Application of Audio Magnetotelluric Sounding and Acoustic Logging in Tunnel Engineering Surveys: A Case Study of a Tunnel in Eastern Fujian
-
摘要:
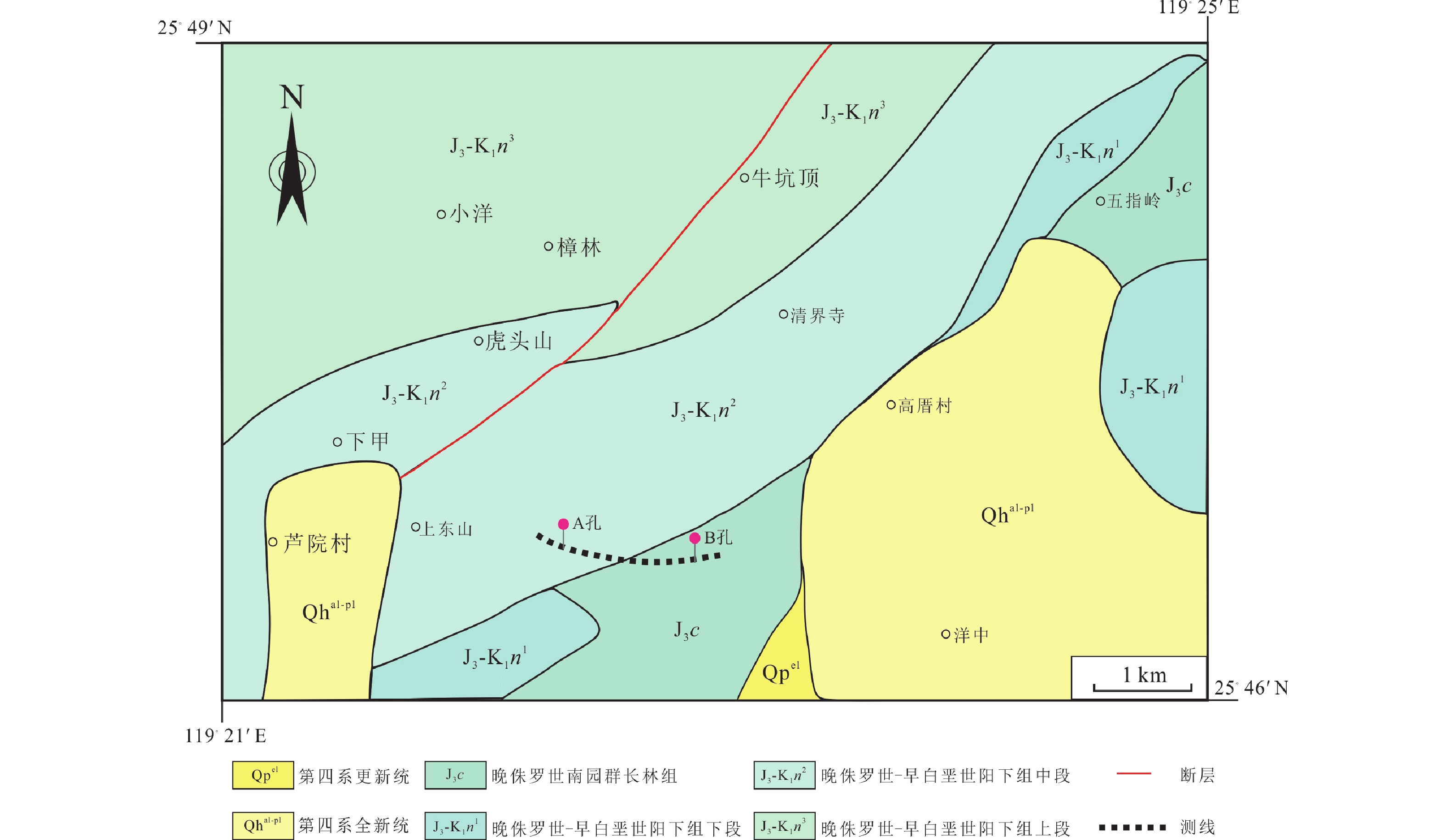
随着隧道工程规模的不断扩大和复杂性的增加,尤其是在复杂的地质条件下,传统的勘察方法已经难以满足现代工程的需求。音频大地电磁法探测范围广、深度大,但地层分辨率相对较低;声波测井虽探测深度和范围有限,却能提供高分辨率的井周围声学数据,弥补了音频大地电磁法在分辨率上的不足;两者结合不仅提高了地层信息的探测精度,还能有效圈定重点区域,指导声波测井的精细测量,为隧道工程勘察提供了高效、全面的解决方案。本文将音频大地电磁测深法和声波测井应用于福建省某隧道工程勘察中,较为准确地探测了地下岩层的电阻率和波速分布。结果显示:P4至P14段电阻率较低,围岩局部较破碎,且埋深较浅,岩石风化比较强,需注意风化层出露后松散塌落;P26至P34、P41至P47段存在两个低阻异常,可能存在含水层,应注意排水重填,以防涌水;P34至P41段埋深最大,电阻率最高,围岩挤压紧密,建议打应力释放孔以释放能量,便于施工。本研究表明将音频大地电磁与声波测井方法结合应用,可为隧道工程勘察提供新的思路。
Abstract:As the scale and complexity of tunnel engineering continue to expand, particularly under complex geological conditions, traditional survey methods have become hard to meet modern engineering needs. The audio magnetotelluric method offers extensive coverage and significant depth but has relatively low stratigraphic resolution. In contrast, acoustic logging, while limited in depth and range, provides high-resolution acoustic data around the borehole, compensating for the shortcomings of the audio magnetotelluric method in resolution. The combination of these two methods not only enhances the accuracy of stratigraphic information but also effectively delineates key areas, guiding precise measurements in acoustic logging, thus offering an efficient and comprehensive solution for tunnel engineering surveys. This study applies audio magnetotelluric sounding and acoustic logging to a tunnel project survey in Fujian Province, accurately detecting the resistivity and velocity distribution of underground rock layers. The results indicate that sections P4 to P14 exhibit relatively low resistivity, with locally fractured surrounding rock and shallow burial depth, where relatively strong rock weathering necessitates caution is needed to prevent loose collapse upon exposure of the weathered layer. Sections P26 to P34 and P41 to P47 show two low-resistivity anomalies, possibly indicating the presence of aquifers, requiring attention to drainage and refilling to prevent water inflow. Section P34 to P41 has the greatest burial depth and highest resistivity, with tightly compressed surrounding rock, and it is suggested that the drilling of stress relief holes can release energy and facilitate construction. This research demonstrates that the combined application of audio magnetotelluric and acoustic logging methods can provide new insights for tunnel engineering surveys.
-

-
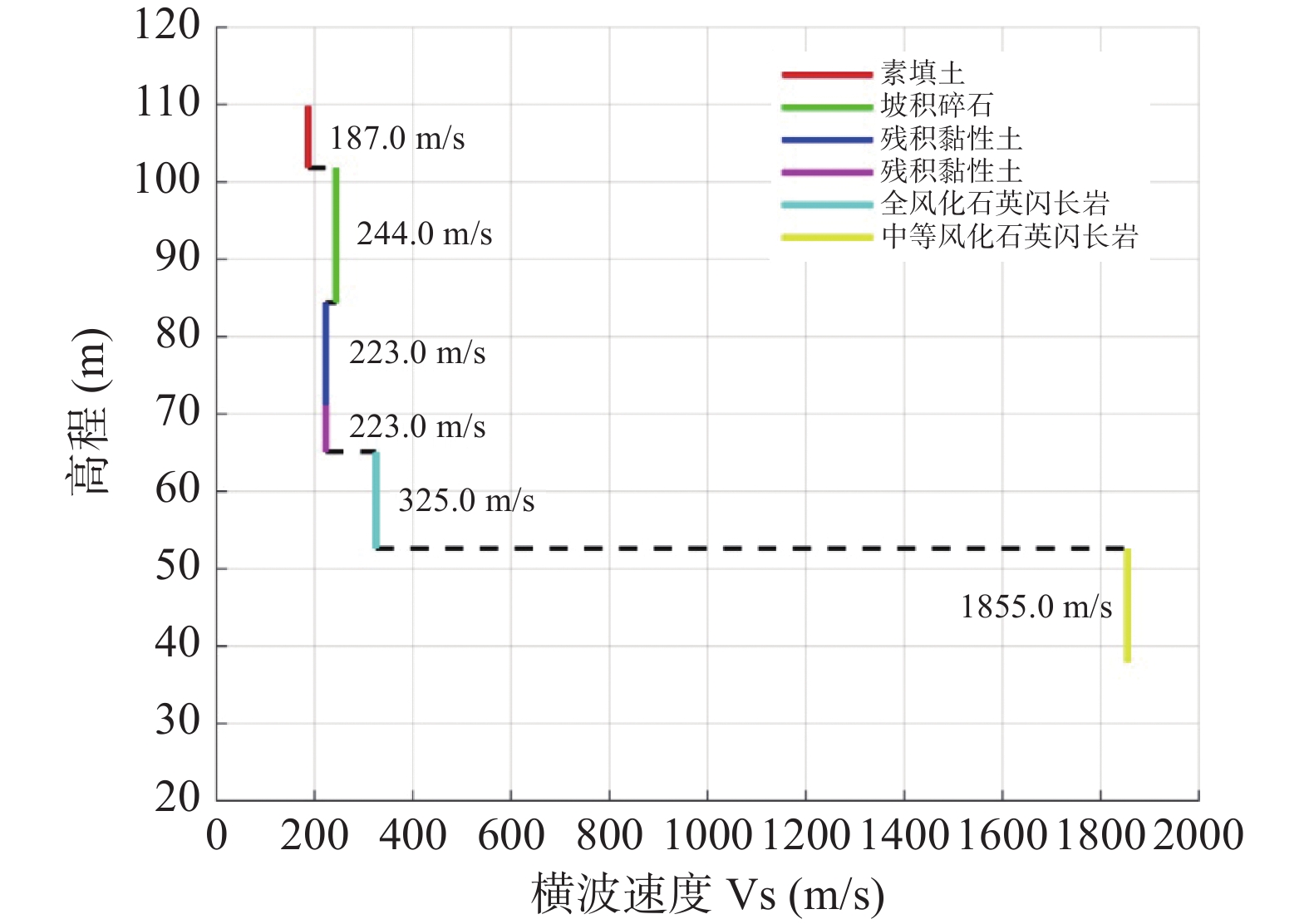
表 1 A孔岩层信息表
Table 1. Rock information of borehole A
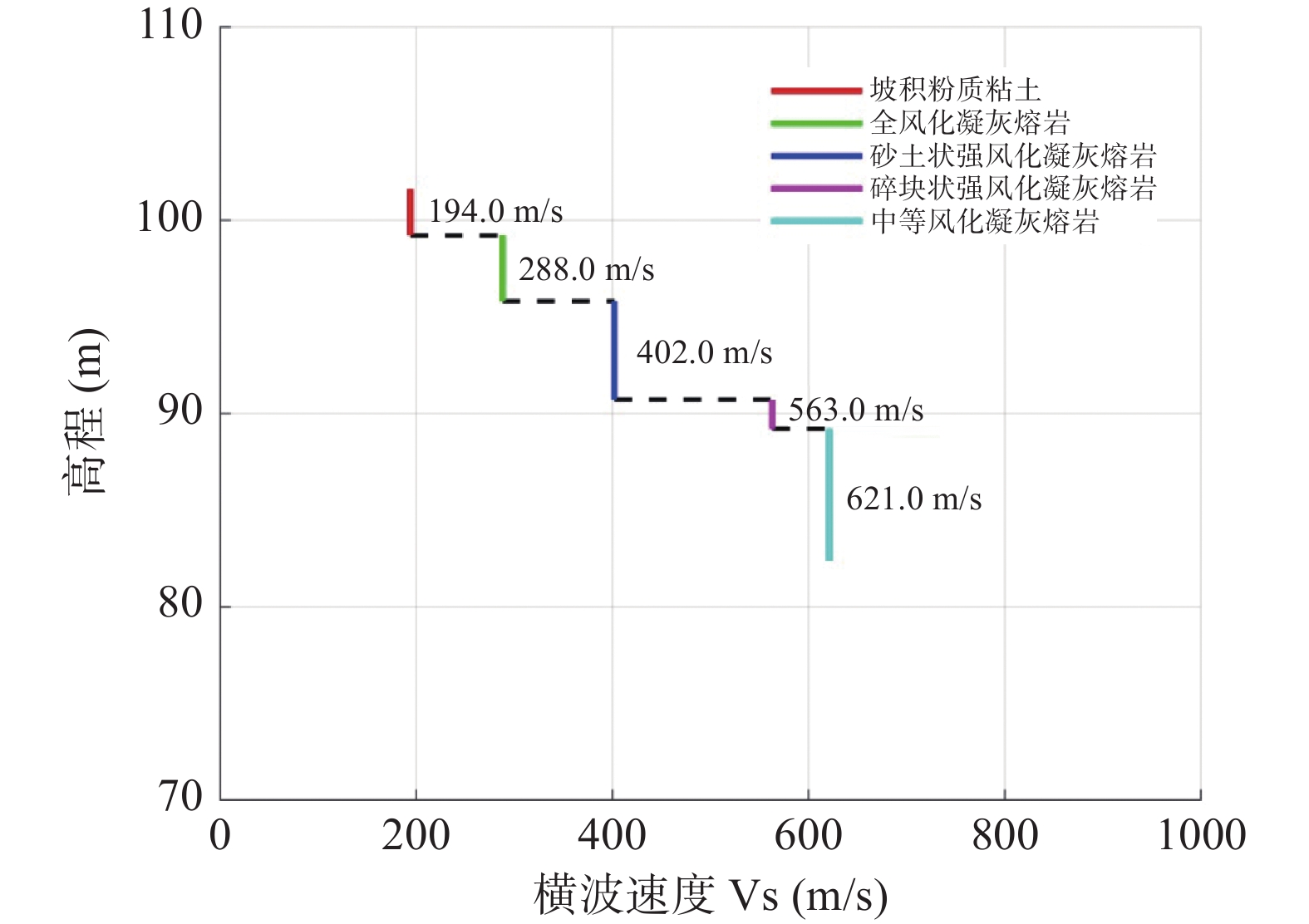
高程(m) 深度(m) 厚度(m) 岩性 横波速度Vs(m/s) 走时(ms) 109.83 ~ 101.83 0 ~ 8.0 8 素填土 187 26.7 101.83 ~ 84.43 8.0 ~ 25.4 17.4 坡积碎石 244 37.3 84.43 ~ 71.23 25.4 ~ 38.6 13.2 残积黏性土 223 26.4 71.23 ~ 65.13 38.6 ~ 44.7 6.1 残积黏性土 223 4.5 65.13 ~ 52.63 44.7 ~ 57.2 12.5 全风化石英闪长岩 325 17.5 52.63 ~ 37.93 57.2 ~ 71.9 14.7 中等风化石英闪长岩 1855 3.5 表 2 B孔岩层信息表
Table 2. Rock information of borehole B
高程(m) 深度(m) 厚度(m) 岩性 横波速度Vs(m/s) 走时(ms) 101.62 ~ 99.22 0 ~ 2.4 2.4 坡积粉质黏土 194 23.6 99.22 ~ 95.82 2.4 ~ 5.8 3.4 全风化凝灰熔岩 288 11.8 95.82 ~ 90.72 5.8 ~ 10.9 5.1 砂土状强风化凝灰熔岩 402 12.7 90.72 ~ 89.22 10.9 ~ 12.4 1.5 碎块状强风化凝灰熔岩 563 1.8 89.22 ~ 82.38 12.4 ~ 19.24 6.84 中等风化凝灰熔岩 621 7.9 -
[1] 陈 松,陈长敬,黄理善,赵信文,曾 敏.2020.音频大地电磁测深反演南沙新区地下空间岩性构造特征[J]. 华南地质,36(3):246-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2020.03.005
[2] 范 剑.2020.CSAMT法在铁路隧道勘察中的应用[J]. 西部探矿工程,32(2):184-187+196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2020.02.058
[3] 刘 宇. 2010. 阵列声波测井理论与应用研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文.
[4] 刘 雪.2019.可控源音频大地电磁法在煤矿水文地质灾害勘查的应用[J]. 内蒙古煤炭经济,(17):225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0155.2019.17.154
[5] 柳建新,童孝忠,郭荣文. 2012. 大地电磁测深法勘探[M]. 北京:科学出版社.
[6] 彭仲义,武 斌,邹 俊.2023.音频大地电磁勘探在复杂隧址勘察中的应用[J]. 四川地质学报,43(S1):94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2023.S1.018
[7] 王家俊,杨炳南,朱大伟.2024.音频大地电磁法在黔西南金矿区域地电特征研究中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,21(4):611-620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2024.04.007
[8] 王建华.2006.声波测井技术综述[J]. 工程地球物理学报,3(5):395-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2006.05.013
[9] 王 平,黄兆辉,赵运新.2024.音频大地电磁法在重庆璧山地热勘查中的应用[J]. 电声技术,48(6):18-21.
[10] 王铁领,赵胜岭,张少雷.2020.CSAMT在北京山区隧道勘察中的应用[J]. 工程技术研究,5(8):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3818.2020.08.004
[11] 杨 凯.2019.隧道工程地质灾害分析及防治对策[J]. 工程技术研究,4(11):220-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3818.2019.11.114
[12] 叶龙珍.2018.福建省地质灾害防治研究现状与展望[J]. 福建地质,37(2):139-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2018.02.004
[13] 张 刚,李彦军,李小平. 2018. 音频大地电磁在铁路隧道勘察中的应用[C]. //2018年全国工程勘察学术大会论文集.
[14] 张顶立.2017.隧道及地下工程的基本问题及其研究进展[J]. 力学学报,49(1):3-21. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-16-348
[15] 赵诚亮.2018.可控源音频大地电磁法在岩溶裂隙型地热勘查中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,15(4):514-518.
[16] 朱律运,孟 桅,杨 仲,许 文,李玉娟,詹旭焘,陈润生.2024.福州寿山石矿床的流体包裹体和H-O同位素特征及其矿床成因意义[J/OL].地球科学,1-19.http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20240516.1627.002.html.
-




 下载:
下载: