Estimation of hydraulic conductivity of landslides based on support vector machine method optimized with genetic algorithm
-
摘要:
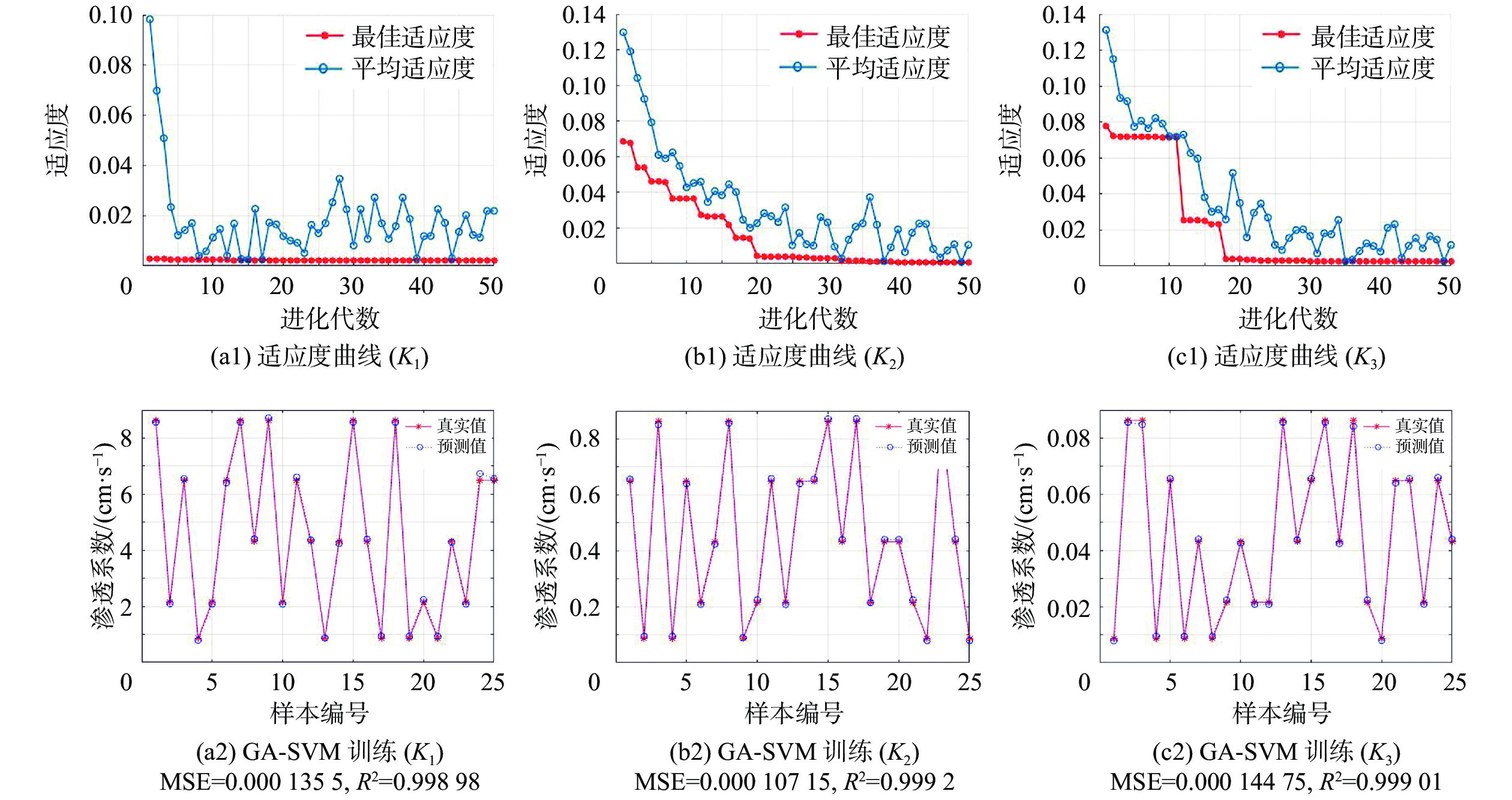
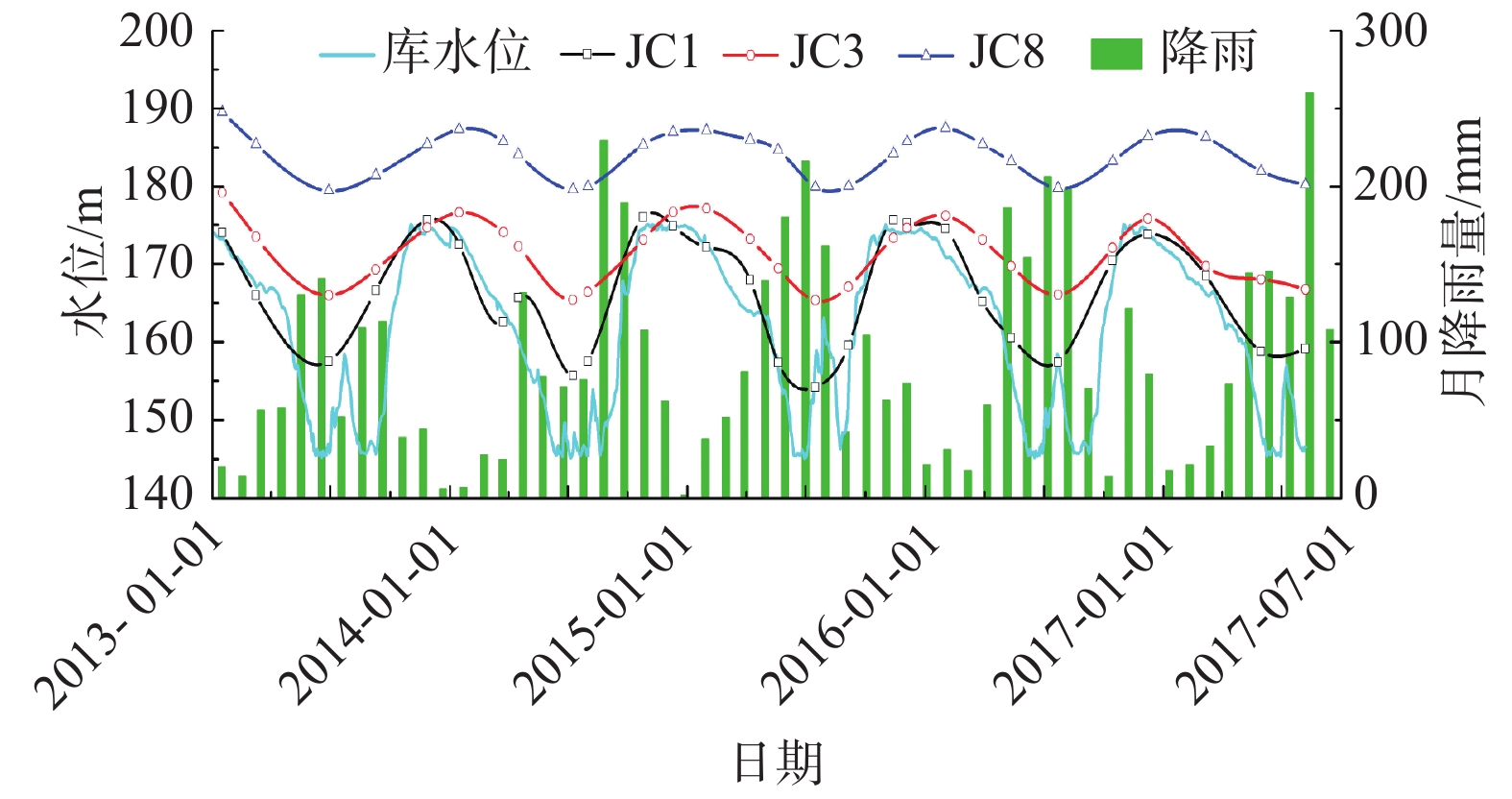
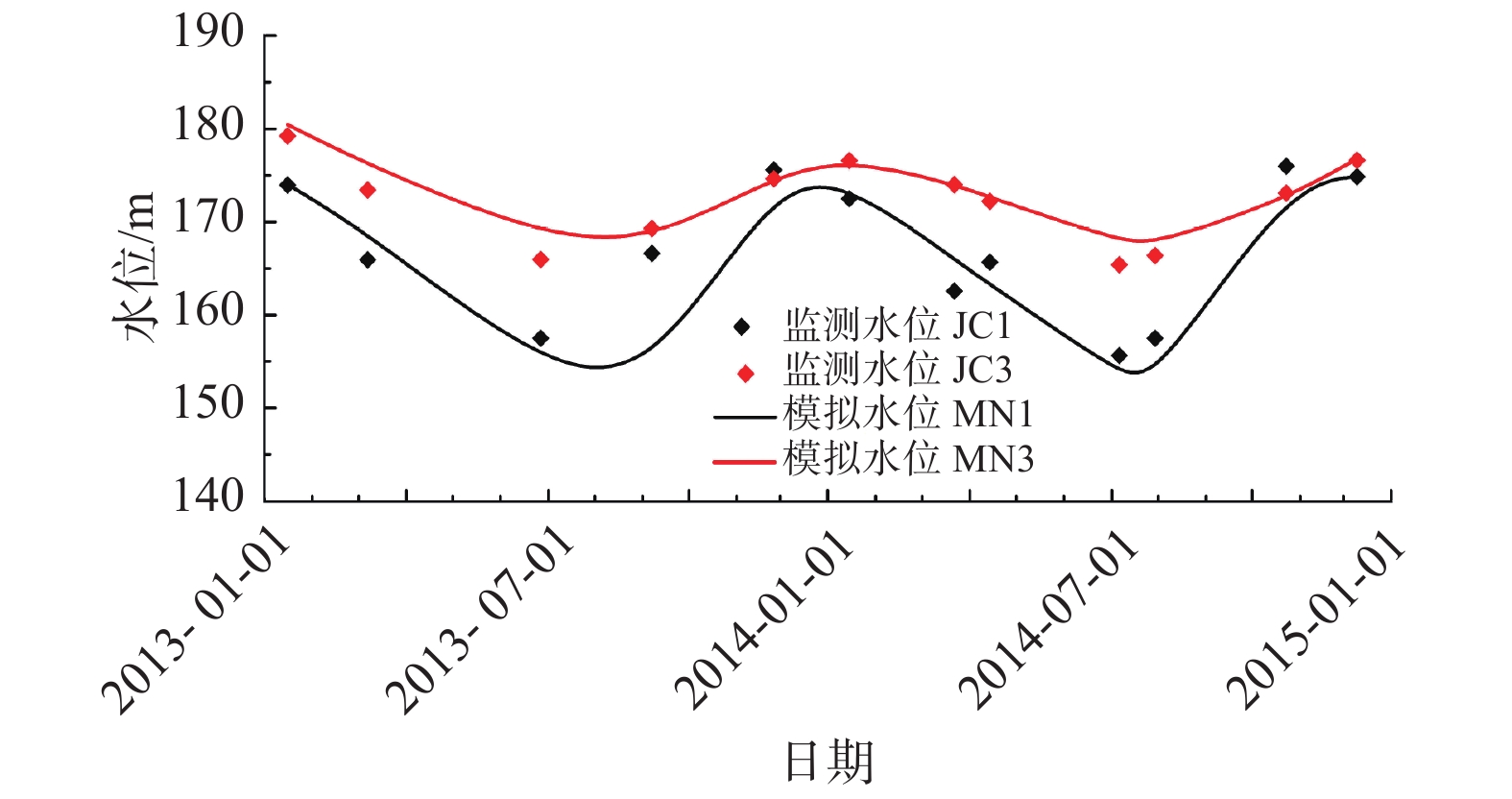
求解库岸边坡岩土体的渗透系数是研究滑坡渗流场及多场演化的基础,一般通过原位试验和室内试验求得,但试验成本较高且试验位置具有一定的随机性。本文以三峡库区马家沟滑坡为例,提出一种利用地下水位动态观测资料反演滑坡岩土层渗透系数的方法。具体步骤为:(1)依据滑坡的勘察资料和水位观测数据,构建滑坡数值模型;(2)利用SPSS生成不同渗透系数正交试验组合,并将渗透系数代入数值模型中计算监测井的水位,得到不同渗透系数及其对应的模拟水位数据;(3)应用遗传算法优化的支持向量机构建坡体模拟水位与渗透系数的非线性映射关系,再通过代入实际动态监测水位值求得滑坡岩土层的渗透系数;(4)将求得的渗透系数代入数值模型,用计算的模拟水位与实际观测水位进行对比验证。研究结果表明:遗传算法优化的支持向量机具有良好的学习预测效果,能准确预测渗透系数与水位的关系。该反演方法具有高效、准确的优点,反演结果的精度满足实际应用需要。
Abstract:Estimation of hydraulic conductivities (K) of the rock media in a landslide is the basis for the study of the seepage field and multi-dimensional evolution of the reservoir bank slope. Traditionally, in-situ tests and indoor tests are used to determine the hydraulic conductivity of landslide rock and soil, but this method is costly and the test location has a certain randomness. In this study, the Majiagou landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area is taken as an example, and a method for inverting the K values of the deformed rock and soil mass using the groundwater level dynamic monitoring data is proposed. The basic idea is as follows. First, build a numerical model of the landslide based on the landslide survey data and water level observation data. Afterwards, SPSS is used to generate different orthogonal test combinations of hydraulic conductivity, substitute the hydraulic conductivity into the numerical model to calculate the water levels of the monitoring wells, and obtain the data of hydraulic conductivity and corresponding simulated water levels. Finally, the support vector machine (SVM) optimized with the genetic algorithm (GA) is used to construct a nonlinear mapping relationship between slope water level and hydraulic conductivities (K). The results obtained are then replaced for the monitored water levels to obtain the hydraulic conductivities of the landslide rock and soil which is used to develop the finite element model. The model is then verified by comparing the simulated water levels with the observed water levels. The inversion of the Majiagou landslide hydraulic conductivity shows that the SVM optimized with GA yields a good agreement between the simulated and real data and has a very efficient and accurate search results. The inversion accuracy of K based on the GA-SVM method meets the needs of practical applications.
-

-
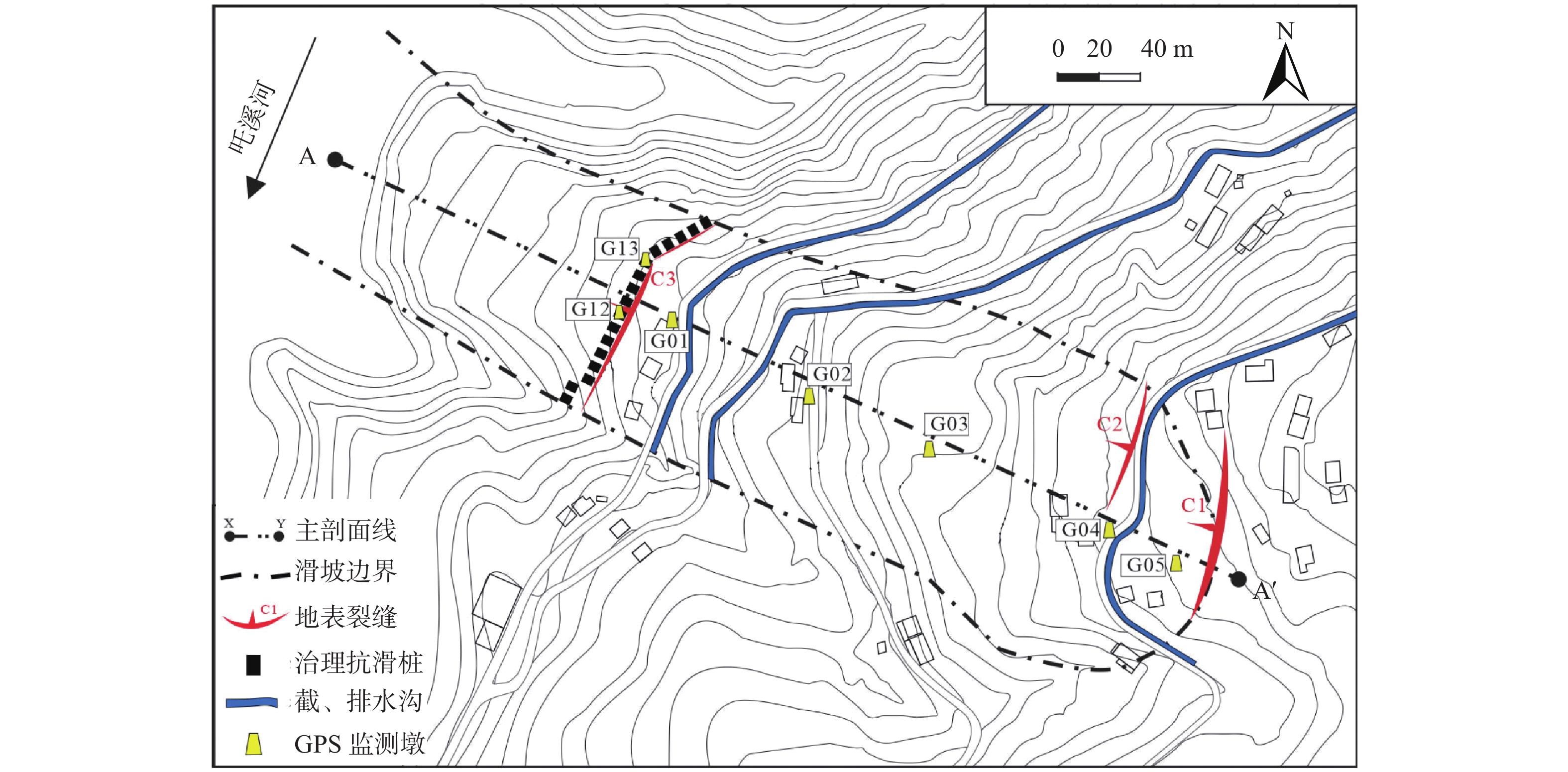
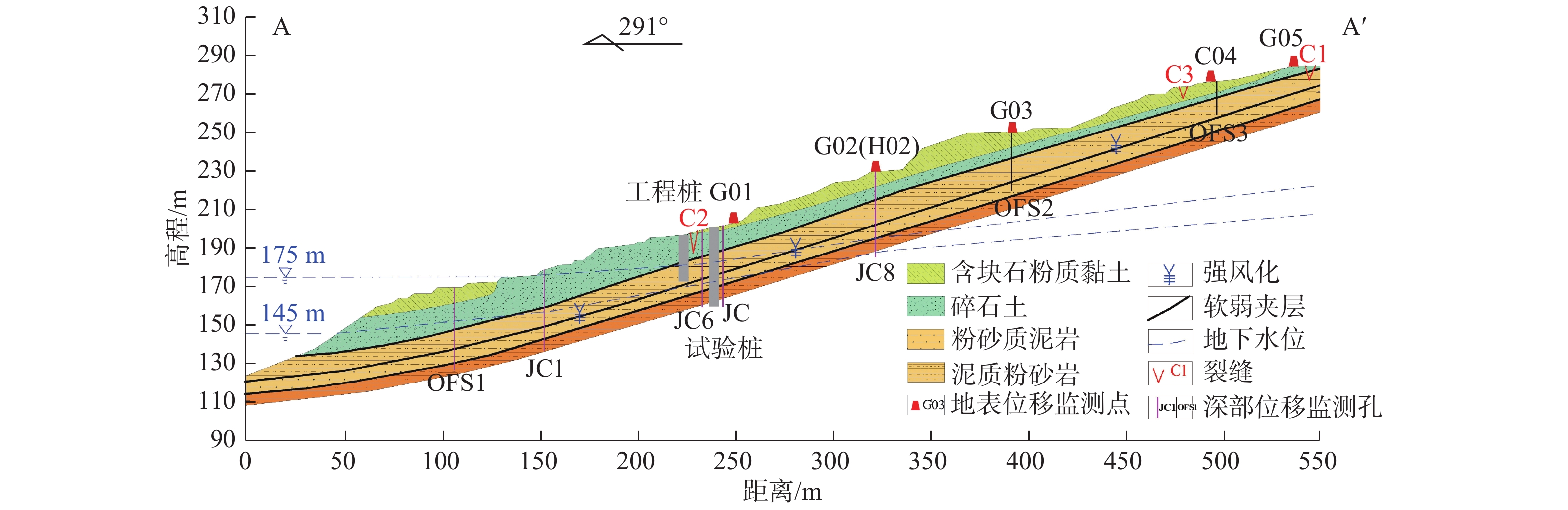
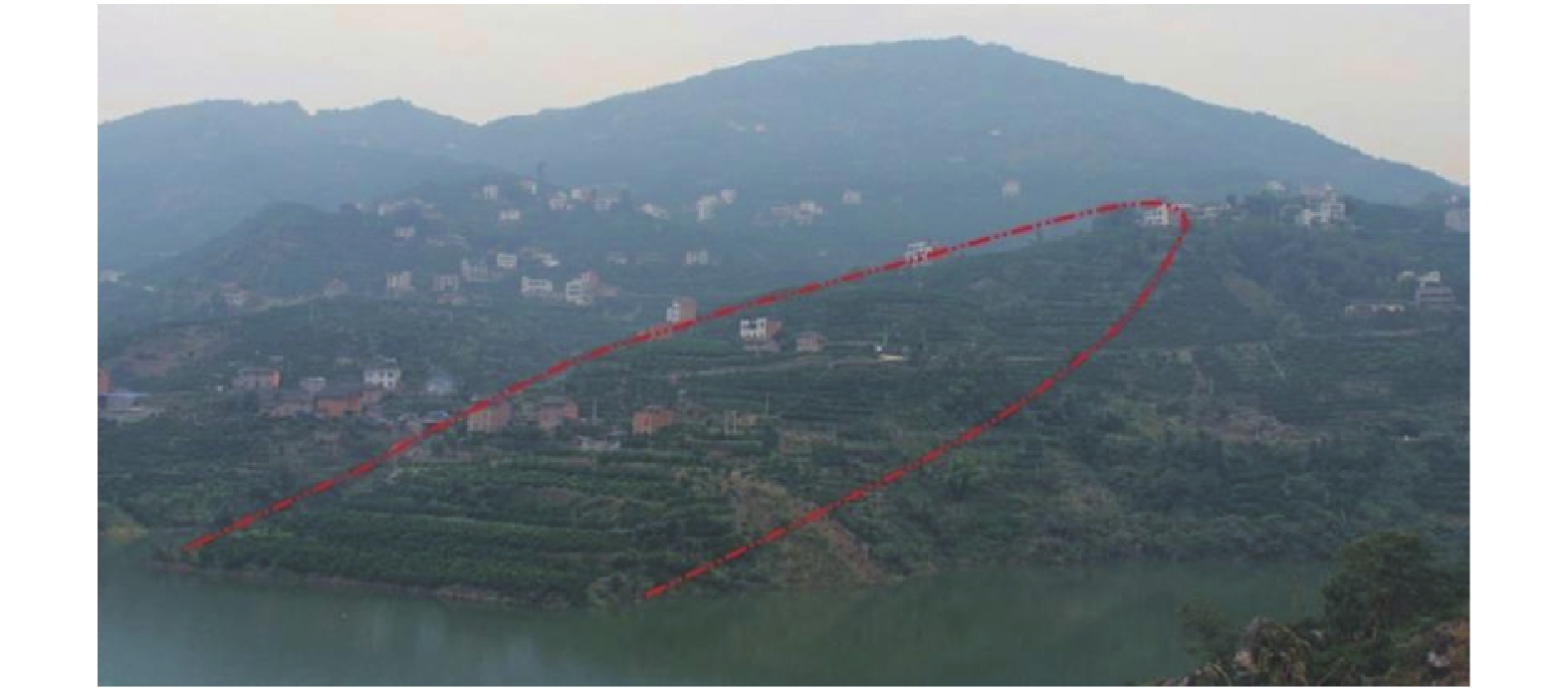
图 1 马家沟滑坡全貌图(据文献[20])
Figure 1.
图 2 马家沟滑坡平面图(据文献[20])
Figure 2.
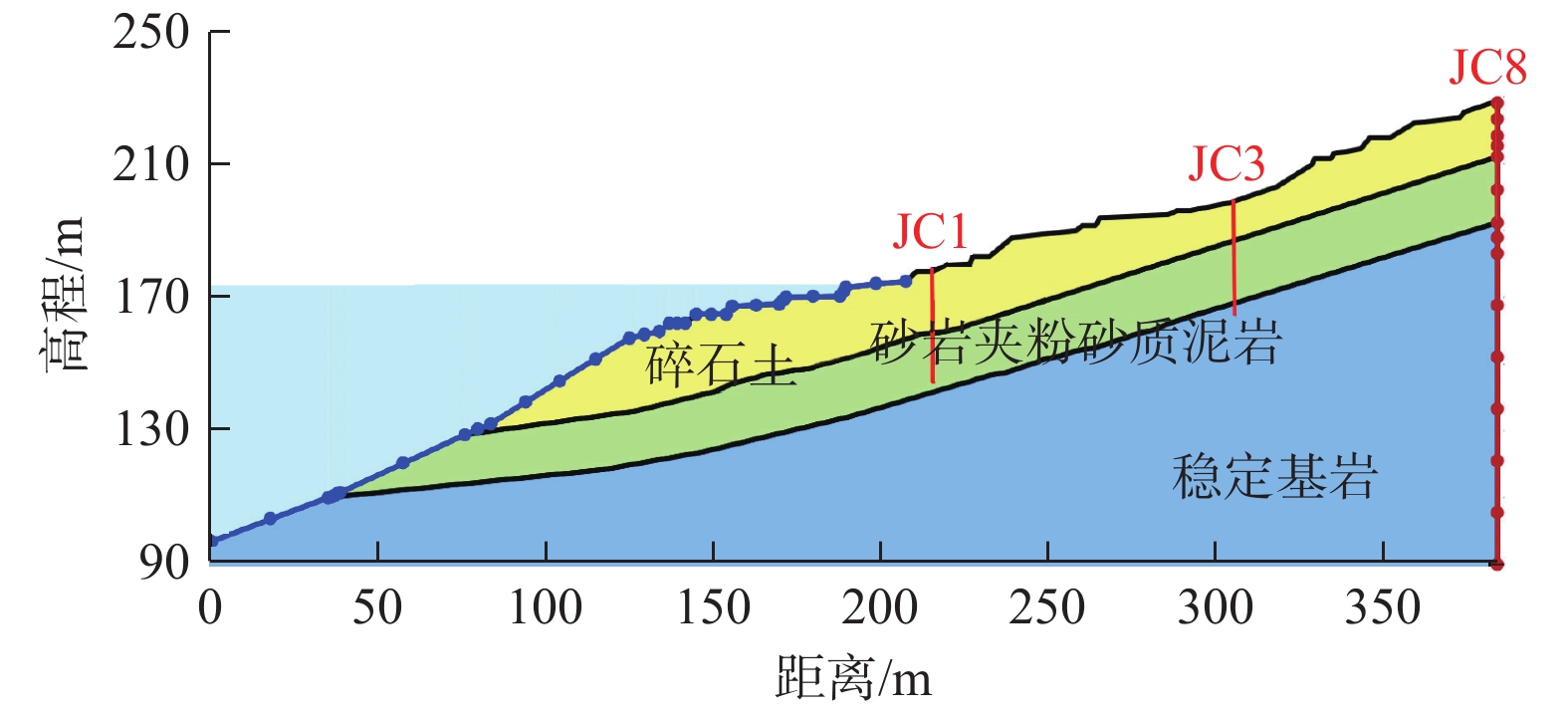
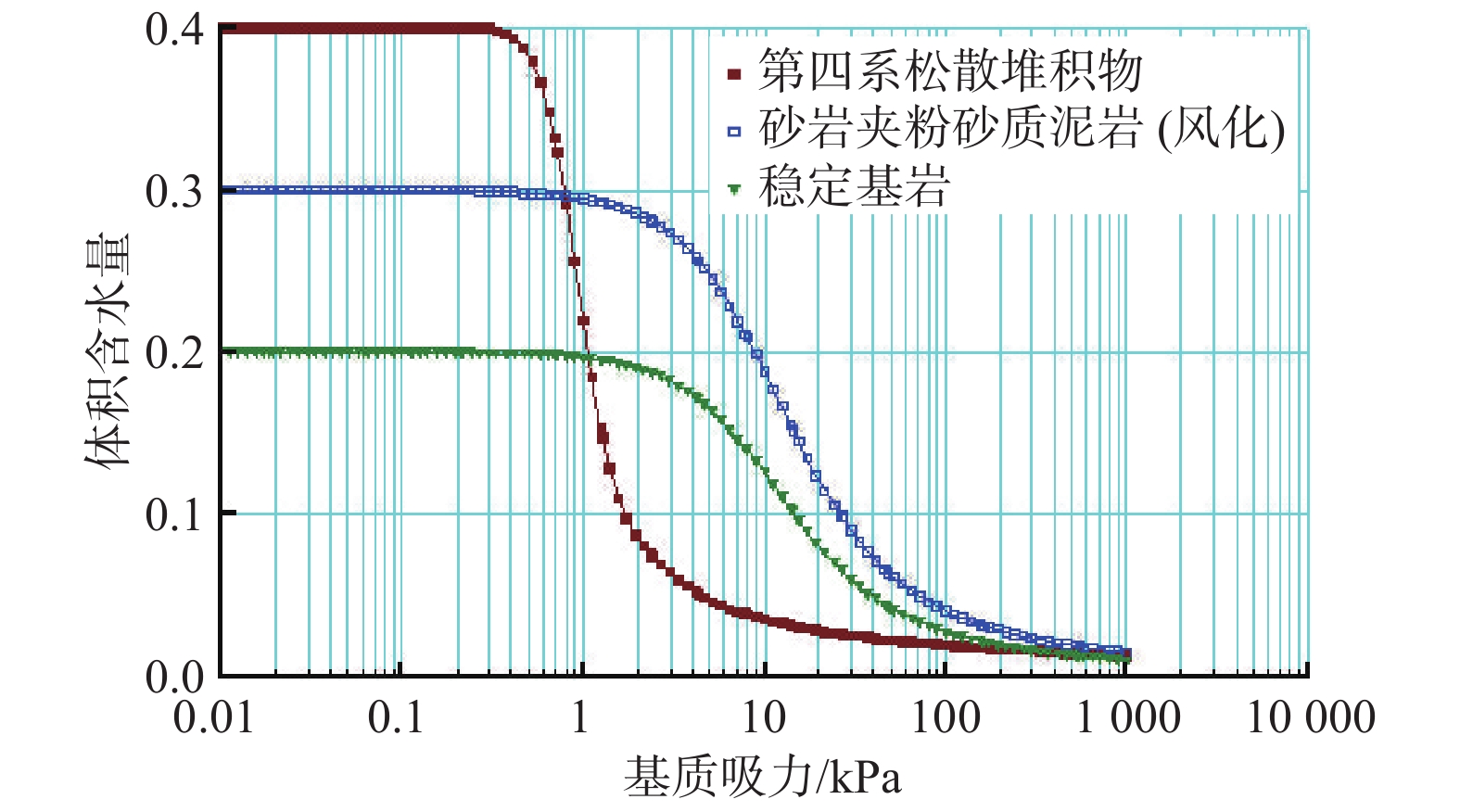
表 2 马家沟滑坡岩土体渗透系数取值范围表
Table 2. Range of K of rock and soil for the Majiagou landslide
滑坡地层 岩土体岩性组成 孔隙率 渗透系数范围/(cm·s−1) 第四系松散堆积层 碎石土 0.4 1.0×10−2~1.0×10−1 砂岩夹粉砂质泥岩 含裂隙岩体 0.3 1.0×10−3~1.0×10−2 基岩 稳定基岩 0.2 1.0×10−4~1.0×10−3 表 1 马家沟滑坡入渗试验结果
Table 1. Infiltration test results for the Majiagou landslide
试验编号 试验深度/m 试验段岩性 渗透系数 /(cm·s−1) ZK4 0.50~0.67 粉质黏土(含块石) 1.38×10−5 ZK10 4.3~4.5 块石土 6.4×10−2 ZK11 6.1~6.3 块石土 0.5 ZK1 6.4~6.6 块石土 1.5 ZK2 10.0~10.3 砂岩块石(强风化) 2.5×10−2 ZK6 10.4~10.6 泥岩(强风化) 6×10−3 表 3 数值模型计算方案表
Table 3. Calculation schemes with the numerical model
样本编号 K1/(cm·s−1) K2/(cm·s−1) K3/(cm·s−1) 样本编号 K1/(cm·s−1) K2/(cm·s−1) K3/(cm·s−1) 1 1.00×10−1 7.50×10−3 1.00×10−4 14 5.00×10−2 7.50×10−3 5.00×10−4 2 2.50×10−2 1.00×10−3 1.00×10−3 15 1.00×10−1 1.00×10−2 7.50×10−4 3 7.50×10−2 1.00×10−2 1.00×10−3 16 5.00×10−2 5.00×10−3 1.00×10−3 4 1.00×10−2 1.00×10−3 1.00×10−4 17 1.00×10−2 1.00×10−2 5.00×10−4 5 2.50×10−2 7.50×10−3 7.50×10−4 18 1.00×10−1 2.50×10−3 1.00×10−3 6 7.50×10−2 2.50×10−3 1.00×10−4 19 1.00×10−2 5.00×10−3 2.50×10−4 7 1.00×10−1 5.00×10−3 5.00×10−4 20 2.50×10−2 5.00×10−3 1.00×10−4 8 5.00×10−2 1.00×10−2 1.00×10−4 21 1.00×10−2 2.50×10−3 7.50×10−4 9 1.00×10−1 1.00×10−3 2.50×10−4 22 5.00×10−2 1.00×10−3 7.50×10−4 10 2.50×10−2 2.50×10−3 5.00×10−4 23 2.50×10−2 1.00×10−2 2.50×10−4 11 7.50×10−2 7.50×10−3 2.50×10−4 24 7.50×10−2 5.00×10−3 7.50×10−4 12 5.00×10−2 2.50×10−3 2.50×10−4 25 7.50×10−2 1.00×10−3 5.00×10−4 13 1.00×10−2 7.50×10−3 1.00×10−3 表 4 滑坡岩土体渗透系数反演值
Table 4. Inversion values of K of landslide rock and soil mass
岩土体材料 K1/(cm·s−1) K2/(cm·s−1) K3/(cm·s−1) 渗透系数反演值 1.31×10−1 1.11×10−2 9.95×10−4 -
[1] 向家松, 文宝萍, 陈明, 等. 结构复杂滑坡活动对库水位变化的响应特征—以三峡库区柴湾滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(4):71 − 77. [XIANG Jiasong, WEN Baoping, CHEN Ming, et al. Activity response of a landslide with complex structure to fluctuation of reservoir water level: a case study of the Chaiwan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(4):71 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] SUN G H, ZHENG H, TANG H M, et al. Huangtupo landslide stability under water level fluctuations of the Three Gorges reservoir[J]. Landslides,2016,13(5):1167 − 1179. doi: 10.1007/s10346-015-0637-7
[3] HU X L, ZHANG M, SUN M J, et al. Deformation characteristics and failure mode of the Zhujiadian landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2015,74(1):1 − 12. doi: 10.1007/s10064-013-0552-x
[4] 周剑, 邓茂林, 李卓骏, 等. 三峡库区浮托减重型滑坡对库水升降的响应规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):136 − 143. [ZHOU Jian, DENG Maolin, LI Zhuojun, et al. Response patterns of buoyancy weight loss landslides under reservoir water level fluctuation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):136 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 何涛, 等. 库岸滑坡地下水位时间序列混沌特征识别与PSO-LSSVM模型预测[J]. 地质科技情报,2015,34(6):186 − 192. [HUANG Faming, YIN Kunlong, HE Tao, et al. Chaotic characteristics identification and prediction using PSO-LSSVM model of reservoir landslide groundwater level time series[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2015,34(6):186 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] SURYANARAYANA C, SUDHEER C, MAHAMMOOD V, et al. An integrated wavelet-support vector machine for groundwater level prediction in Visakhapatnam, India[J]. Neurocomputing,2014,145:324 − 335. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.05.026
[7] HE Z B, WEN X H, LIU H, et al. A comparative study of artificial neural network, adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and support vector machine for forecasting river flow in the semiarid mountain region[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2014,509:379 − 386. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.054
[8] LAKSHMI PRASAD K, RASTOGI A K. Estimating net aquifer recharge and zonal hydraulic conductivity values for Mahi Right Bank Canal project area, India by genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2001,243(3/4):149 − 161.
[9] 魏进兵, 邓建辉, 高春玉, 等. 三峡库区泄滩滑坡非饱和渗流分析及渗透系数反演[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(8):2262 − 2266. [WEI Jinbing, DENG Jianhui, GAO Chunyu, et al. Unsaturated seepage analysis and back analysis of permeability coefficient for Xietan landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(8):2262 − 2266. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.08.045
[10] 崔皓东, 朱岳明. 二滩高拱坝坝基渗流场的反演分析[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(10):3194 − 3199. [CUI Haodong, ZHU Yueming. Back analysis of seepage field of Ertan high arch dam foundation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(10):3194 − 3199. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.10.052
[11] 姜谙男, 梁冰. 基于粒子群支持向量机的三维含水层渗流参数反馈识别[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(5):1527 − 1531. [JIANG Annan, LIANG Bing. Feedback identifying seepage parameters of 3D aquifer based on particle swarm optimization and support vector machine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(5):1527 − 1531. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.059
[12] 倪沙沙, 迟世春. 基于粒子群支持向量机的高心墙堆石坝渗透系数反演[J]. 岩土工程学报,2017,39(4):727 − 734. [NI Shasha, CHI Shichun. Back analysis of permeability coefficient of high core rockfill dam based on particle swarm optimization and support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(4):727 − 734. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201704019
[13] 向家松, 文宝萍, 高幼龙, 等. 地下水位监测频率和时长对滑体渗透系数反演结果的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):86 − 92. [XIANG Jiasong, WEN Baoping, GAO Youlong, et al. Effects of frequency and interval of groundwater monitoring on the inversion coefficients of permeability of materials of a landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):86 − 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李端有, 甘孝清. 滑坡体力学参数反分析研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2005,22(6):44 − 48. [LI Duanyou, GAN Xiaoqing. Mechanical parameter back analysis of landslide[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2005,22(6):44 − 48. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2005.06.014
[15] SU H Z, LI X, YANG B B, et al. Wavelet support vector machine-based prediction model of dam deformation[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2018,110:412 − 427. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.03.022
[16] SUN G H, ZHENG H, HUANG Y Y, et al. Parameter inversion and deformation mechanism of Sanmendong landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir region under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,205:133 − 145. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.10.014
[17] 陈海洋, 滕彦国, 王金生. 基于GA-SVR的渗透系数参数反演方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2011,38(2):14 − 18. [CHEN Haiyang, TENG Yanguo, WANG Jinsheng. Methods of estimation of hydraulic conductivity with genetic algorithm-support vector regression machine[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2011,38(2):14 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.02.003
[18] 刘广润, 徐开祥. 三峡水库沿岸移民区地质灾害防治研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2003,14(4):1 − 4. [LIU Guangrun, XU Kaixiang. Investigation on prevention and control of geologic hazards in the migration area along bank of the Three Gorges reservoir[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2003,14(4):1 − 4. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.04.001
[19] ZHANG Y M, HU X L, TANNANT D D, et al. Field monitoring and deformation characteristics of a landslide with piles in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Landslides,2018,15(3):581 − 592. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0945-9
[20] 张玉明. 水库运行条件下马家沟滑坡—抗滑桩体系多场特征与演化机理研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.
ZHANG Yuming. Multi-field characteristics and evolution mechanism of Majiagou landslide-stablizing piles system under reservoir operations[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] CHANG C C, LIN C J. Libsvm:a library for support vector machinea library for support vector machine[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology,2011,2(3):1 − 27.
[22] 史峰, 王小川, 郁磊, 等. MATLAB神经网络30个案例分析[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2010: 102−135.
SHI Feng, WANG Xiaochuan, YU Lei, et al. Analysis of 30 cases of MATLAB neural network[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2010: 102−135. (in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: