THE ACID-INTERMEDIATE INTRUSIVE ROCKS IN THE EAST SECTION OF MIDDLE QILIAN OROGENIC BELT: LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age and Tectonic Implications
-
摘要:
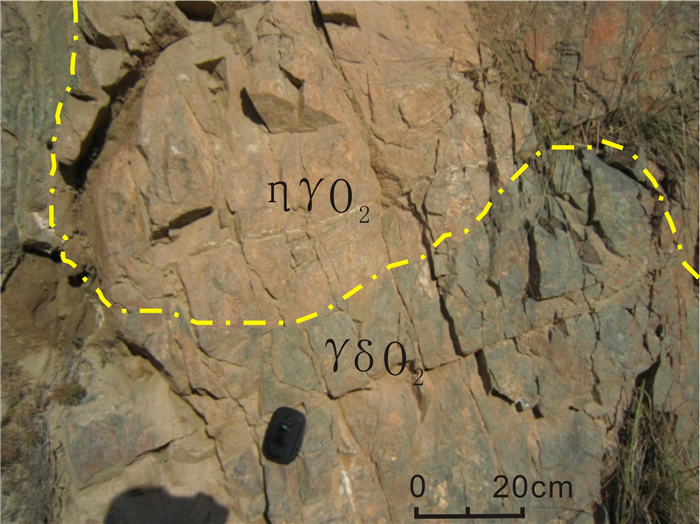
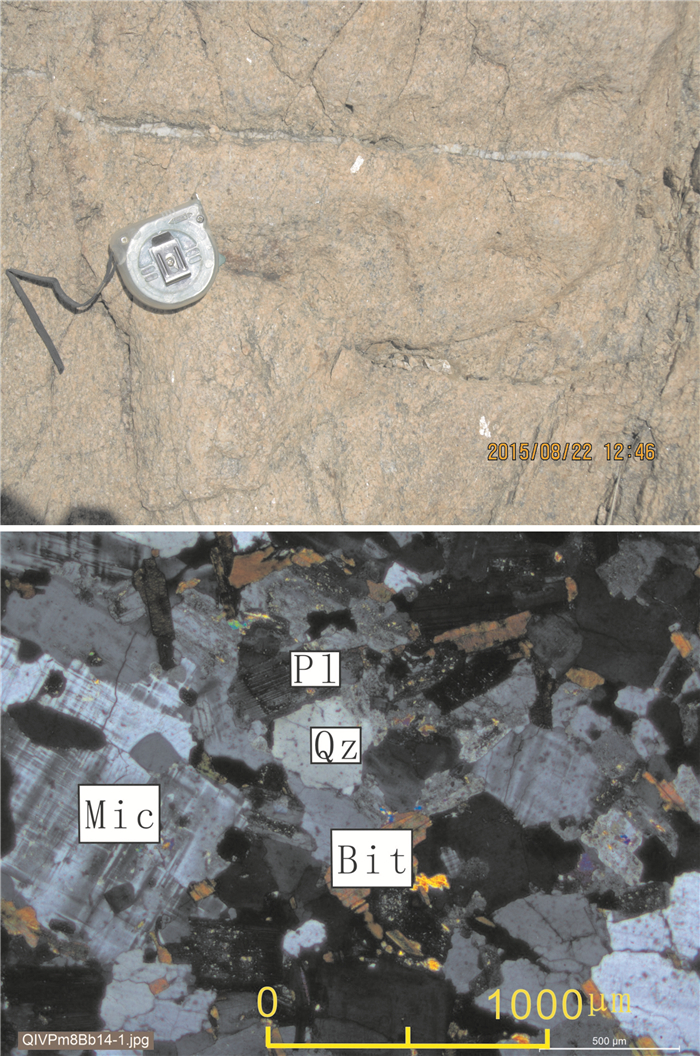
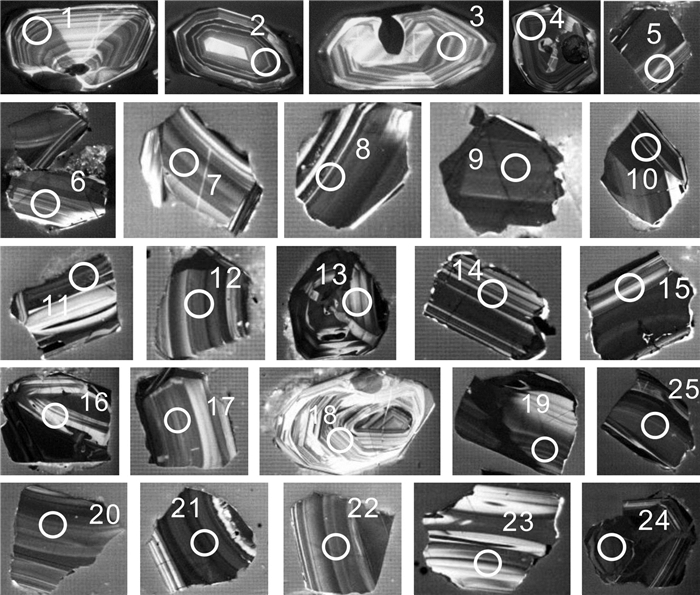
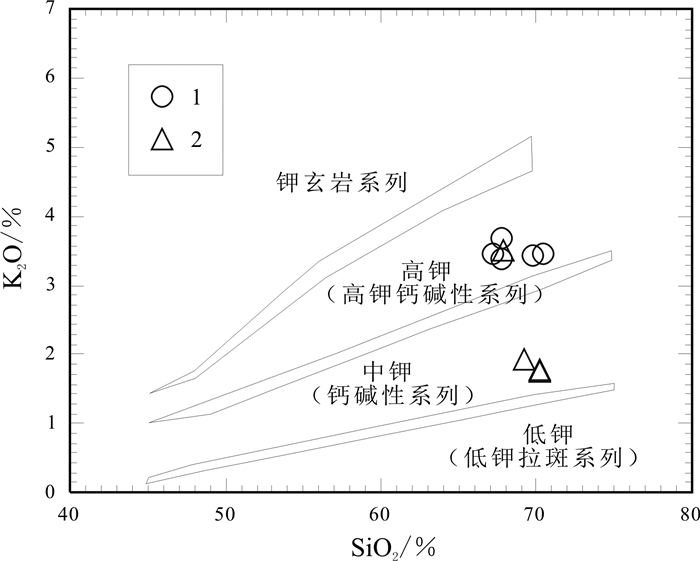
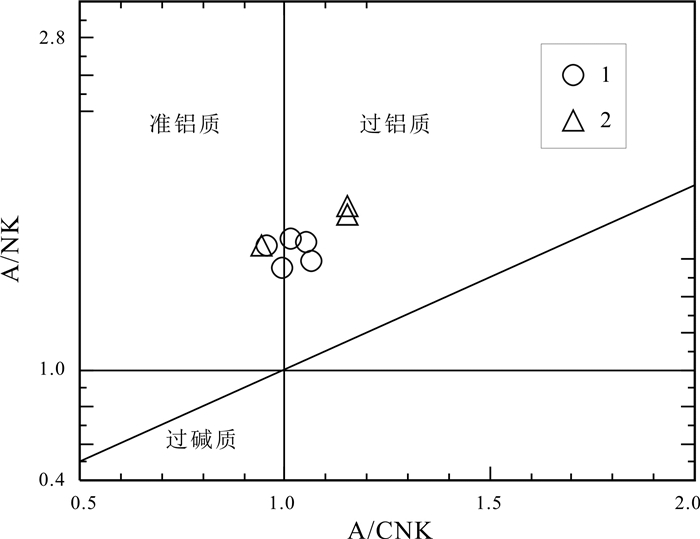
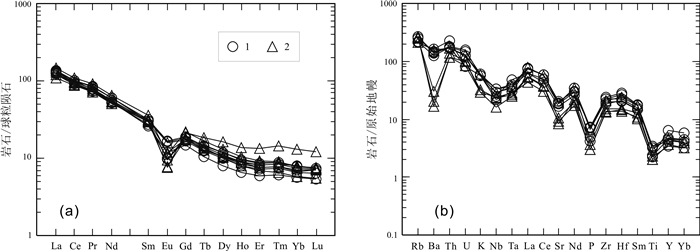
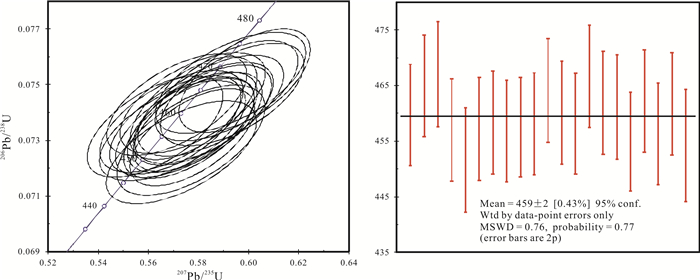
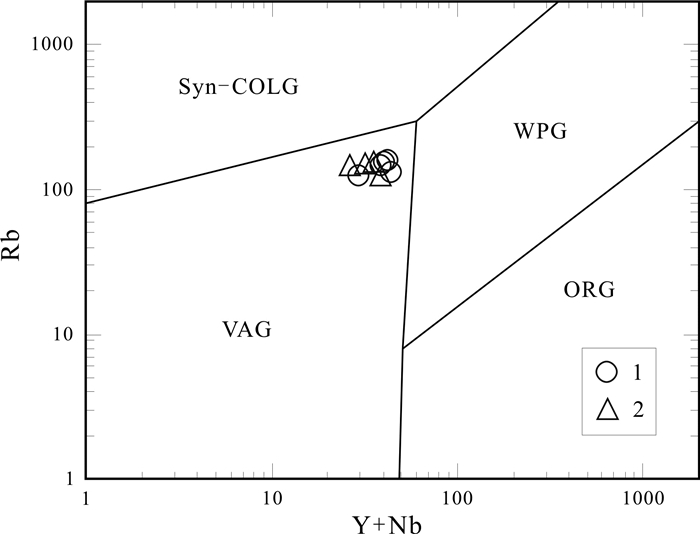
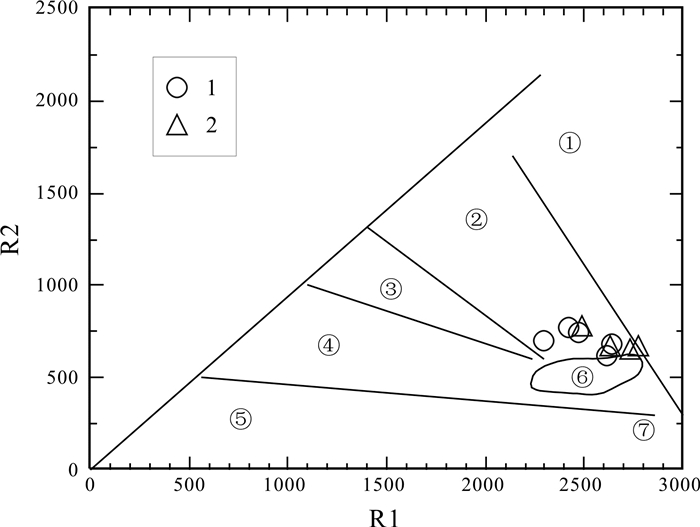
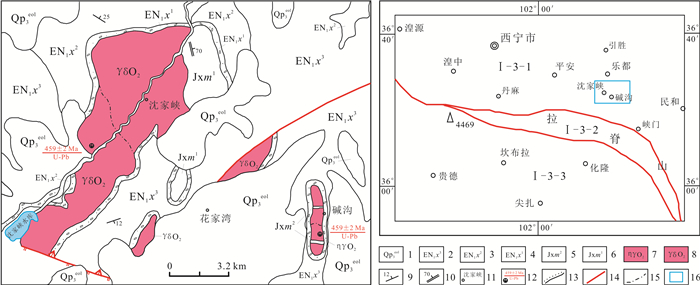
青海省中祁连东段乐都沈家峡-碱沟一带发育有中酸性侵入体.野外地质调查和和岩相学等研究表明,侵入体呈岩株状,主要由二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩组成,两者间呈脉动接触.对2件二长花岗岩样品进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测年,获得的加权平均年龄分别为465.7±2.2 Ma(n=24,MSWD=0.031)、459±2 Ma(n=21,MSWD=0.76),表明侵入体时代为中奥陶世.岩石地球化学特征表明,该期侵入体属准铝质-过铝质中高钾钙碱性系列岩石,岩石(La/Yb)N为10.57~23.126,δEu为0.47~0.69,稀土配分曲线具"V"型右倾特征;大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba、Th、K、La、Ce、Sm、Nd强富集,Zr、Hf弱富集,高场强元素Nb、Ta、P、Ti强亏损;岩石具有岛弧型岩浆岩特征,其形成可能与北祁连洋向南俯冲有关.
Abstract:The acid-intermediate intrusions are developed in Shenjiaxia-Jiangou area in the east section of Middle Qilian Mountains, Qinghai Province. The field geological survey and petrographic study show that the intrusions occur in stock, mainly consisting of monzogranite and granodiorite which are in pulsation contact with each other. The LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic dating of 2 monzogranite samples gains the weighted average ages of 465.7±2.2 Ma (n=24, MSWD=0.031) and 459±2 Ma (n=21, MSWD=0.76) respectively, indicating that the intrusions were formed in Middle Ordovician. The lithogeochemical characteristics reveal that the intrusions belong to quasialuminous-peraluminous medium-high K calc-alkaline series with the (La/Yb)N of 10.57-23.126 and δEu of 0.47-0.69. The REE patterns show right-dipping "V" shaped curves. The LILEs such as Rb, Ba, Th, K, La, Ce, Sm and Nd are strongly enriched, Zr and Hf weakly enriched, while the HSFEs (Nb, Ta, P and Ti) are strongly depleted. The rocks are characterized by island arc magmatite, which may be related to the southward subduction of North Qilian Ocean.
-
Key words:
- monzogranite /
- granodiorite /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age /
- island arc /
- Northern Qilian Ocean /
- Qinghai Province
-

-
表 1 沈家峡-碱沟地区中酸性侵入岩岩石地球化学分析结果
Table 1. Geochemical composition of acid-intermediate intrusive rocks in Shenjiaxia-Jiangou area
样品号 花岗闪长岩 二长花岗岩 PM08GS5-1 PM08GS7-1 PM08GS8-1 PM08GS9-1 PM08GS25-1 PM08GS6-1 PM26GS14-2 PM26GS14-3 PM26GS14-4 SiO2 69.44 66.74 66.07 66.8 68.45 66.65 69.52 68.46 69.54 TiO2 0.51 0.73 0.74 0.68 0.48 0.65 0.43 0.5 0.44 Al2O3 14.33 14.75 14.58 14.92 14.56 14.49 15.54 15.67 15.49 Fe2O3 0.71 1.32 1.15 0.85 0.93 0.79 0.86 0.84 0.86 FeO 2.7 2.85 3.45 3.35 2.6 3.3 2.75 3.3 2.92 MnO 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.09 0.05 0.06 0.06 MgO 1.36 1.56 1.76 1.66 1.54 1.67 1.09 1.22 0.97 CaO 2.48 2.97 3.61 3.34 2.86 3.72 2.87 2.82 2.78 Na2O 3.26 3.43 3.06 3.11 3.03 3.01 3.86 3.92 3.98 K2O 3.41 3.62 3.4 3.35 3.37 3.44 1.77 1.91 1.75 P2O5 0.21 0.31 0.31 0.3 0.18 0.28 0.13 0.16 0.13 H2O+ 1.17 1.13 1.16 1.16 1.27 1.22 0.93 0.94 0.86 CO2 0.04 0.25 0.38 0.11 0.4 0.4 0.05 0.05 0.02 LOI 0.99 1.07 1.16 0.92 1.38 1.30 0.69 0.64 0.61 总量 99.47 99.43 99.38 99.37 99.46 99.39 99.56 99.5 99.53 σ 1.67 2.07 1.78 1.73 1.59 1.73 1.19 1.32 1.23 A/NK 1.58 1.54 1.67 1.71 1.69 1.67 1.88 1.84 1.84 A/CNK 1.06 0.99 0.95 1.01 1.05 0.94 1.15 1.15 1.15 K2O/Na2O 1.05 1.06 1.11 1.08 1.11 1.14 0.46 0.49 0.44 La 40.36 40.96 50.25 49.50 47.89 50.74 34.55 35.06 28.49 Ce 72.71 82.65 98.86 98.71 97.35 96.36 61.6 63.39 51.26 Pr 9.12 9.80 11.62 11.70 10.67 11.69 6.89 7.28 5.85 Nd 32.28 36.89 43.38 43.08 38.23 43.68 24.9 26.75 21.38 Sm 6.06 6.37 7.37 7.07 6.03 7.12 4.47 5.2 4.14 Eu 1.05 1.33 1.46 1.44 1.03 1.40 0.78 0.76 0.69 Gd 5.33 5.07 5.82 5.50 4.59 5.32 3.7 4.4 3.72 Tb 0.92 0.72 0.83 0.75 0.61 0.79 0.51 0.66 0.55 Dy 5.26 3.73 4.25 3.97 3.06 4.06 3.06 3.99 3.22 Ho 1.00 0.67 0.77 0.72 0.56 0.75 0.58 0.73 0.6 Er 2.88 1.83 2.07 1.92 1.50 2.04 1.52 1.96 1.55 Tm 0.43 0.27 0.30 0.28 0.22 0.30 0.22 0.28 0.22 Yb 2.58 1.76 1.97 1.78 1.40 1.87 1.4 1.71 1.4 Lu 0.36 0.27 0.29 0.27 0.21 0.28 0.22 0.27 0.22 Sr 331.2 366.1 365.2 386.1 404.7 376.7 210.2 167.4 184.6 Rb 133.3 158.2 161.6 150.4 127.3 126.9 149.9 160.7 156.3 Ba 833.6 915.4 954.5 974.8 1066 1033 199.3 110.3 135.6 Th 13.69 13.79 14.27 13.49 17.99 13.34 10.95 9.32 9.26 Ta 1.79 1.37 1.46 1.28 1.13 1.35 0.92 0.99 1.06 Nb 16.13 22.02 21.85 19.56 14.55 18.89 10.76 15.21 16.07 Zr 196.6 238.7 250.6 237.7 209.9 222.4 141.6 159.3 140.3 Hf 5.8 6.3 7.9 7.4 5.7 6.70 3.80 4.20 4.10 Cr 12.07 19.58 29.09 24.38 16.99 16.53 16.06 19.24 18.11 Pb 25.9 18.58 19.46 14.41 16.42 25.16 - - - U 1.61 2.95 3.14 2.46 1.61 2.56 2.07 1.96 1.70 Y 27.51 18.15 20.5 18.95 14.72 20.02 15.64 19.91 15.93 Sc 7.89 9.01 11.29 10.18 9.21 10.42 8.44 9.78 8.76 Cs 5.97 13.06 13.09 9.72 6.11 9.31 7.52 6.67 6.30 Ga 16.99 18.22 19.14 18.56 17.15 17.97 18.92 20.24 22.10 ∑REE 180.34 192.32 229.24 226.69 213.35 226.40 144.40 152.44 123.29 LREE 161.58 178.00 212.94 211.50 201.20 210.99 133.19 138.44 111.81 HREE 18.76 14.32 16.30 15.19 12.15 15.41 11.21 14.00 11.48 LREE/HREE 8.61 12.43 13.06 13.92 16.56 13.69 11.88 9.89 9.74 (La/Yb)N 10.57 15.73 17.24 18.79 23.12 18.34 16.68 13.85 13.75 δEu 0.55 0.69 0.66 0.68 0.58 0.67 0.57 0.47 0.53 (La/Sm)N 4.19 4.04 4.29 4.40 5.00 4.48 4.86 4.24 4.33 (Gd/Yb)N 1.67 2.32 2.38 2.49 2.65 2.30 2.13 2.08 2.14 含量单位:氧化物为%,微量、稀土元素为10-6. 表 2 沈家峡二长花岗岩U-Pb年龄同位素参数特征表
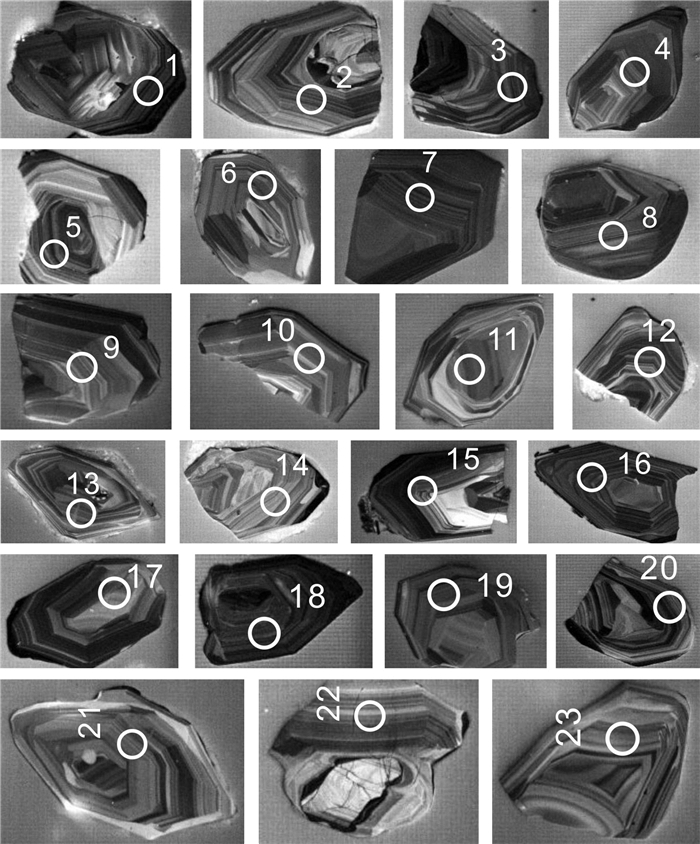
Table 2. U-Pb isotopic parameter characteristics of Shenjiaxia monzogranite
点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 168.2 591.66 0.47 0.05622 0.00113 0.58222 0.01164 0.0751 0.00089 0.02201 0.0004 461 24 466 7 467 5 2 77.1 273.04 0.69 0.05619 0.00127 0.57807 0.01291 0.07461 0.00091 0.02187 0.00042 460 28 463 8 464 5 3 145.44 513.28 0.53 0.05598 0.00118 0.57809 0.01209 0.07488 0.0009 0.02119 0.0004 452 26 463 8 465 5 4 81.24 286.45 0.53 0.0562 0.00134 0.58098 0.0137 0.07496 0.00094 0.02124 0.00045 460 31 465 9 466 6 5 75.97 268.47 0.49 0.05616 0.00128 0.57948 0.01313 0.07482 0.00092 0.02222 0.00044 459 29 464 8 465 6 6 105.94 372.65 0.50 0.05499 0.00121 0.57003 0.01241 0.07517 0.00091 0.02272 0.00044 412 28 458 8 467 5 7 107.37 378.91 0.43 0.05628 0.00128 0.58168 0.01316 0.07495 0.00092 0.02148 0.00044 463 29 466 8 466 6 8 102.48 362.13 0.41 0.05551 0.00128 0.57307 0.0131 0.07486 0.00092 0.02244 0.00048 433 30 460 8 465 6 9 80.49 284.3 0.47 0.05625 0.00133 0.5811 0.0136 0.07491 0.00092 0.02176 0.00045 462 31 465 9 466 6 10 102.09 361.08 0.46 0.05634 0.00124 0.58135 0.01273 0.07482 0.00091 0.02219 0.00044 466 28 465 8 465 5 11 110.42 391.57 0.42 0.05559 0.00123 0.57224 0.01259 0.07464 0.00091 0.02263 0.00046 436 28 459 8 464 5 12 129.2 456.43 0.68 0.06228 0.00137 0.64368 0.01403 0.07494 0.00091 0.02352 0.00045 684 26 505 9 466 5 13 77.76 274.1 0.54 0.0582 0.00152 0.60297 0.01558 0.07512 0.00095 0.02388 0.00051 537 35 479 10 467 6 14 111.46 393.86 0.44 0.0558 0.00125 0.57679 0.01282 0.07495 0.00091 0.02183 0.00045 444 28 462 8 466 5 15 129.15 456.53 0.68 0.05697 0.00126 0.58878 0.01294 0.07494 0.00091 0.02153 0.00041 490 28 470 8 466 5 16 65.4 231.81 0.51 0.05622 0.00148 0.57955 0.01508 0.07475 0.00094 0.02236 0.00049 461 36 464 10 465 6 17 84.23 298.05 0.42 0.05632 0.00143 0.58167 0.01456 0.0749 0.00096 0.02172 0.00051 465 33 466 9 466 6 18 115.68 409.76 0.46 0.05639 0.00124 0.5819 0.01269 0.07483 0.00091 0.0211 0.00043 468 27 466 8 465 5 19 105.07 371.01 0.37 0.05618 0.00127 0.58169 0.01304 0.07508 0.00092 0.02155 0.00046 459 29 466 8 467 6 20 119.76 423.57 0.53 0.05632 0.00122 0.58234 0.01258 0.07497 0.00091 0.02152 0.00043 465 27 466 8 466 5 21 95.02 336.04 0.53 0.05812 0.00133 0.60138 0.01369 0.07503 0.00092 0.01992 0.00041 534 29 478 9 466 6 22 91.16 323.79 0.54 0.05632 0.00129 0.5803 0.01322 0.07471 0.00092 0.01998 0.00041 465 29 465 8 464 6 23 88.61 313.11 0.49 0.05633 0.00135 0.58354 0.01383 0.07511 0.00094 0.02187 0.00047 465 31 467 9 467 6 24 225.65 371.91 0.44 0.08606 0.00177 1.91171 0.0392 0.16108 0.00194 0.06682 0.0013 1340 22 1085 14 963 11 25 85.6 302.91 0.45 0.05626 0.00129 0.58225 0.01329 0.07504 0.00093 0.0217 0.00046 463 29 466 9 466 6 测试单位:天津地质矿产研究所. 表 3 碱沟二长花岗岩U-Pb年龄同位素参数特征表
Table 3. U-Pb isotopic parameter characteristics of Jiangou monzogranite
点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 21 292 0.30 0.0571 0.0011 0.5815 0.0113 0.0739 0.0007 0.0173 0.0003 460 5 465 9 494 41 2 25 337 0.43 0.0573 0.0011 0.5912 0.0116 0.0748 0.0007 0.0185 0.0002 465 5 472 9 505 42 3 39 532 0.19 0.0578 0.0010 0.5984 0.0107 0.0751 0.0008 0.0255 0.0004 467 5 476 9 521 37 4 23 319 0.34 0.0567 0.0011 0.5746 0.0113 0.0735 0.0007 0.0189 0.0003 457 5 461 9 481 41 5 20 284 0.23 0.0573 0.0012 0.5732 0.0123 0.0726 0.0008 0.0247 0.0007 452 5 460 10 502 45 6 25 334 0.39 0.0555 0.0010 0.5626 0.0111 0.0735 0.0007 0.0193 0.0002 457 5 453 9 433 41 7 22 300 0.29 0.0560 0.0011 0.5692 0.0117 0.0737 0.0007 0.0193 0.0003 458 5 458 9 454 43 8 30 417 0.24 0.0569 0.0010 0.5762 0.0107 0.0734 0.0007 0.0229 0.0003 457 5 462 9 488 39 9 29 400 0.30 0.0563 0.0010 0.5707 0.0107 0.0736 0.0007 0.0214 0.0002 458 4 458 9 463 40 10 26 366 0.24 0.0569 0.0010 0.5775 0.0106 0.0737 0.0007 0.0219 0.0002 458 5 463 8 486 38 11 22 272 0.53 0.0577 0.0011 0.5935 0.0117 0.0746 0.0008 0.0247 0.0002 464 5 473 9 517 41 12 49 1624 0.08 0.0501 0.0011 0.1983 0.0038 0.0287 0.0007 0.0535 0.0022 182 5 184 3 199 50 13 27 374 0.27 0.0571 0.0010 0.5822 0.0113 0.0740 0.0007 0.0228 0.0004 460 5 466 9 494 40 14 33 448 0.24 0.0571 0.0010 0.5797 0.0105 0.0737 0.0007 0.0280 0.0005 458 5 464 8 494 38 15 21 262 0.55 0.0573 0.0011 0.5928 0.0123 0.0751 0.0007 0.0243 0.0003 467 5 473 10 502 43 16 22 294 0.32 0.0558 0.0011 0.5714 0.0114 0.0743 0.0007 0.0220 0.0002 462 5 459 9 444 42 17 97 340 0.47 0.0958 0.0015 3.5402 0.0596 0.2679 0.0028 0.0751 0.0007 1530 16 1536 26 1545 29 18 35 492 0.22 0.0565 0.0009 0.5780 0.0103 0.0742 0.0008 0.0214 0.0002 461 5 463 8 473 37 19 30 427 0.14 0.0573 0.0010 0.5775 0.0101 0.0731 0.0007 0.0218 0.0004 455 4 463 8 503 37 20 17 233 0.27 0.0564 0.0011 0.5777 0.0119 0.0743 0.0007 0.0217 0.0004 462 5 463 10 467 44 21 22 284 0.53 0.0563 0.0011 0.5696 0.0119 0.0733 0.0007 0.0220 0.0001 456 5 458 10 465 44 22 20 265 0.35 0.0571 0.0011 0.5849 0.0119 0.0742 0.0007 0.0213 0.0002 462 5 468 10 497 43 23 27 383 0.21 0.0573 0.0011 0.5770 0.0121 0.0730 0.0008 0.0241 0.0005 454 5 463 10 504 43 测试单位:天津地质矿产研究所. -
[1] 李春昱.用板块构造学说对中国部分地区构造发展的初步分析[J].地球物理学报, 1975, 18(1):52-76.
[2] 李春昱, 刘仰文, 朱宝清, 等.秦岭及祁连山构造发展史[C]//国际交流地质学术论文集(1).北京: 地质出版社, 1978: 174-187.
http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBDI197804000.htm [3] 肖序常, 陈国铭, 朱志直.祁连山古蛇绿岩的地质构造意义[J].地质学报, 1978, 54(4):287-295. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE197804002.htm
[4] Song S G, Niu Y L, et al. Tectonics of the North Qilian orogen, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4):1378-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004
[5] Xiao W J, Windley F, Yong Y. Early Paleozoic to Devonian multiple-accretionary model for the QiLian Shan, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35(3/4):323-333. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.jseaes.2008.10.001/
[6] Xu Z Q, Yang J S, Wu C L, et al. Timing and mechanism of formation and exhumation of the Northern Qaidam ultrahigh-pressuremetamo rphic belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 28(2/3):160-173. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c37aae5bcd861f663b9bedde7c7b8033&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28(1):211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
[8] Zhang J X, Meng F C, Wan Y S. A cold Early Palaeozoic subduction zone in the North QiLian Mountains, NW China:Petrological and U-Pb geochronological constraints[J]. Journal of metamorphic Geology, 2007, 25(3):285-304. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2006.00689.x
[9] Wu C L, Gao Y H, Frost B R, et al. An early Palaeozoic double-subduction model for the North QiLian oceanic plate:Evidence from zircon SHRIMP dating of granites[J]. International Geology Review, 2011, 53(2):157-181. doi: 10.1080/00206810902965346
[10] Tseng C Y, Yang H J, Yang H Y, et al. Continuity of the North QiLian and North QinLing orogenic belts, Central Orogenic System of China:Evidence from newly discovered Paleozoic adakitic rocks[J]. Gondwana Research, 2009, 16(2):285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.04.003
[11] Xia L Q, Xia Z C, Xiu X Y. Magmagenesis in the ordovician backarc basins of the Northern QiLian Mountains, China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2003, 115(12):1510-1522. doi: 10.1130/B25269.1
[12] Gehrels G E, Yin A, Wang X. Magmatic history of the northeastern Tibetan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 2003, 108(B9):2423. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-2002JB001876/
[13] Cowgill E, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Reconstruction of the Altyn Tagh fault based on U-Pb geochronology:Role of back thrusts, mantle sutures, and heterogeneous crustal strength in forming the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 2003, 108(B7):2346. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-2002JB002080/
[14] Zhang H F, Zhang B R, Harris N, et al. U-Pb zircon SHRIMP ages, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of intrusive rocks from the Longshan-Tianshui area in the southeast corner of the Qilian orogenic belt, China:Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic affinity[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 27(6):751-764. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.07.008
[15] Chen Y X, Song S G, Niu Y L, et al. Melting of continental crust during subduction initiation:A case study from the Chaidanuo peraluminous granite in the North Qilian suture zone[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 13(2):311-336. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8a8a89fc231a0a2e31fe3373609f6223&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[16] 冯益民, 何世平.祁连山大地构造与造山作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996:13-20.
[17] Manetti P, Peccerillo A, Poli G, et al. Petrochemical constraints on the models of Cretaceous-Eocene tectonic evolution of the Eastern Pontic chain(Turkey)[J]. Cretaceous Resrarch, 1983, 4(2):159-172, 195-6671. doi: 10.1016/0195-6671(83)90047-2
[18] 齐瑞荣.中祁连西段巴嘎德尔基岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].沉积于特提斯地质, 2012, 32(4):86-93. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yxgdl201204013
[19] Yan Z, Aitchison J, Fu C, et al. HuaLong Complex, South QiLian terrane:U-Pb and Lu-Hf constraints on Neoproterozoic micro-continental fragments accreted to the northern Proto-Tethyan margin[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 266:65-85. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.05.001
[20] 雍拥, 肖文交, 袁超, 等.中祁连东段古生代花岗岩的年代学、地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):855-866. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200804024
[21] 陈隽璐, 徐学义, 曾佐勋, 等.中祁连东段什川杂岩基的岩石化学特征及年代学研究[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):841-854. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200804023
[22] Rubatto D, Gebauer G, Compagnoni R. Dating of eclogite-facies zircons:The age of Alpine metamorphism in the Sesia-Lanzo Zone (Western Alps)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 16(7):141-158. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=91f1744b55069696a7dcb10988c1229a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] Rubatto D, Hermann J. Zircon formation during fluid circulation in eclogites (Monviso, Western Alps):Implications for Zr and Hf budget in subduction zones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(12):2173-2187 doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01321-2
[24] Dubinska E, Bylinab P, Kozlowskia A, et al. U-Pb dating of serpentinization:Hydrothermal zircon from a metasomatic rodingite shell (Sudetic ophiolite, SW Poland)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 20(3):183-203. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=aa160ce6f6a4e71032461d135a5bc94c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] Liati A, Gebauer D. Constraining the pregrade and regrade P-T-t path of Eocene HP rocks by SHRIMP dating difference zircon domain:Inferred rated of heating-burial, cooling and exhumation for central Rhodope, northern Greece[J]. Contrib Minern Petrol, 1999, 13(5):340-354.
[26] 左国朝, 吴汉泉.北祁连山中段早古生代双向俯冲一碰撞造山模式剖析[J].地球科学进展, 1997, 12(4):315-323. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1997.04.002
[27] 吴才来, 杨经绥.北祁连洋早古生代双向俯冲的花岗岩证据[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1197-1208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.06.002
-



 下载:
下载: