THE NAMUQIN GOLD-POLYMETALLIC DEPOSIT IN WESTERN BANGONGHU-NUJIANG METALLOGENIC BELT, TIBET: Geology and Genesis
-
摘要:
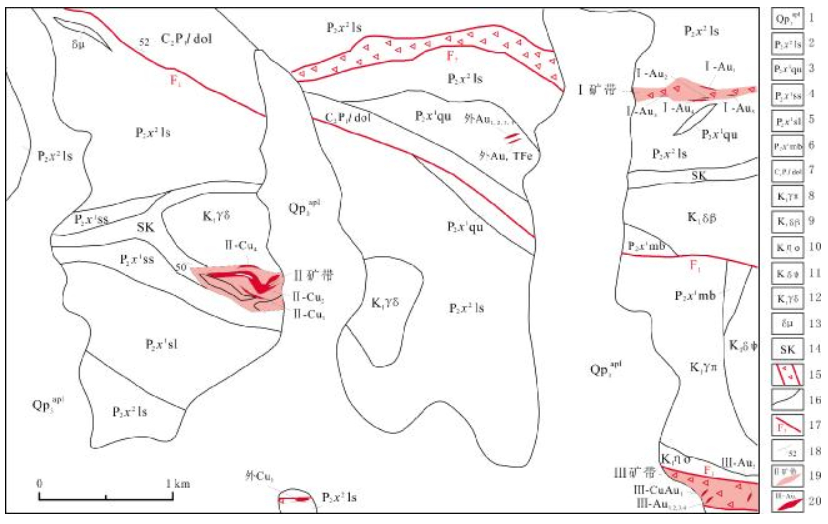
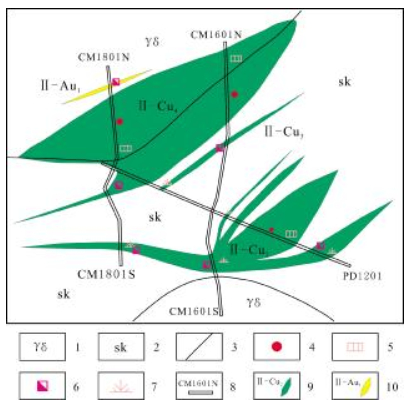
钠木钦金多金属矿位于西藏班公湖-怒江成矿带西段,区域成矿以铜、金、铁矿为主.研究认为,钠木钦铜矿体受中二叠世下拉组地层与早白垩世中酸性侵入岩接触带——夕卡岩控制,而金矿体则主要受近东西向断裂构造控制,铜矿成矿类型为夕卡岩型,金矿成矿类型为构造蚀变岩型,成矿时代为早白垩世.矿区Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ号矿体的深部及Ⅱ号铜矿体的西部还具有较大的找矿空间.对矿区矿床特征的研究发现,钠木钦矿与区域上的尕尔穷等矿床具有较为相似的地质背景及成矿特征,但也有其独特之处.
Abstract:The Namuqin gold-polymetallic deposit is located in the western section of Bangonghu-Nujiang metallogenic belt in Tibet, with regional mineralization dominated by copper, gold and iron. The study indicates that the copper orebodies in Namuqin deposit are controlled by skarn in the contact zone between the Middle Permian Xiala Formation and Early Cretaceous acid-intermediate intrusive rocks, while the gold orebodies are mainly controlled by the near E-W-trending fault. The metallogenesis of copper and gold are skarn type and structural altered rock type respectively, with the ore-forming age of Early Cretaceous. The deep of Nos. Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ orebodies and west of No. Ⅱ copper orebody in the orefield still have great prospecting potential. Study shows that the Namuqin deposit shares similar geological background and metallogenic characteristics with Garqiong deposit in the region, but also with special features.
-
Key words:
- gold polymetallic deposit /
- geological characteristic /
- genesis of deposit /
- Namuqin /
- Tibet
-

-
表 1 矿体基本特征一览表
Table 1. Characteristics of orebodies
矿带编号 矿体编号 矿体长度/m 平均厚度/m 平均品位 产状 Cu/10-2 Au/10-6 Ag/10-6 TFe/10-2 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) Ⅰ Ⅰ-Au1 324 4.14 0.38 4.36 15 70 Ⅰ-Au2 220 2.24 2.49 52.2 29 52 Ⅰ-Au3 80 3.81 4.66 358 58 Ⅰ-Au4 216 4.08 12.2 63.62 358? 42 Ⅰ-Au5 80 1.13 1.56 0 70 Ⅱ Ⅱ-Cu1 190 2.84 0.43 165 32 Ⅱ-Cu2 570 20.35 0.59 142-185 43-60 Ⅱ-Cu3 145 2.39 0.31 150 37 Ⅱ-Cu4 285 23.85 0.81 151 39 Ⅱ-Au1 80 1.74 1.95 151 39 Ⅲ Ⅲ-Au1 80 11.16 20.6 155 75 Ⅲ-Au2 80 1.24 20.8 155 75 Ⅲ-Au3 80 1.24 4.03 155 75 Ⅲ-Au4 80 3.72 27.35 155 75 Ⅲ-Au5 80 2.88 6.54 130 75 Ⅲ-Cu、Au1 80 2.48 0.35 5.42 155 75 外Cu1 160 23.52 0.28 195 79 外Au1 80 1.12 1.15 336 61 外Au2 80 2.93 1.2 336 61 外Au3 80 7.02 1.77 336 61 外Au、TFe1 80 9.52 2.26 20.9 336 61 -
[1] 潘桂棠.青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013:15-130.
[2] 吕立娜, 赵元艺, 宋亮, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江成矿带西段富铁矿与铜(金)矿C、Si、O、S和Pb同位素特征及地质意义[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(8):1291-1304. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201108005
[3] 胡正华, 丁枫, 唐菊兴, 等.西藏革吉县尕尔穷铜金矿床地质特征及其成因意义[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(4):588-600. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.04.19
[4] 张志, 唐菊兴, 陈毓川, 等.西藏班-怒结合带尕尔穷铜金矿床矽卡岩矿物学特征及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(3):305-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.03.003
[5] 陈红旗, 曲晓明, 范淑芳.西藏改则县多龙矿集区斑岩型铜金矿床的地质特征与成矿-找矿模型[J].矿床地质, 2015, 34(2):321-332. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201502008
[6] 段志明, 李光明, 张晖, 等.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带北缘多龙矿集区晚三叠世-侏罗纪增生杂岩结构及其对成矿地质背景的约束[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(5):742-750. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.05.007
[7] 高轲, 钟康惠, 唐菊兴, 等.西藏多龙矿集区拿若铜矿床地质特征与找矿前景探讨[J].矿物学报, 2013(S2):763-764. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8301358
[8] 李玉彬, 钟婉婷, 张天平, 等.西藏改则县波龙斑岩型铜金矿床地球化学特征及成因浅析[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(4):579-587. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.04.18
[9] 方向, 唐菊兴, 丁帅, 等.西藏多龙矿集区尕尔勤岩石地球化学特征及构造环境[J].矿物学报, 2013(S2):306-307. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8301008
[10] 何建娟, 肖渊甫, 郭龙, 等.西藏嘎拉勒铜金矿床金和银的赋存状态研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(6):1143-1150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.06.012
[11] 冯国胜, 陈振华, 廖六根, 等.西藏日土地区弗野玢岩铁矿的地质特征及找矿意义[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(8):1041-1047. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.08.018
[12] 胡为正, 廖辉宝, 黄东荣.西藏日土县材玛铁矿地质特征及找矿方向[J].资源调查与环境, 2014, 35(2):120-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2014.02.005
-




 下载:
下载: