NUMERICAL STUDY ON THE DIFFERENCE OF GEOMORPHIC DYNAMICS BETWEEN THE CURRENT AND ABANDONED ESTUARY COASTS OF THE YELLOW RIVER
-
摘要:
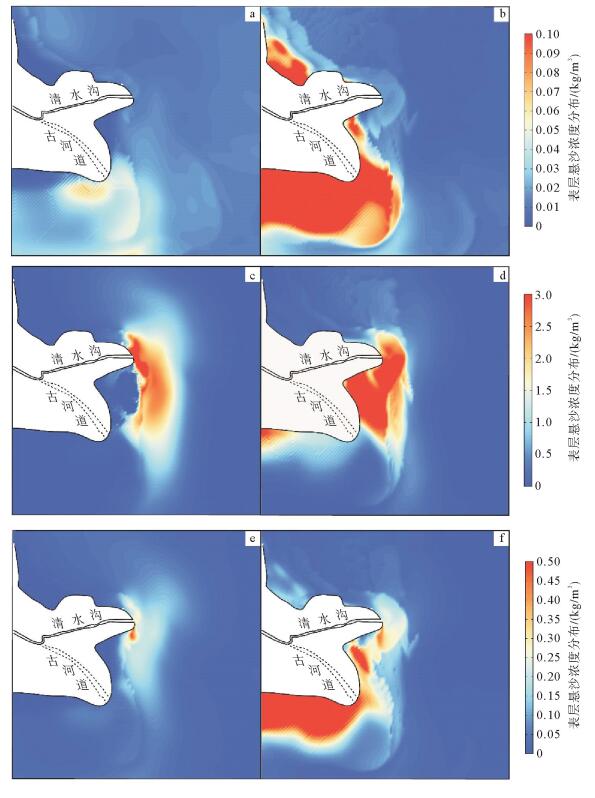
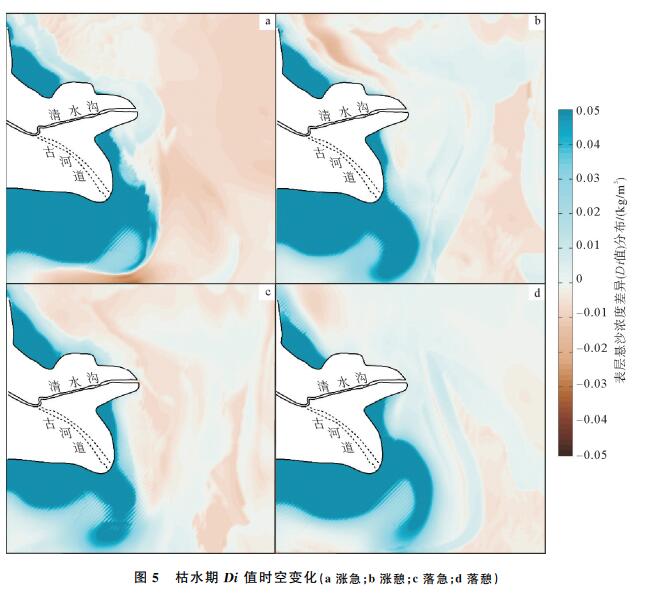
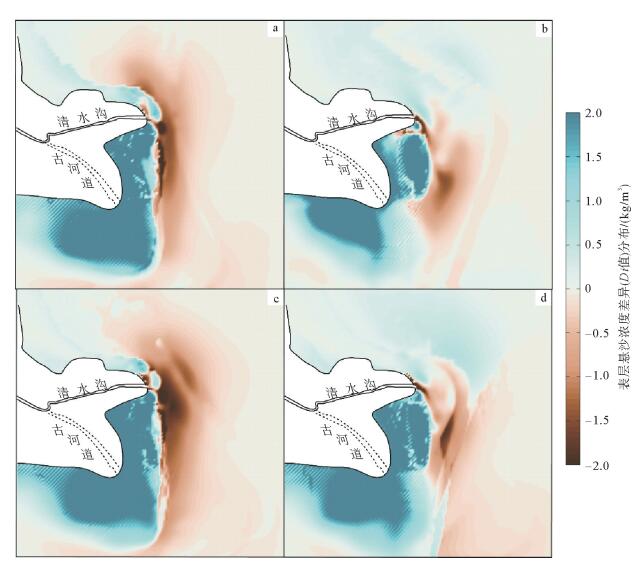
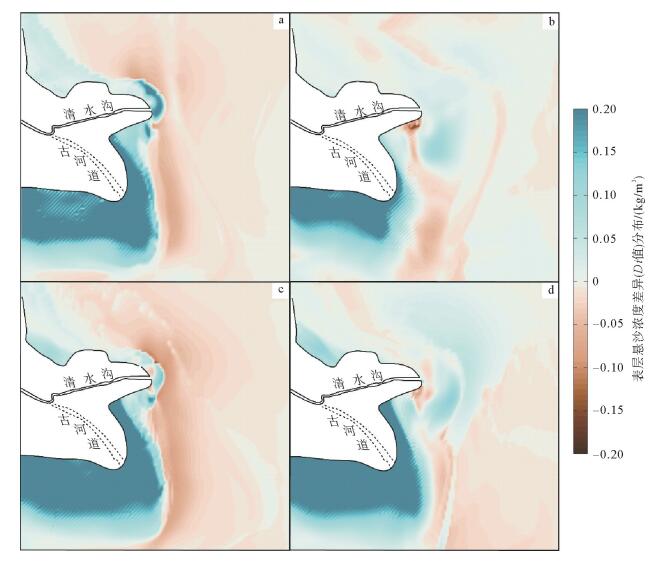
波浪是塑造黄河三角洲河口与海岸地貌的重要动力因素之一。基于Delft3D模型耦合水动力与泥沙输运模块,模拟了黄河不同入海水沙条件下的表层悬沙浓度的分布变化,通过悬沙浓度差异值(Di值)定量研究了黄河清水沟流路现行河口与废弃河口之间的海洋动力差异,进而揭示了潮流与波浪在不同时期黄河三角洲地貌演变中的塑造作用。研究结果表明,在不同时期不同入海泥沙条件下,废弃河口及其近岸区域Di值普遍较高且为正值;但现行河口近岸的Di值分布普遍为负值。在废弃河口波浪使已沉积的粉砂、黏土起动、再悬浮,由潮流将其搬离海岸,从而使海岸发生蚀退;但现行河口由于大量黄河粉砂、黏土快速输入,潮流无法在短时间内将其全部搬离河口,进而使河口及两侧海岸向海淤进。比较而言,波浪在废弃河口及海岸的地貌作用较强,在现行河口相对较弱。这些研究结果对了解黄河三角洲动力地貌演变机理有重要的理论价值。
Abstract:Waves are one of the important driving factors that shape the estuary and coastal landscape of the Yellow River Delta. Based on the Delft3D model coupled hydrodynamic and sediment transport module, this study aims to simulate the variation of surface suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow River under different seawater conditions. The current estuary and waste of the Qingshuigou channel of the Yellow River are quantitatively studied by the difference of suspended sediment concentration (Di value). The differences in ocean dynamics between the estuaries reveal the shaping of tidal currents and waves in the evolution of the Yellow River Delta in different periods. The results show that the suspended sediment concentration difference along the abandoned estuary and its nearshore area is generally high and positive under different sediment conditions in different periods. However, the Di value in the current estuary is generally negative. The abandoned estuary waves resuspend the deposited silt and clay, and move it off the coast by the tidal current, thus causing the coast to eclipse. However, due to the rapid input of a large number of Yellow River silt and clay, the current estuary cannot transport all of them out of the estuary in a short period of time, and thus the estuary and the coasts on both sides are deposited into the sea. In comparison, waves have a strong geomorphological effect on abandoned estuaries and coasts, and are relatively weak in the current estuary. These findings have important theoretical significance for understanding the evolution mechanism of dynamic geomorphology in the Yellow River Delta.
-
Key words:
- Yellow River Delta /
- wave /
- tidal /
- coastal landform /
- morphodynamics
-

-
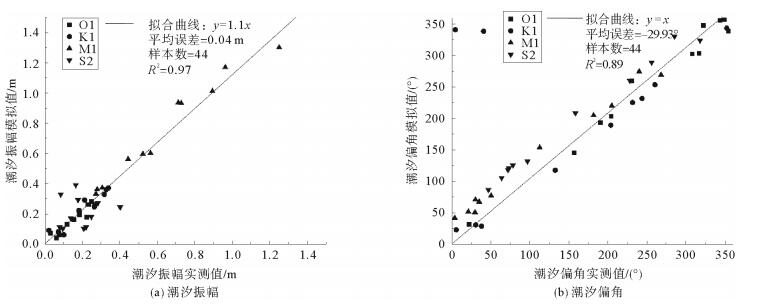
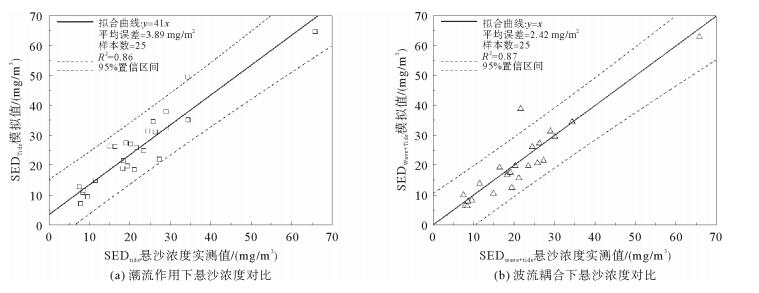
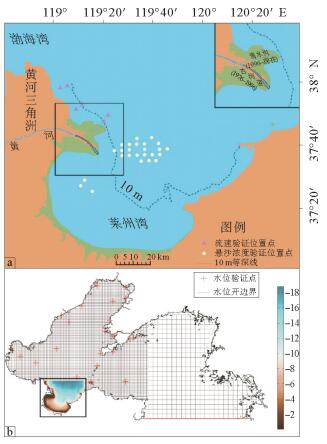
表 1 实测与模拟流速对比
Table 1. Comparison of velocity between simulation and observation
站位 层位 最大流速实测值/(cm/s) 最大流速模拟值/(cm/s) 相对误差/% 多壁层 过渡层 宽层 窄层 宽层 窄层 五号桩 E1 表层 59 65 62 70 5.08 7.69 底层 46 25 46 28 0.00 12.00 E2 表层 63 66 65 68 3.17 3.03 底层 50 50 52 54 4.00 8.00 孤东海域 B1 表层 21 68 20 60 4.76 11.76 底层 31 21 31 24 0.00 14.29 B2 表层 33 62 38 66 15.15 6.45 底层 37 30 40 30 8.11 0.00 河口处 A1 表层 94 80 101 88 7.45 10.00 底层 68 50 65 50 4.41 0.00 A2 表层 85 79 93 84 9.41 6.33 底层 63 49 66 53 4.76 8.16 表 2 黄河不同入海水沙条件设置
Table 2. Differentsettings of water andsediment discharge from the Huanghe River
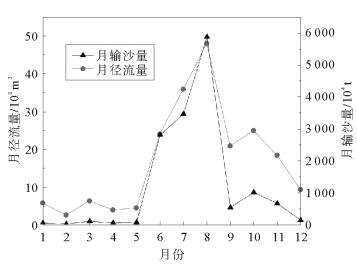
时间 黄河入海水沙 含沙量/
(kg/m3 )流量/
(m3/s)平水期(2月) 0.1 107.9 汛期 调水调沙中(8月)
调水调沙后(9月)15.1
2796.32.5
766.9 -
[1] Wang H J, Wu X, Bi N S, et al. Impacts of the dam-orientated water-sediment regulation scheme on the lower reaches and delta of the Yellow River (Huanghe): A review[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2017, 157: 93-113. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.08.005
[2] Chu Z X, Sun X G, Zhai S K, et al. Changing pattern of accretion/erosion of the modern Yellow River (Huanghe) subaerial delta, China: Based on remote sensing images[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 227(1/2): 13-30. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=78671852ebceec8105a889b5e224059f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] Cui B L, Li X Y. Coastline change of the Yellow River estuary and its response to the sediment and runoff (1976-2005) [J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 127(1/2): 32-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f625634696a969e531eaad5b005e50ae
[4] 刘鹏, 王庆, 战超, 等.基于DSAS和FA的1959—2002年黄河三角洲海岸线演变规律及影响因素研究[J].海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(3):585-594. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201503015
[5] Huang H J, Liu Y X, Qiu Z F. Morphodynamic evolution of the Xiaoqing River mouth: a Huanghe River-derived mixed energy estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2012, 30(5): 889-904. doi: 10.1007/s00343-012-1295-4
[6] Liang B C, Li H J, Zhang J. Study of wave induced radiation stress and vertical mixing in the Yellow River runoff diffusion[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 22(5): 97-100. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6e82df9dde6ab06987443797f7264b8d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] Bing L F, Shao Q Q, Liu J Y. Runoff characteristics in flood and dry seasons based on wavelet analysis in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2012, 22(2): 261-272. doi: 10.1007/s11442-012-0925-2
[8] Qiao S Q, Shi X F, Gao J J, et al. The distribution and variation of elements in sediments off the Huanghe (Yellow) River mouth[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(4): 876-885. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2126-y
[9] Zhou L Y, Liu J, Saito Y, et al. Modern sediment characteristics and accumulation rates from the delta front to prodelta of the Yellow River (Huanghe)[J]. Geo Marine Letters, 2016, 36(4): 247-258. doi: 10.1007/s00367-016-0442-x
[10] 王 庆, 王小鲁,李雪艳,等.黄河三角洲南部废弃三角洲潮间滩涂表层沉积粒度特征及其粗化现象[J].第四纪研究, 2017, 37(2):353-367. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj201702013
[11] Dai P, Zhang J S, Zheng J H. Predictions for Dynamic Tidal Power and Associated Local Hydrodynamic Impact in the Taiwan Strait, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2017, 33(1): 149-157. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=41c2c13fa78a9b396ca7c8cdd357469c
[12] Da Silva G V, Toldo E E, Klein A H D, et al. The influence of wave-, wind- and tide-forced currents on headland sand bypassing - Study case: Santa Catarina Island north shore, Brazil[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 312: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.03.026
[13] De Mendoza F P, Bonamano S, Martellucci R, et al. Circulation during storms and dynamics of suspended matter in a sheltered coastal Area [J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4):602-630. doi: 10.3390/rs10040602
[14] Anthony E J, Héquette A. The grain-size characterisation of coastal sand from the Somme estuary to Belgium: Sediment sorting processes and mixing in a tide- and storm-dominated setting[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 202(3): 369-382. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8500f0ca482b3c5d6c540941bcf8e000&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Anthony E J, Gardel A, Gratiot N, et al. The Amazon-influenced muddy coast of South America: A review of mud-bank-shoreline interactions[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2010, 103(3/4): 99-121. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e23acd9b208101bd266e1ed8e1de4da1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[16] 中国海湾志编纂委员会.中国海湾志(第三分册)[M].海洋出版社,1998.
[17] 王厚杰, 杨作升, 毕乃双. 黄河口泥沙输运三维数值模拟Ⅰ——黄河口切变锋[J]. 泥沙研究,2006(2):1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.02.001
[18] 臧启运. 黄河三角洲近岸泥沙[M].海洋出版社,1996.
[19] 计建强, 汪一航, 王新怡, 等. 夏季黄河入海泥沙的数值模拟研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2016,40(3):118-127. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201603017
[20] Pacheco A, Ferreira ó. Hydrodynamic changes imposed by tidal energy converters on extracting energy on a real case scenario[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 180: 369-385. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.132
[21] Zhu Q G, Wang Y P, Ni W F, et al. Effects of intertidal reclamation on tides and potential environmental risks: a numerical study for the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(23):1472. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6275-0
[22] 邢国攀, 宋振杰, 张勇, 等.黄河钓口河口行水期泥沙输运过程的三维数值模拟[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5):21-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201605004
[23] 刘 锋.黄河口及其邻近海域泥沙输运及其动力地貌过程[D]. 上海:华东师范大学, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10269-1012435997.htm [24] Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H, et al. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 95(1): 39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.08.001
[25] Lu J, Qiao F, Wang X, et al. Modeling the Yellow River sediment flux and its deposition patterns under climatological conditions[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2013, 63(6): 709-722. doi: 10.1007/s10236-013-0626-0
[26] Escobar C A, Velasquez-Montoya L. Modeling the sediment dynamics in the gulf of Uraba colombian Caribbean sea[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 147: 476-487. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.10.055
[27] 李蒙蒙, 王 庆, 张安定, 等. 最近50a来莱州湾西—南部潮流动力演变的数值模拟研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2014,(5):68-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.05.008
[28] Bi N S, Yang Z S, Wang H J, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.007
[29] Li G S, Wang H L, Liao H P. Numerical simulation on seasonal transport variations and mechanisms of suspended sediment discharged from the Yellow River to the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2010, 20(6): 923-937. doi: 10.1007/s11442-010-0821-6
[30] 王崇浩,曹文洪,张世奇.黄河口潮流与泥沙输移过程的数值研究[J].水利学报,2008(10):1256-1263. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2008.10.015
[31] Bi N S, Yang Z S, Wang H J, et al. Sediment dispersion pattern off the present Huanghe (Yellow River) subdelta and its dynamic mechanism during normal river discharge period[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 86(3): 352-362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.06.005
[32] 寿玮玮,宗海波,丁平兴.夏季黄河入海径流对黄河口及附近海域环流影响的数值研究[J].海洋学报,2016,38(7):1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.07.001
[33] Yang Z S, Ji Y J, Bi N S, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005
[34] 孔岩,王红,任立良.黄河入海径流变化及影响因素[J].地理研究,2012,31(11):1981-1990. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200705012
[35] 刘 锋, 陈沈良, 彭俊, 等.近60年黄河入海水沙多尺度变化及其对河口的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(3):313-323. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlxb201103003
[36] Lu Y C, Shen Y M. Influence of bathymetry evolution on position of tidal shear front and hydrodynamic characteristics around the Yellow River estuary [J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2012, 6(4): 405-419. doi: 10.1007/s11707-012-0334-y
[37] Boudet L, Sabatier F, Radakovitch O. Modelling of sediment transport pattern in the mouth of the Rhone delta: Role of storm, and flood events[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2017, 198: 568-582. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.10.004
[38] De Marchis M, Freni G, Napoli E. Three-dimensional numerical simulations on wind- and tide-induced currents: The case of Augusta Harbour (Italy)[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2014, 72: 65-75 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300414001605
-



 下载:
下载: