Seepage Characteristics and Stability Analysis of Wanzhou Shilongmen Landslide Under the Combined Effect of Rainfall and Reservoir Water
-
摘要:
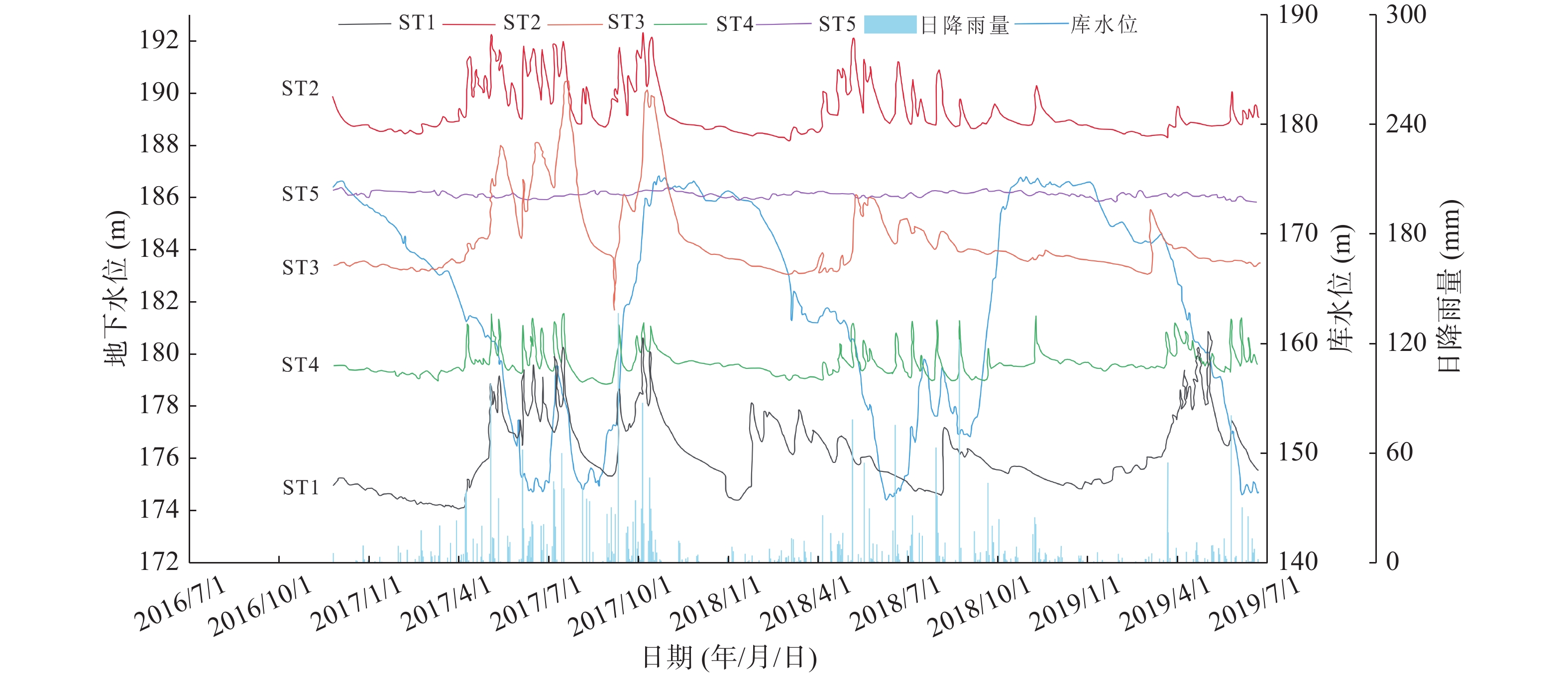
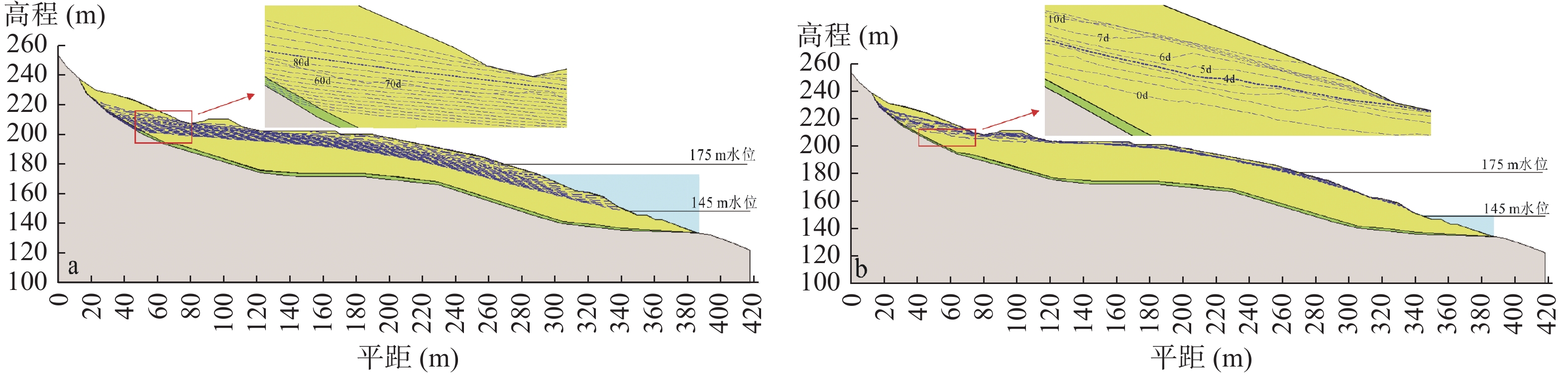
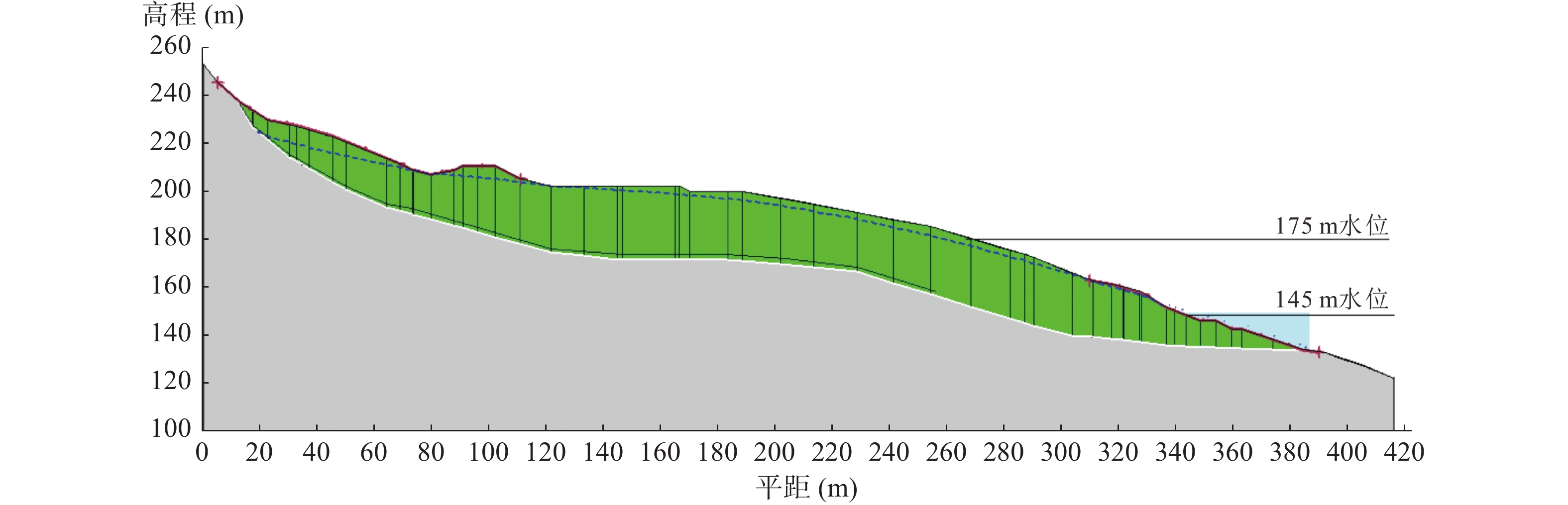
三峡库区库岸堆积层滑坡广泛发育,其稳定性主要受降雨和库水位变动联合作用影响。本文以重庆市万州区石龙门堆积层滑坡为例,建立精细地质模型,采用有限元方法对该滑坡开展了数值模拟研究,探讨其变形与稳定性的变化特征,总结在降雨和库水位联合作用下堆积层滑坡的渗流响应规律。结果表明:降雨和库水位下降是滑坡的关键诱因,降雨会提升滑坡中后部地下水位,当降雨强度超出土体入渗能力后,新增降雨多以坡面径流排泄,而库水位变动影响前缘地下水位及孔隙水压力。在库水位下降联合降雨作用下,滑坡内部应力-应变及稳定性显著恶化,渗流与水力梯度的增强加剧了滑坡不稳定性。本文研究可为堆积层滑坡的变形机制分析及监测预警提供参考。
Abstract:In the Three Gorges Reservoir area, piling layer landslides on the bank of the reservoir are widely developed, and their stability is mainly affected by the combined effect of rainfall and reservoir water level change. This paper takes Wanzhou Shilongmen piling layer landslide as an example, establishes a refined geological model, and carries out numerical simulation research on the landslide using the finite element method, to study the characteristics of the change of its deformation and stability, and to explore the seepage response law of the piling layer landslide under the combined effect of rainfall and reservoir level. The results show that: rainfall and reservoir level decline are the key triggers of landslides, rainfall will raise the groundwater level in the middle and back of landslides, and when the intensity of rainfall exceeds the infiltration capacity of the soil body, the additional rainfall is mostly discharged as slope runoff. The change of the reservoir level affects the groundwater level and pore water pressure at the leading edge. Under the combined effect of the reservoir water level drop and rainfall, the internal stress-strain and stability of the landslide deteriorate significantly, and the enhancement of seepage and hydraulic gradient aggravates the landslide instability. This paper provides a useful reference for analyzing the deformation mechanism and monitoring and early warning of landslides in the accumulation layer.
-

-
表 1 滑坡岩土体参数取值
Table 1. Parameter value of landslide rock and soil mass
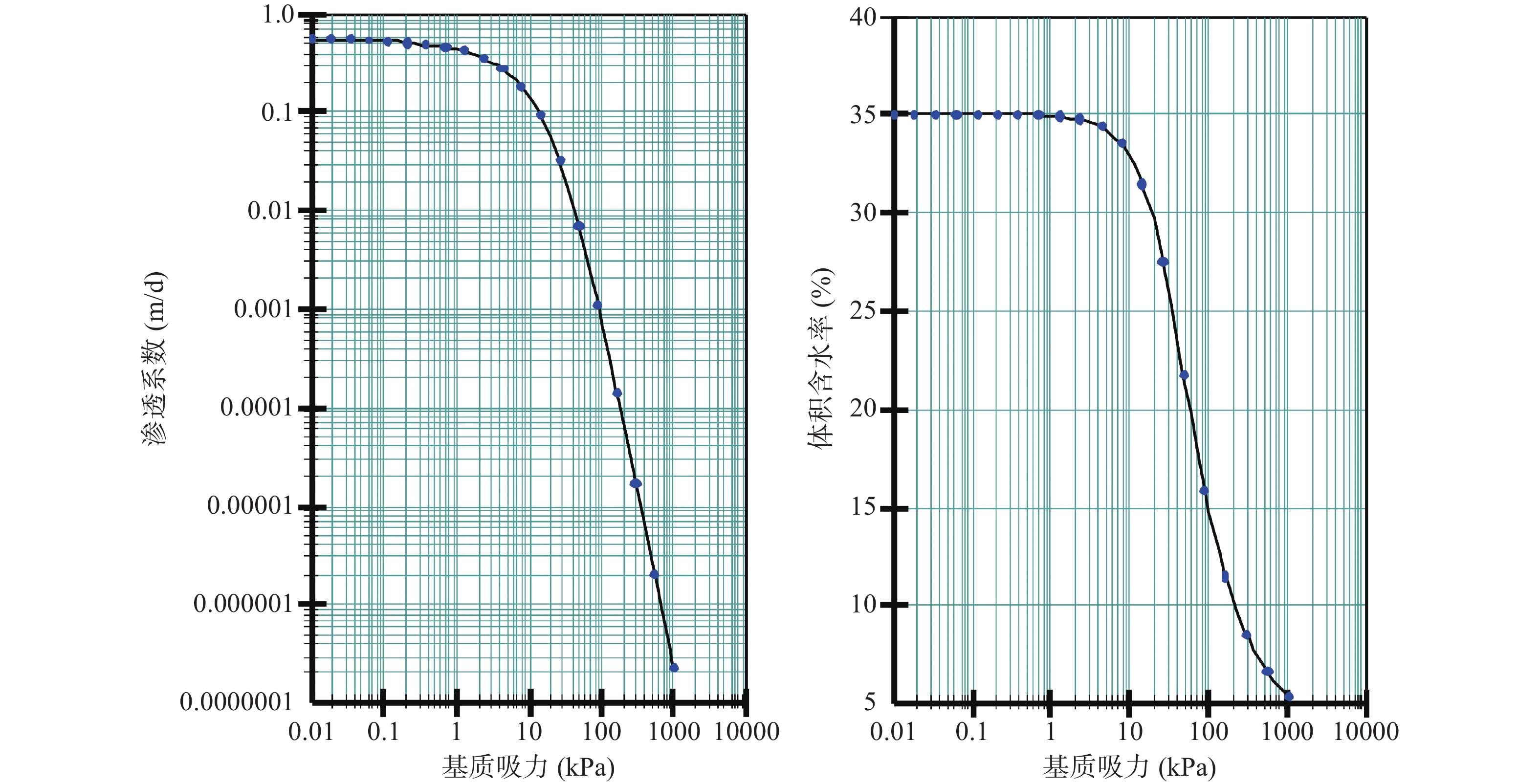
位置 重度(kN·m−3) 弹性模量(Mpa) 泊松比 内摩擦角c(°) 粘聚力 $ \mathit{\varphi } $ (kpa)天然 饱和 天然 饱和 滑体 20.1 20 0.3 15.2 13.5 38 29 滑床 30 16000 0.4 38.2 1120 滑带 21.0 10 0.2 12.9 8.7 27 22 表 2 万州区降雨重现期统计表
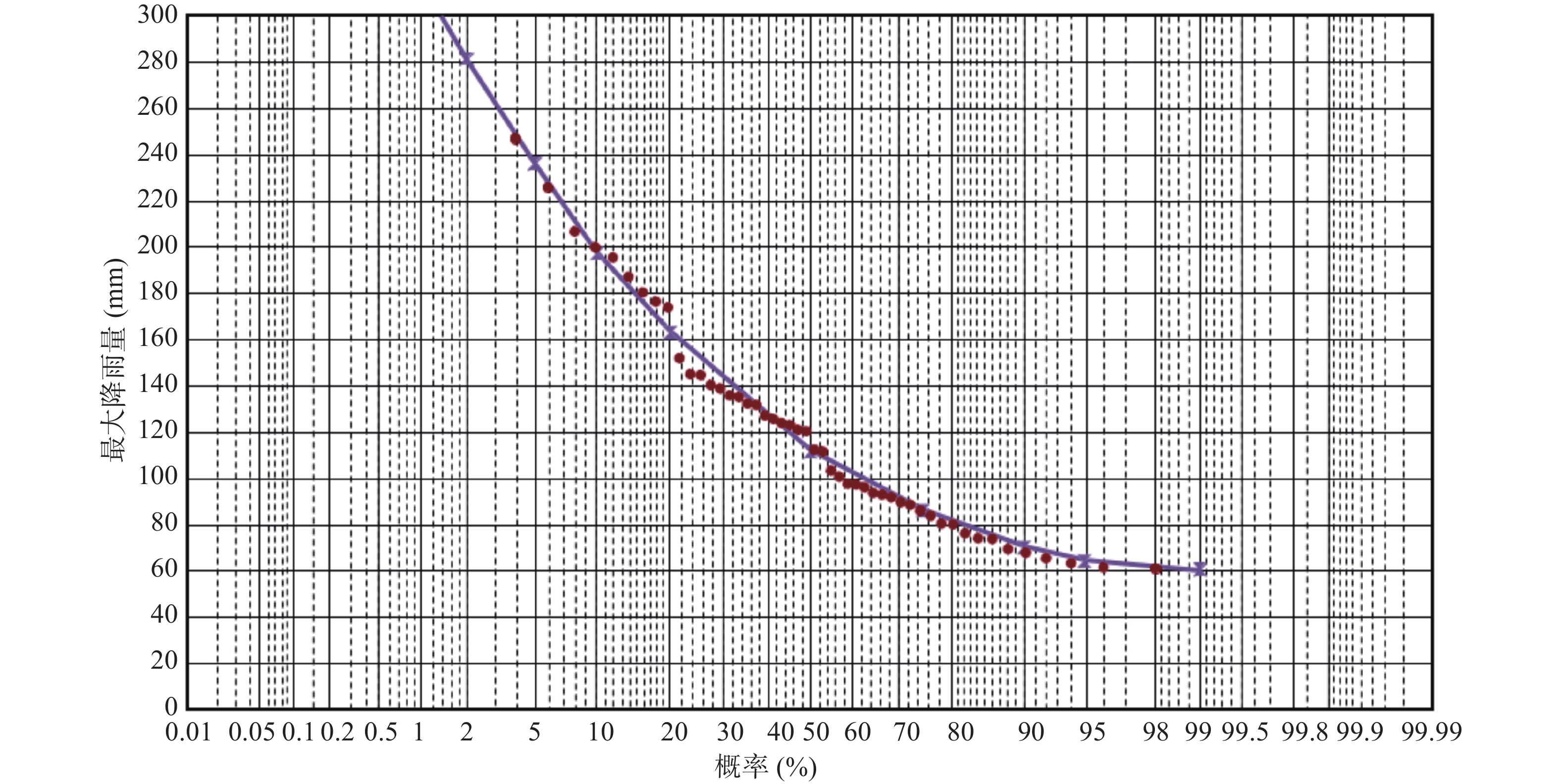
Table 2. Statistics of rainfall return period in Wanzhou
重现期(a) 5 10 20 50 100 降雨极值(mm) 168.5 199.8 253.2 281.4 320.1 平均降雨强度(mm/d) 56.2 66.6 84.4 93.8 106.7 表 3 石龙门滑坡数值模拟工况设计
Table 3. Design of numerical simulation conditions for Shilongmen landslide
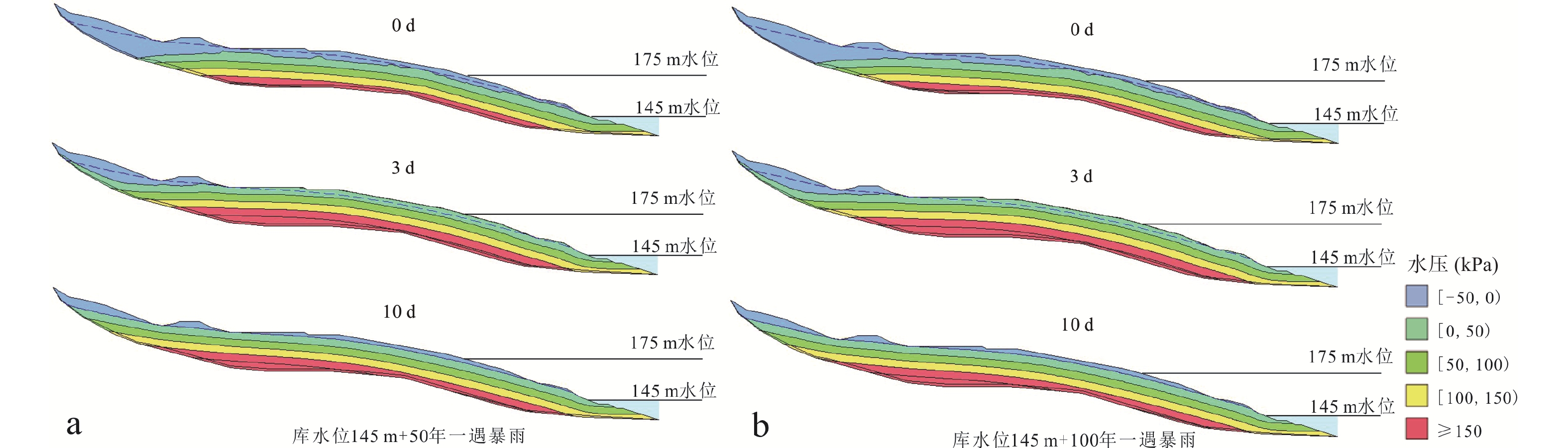
工况分类 工况编号 工况条件 模拟时间(d) 降雨 工况1 库水位145 m+50年一遇暴雨 10 工况2 库水位145 m+100年一遇暴雨 10 库水位升降 工况3 库水位从145 m上升到175 m 75 工况4 库水位从175 m下降到145 m 170 库水位下降
叠加降雨工况5 库水位从175 m下降到145 m+50年一遇暴雨 170 工况6 库水位从175 m以3 m/d下降速度下降至145 m+100年一遇暴雨(极端条件) 10 表 4 石龙门滑坡稳定性系数变化统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of changes in stability coefficients of the Shilongmen landslide
工况条件 工况编号 稳定性系数 变幅(%) 初始值 最小值 最终值 静止水位+暴雨 工况1 1.202 1.065 1.181 11.4 工况2 1.202 1.059 1.137 11.9 水位涨落 工况3 1.202 1.202 1.227 2.1 工况4 1.271 1.257 1.257 1.0 库水位下降+降雨 工况5 1.271 1.028 1.028 19.1 工况6 1.271 0.932 0.932 26.6 -
[1] 贲琰棋,易 武,黄晓虎,魏兆亨,肖宇煌,邓欣雨.2023.基于有效降雨量的“阶跃型”滑坡递进式预警模型研究[J]. 华南地质,39(3):492-501.
[2] 常 宏.2023.三峡库区堆积体复活失稳的宏观判据初探[J]. 华南地质,39(3):428-444.
[3] 常 宏.2024.三峡库区今后仍需重点关注的滑坡崩塌成灾模式[J]. 华南地质,40(4):725-736.
[4] 陈慧娟,邹 浩,訚 遥,王 超,毛 帅.2023.持续强降雨影响下黄梅县袁山村三组滑坡破坏特征与成因分析[J]. 华南地质,39(3):482-491.
[5] 代贞伟,李 滨,陈云霞,冯 振,赵瑞欣,贺 凯,高 杨.2016.三峡大树场镇堆积层滑坡暴雨失稳机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,43(1):149-156.
[6] 高晨曦,石长柏,闫 巍,侯时平,唐 玄,安知利,路永强.2024.堆积层滑坡在库水位变动与降雨共同作用下的阈值研究——以墓坪滑坡为例[J]. 资源环境与工程,38(1):73-82.
[7] 高文军,丛 凯,杜全云.2021.强降雨条件下堆积层滑坡入渗规律及稳定性分析[J]. 甘肃科学学报,33(1):101-105.
[8] 黄 达,顾东明,陈智强,朱 宏,陈赐金.2017.三峡库区塔坪H2古滑坡台阶状复活变形的库水–降雨耦合作用机制[J]. 岩土工程学报,39(12):2203-2211.
[9] 江强强,焦玉勇,宋 亮,王 浩,谢壁婷.2019.降雨和库水位联合作用下库岸滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,40(11):4361-4370.
[10] 抗兴培,孟凡成,曾 超,王彪龙,郭 将,刘 晓.2019.强降雨条件下弃土场边坡稳定性历程分析[J]. 中外公路,39(3):34-39.
[11] 李 卓,何勇军,盛金保,李宏恩,李 铮,杨 阳.2017.降雨与库水位共同作用下近坝库岸边坡滑坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,39(3):452-459. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201703008
[12] 梁 宇,严 磊,苏培东,邱 鹏,龙 伟,汪意凌.2021.溪洛渡库区河口滑坡变形特征和形成机制[J]. 科学技术与工程,21(34):14500-14507. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.34.005
[13] 刘才华,陈从新,冯夏庭.2005.库水位上升诱发边坡失稳机理研究[J]. 岩土力学,26(5):769-773. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.05.018
[14] 罗世林,刘华亮,蒋建清.2024.库水—降雨作用下靠椅状基覆面堆积层滑坡响应机理[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),64(8):1336-1346.
[15] 王鲁男,晏鄂川,陆文博,柳万里.2016.库水变动下堆积层滑坡加卸载响应规律与稳定性预测[J]. 工程地质学报,24(6):1048-1055.
[16] 吴火珍,冯美果,焦玉勇,李海波.2010.降雨条件下堆积层滑坡体滑动机制分析[J]. 岩土力学,31(S1):324-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.z1.051
[17] 许 强,黄润秋.1995.用加卸载响应比理论探讨斜坡失稳前兆[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,6(2):25-30.
[18] 许艺林,李远耀,李思德,石 浩.2024.库水位下降叠加降雨作用时堆积层滑坡渗流-变形机制[J]. 地质科技通报,43(1):216-228.
[19] 杨诗诗,叶润青,付小林,吴润泽,熊 能,文天龙.2023.三峡库区降雨型滑坡预警雨量阈值研究[J]. 华南地质,39(3):445-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2023.03.004
[20] 叶润青,付小林,郭 飞,易庆林,张俊义,李长明,侯时平,刘 娜.2021.三峡水库运行期地质灾害变形特征及机制分析[J]. 工程地质学报,29(3):680-692.
[21] 殷跃平,张晨阳,闫 慧,肖明友,侯雪峰,朱赛楠,黄波林,代贞伟,张 楠.2022.三峡水库蓄水运行滑坡渗流稳定和防治设计研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,41(4):649-659.
[22] 张 群,许 强,甯 娜.2014.降雨条件下低缓浅层土质滑坡稳定性影响因素及耦合研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,41(5):90-94+117.
[23] 张桂荣,程 伟.2011.降雨及库水位联合作用下秭归八字门滑坡稳定性预测[J]. 岩土力学,32(S1):476-482.
[24] 周永强,盛 谦.2014.库水位变化和降雨作用下付家坪子高陡滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,31(2):57-61+67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2014.02.012
[25] 朱元甲,贺 拿,钟 卫,孔纪名.2020.间歇型降雨对堆积层斜坡变形破坏的物理模拟研究[J]. 岩土力学,41(12):4035-4044.
[26] 邹祖银,朱占元,张 锋,陈婷婷,张自兴.2016.连续降雨条件下某震后高边坡稳定性分析[J]. 地震工程学报,38(4):541-548. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2016.04.0541
[27] Alonso E, Gens A, Lioret A, Delahaye C H. 1995. Effect of rain infiltration on the stability of slopes[J]. Unsaturated Soils, (1): 241-249.
[28] Coe J A, Ellis W L, Godt J W, Savage W Z, Savage J E, Michael J A, Kibler J D, Powers P S, Lidke D J, Debray S. 2003. Seasonal movement of the Slumgullion landslide determined from Global Positioning System surveys and field instrumentation, July 1998-March 2002[J]. Engineering Geology, 68(1-2): 67-101. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00199-0
[29] Iadanza C, Trigila A, Napolitano F. 2016. Identification and characterization of rainfall events responsible for triggering of debris flows and shallow landslides[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 541: 230-245. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.01.018
[30] Pang G X, Qiang Y. 2016. Formation Mechanism and Stability Analysis of Typical Accumulation landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[C]. International Conference On Smart City and Systems Enginerring, 50-53.
-




 下载:
下载: