RESEARCH OF MICROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF SUBMARINE SAND WAVES IN DAISHAN HOUSHAYANG OF ZHOUSHAN ISLANDS
-
摘要:
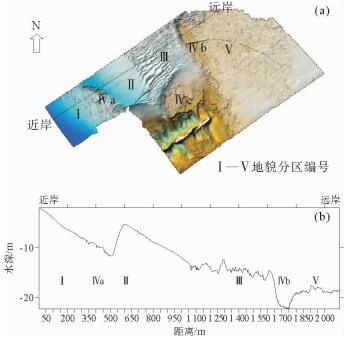
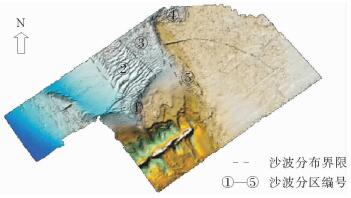
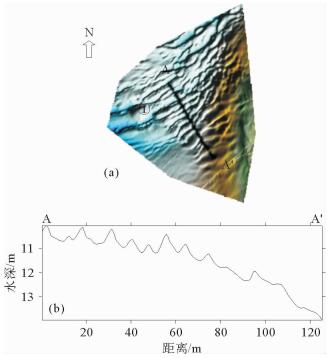
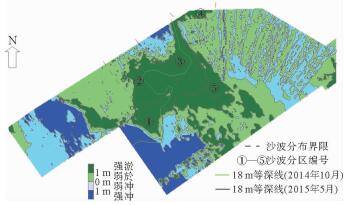
利用多波束测深系统和浅地层剖面系统,对舟山群岛岱山后沙洋进行高精度探测,结果表明:①区内微地貌形态具有明显的分带性,依次出现岸坡区、沙脊区、缓坡区、沟槽区和深水平坦区;②海底沙波主要集中在缓坡区、沙脊区南侧及东侧边缘、沟槽区北侧及沟槽内2个小沟槽交界处的迎水流斜坡上;③海底沙波多发育于水深10.0~21.1 m之间,地形相对平缓,坡度0.09°~2.8°;④区内海底沙波可分为小型、中型和大型沙波;⑤区内海底沙波是潮流动力形成的现代强运动型沙波。
Abstract:Sand waves in the Daishan Houshayang of the Zhoushan Islands were surveyed with multibeam sounding system and subbottom profiler. Results show that, 1) bedforms are distributed in the zones of shore slope, sand ridge, gentle slope, trench and flat bed seawards from the coast; 2) sand waves are mainly developed in the gentle slope zone, the south and east to the sand ridge zone, the north of the trench and the slopes between small trenches; 3) sand waves are usually distributed in relatively flat terrain within a depth of 10m to 21.1m on a slope less than 0.09 degree to 2.8 degree; 4) sand waves can be divided into small, medium and large ones in a zone. 5) sand waves move actively under the action of tidal current.
-
Key words:
- Daishan Houshayang /
- marine topography /
- microrelief character /
- submarine sand waves /
- Zhoushan Islands
-

-
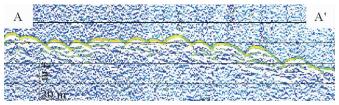
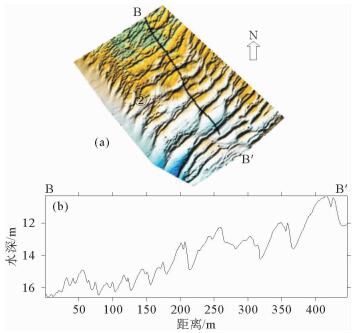
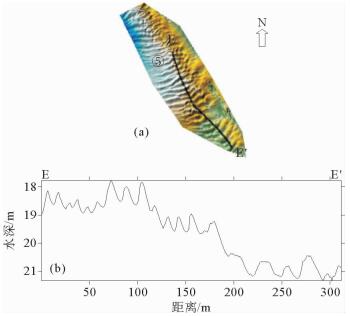
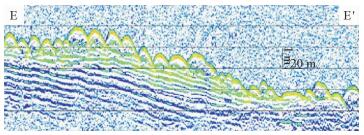
图 5 沙波①区浅地层剖面(位置同图 4)
Figure 5.
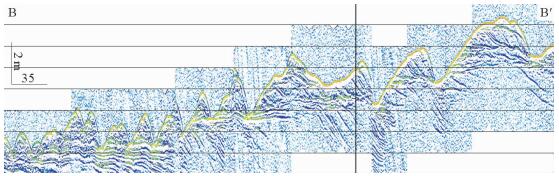
图 7 沙波②区浅地层剖面(位置同图 6)
Figure 7.
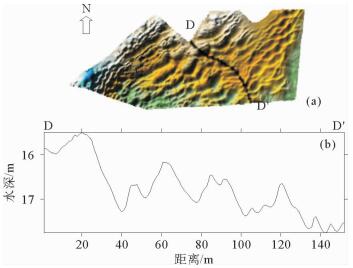
图 9 沙波③区浅地层剖面(位置同图 8)
Figure 9.
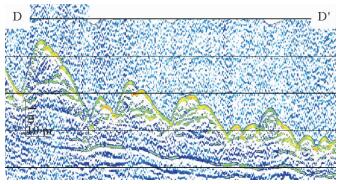
图 11 沙波④区浅剖剖面(位置同图 10)
Figure 11.
图 13 沙波⑤区浅地层剖面(位置同图 12)
Figure 13.
-
[1] Anthony D, Leth J O. Large-scale bedforms, sediment distribution and sand mobility in the eastern North Sea off the Danish west coast[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 182(3-4):247-263. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00245-6
[2] Santoro V C, Amore E, Cavallaro L, et al. Evolution of sand waves in the Messina Strait, Italy[J].Ocean Dynamics, 2004, 54(3-4):392-398. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=283b2636a5f53a7a9e912ebe8d2b3cfe
[3] Idier D, Ehrhold A, Garlan T. Morphodynamics of an undersea sand wave of the Dover Straits[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2002, 334(15):1079-1085. doi: 10.1016/S1631-0713(02)01852-7
[4] Kennedy A B, Slatton K C, Hsu T, et al. Ephemeral sand waves in the hurricane surf zone[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 250(3-4):276-280. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.01.015
[5] Todd B J. Morphology and composition of submarine barchans dunes on the Seotian Shelf, Canadian Ailantiemargin[J]. Geomorphology, 2005, 67(3-4):487-500. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.11.016
[6] Perillo G M E, Ludwiek J C. Geomorphology of a sand wave in lower Chesapeake Bay, Virginia, U.S.A.[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1994, 4(2):105-112. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02277080
[7] Ludwiek J C. Sand waves in the tidal entrance to Chesapeake Bay Preliminary observations[J]. Earth and Environmental Seience, 1970, 11(2):98-110. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f9f1cc084acc22a0960eb71137923ddd&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[8] 吴建政, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等.南海北部海底沙波研究[J].中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(6):1019-1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5174.2006.06.033
[9] 张晶晶, 庄振业, 曹立华.南海北部陆架陆坡沙波底形[J].海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(7):11-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201507002
[10] 白玉川, 杨细根, 田琦, 等.南海北部海域海底沙波演化特征[J].水利学报, 2009, 40(8):941-947. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=slxb200908007
[11] 李泽文, 阎军, 栗振东, 等.海南岛西南海底沙波形态和活动性的空间差异分析[J].海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(7):24-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDT201007007.htm
[12] 曹立华, 徐继尚, 李广雪, 等.海南岛东方岸外沙波的高分辨率形态特征[C]//第九届全国河口海岸学术研讨会, 2006.
[13] 李近元, 范奉鑫, 徐涛, 等.莱州湾东部沙波地貌分布特征及其形成演化[J]海洋湖沼通报, 2007(增刊):51-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hykx201107010
[14] 余威, 吴自银, 周洁琼, 等.台湾浅滩海底沙波精细特征、分类与分布规律[J].海洋学报, 2015, 37(10):11-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201510002
[15] 龙海燕, 庄振业, 刘升发, 等.扬子浅滩沙波底形活动性评估[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6):17-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200706003
[16] 俞康定.崇明东滩大型沙波特征及其成因讨论[D].上海: 华东师范大学, 2007.
[17] 边淑华, 夏东兴, 陈义兰, 等.胶州湾口海底沙波的类型、特征及发育影响因素[J].中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(2):327-330. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200602032
[18] 刘振夏, 汤毓祥, 王揆洋, 等.渤海东部潮流动力地貌特征[J].黄渤海海洋, 1996, 14(1): 7-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH601.001.htm
[19] Swift D J P, Field M E. Evolution of a classic sand ridge:Maryland sector, North American inner shelf[J]. Sedimentary, 1981, 28 :461-482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1981.tb01695.x
[20] Allen J R L. Sedimentary structures, their character and physical basis[T].Earth Science Revieus, 1983, 19(4): 362-363.
[21] Allen J R L. Sand waves: A model of origin and internal structure[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1980, 26(4): 281-328 doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(80)90022-6
[22] Stride A H. Offshore Tidal Sands Processes and Deposits[M].London:New York Chopm an and Hall, 1982 :222.
[23] 庄振业, 曹立华, 刘升发, 等.陆架沙丘(波)活动量级和稳定性标志研究[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 38(6):1001-1007. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200806033
[24] Ashley G M. Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms:A new look at an old problem[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1990, 60(1) : 160 -172. doi: 10.2110/jsr.60.160
[25] Flemming B W. Zur Klassifikation Subaquatischer, Strömungstransversaler Transpörtkrper. Boch[C]//Geol. Geotech. Arb. 29 (Bochumer Geologische und Geotechnische Arbeiten 29), 1988: 44-47.
[26] 刘振夏, 夏东兴.中国近海潮流沉积沙体[M].北京:海洋出版社:46-53.
[27] Daniell J J, Hughes M. The morphology of barchans-shaped sand banks from western Torres Strait, northern Australia[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 202(4):638-652. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0e7119fc614b87fa776eeb9910b58ede
[28] 庄振业, 林振宏, 周江, 等.陆架沙丘(波)形成发育的环境条件[J].海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(4): 5-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt200404002
[29] 韩月.舟山北部海域海底第四系水文地质条件研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
-



 下载:
下载: