A study of GPS ground deformation monitoring of Jinfeng coal mine in Ningdong coal base
-
摘要:
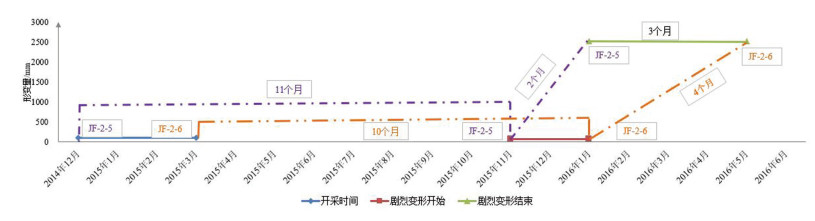
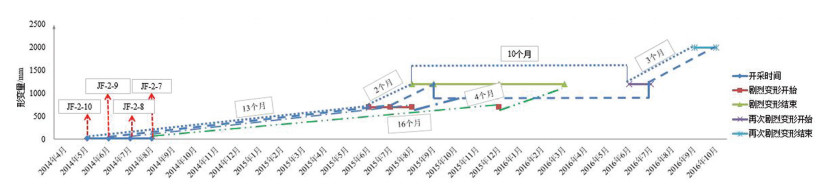
掌握采空区地面变形规律是科学预防和治理地面塌陷的前提与基础,是煤矿地质环境动态变化的重要监测内容。以宁东煤炭基地金凤煤矿为例,在收集、了解金凤煤矿0110202和011805工作面开采时间、开采深度、开采煤厚、工作面长度、工作面宽度、工作面走向等参数的基础上,建立工作面地表自动化GPS监测点,将工作面开采进程与地面变形时间、空间统一起来,研究工作面地面变形时间和变形量的规律。结果表明,金凤煤矿011202工作面地面变形一般在采后13个月左右进入变形活跃阶段,从开始变形到地面开始稳定的持续时间为16~19个月,最大累积变形量约为3300mm;011805工作面采空区地面变形一般在采后10~11个月进入变形活跃阶段,从开始变形到地面开始稳定的持续时间为13~16个月,最大累积变形量约为2600mm。研究结果为金凤煤矿后续工作面开采地表变形规律及类似开采条件下采空塌陷的预防与治理提供了定量化的依据。
Abstract:To master the law of ground deformation in the goaf is the prerequisite and foundation for scientific prevention and control of ground collapse, and also an important monitoring content for the dynamic change of the geological environment of the mine. With Jinfeng coal mine in Ningdong coal base as a study case and on the basis of collecting and understanding the mining time, mining depth, mining coal thickness, length of working face, width of working face and direction of working face, the authors set up the automatic GPS monitoring point on the surface of the working face of Jinfeng coal mine. The mining process is unified with the time and space of ground deformation. The authors tried to study the law of ground deformation time and deformation under mining and similar mining conditions. The result shows that the ground deformation of 011202 working face was usually subjected to severe deformation about 13 months after mining and reached the stability 15-17 months after the beginning of deformation, with the maximum cumulative variable being about 3300mm. The ground deformation in the goaf of 011805 working face usually occurred violently 10-11 months after mining and reached the stability 13-16 months after the beginning of deformation, with the maximum cumulative variable being about 2600mm. The research results provide quantitative basis for the prevention of surface subsidence and the prevention and treatment of gob collapse under similar mining conditions.
-
Key words:
- coal-mining area /
- ground deformation /
- GPS monitoring /
- deformation law /
- Jinfeng coal mine
-

-
表 1 金凤煤矿地面变形GPS监测点数据
Table 1. Statistic table of ground deformation data for each GPS monitoring point
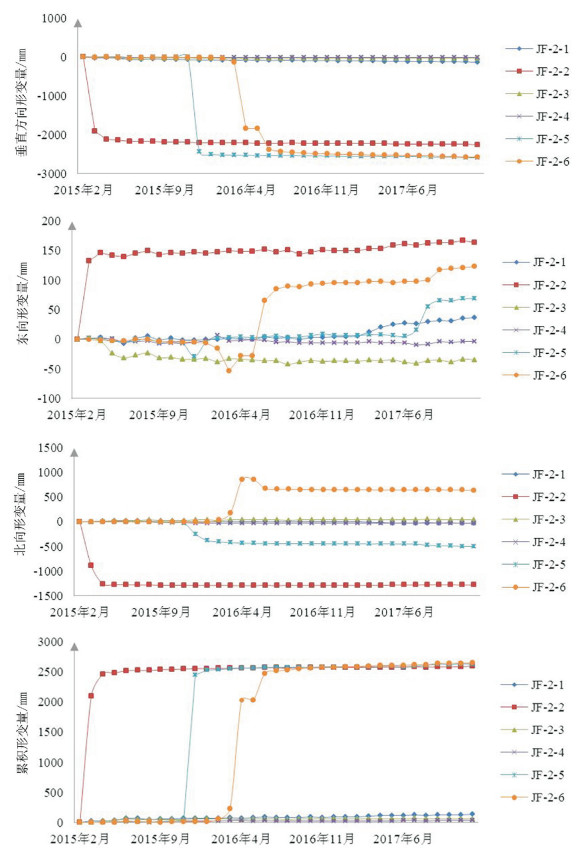
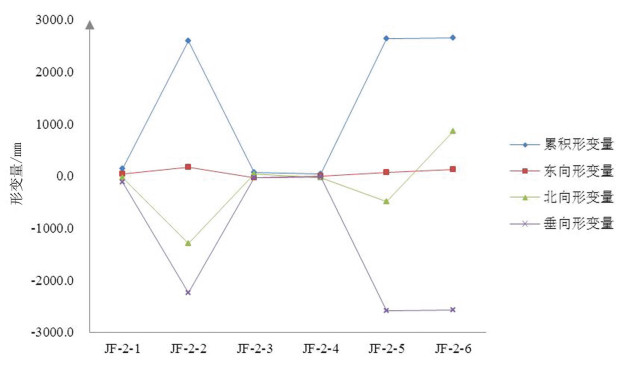
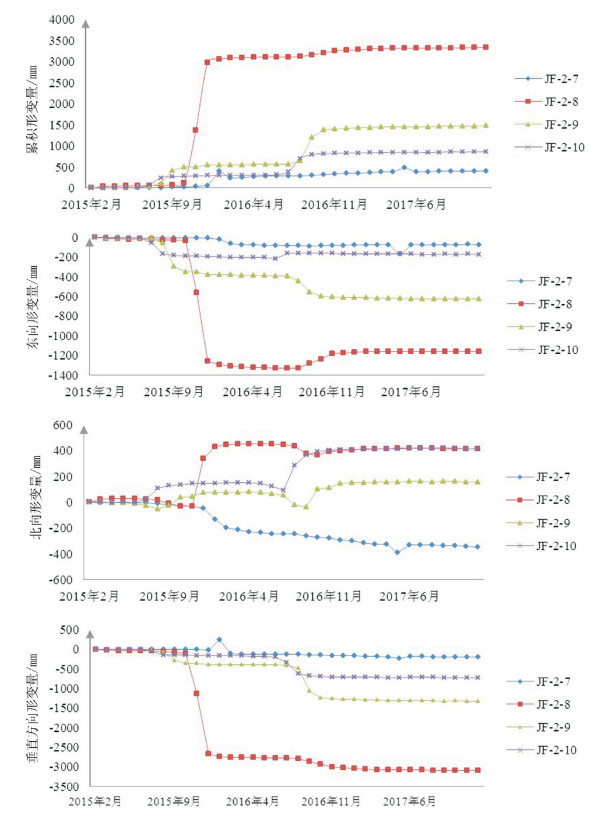
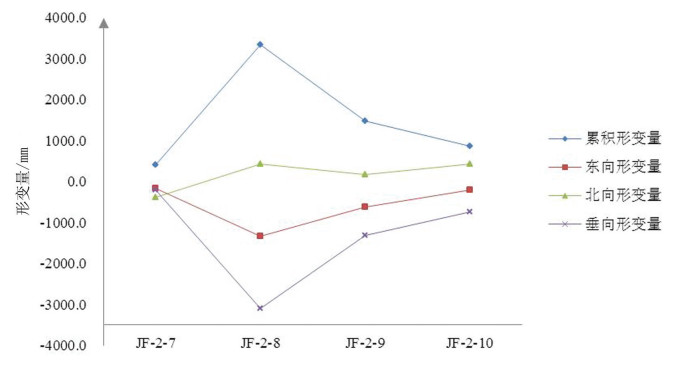
工作面 监测点编号 累积变形量 东向变形量 北向变形量 垂向变形量 011805 JF-2-1 134.4 36.2 -30.7 -125.7 011805 JF-2-2 2593.5 163.7 -1294.4 -2249.1 011805 JF-2-3 63.8 -40.4 40.7 -32.5 011805 JF-2-4 35.8 -9.5 -31.6 -18.2 011805 JF-2-5 2634.1 69.0 -498.9 -2585.5 011805 JF-2-6 2651.5 123.4 852.4 -2570.5 011202 JF-2-7 405.8 -166.7 -392.3 -201.8 011202 JF-2-8 3334.1 -1329.0 421.9 -3098.3 011202 JF-2-9 1474.2 -625.9 160.5 -1326.1 011202 JF-2-10 859.9 -214.1 423.2 -733.4 表 2 金凤煤矿地面变形监测成果对比
Table 2. Comparison of monitoring results of ground deformation in Jinfeng coal mine
工作面 经验公式变形时间/d 经验公式最大垂向沉降量/mm GPS监测时间/m GPS监测垂向变形量/mm 011202 200~375 1816 16~19 3098.3 011805 535~538 3080 13~16 2585.5 -
[1] 尚慧.宁夏矿山地质环境评价与动态监测分析[D].长安大学博士学位论文, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-1014024032.htm [2] 贾向前.采空区变形监测技术分析[J].山西水利, 2015, (7):29-30+49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7042.2015.07.018
[3] 李志刚. GPS在万家寨引黄工程北干煤矿采空区变形监测中的应用[C]//山西省水利学会.GPS在水利行业应用研讨会论文集.山西省水利学会, 2007: 54-60.
[4] 陈勇亮, 李福渝.GPS技术在姑山地表形变监测中的应用[J].现代矿业, 2013, 29(1):67-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2013.01.019
[5] 王建鹏.矿山变形灾害监测相关理论及模型研究[D].中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2010.
[6] 李培现.深部开采地表沉陷规律及预测方法研究——以徐州矿区为例[D].中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2012.
[7] 吕伟才.煤矿开采沉陷自动化监测系统研究[D].中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2016.
https://lib.xust.edu.cn/info/5608/3814.htm [8] 潘焱清, 颜荣贵, 陈光辉.矿区GPS变形监测[J].地矿测绘, 2002, (2):4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9394.2002.02.002
[9] 石玉泉, 付培义.矿山GPS沉陷与变形监测体系[J].太原理工大学学报, 2003, (2):166-168, 177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2003.02.018
[10] 王玉龙.矿区由于采动引起地表移动变形规律及地表移动变形参数的监测分析[J].华北国土资源, 2016, (4):80-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7487.2016.04.031
[11] 郭庆彪, 郭广礼, 陈龙浩, 等.毛乌素沙漠区煤层开采地表移动变形规律研究[J].金属矿山, 2014, (12):147-151. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsks201412032
[12] 高永芹.矿区开采沉降监测中GPS的应用研究.煤炭技术, 2013, 32(4):124-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8725.2013.04.062
-




 下载:
下载: