Application of Multi-polarized Magnetotelluric Method in the Exploration of Buried Manganese Ore Bodies: A Case Study of Chenjialun area, Anhua County, Hunan Province
-
摘要:
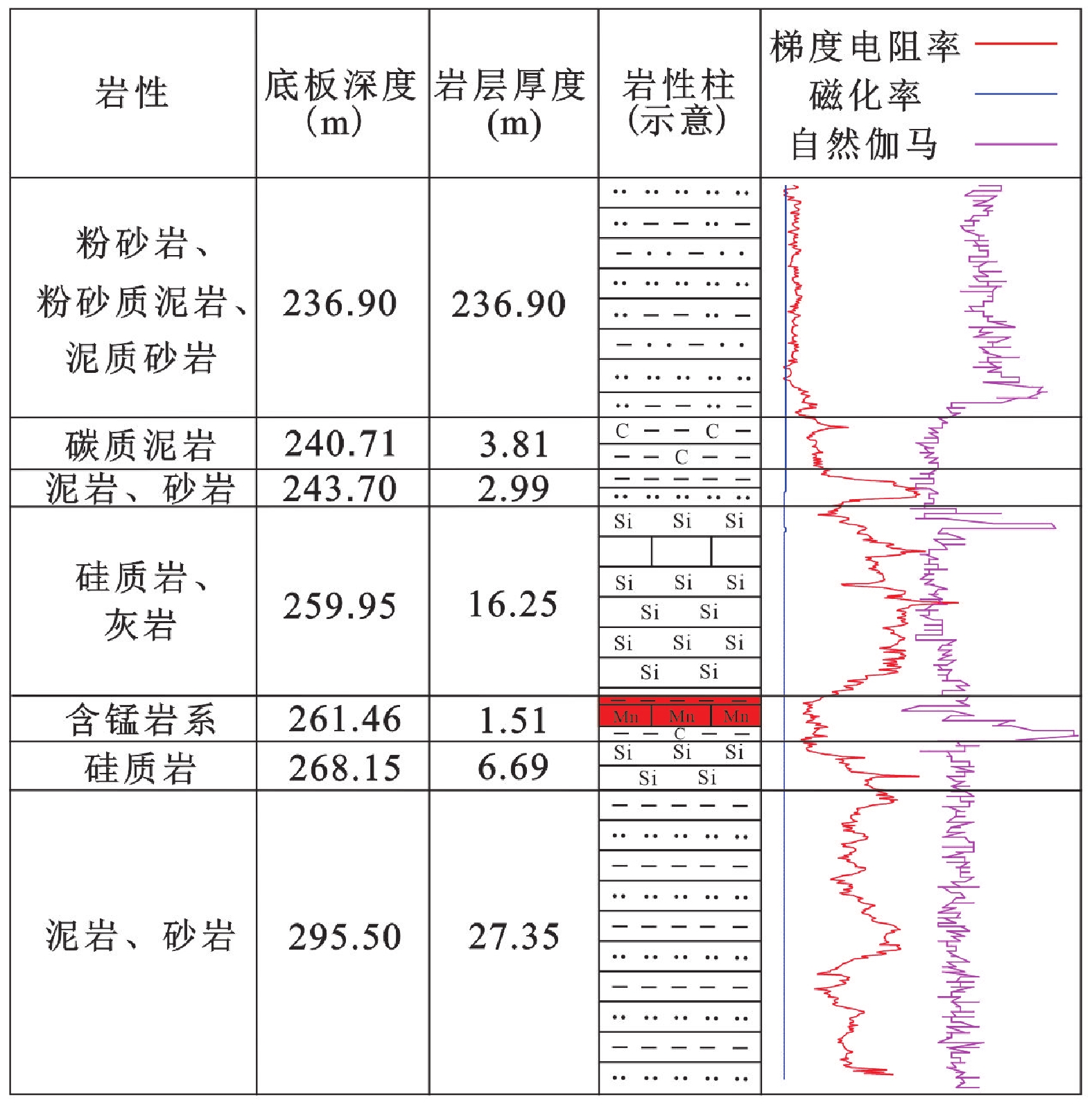
多极化大地电磁法分辨率高、抗干扰能力强、对薄层地质体的识别效果较好。湘中地区“桃江式”锰矿床是当前锰矿勘查与研究的热点,该类矿床矿层较薄、埋藏较深,为多极化大地电磁法在锰矿勘探上的运用提供了良好的研究对象。本文以湖南省安化县谌家仑地区为例,采用多极化大地电磁法对谌家仑地区的浅层电磁结构进行探测,旨在识别奥陶系烟溪组含锰地层与围岩的界线,推测隐伏锰矿体的深部延伸情况。结果表明,谌家仑地区奥陶系烟溪组含锰矿层表现为低阻高磁特征。经钻孔验证,在深部259.75 m处揭露了隐伏锰矿体,见矿深度、钻孔测井曲线与多极化大地电磁反演结果基本一致。该结果验证了多极化大地电磁法在谌家仑地区隐伏锰矿体勘查中的可行性和有效性,为该地区锰矿找矿工作提供了参考。
Abstract:The multi-polarized magnetotelluric method has high resolution, strong anti-interference capability, and performs well in identifying thin-layer geological bodies. The "Taojiang-type" manganese deposits in the central Hunan region are a current hotspot for manganese exploration and research. These deposits, characterized by thin ore layers and deep burial, have been well researched for the application of the multi-polarized magnetotelluric method in manganese exploration. In this paper, the multi-polarized magnetotelluric method is used to detect the shallow electromagnetic structure in Chenjialun area, Anhua County, aiming at identifying the boundary between the manganese-bearing strata of the Ordovician Yanxi Formation and the surrounding rocks, and inferring the deep extension of the buried manganese ore body. The results show that the manganese bearing deposits of the Ordovician Yanxi Formation in the Chenjialun area are characterized by low resistivity and high magnetism. The buried manganese ore body was discovered at a depth of 259.75 m through drilling verification. The depth of the ore body and the well logging curves are basically consistent with the output of the multi-polarized magnetotelluric inversion. The results verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the multi-polarized magnetotelluric method in the exploration of buried manganese ore bodies in Chenjialun area, and provide a reference for manganese ore prospecting in this area.
-

-
表 1 谌家仑地区岩、矿石标本电阻率及磁化率测试结果统计表
Table 1. Statistics of resistivity and magnetic susceptibility test results of rock and ore samples in Chenjialun area
地层 岩性 块数 电阻率ρ (Ω·m) 磁化率k(×10−4 SI) 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 两江河组 粉砂岩 20 800~2000 1300 0.01~0.07 0.04 龙马溪组 硅质页岩 9 600~ 1500 950 0.03~0.10 0.06 粉砂质泥岩 8 300~ 1000 650 0.04~0.09 0.06 炭质页岩 9 10~400 220 0.16~0.96 0.45 含锰地层 碳酸锰矿石 12 10~400 170 2.0~21.5 7.5 含锰灰岩 8 100~500 350 1.5~14.0 4.5 桥亭子组 粉砂质泥岩 20 500~ 1700 1100 0.02~0.07 0.05 -
[1] 柏道远,唐分配,李 彬,曾广乾,李银敏,姜 文.2022.湖南省成矿地质事件纲要[J]. 中国地质,49(1):151-180. doi: 10.12029/gc20220110
[2] 程 湘,胡 鹏,张海坤,姜军胜.2021.锰矿主要类型、分布特点及开发现状[J]. 中国地质,48(1):102-119. doi: 10.12029/gc20210107
[3] 付胜云,石金江,杜 云.2014.湖南奥陶纪天马山组中沉积型氧化锰矿成矿地质条件[J]. 中国锰业,32(3):13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4336.2014.03.004
[4] 付彦平,宋旭锋,吕许朋.2017.激电测深法在滇东南某锰矿勘查中的试验效果[J]. 云南地质,36(3):410-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2017.03.020
[5] 傅群和.2001.“桃江式”锰矿床地质特征及其地球化学特征[J]. 湖南地质,20(1):15-20.
[6] 何 辉.2017.锰矿资源现状与锰矿勘察研究[J]. 中国锰业,35(1):23-24.
[7] 黄 屹,陈广义,田郁溟,李朗田,雷玉龙,李连支,张之武,杨 朋,黄丽梅.2021.中国锰业存在的主要问题及对策建议[J]. 地质与勘探,57(2):294-304. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2021.02.005
[8] 匡清国,赵银海,吴永胜,雷玉龙.2003.构造对“桃江式”锰矿空间分布的影响及其找矿意义探讨[J]. 地质与勘探,39(1):32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2003.01.008
[9] 廖凤鸣.2019.“桃江式锰矿”研究现状浅析[J]. 国土资源导刊,16(3):49-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2019.03.012
[10] 林乐夫,李小聪,谭 双,端葛鸿.2016.湖南省安化县大福坪乡锰矿床地质特征研究[J]. 绿色科技,16:241-243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2016.16.095
[11] 刘 虎,李庆宏,陈 艳,吴继兵,黄 飞,王 哲,龚光林,刘东升.2019.湖南桃江响涛源锰矿地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 地质与勘探,55(3):712-722. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2019.03.004
[12] 刘延年,陈 旭,李连支,许 明,刘东升.2018.隐伏碳酸锰矿床定位预测技术方法[J]. 华南地质与矿产,34(2):150-159.
[13] 刘 雨.2015.湖南“桃江式”锰矿地质特征及找矿前景分析[J]. 矿产与地质,29(4):444-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.04.006
[14] 刘陟娜,许 虹,王秋舒,陈 梅.2015.中国锰矿供需现状及可持续发展建议[J]. 资源与产业,17(6):38-43.
[15] 潘汉军,侯景儒,张廷勋.1995.湘中“桃江式”锰矿含锰岩系的定量研究及其找矿意义[J]. 地质找矿论丛,10(2):16-27.
[16] 彭三国,付群和,张殿春.2008.湘中奥陶纪锰矿带成矿特征及资源前景[J]. 矿床地质,27(5):622-630. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.05.009
[17] 任 辉,刘 敏,王自国,吴 昊,毛景文.2022.我国锰矿资源及产业链安全保障问题研究[J]. 中国工程科学,24(3):20-28.
[18] 沈小庆,杨炳南,何 帅,张德实.2021.音频大地电磁法在深部隐伏锰矿找矿中的应用——以贵州松桃普觉锰矿为例[J]. 地质力学学报,27(6):987-997. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.06.080
[19] 孙宏伟,王 杰,任军平,张伟波,唐文龙,吴兴源,古阿雷.2020.全球锰资源现状及对我国可持续发展建议[J]. 矿产保护与利用,40(6):169-174.
[20] 王 斌. 2020. 综合物探方法在青海省都兰县三通沟北锰矿区的应用研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文.
[21] 王品丰. 2017. 贵州松桃“大塘坡式”锰矿电性结构特征及识别研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文.
[22] 王 帅,戴 婷,钟 宏.2018.锰资源利用技术研究进展[J]. 中国锰业,36(2):1-5.
[23] 韦洪兰,龙 霞,席振铢,陈兴朋,王 亮,王 威,薛文韬.2023.多极化大地电磁系统及其在金属矿勘探中的应用[J]. 黄金,44(1):68-74. doi: 10.11792/hj20230114
[24] 徐 昱,王建平,吴景荣,邹君宇,宓奎峰.2013.我国锰资源存在的问题及可持续开发对策[J]. 矿业研究与开发,33(3):111-115.
[25] 许志彬,焦俊俊,刘建鹏,陈 静.2019.综合物探方法在铜锰矿区勘查中的应用研究[J]. 西部探矿工程,31(5):159-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2019.05.055
[26] 张泾生,周光华.2006.我国锰矿资源及选矿进展评述[J]. 中国锰业,24(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4336.2006.01.001
[27] 周 琦,杜远生,袁良军,张 遂,余文超,杨胜堂,刘 雨.2016.黔湘渝毗邻区南华纪武陵裂谷盆地结构及其对锰矿的控制作用[J]. 地球科学,41(2):177-188.
[28] 朱志刚.2016.中国锰矿资源开发利用现状[J]. 中国锰业,34(2):1-3.
[29] Araffa S, Rabeh T, Mousa S, Nabi S, Deep M. 2020. Integrated geophysical investigation for mapping of manganese-iron deposits at Wadi Al Sahu area, Sinai, Egypt-a case study[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13: 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12517-019-5007-7
[30] Du Q D, Yi H S, Hui B, Li S J, Xia G Q, Yang W, Wu X F. 2013. Recognition, genesis and evolution of manganese ore deposits in southeastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 55: 99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.05.001
[31] Fan D L, Yang P J. 1999. Introduction to and classification of manganese deposits of China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 15: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(99)00011-6
[32] Gao L F, Xu S, Hu X Y, Liu S, Zhou Q, Yang B N. 2021. Sedimentary setting and ore-forming model in the songtao manganese deposit, Southwestern China: Evidence from audio-frequency magnetotelluric and gravity data[J]. Minerals, 11(11): 1273. doi: 10.3390/min11111273
[33] Guo Z W, Xue G Q, Liu J X, Wu X. 2020. Electromagnetic methods for mineral exploration in China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 118: 103357. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103357
[34] Peng B, Piestrzynski A, Pieczonka J, Xiao M L, Wang Y Z, Xie S R, Tang X Y, Yu C X, Song Z. 2007. Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on environmental impacts from waste rock at Taojiang Mn-ore deposit, central Hunan, China[J]. Environmental geology, 52: 1277-1296. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0567-8
[35] Ramazi H, Mostafaie K. 2013. Application of integrated geoelectrical methods in Marand (Iran) manganese deposit exploration[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6: 2961-2970. doi: 10.1007/s12517-012-0537-2
[36] Srigutomo W, Pratomo P. 2016. 2D resistivity and induced polarization measurement for manganese ore exploration[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 739(1): 012138.
[37] Xiao J F, He J Y, Yang H Y, Wu C Q, Xu J B, Li Y T. 2019. Geochemical Characteristics and Genetic Significance of Datangpo-Type Manganese Ore Deposits during the Cryogenian Period[J]. Resource Geology, 69(3): 227-248. doi: 10.1111/rge.12199
[38] Yang Y, Ye L L, Chen F B, Peng S X, Shan H M. 2024. Exploration of Metallogenic Structure of Manganese Ore Using Magnetotelluric Method: A Case Study in Minle Region, Hunan Province, China[J]. Natural Resources Research, 33: 2457-2472. doi: 10.1007/s11053-024-10376-8
[39] Ye L J, Fan D L, Yang P J. 1988. Characteristics of manganese ore deposits in China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 4(1-2): 99-113. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(88)90006-6
[40] Zaid H, Arifin M, Hussin H, Basori M, Umor M, Hazim S. 2022. Manganese ore exploration using electrical resistivity and induced polarization methods in Central Belt, Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 20(6): 679-696.
-




 下载:
下载: