训,彭三国,彭练红,许 珂.2017.南秦岭竹山地区早古生代碱性岩浆活动及其相关铌稀土成矿的若干认识[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,36(5):681-690.
[43] 邹天人,徐 珏,陈伟十,夏凤荣.2002.塔里木盆地北缘碱性岩型稀有稀土矿床[J]. 矿床地质,21(S1):845-848.
[44] Anenburg M, Broom-Fendley S, Chen W. 2021. Formation of rare earth deposits in carbonatites[J]. Elements, 17(5): 327-332.
[45] Bell K, Tilton G R. 2001. Nd, Pb and Sr isotopic compositions of East African carbonatites: Evidence for mantle mixing and plume inhomogeneity[J]. Journal of Petrology, 42(10): 1927-1945.
[46] Berndt J, Klemme S. 2022. Origin of carbonatites-liquid immiscibility caught in the act[J]. Nature Communications, 13: 2892.
[47] Chen W, Lu J, Jiang S Y, Ying Y C, Liu Y S. 2018. Radiogenic Pb reservoir contributes to the rare earth element (REE) enrichment in South Qinling carbonatites[J]. Chemical Geology, 494: 80-95.
[48] Dalton J A, Presnall D C. 1998. Carbonatitic melts along the solidus of model lherzolite in the system CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-CO2 from 3 to 7 GPa[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 131(2-3): 123-135.
[49] Fan H R, Hu F F, Yang K F, Wang K Y. 2006. Fluid unmixing/immiscibility as an ore-forming process in the giant REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolian, China: evidence from fluid inclusions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 89: 104-107.
[50] Fan H R, Yang K F, Hu F F, Liu S, Wang K Y. 2016. The giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, China: Controversy and ore genesis[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(3): 335-344.
[51] Foley S F, Yaxley G M, Rosenthal A, Buhre S, Kiseeva E S, Rapp R P, Jacob D E. 2009. The composition of near-solidus melts of peridotite in the presence of CO2 and H2O between 40 and 60 kbar[J]. Lithos, 112: 274-283.
[52] Gervasoni F, Klemme S, Rohrbach A, Grützner T, Berndt J. 2017. Experimental constraints on the stability of baddeleyite and zircon in carbonate- and silicate-carbonate melts[J]. American Mineralogist, 102(4): 860-866.
[53] Hart S R, Hauri E H, Oschmann L A, Whitehead J A. 1992. Mantle plumes and entrainment: isotopic evidence[J]. Science, 256: 517-520.
[54] Hou Z Q, Liu Y, Tian S H, Yang Z M, Xie Y L. 2015. Formation of carbonatite related giant rare-earth-element deposits by the recycling of marine sediments[J]. Scientific Reports, 5: 10231.
[55] Kessel R, Schmidt M, Ulmer P, Pettke T. 2005. Trace element signature of subduction-zone fluids, melts and supercritical liquids at 120-180 km depth[J]. Nature, 437: 724-727.
[56] Kjarsgaard B A. 1998. Phase relations of a carbonated high CaO nephelinite at 0.2 and 0.5 GPa[J]. Journal of Petrology, 39(11-12): 2061-2075.
[57] Liu Y, Hou Z Q. 2017. A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite-syenite-hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 35-79.
[58] Ma R L, Chen W T, Zhang W, Chen Y W. 2021. Hydrothermal upgrading as an important tool for the REE mineralization in the Miaoya carbonatite-syenite complex, Central China[J]. American Mineralogist, 106: 1690-1703.
[59] Mariano A N. 1989. Carbonatites: genesis and evolution: Nature of economic mineralization in carbonatites and related rocks[M]. London: Unwin Hyman, Bell K.
[60] Migdisov A, Williams-Jones A E, Brugger J, Caporuscio F A. 2016. Hydrothermal transport, deposition, and fractionation of the REE: Experimental data and thermodynamic calculations[J]. Chemical Geology, 439: 13-42.
[61] Pintér Z, Foley S F, Yaxley G M, Rosenthal A, Rapp R P, Lanati A W, Rushmer T. 2021. Experimental investigation of the composition of incipient melts in upper mantle peridotites in the presence of CO2 and H2O[J]. Lithos, 396-397: 106224.
[62] Plank T, Langmuir C H. 1998. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 145: 325-394.
[63] Smith M P, Moore K, Kavecsanszki D, Finch A A, Kynicky J, Wall F. 2016. From mantle to critical zone: A review of large and giant sized deposits of the rare earth elements[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 7: 315-334.
[64] Su J H, Zhao X F, Li X C, Hu W, Chen M, Xiong Y L. 2019. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Miaoya syenite-carbonatite complex, Central China: Implications for the origin of REE-Nb-enriched carbonatite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 113: 103101.
[65] Su J H, Zhao X F, Li X C, Hu W, Chen W, Slezak P. 2022. Unmixing of REE-Nb enriched carbonatites after incremental fractionation of alkaline magmas in the Shaxiongdong complex, Central China[J]. Lithos, 416-417: 106651.
[66] Su J H, Zhao X F, Li X C, Su Z K, Liu R, Qin Z J, Chen M. 2021. Fingerprinting REE mineralization and hydrothermal remobilization history of the carbonatite alkaline complexes, Central China: Constraints from in situ elemental and isotopic analyses of phosphate minerals[J]. American Mineralogist, 106: 1545-1558.
[67] Wallace M E, Green D H. 1988. An experimental determination of primary carbonatite magma composition[J]. Nature, 335: 343-346.
[68] Weidendorfer D, Schmidt M W, Mattsson H B. 2016. Fractional crystallization of Si undersaturated alkaline magmas leading to unmixing of carbonatites on Brava Island (Cape Verde) and a general model of carbonatite genesis in alkaline magma suites[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 171: 43.
[69] Wu B, Hu Y Q, Bonnetti C, Xu C, Wang R C, Zhang Z S. 2021. Hydrothermal alteration of pyrochlore group minerals from the Miaoya carbonatite complex, central China and its implications for Nb mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 132: 104059.
[70] Wu H H, Huang H, Zhang Z C, Wang T, Guo L, Gao Y B, Zhang Z. 2023. Highly differentiated trachytic magma linked with rare metal mineralization: a case study from the Shuanghekou Nb deposit South Qinling[J]. Lithos, 438: 106990.
[71] Xia Y H, Lai S C, Yang H, Zhu Y, Qin J F, Zhu R Z, Liu M, Zhang F Y, Zhong Z H. 2024. Liquid immiscibility acting on the formation of the Miaoya carbonatite-syenite complex in the South Qinling Belt, Central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 264: 106072.
[72] Xie Y L, Hou Z Q, Yin S B, Dominy S C, Xu J H, Tian S H, Xu W Y. 2009. Continuous carbonatitic melt-fluid evolution of a REE mineralization system: Evidence from inclusions in the Maoniuping REE deposit, western Sichuan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 36: 90-105.
[73] Xu C, Campbell I H, Kynicky J, Alle C M, Chen Y J, Huang Z L, Qi L. 2008. Comparison of the Daluxiang and Maoniuping carbonatitic REE deposits with Bayan Obo REE deposit, China[J]. Lithos, 106(1-2): 12-24.
[74] Xu C, Chakhmouradian A R, Kynický J, Li Y X, Song W L, Chen W. 2019. A Paleoproterozoic mantle source modified by subducted sediments under the North China craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 245: 222-239.
[75] Xu C, Chakhmouradian A R, Taylor R N, Kynicky J, Li W B, Song W L, Fletcher I R. 2014. Origin of carbonatites in the South Qinling orogen: Implications for crustal recycling and timing of collision between the South and North China Blocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 189-206.
[76] Xu C, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian A N, Campbell I H, Allen C M. 2010. Trace-element modeling of the magmatic evolution of rare-earth-rich carbonatite from the Miaoya deposit, central China[J]. Lithos, 118: 145-155.
[77] Yang K F, Fan H R, Pirajno F, Li X C. 2019. The Bayan Obo (China) giant REE accumulation conundrum elucidated by intense magmatic differentiation of carbonatite[J]. Geology, 47: 1198-1202.
[78] Yang K F, Fan H R, Santosh M, Hu F F, Wang K Y. 2011. Mesoproterozoic carbonatitic magmatism in the Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia, North China: constraints for the mechanism of super accumulation of rare earth elements[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 40: 122-131.
[79] Yang W B, Niu H C, Li N B, Hollings P, Zurevinski S, Xing C M. 2020. Enrichment of REE and HFSE during the magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the Baerzhe alkaline granite, NE China: Implications for rare metal mineralization[J]. Lithos, 358-359: 105411.
[80] Ying Y C, Chen W, Lu J, Jiang S Y, Yang Y H. 2017. In situ U-Th-Pb ages of the Miaoya carbonatite complex in the South Qinling orogenic belt, central China[J]. Lithos, 290-291: 159-171.
[81] Ying Y C, Chen W, Simonetti A, Jiang S Y, Zhao K D. 2020. Significance of hydrothermal reworking for REE mineralization associated with carbonatite: Constraints from in situ trace element and C-Sr isotope study of calcite and apatite from the Miaoya carbonatite complex (China)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 280: 340-359.
[82] Ying Y C, Chen W, Chakhmouradian A R, Zhao K D, Jiang S Y. 2023. Textural and compositional evolution of niobium minerals in the Miaoya carbonatite-hosted REE-Nb deposit from the South Qinling Orogen of central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 58: 197-220.
[83] Zhang D X, Liu Y, Pan J Q, Dai T G, Bayless R C. 2019. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the Miaoya REE prospect, Qinling orogenic Belt, China: Insights from Sr-Nd-C-O isotopes and LA-ICP-MS mineral chemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 110: 102932.
[84] Zhang W, Chen W T, Gao J, Chen H, Li J. 2019. Two episodes of REE mineralization in the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China: in-situ U-Th-Pb dating of bastnäsite and monazite[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 54(8): 1265-1280.
[85] Zhao X C, Yan S, Niu H C, Zhang Q B, Zhao X, Wu J, Yang W B. 2021. Isotopic fingerprints of recycled eclogite facies sediments in the generation of the Huanglongpu carbonatite, central China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 139(5): 104534.
[86] Zhu J, Wang L X, Peng S G, Peng L H , Wu C X, Qiu X F. 2017. U-Pb zircon age, geochemical and isotopic characteristics of the Miaoya syenite and carbonatite complex, central China[J]. Geological Journal, 52: 938-954.
[87] Zhu X X, Liu Y, Hou Z Q. 2023. Massive rare earth element storage in sub-continental lithospheric mantle initiated by diapirism, not by melting[J]. Geology, 52(2): 105-109.
[88] Zindler A S H. 1986. Chemical Geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 14(1): 493-571.
-



 下载:
下载: