Terrestrial heat flow and geothermal genesis mechanism of geothermal resources in northern Ningdu County, Jiangxi Province
-
摘要:
江西省宁都县北部地区地热资源丰富,但地热地质研究程度较低,制约着区域地热资源的研究与可持续发展。在前人研究基础上,依托中国地质调查工作,对研究区大地热流特征及地热成因机制进行分析。基于钻孔测温与热导率测试数据,分析校正得到区域内大地热流平均值为93.6 mW/m2,远高于中国陆区平均值62.5 mW/m2,区域热背景值较高。通过放射性测试可知本区大面积出露的花岗岩与混合岩放射性生热率平均值为6.47 μW/m3,属高放射性岩体,岩石的放射性衰变产热应是本区大地热流值较高的重要原因,幔源供热的基础上附加壳源产热,提供了稳定的热源。在此基础上,穿越本区的2条深大断裂及其次生断裂则为地下热水深循环提供了传热与导水通道。因此推测,研究区地热资源成因机制为"高热流与高产热花岗岩体生热+多级次断裂控热导水"的成因模式,该模式代表性较强,可为赣南地区地热找矿提供指导。
Abstract:The northern area of Ningdu Country is rich in geothermal resources; nevertheless, the blank research on terrestrial heat flow and geothermal mineralization background restricts the exploitation and utilization of geothermal resources seriously.Based on previous research and geological survey, the authors analyzed the terrestrial heat flow and geothermal genesis mechanism of the study area.The conclusions are as follows:firstly, based on well temperature measurement and thermal conductivity data, the authors detected that the average terrestrial heat flow is 93.6 mW/m2 in this region, which is far higher than the average terrestrial heat flow 62.5 mW/m2 in China's continental regions.This area has a relatively strong strength of geothermal background.Secondly, the average radiation heat generation rate of the exposed granite and migmatite in this area is 6.47 W/m3, suggesting a highly radioactive rock mass.The radioactive decay heat generation of the rock is an important reason for high terrestrial heat flow in this area.Besides heating from mantle source, shell source heat generation is added to provide a stable heat source.On the other hand, two deep faults and their secondary faults across this region has provided heat transfer and water flowing channels for deep circulation of hot groundwater.Therefore, it is inferred that the formation mechanism of geothermal resources in the research area could be described as the "high heat flow background + rocks with high heat production +multi-level thermal control and water conducted faults ".This study provides guidance for geothermal prospecting in Gannan area.
-

-
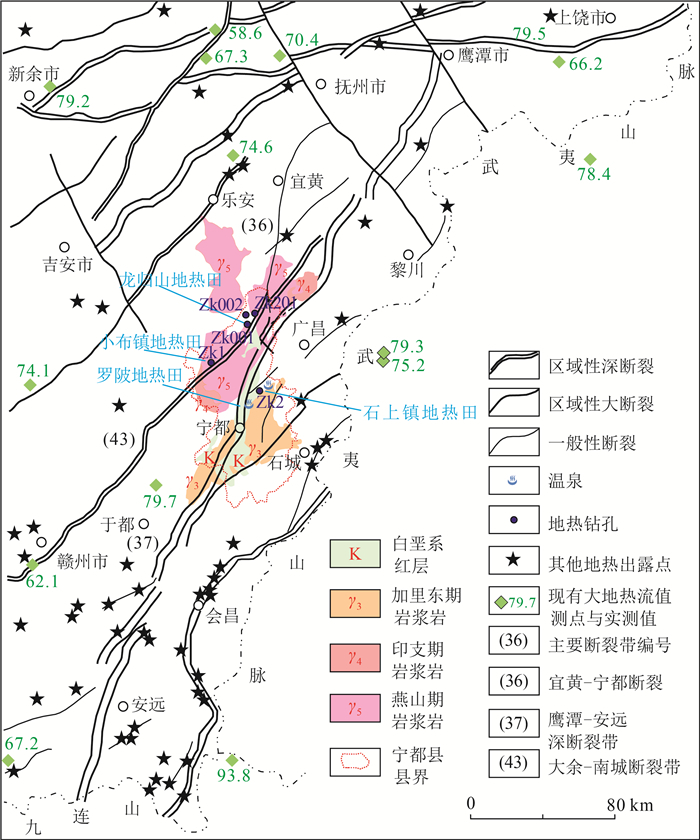
图 1 研究区位置及地热地质条件略图(据参考文献[9]修改)
Figure 1.
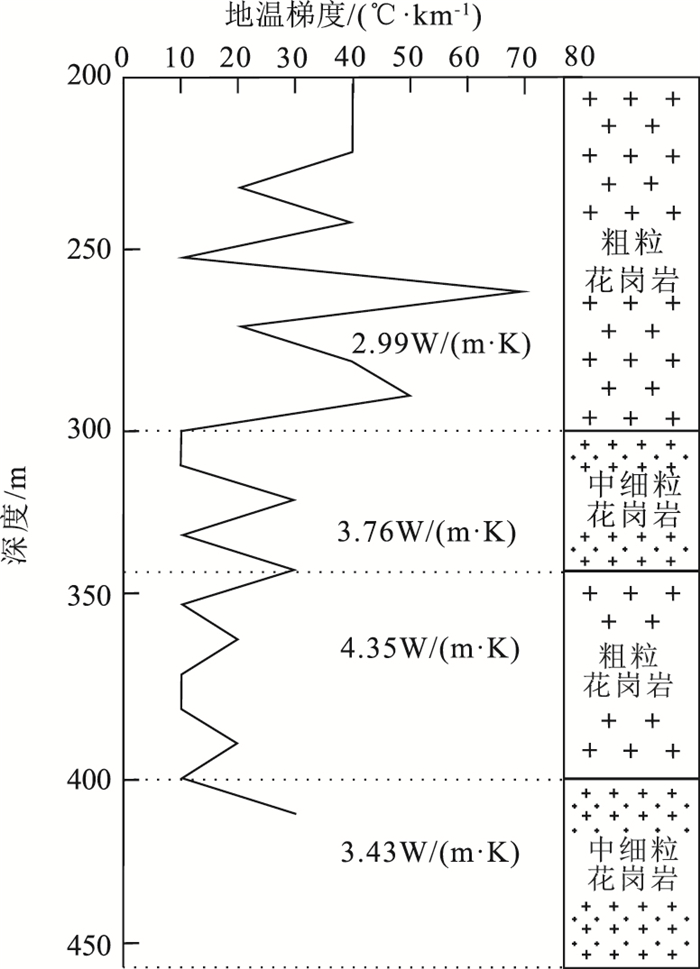
表 1 宁都县北部主要钻孔岩性热导率与放射性参数
Table 1. Lithologic heat conductivity and radioactive parameters for main wells innorthern Ningdu County
样品编号 取样钻孔 取样深度
/m岩性 热导率
/(W·m-1·K-1)密度
/(g·cm-3)U/10-6 Th/10-6 K
/%放射性生热率/(μW·m-3) NDZK1-1 小布镇ZK1 87.9 粗粒花岗岩 3.525 2.66 7.5 24.48 3.38 3.87 NDZK1-2 小布镇ZK1 161.1 粗粒花岗岩 2.455 2.63 7.71 15.38 4.21 3.35 NDZK1-3 小布镇ZK1 233.0 粗粒花岗岩 2.884 2.66 8.19 32.68 3.02 4.58 NDZK1-4 小布镇ZK1 302.3 中细粒花岗岩 3.759 2.65 14.6 31.21 4.32 6.2 NDZK1-5 小布镇ZK1 372.0 粗粒花岗岩 4.353 2.63 18.49 40.13 4.25 7.73 NDZK1-6 小布镇ZK1 453.2 中细粒花岗岩 3.458 2.68 10.22 37.54 2.72 5.44 NDZK1-7 小布镇ZK1 526.1 中细粒花岗岩 3.402 2.66 10.56 35.12 4.04 5.45 NDZK1-8 小布镇ZK1 608.0 粗粒花岗岩 2.952 2.70 8.88 46.98 4.39 5.94 LGS-3-1 龙归山ZK002 237.1 黑云母花岗斑岩 3.176 2.67 10.6 72.3 4.66 8.46 LGS-6 龙归山ZK002 251.1 细晶岩 3.565 2.70 19.1 43.0 5.24 8.68 LGS-2-1 龙归山ZK002 274.3 条带状混合岩 3.113 2.67 7.87 52.6 4.06 6.26 LGS-1-1 龙归山ZK002 292.9 弱硅化混合岩 3.243 2.66 6.09 29.7 3.69 4.11 LGS-4-1 龙归山ZK002 337.6 混合岩 3.289 2.69 5.86 49.0 4.14 5.48 LGS-5 龙归山ZK002 411.1 混合岩 3.302 2.68 17.5 139 4.77 15.09 表 2 宁都县北部大地热流值计算成果
Table 2. Terrestrial heat flows calculation results innorthern Ningdu County
经纬度 测量钻孔 大地热流值
/(mW·m-2)校正值
/(mW·m-2)测温段长度/m 热导率样品数/个 数据
质量115.82°E,26.80°N 小布镇ZK1 83.77 81.13 220 8 A 116.05°E, 27.06°N 龙归山ZK002 107.83 105.99 90 6 B -
[1] 陈爱华, 徐行, 罗贤虎, 等.南海北康盆地热流分布特征及其构造控制因素探讨[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(8):1720-1728. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.005
[2] 罗璐, 朱霞, 何春燕, 等.陕西咸阳地热田地热流体成因研究[J].地质论评, 2019, 65(6):1422-1430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201906013.htm
[3] Furlong K P, Chapman D S.Thermal state of the lithosphere[J].Reviews of Geophysics, 1987, 25(6):1255-1264.
[4] Pollack H N, Hurter S J, Johnson J R.Heatflow from the Earth's interior:Analysis of the global data set[J].Reviews of Geophysics, 1993, 31(3):267-280.
[5] 汪集旸, 孙占学.神奇的地热[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2001:1-114.
[6] (西德)卡普迈耶O, 海涅尔R.地热学及其应用[M].佟伟, 廖志杰, 过帼颖, 等译著.1981: 18-35.
[7] Liu F, Lang X J, Lu C, et al.Thermophysical parameters and lithospheric thermal structure in Guide Basin, Northeast Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J].Environmental Earth Science, 2017, 76(5):199.1-199.12.
[8] 姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等.中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J].地球物理学报, 2016, 59(8):2892-2910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201608015.htm
[9] 李建鸿.浅析次级断裂构造在地热水勘查中的标志性作用——以江西省宁都县龙归山地热为例[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 2019, 4:85-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB201904018.htm
[10] 杨世文.赣南兴国-宁都成矿带萤石矿床成因[D].中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2019.
[11] He L J, Hu S B, Huang S P, et al.Heat flow study at the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling site:Borehole temperature, thermal conductivity, and radiogenic heat production[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 2008, 113:B02404(1-16).
[12] 胡圣标, 黄少鹏.中国陆地大地热流[C]//汪集旸, 等.地热学及其应用.北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 64-122.
[13] 龚育龄, 王良书, 刘绍文.中国东部渤海湾盆地热结构和热演化[M].北京:原子能出版社, 2011.
[14] 汪集旸, 黄少鹏.中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编[J].地质科学, 1988, (2):196-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198802010.htm
[15] 汪集旸, 黄少鹏.中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第二版)[J].地震地质, 1990, 12(4):351-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199004010.htm
[16] 胡圣标, 何丽娟, 汪集旸.中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第三版)[J].地球物理学报, 2001, 44(5):611-626. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2001.05.005
[17] 林乐夫, 王安东, 孙占学, 等.江西省实测地表热流值及特征[J].能源研究与管理, 2017, 3:91-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXLY201703023.htm
[18] Hu S B, He L J, Wang J Y.Heat flow in the continental area of China:A new data set[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 179(2):407-418.
[19] 张子祥, 李文鑫.兰州市永登县地热水成因模式和地质模型[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2):196-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502029.htm
[20] 邱楠生, 胡圣标, 何丽娟, 等.沉积盆地热体制研究的理论与应用[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2004:10-18.
[21] 蔺文静, 刘志明, 马峰, 等.我国陆区干热岩资源潜力估算[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(6):1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201205018.htm
[22] 赵继龙, 袁晏明, 李德威, 等.青藏高原及周边地区下地壳地球物理异常及成因[J].地球科技情报, 2007, 26(2):16-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200702002.htm
[23] 欧新功, 金振民, 王璐, 等.中国大陆科学钻探主孔100~2000m岩石热导率及其各向异性:对研究俯冲带热结构的启示[J].岩石学报, 2004, 1:109-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200401008.htm
[24] 张超, 胡圣标, 宋荣彩, 等.共和盆地干热岩地热资源的成因机制:来自岩石放射性生热率的约束[J].地球物理学报, 2020, 63(7):2697-2709. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202007019.htm
[25] 杨立中.漳州地区典型花岗岩体放射性生热特征及干热岩资源潜力研究[D].东华理工大学硕士学位论文, 2016.
[26] Rybach L.Radioactive heat production in rocks and its relation to other petrophysical parameters[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1976, 114(2):309-317.
[27] Siegel C, Schrank C E, Bryan S E, et al.Heat-producing crust regulation of subsurface temperatures:A stochastic model reevaluation of the geothermal potential in southwestern Queensland, Australia[J].Geothermics, 2014, 51:182-200.
[28] Singh A K, Vallinayagam G.Radioactive element distribution and rare-metal mineralization in anorogenic acid volcano-plutonic rocks of the Neoproterozoic Malani Felsic Province, Western Peninsular India[J].Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2009, 73:837-853. doi: 10.1007/s12594-009-0067-z
[29] 蔺文静, 刘志明, 马峰, 等.我国陆区干热岩资源潜力估算[J].地质学报, 2012, 33(5):807-811. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201205018.htm
[30] 汪集旸, 胡圣标, 庞忠和, 等.中国大陆干热岩地热资源潜力评估[J].科技导报, 2012, 30(32):25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201232017.htm
[31] 赵平.中国东南地区岩石生热率研究[D].中国科学地质与地球物理研究所博士学位论文, 1993: 1-87.
[32] 庄庆祥.福建省干热岩研究第1期工程项目中地热发电内容的探讨[J].能源与环境, 2012, 2:53-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJNJ201202025.htm
[33] Arniaud D, Dostal D C.Geochemistry of Auriat granite(Massif Central, France)[J].Chemical Geology, 1984, 45:263-277.
[34] 袁学诚.阿尔泰-台湾地学断面论文集[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1997.
[35] 柯柏林, 林天懿, 李文, 等.北京西山谷积山背斜地热系统成因模式及远景区预测[J].地质通报, 2019, 38(8):1378-1385. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190814&flag=1
[36] 刘峰, 王贵玲, 张薇, 等.燕山中部大地热流及岩石圈热结构特征[J].地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1950-1959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202007004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: