Analysis of Tectonic Activity in the Central-southern Segments of the Luohu Faults, Guangdong Province
-
摘要:
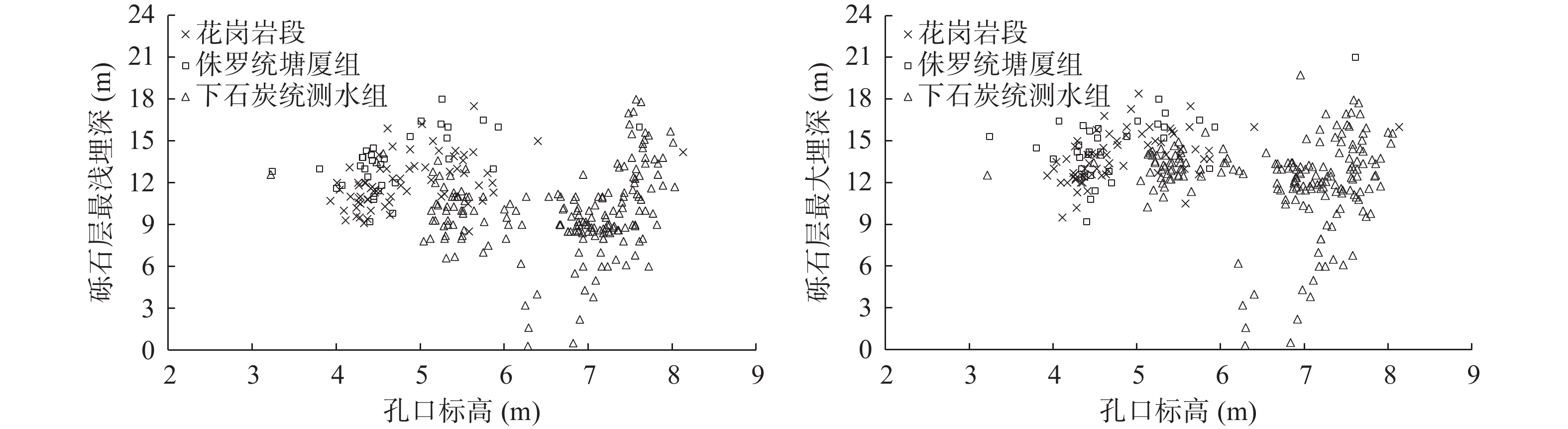
断裂的构造活动性对区域地壳稳定性、地震与变形监测、重大工程的设计和施工等具有重大的影响。本文对罗湖断裂中南段进行地层组成与分布特征、构造变形特征等方面进行研究,结合放射性14C法和伊利石40K-39Ar法等年代学测试手段,发现自中更新世晚期以来,区内断裂带再无明显活动。罗湖断裂先后经历了早白垩世初期的韧性变形和晚白垩世末期的脆性变形,晚白垩世末期的脆性变形活动可能一直持续到古新世早期;始新世中期,罗湖断裂中南段可能又发生了一期构造活动。
Abstract:The tectonic activity of the fault zone has a significant impact on regional crustal stability, earthquake and deformation monitoring, as well as the design and construction of major projects. We focus on studying of the stratigraphic composition, distribution characteristics, and structural deformation characteristics of the central-southern sections of the Luohu Faults, and adopt chronological testing methods such as the radioactive 14C of the strata and the illite 40K-39Ar of the fault gouge, then find that there has been no obviously activity of the Luohu faults since the late Middle Pleistocene. Besides, the Luohu Faults had experienced ductile deformation in the Early Cretaceous and brittle deformation in the Late Cretaceous. The brittle deformation activity in the Late Cretaceous may have continued until the early Paleocene. In the middle Eocene, another phase of tectonic activity may have occurred in the central-southern sections of the Luohu Faults.
-
Key words:
- Luohu faults /
- tectonic activity /
- structural deformation /
- 40K-39Ar method
-

-
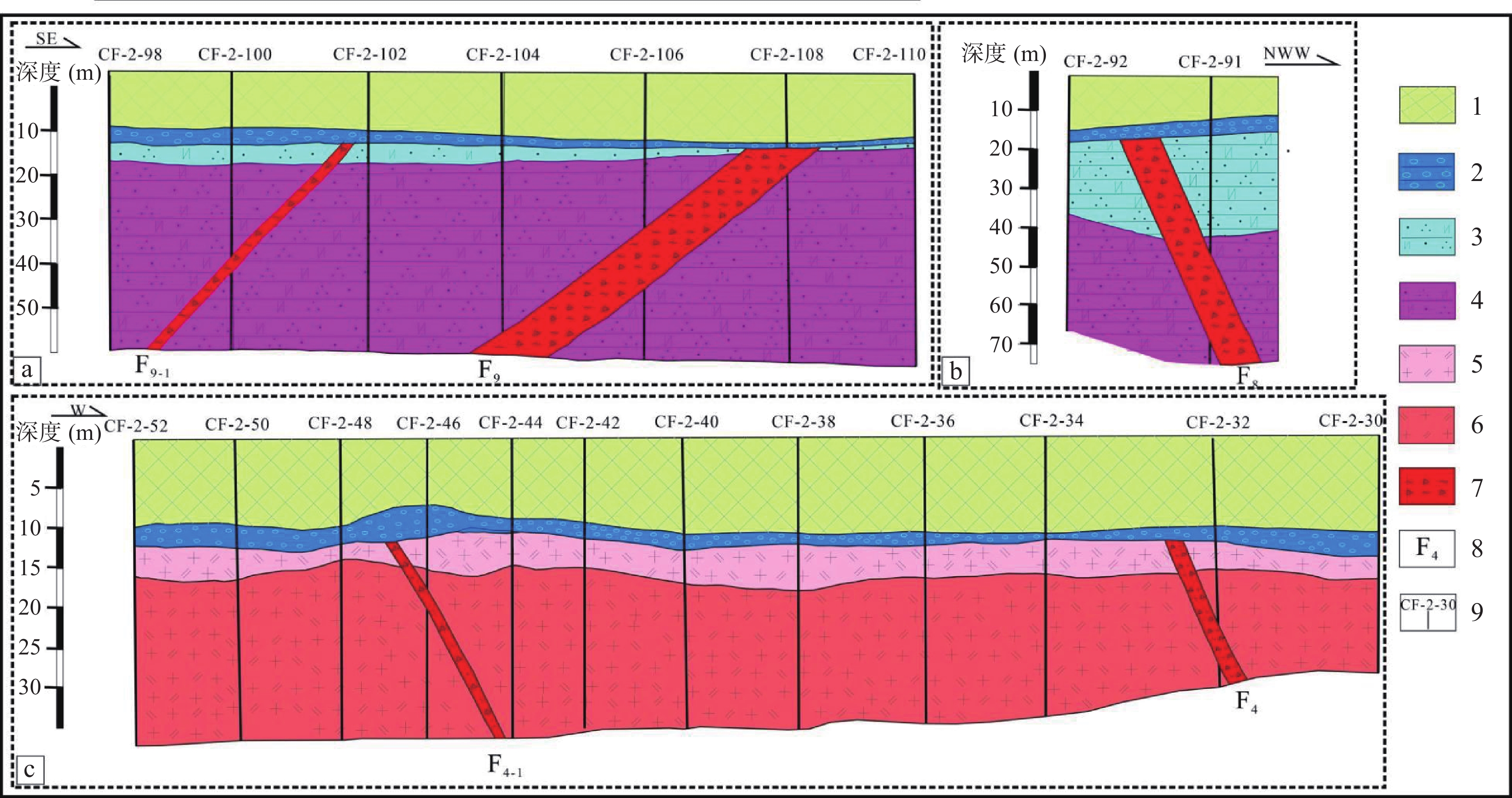
表 1 罗湖断裂钻孔中泥炭的14C测年结果
Table 1. 14C dating results of peat in boreholes in Luohu fauts
样品号 采样地点 采样深度(m) 年龄(a) ZK44 鹿丹村NW侧200 m 6.2 ~ 6.7 36260 ±890ZK133 深圳站E侧300 m 6.4 ~ 7.0 30590 ±1130 表 2 罗湖断裂40K-39Ar法测年结果
Table 2. Dating Results of 40K-39Ar Method for the Luohu Faults
样品号 测试矿物 K(wt.%) 辐射40Ar吸附量(×10−8ccSTP/g) K-Ar年龄(Ma) 非辐射 40Ar占比(%) ZK32 伊利石 6.990±0.140 1858.6 ±20.567.3±1.5 11.6 ZK105 伊利石 7.561±0.151 1901.0 ±19.763.7±1.4 6.1 ZK301 伊利石 5.861±0.117 1077.0 ±16.146.7±1.2 31.0 -
[1] 陈挺光.1989.深圳断裂带基本特征及其现今活动性[J]. 广东地质,4(1):51-61.
[2] 戴 竹,詹 文,石 威,吴鹏飞,余 方.2023.鄂东罗田县典型地热田水文地球化学特征及相关性[J]. 资源环境与工程,37(3):272-280.
[3] 地质矿产部. 1991. 深圳市区域稳定性评价[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
[4] 广东省地质矿产局. 1988. 广东省区域地质志[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
[5] 韩基弘,唐 石,黄长生,陈 威,李 璇,王芳婷,侯萍萍,邹 金,任崇贺.2024.基于水化学特征的赣东南石城-寻乌断裂带地热水成因模式[J]. 华南地质,40(2):413-434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2024.02.016
[6] 贾建业,孙 杰,詹文欢,易顺民.2006.深圳断裂带活动性分析[J]. 广东地质,21(4):1-6.
[7] 康镇江. 2009. 深圳地质[M]. 北京:地质出版社.
[8] 雷东宁,姚运生,但 卫,李 雪,蔡永建,余 松.2018.深圳横岗‒罗湖断裂中南段活动特征及现今构造变形监测[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,42(2):225-234.
[9] 李建超,丘元禧.1990.广东莲花山燕山早期断裂动热变质带的基本特征及形成机制的探讨[J]. 长春地质学院学报,20(1):11-20+123.
[10] 卢演俦,孙建中.1991.广东深圳断裂带活动性的第四纪地质和地貌研究[J]. 地震地质,13(2):138-146.
[11] 马浩明,陈庞龙.2009.深圳市横岗—罗湖断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地质科学,4(3):266-274.
[12] 马淑芝,贾洪彪,易顺民,龚淑云.2006.罗湖断裂带地应力场三维有限元模拟分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,25(S2):3898-3903. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.z2.088
[13] 深圳市地质局. 2013.1:50000深圳市地质图及说明书[M]. 深圳:广东省地图出版社.
[14] 孙 杰,贾建业,詹文欢,易顺民.2007.深圳断裂带构造活动性分析[J]. 地球科学进展,22(3):234-240. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.03.003
[15] 唐 宇. 2017. 深圳罗湖断裂带构造活动性研究及对工程的影响[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文.
[16] 田婷婷,吴中海,张克旗,张绪教.2013.第四纪主要定年方法及其在新构造与活动构造研究中的应用综述[J]. 地质力学学报,19(3):242-266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.03.002
[17] 童 馗,李智武,刘树根,I. Tongu UYSAL,施泽进,李金玺,Andrew TODD,武文慧,王自剑,刘升武,李 轲,华 天.2024.始新世中期安宁河断裂冲断变形特征及其构造意义:来自断层泥自生伊利石K-Ar定年的证据[J]. 地学前缘,31(4):297-313.
[18] 王 军,汪礼明,公凡影,王 艳,王成明,卜 安,朱沛云.2021.粤东莲花山断裂带韧性剪切的温压条件及其对钨锡铜多金属成矿作用的约束[J]. 岩石学报,37(6):1921-1932. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.06.17
[19] 王建军,张鸿旭,李荣强,赵营海,陈加红.2002.深圳市罗湖断裂带活动性及建筑物安全监测系统设计[J]. 灾害学,17(3):14-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2002.03.004
[20] 王晓虎,张文高,陈正乐,周荣德,陈柏林,许典葵,霍海龙,李季霖,张 涛,丁志磊,李效壮.2020.华南沿海莲花山断裂带控矿构造变形时限:来自锆石U-Pb年龄与地层时代的约束[J]. 中国地质,47(4):985-997. doi: 10.12029/gc20200406
[21] 王战鹏,朱珍德,易顺民.2005.深圳罗湖断裂带黄贝岭F8断层流变有限元分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,26(S2):211-214.
[22] 徐 俊,余成华,张桂香,肖 兵,蒋 鹏,陈庞龙.2013.钻孔及探槽探测鉴定横岗-罗湖断裂活动性[J]. 城市勘测,(2):170-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2013.02.047
[23] 徐先兵,邓 飞,王 墩,罗锡宜.2022.基岩区断层泥的物质组成、定年方法与地震断层弱化机制研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,41(5):122-131.
[24] 余成华. 2010. 深圳市断层活动性和地震危险性研究[D]. 浙江大学博士学位论文.
[25] 张 彦,陈克龙,刘新宇.2007.沉积岩中自生伊利石K-Ar定年研究—存在问题及原因讨论[J]. 岩矿测试,26(2):117-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.02.009
[26] 张有瑜,刘可禹,罗修泉. 2016. 自生伊利石年代学研究——理论、方法与实践[M]. 北京:科学出版社.
[27] 赵 奇,闫 义.2021.伊利石K-Ar/Ar-Ar年龄约束浅地表断层活动时间:原理和潜力[J]. 地球科学进展,36(7):671-683.
[28] 郑 勇,李海兵,王世广,白明坤.2019.断层泥自生伊利石年龄分析及其在龙门山断裂带的应用[J]. 地球学报,40(1):173-185. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.102901
[29] 邹和平,王建华,丘元禧.2000.广东南澳和莲花山韧性剪切带40Ar/39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报,21(4):356-364. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.04.004
[30] 邹司雅,季军良,徐亚东,朱 宁.2024.川西高原毛垭坝盆地全新世气候变化[J]. 地质科技通报,43(1):173-183.
[31] Clauer N. 2013. The K-Ar and 40Ar/39Ar methods revisited for dating fine-grained K-bearing clay minerals[J]. Chemical Geology, 354: 163-185. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.030
[32] Davids C, Bergh S G, Wemmer K. 2010. K-Ar and 40Ar/39Ar Dating of Post-Caledonian Brittle Faults in Northern Norway[C]. Thermo, 12th international Conference on Thermochronology, Glasgow, UKl, 16-20.
[33] Davids C, Wemmerb K, Zwingmann H, Kohlmann F, Jacobs J, Bergh S G. 2013. K-Ar illite and apatite fission track constraints on brittle faulting and the evolution of the northern Norwegian passive margin[J]. Tectonophysics, 608: 196-211. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.09.035
[34] Li J H, Cawood P A, Ratschbacher L, Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Xin Y J, Yang H, Zhang P X. 2020. Building Southeast China in the late Mesozoic: Insights from alternating episodes of shortening and extension along the Lianhuashan fault zone[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 201: 103056. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103056
[35] Nagao K. 1984. An age determination by K-Ar method[J]. Bulletin of the Hiruzen Research Institute, 9: 19-38.
[36] Solum J G, van der Pluijm B A, Peacor D R. 2005. Neocrystallization, fabrics and age of clay minerals from an exposure of the Moab Fault, Utah[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 27(9): 1563-1576.
[37] Surace I R, Clauer N, Thélin P, Pfeifer H R. 2011. Structural analysis, clay mineralogy and K-Ar dating of fault gouges from Centovalli Line (Central Alps) for reconstruction of their recent activity[J]. Tectonophysics, 510(1-2): 80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.06.019
[38] Zwingmann H, Offler R, Wilson T, Cox S F. 2004. K-Ar dating of fault gouge in the northern Sydney Basin, NSW, Australia—implications for the breakup of Gondwana[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 26(12): 2285-2295. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2004.03.007
[39] Zwingmann H, Mancktelow N, Antognini M, Lucchini R. 2010. Dating of shallow faults: new constraints from the AlpTransit tunnel site (Switzerland)[J]. Geology, 38(6): 487-490. doi: 10.1130/G30785.1
-




 下载:
下载: