An analysis of gas hydrate accumulation condition in the Duck Lake area, Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet
-
摘要:
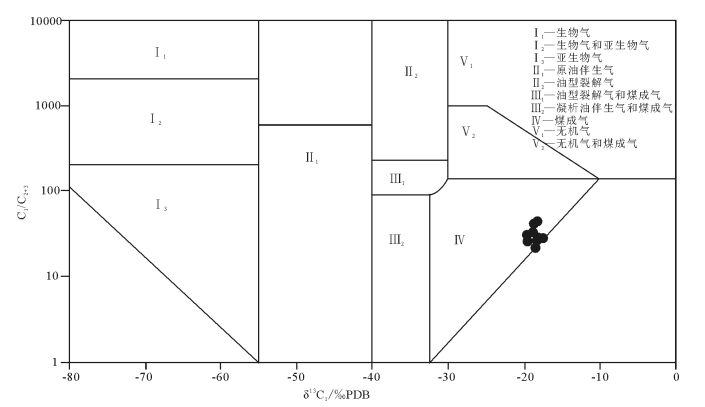
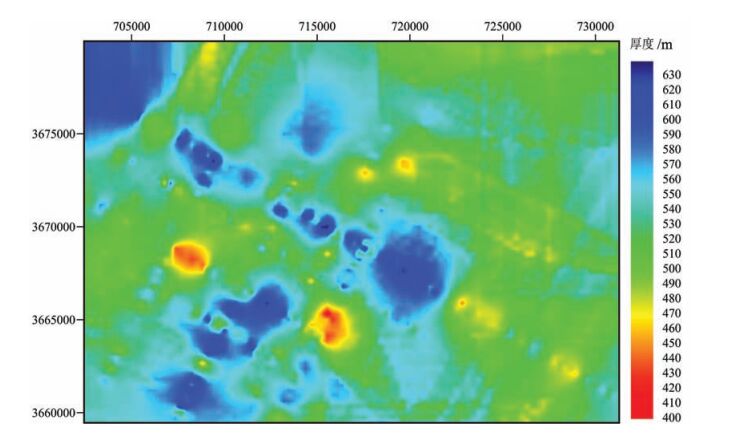
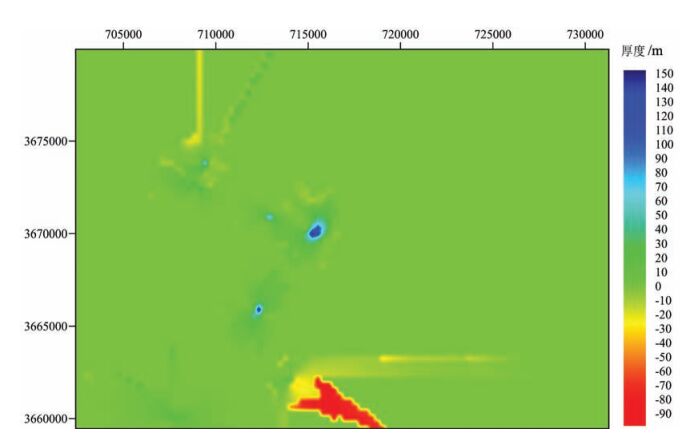
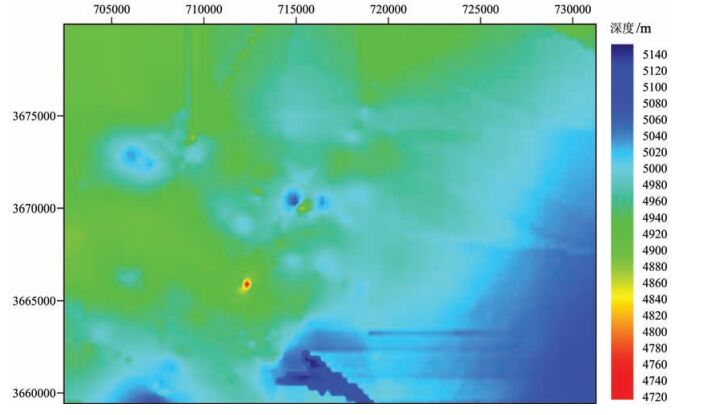
近年来中国陆域冻土区天然气水合物调查研究结果表明,气源条件是制约羌塘盆地天然气水合物找矿突破的关键因素。为明确鸭湖地区天然气水合物成藏潜力,基于近年来的钻探调查成果,从陆域冻土区天然气水合物成藏系统理论出发,系统分析了影响天然气水合物成藏的冻土、气源、储集、构造等地质因素。分析结果显示,鸭湖地区局部具有较好的冻土、地温、气源、储集、构造及水源条件,具备一定的天然气水合物成藏潜力,继续寻找充足的烃类气源是下一步天然气水合物调查的主要方向。同时,选取钻探调查获取的地温梯度、气体组分等参数,结合音频大地电磁测深(AMT)冻土厚度调查成果,对鸭湖地区天然气水合物稳定带的厚度和底界深度进行了预测。结果显示,当甲烷为85%、乙烷为9%、丙烷为6%时,天然气水合物稳定带厚度与冻土厚度分布变化基本一致,稳定带厚度400~630m,底界深度400~680m。当甲烷为98%、乙烷为2%时,天然气水合物稳定带厚度急剧减薄,大部分地区仅有0~30m,最厚仅有150m,局部地区稳定带底界最深仅为240m。结合气测录井结果,认为渐新世唢呐湖组比上三叠统土门格拉组更具备天然气水合物成藏潜力,土门格拉组自身具备较强的生排烃能力,可作为寻找常规油气或页岩气的一个重要层位。
Abstract:In recent years, the gas hydrate investigation in the permafrost region of China shows that the gas source condition is the key factor for controlling the breakthrough of gas hydrate exploration in the Qiangtang Basin. In order to further clarify the potential of gas hydrate accumulation in the Duck Lake area, the authors systematically analyzed such geological factors as permafrost, gas source, reservoir and structure based on the drilling results in recent years. The results show that there are good conditions of permafrost, geothermal gradient, gas source, reservoir, structure and water source in some areas, indicating that Duck Lake area has a certain gas hydrate accumulation potential. Finding sufficient hydrocarbon gas sources will be the main direction of the next gas hydrate investigation. In addition, the thickness of the gas hydrate stability zone (GHSZ) and the depth of bottom of GHSZ in the Duck Lake area were predicted by the data of the geothermal gradient and the gas composition obtained from the drilling and AMT results. Predictive results show that, when the methane is 85%, ethane is 9% and propane is 6%, the thickness distribution of GHSZ is basically the same as that of the permafrost. The thickness of GHSZ is between 400m and 630m, and the depth of the bottom of GHSZ is between 400m and 680m. Where methane is 98% and ethane is 2%, the thickness of GHSZ is sharply thinned, only 0~30m in most areas and only 150m thick in certain areas, and the depth of the deepest bottom of GHSZ is only 240m. Based on the results of gas logging, it is concluded that the Oligocene Suonahu Formation has more potential gas hydrate accumulation potential than the Upper Triassic Tumengela Formation in Duck Lake area, while Tumengela Formation has strong hydrocarbon generation and expulsion capability, which thus can be regarded as an important horizon for exploration of conventional oil and gas or shale gas.
-
Key words:
- gas hydrate /
- accumulation condition /
- Duck Lake area /
- Qiangtang Basin
-

-
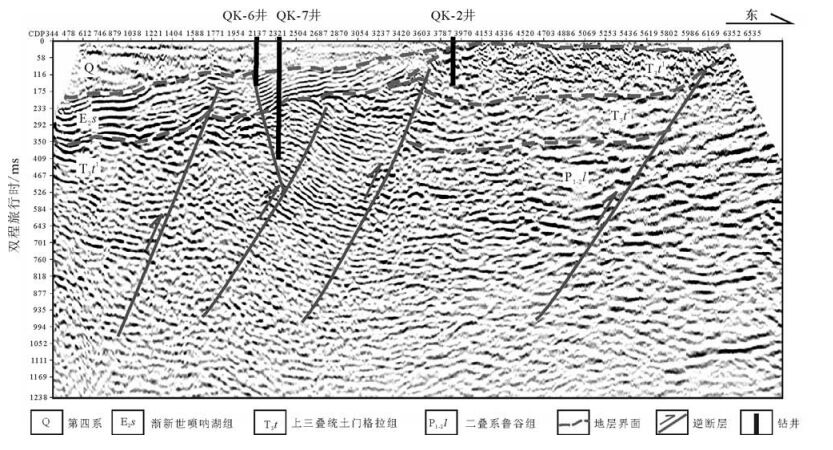
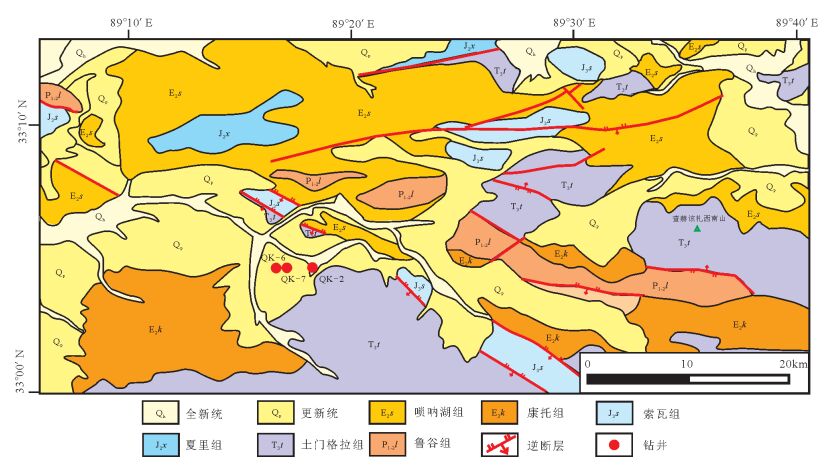
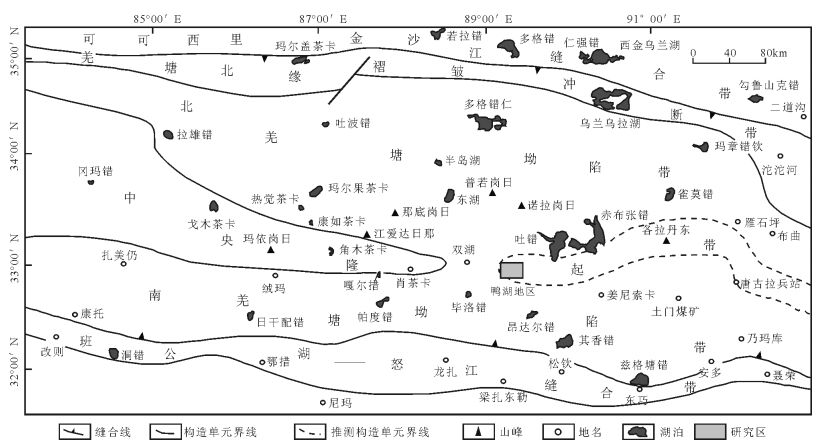
图 1 羌塘盆地构造单元划分[24]及鸭湖地区位置
Figure 1.
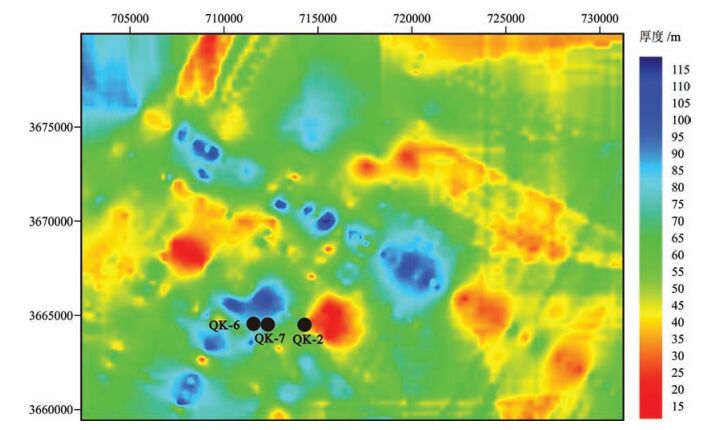
图 2 鸭湖地区地质图 ① 及天然气水合物地质调查井位置
Figure 2.
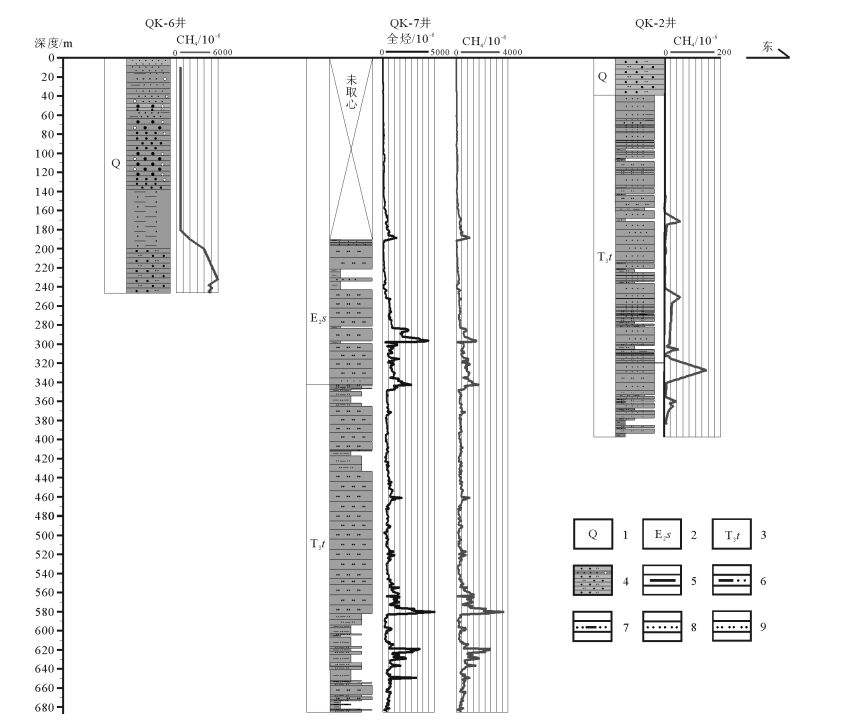
表 1 鸭湖地区天然气水合物调查井钻探概况
Table 1. Overview of gas hydrate investigation wells in Duck Lake area
钻井
编号海拔/m 井深/m 冻土层
厚度/m冻土层以内地温
梯度(/ ℃· 100m-1)冻土层以下地温
梯度(/ ℃· 100m-1)钻遇地层 主要岩性 异常特征 QK-2 4970 389.85 38 未测得 2.15 Q,T3t 第四系沉积物、细-中砂岩、泥
岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩H2S气体,自生黄
铁矿和方解石QK-6 4960 246.4 未测井 未测井 未测井 Q 第四系沉积物 烃类气体异常 QK-7 4960 684 120 1.24 3.66 Q,E2s,T3t 第四系沉积物、泥灰岩、泥岩、
泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩丰富烃类气体 注:地层代号同图 2 表 2 鸭湖地区天然气水合物潜在储集岩类型
Table 2. Types of gas hydrate potential reservoir rocks in Duck Lake area
地层 岩石类型 成岩作用 主要储集类型 储集性 第四系(Q) 松散沉积物 差 孔隙型 好 渐新世唢呐湖组(E2s) 泥岩、泥灰岩、粗砂岩、中砂岩、细砂岩、粉砂岩 较差 孔隙型为主,裂隙型次之 较好 上三叠统土门格拉组(T3t) 粗砂岩、中砂岩、细砂岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、泥岩 强 裂隙型为主,孔隙型次之 一般 -
[1] Kvenvolden K A. A primer in gas hydrate[C]//Howell D G. The fu-ture of energy gases. U. S. Geological Survey, 1993, 1570:279-292.
[2] Sloan E D. Clathrate Hydrate of Natural Gases (Second edit)[M]. New York:Marcel Dekker Inc., 1998:1-628.
[3] Collett T S. Permafrost-associated gas hydrate[C]//Max M D. Natu-ral gas hydrate in oceanic and permafrost environments. The Nether-lands, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000:43-60.
[4] Kvenvolden K A, Lorenson T D. The global occurrence of natural gas hydrate[J]. American Geophysical Union, 2001, 124:3-18. https://www.onepetro.org/download/conference-paper/ISOPE-I-01-069?id=conference-paper%2FISOPE-I-01-069
[5] 祝有海, 张永勤, 文怀军, 等.青海祁连山冻土区发现天然气水合物[J].地质学报, 2009, 83(11):1761-1770. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200911020.htm
[6] Dallimore S R, Collett T S. Summary and implication of the Mallik 2002 gas hydrate production research well program[C]//Dallimore S R, Collett T S. Scientific Results from the Mallik 2002 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well Program, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada. Geological Survey of Canada, 2005, 585:1-36.
[7] Makogon Y F, Holditch S A, Makogon T Y. Natural gas-hydrates-A potential energy source for the 21st Century[J]. Journal of Petro-leum Science and Engineering, 2007, 56:14-31. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2005.10.009
[8] 祝有海, 卢振权, 谢锡林.青藏高原天然气水合物潜在分布区预测[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(12):1918-1926. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.12.016 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20111216&journal_id=gbc
[9] 祝有海, 赵省民, 卢振权.中国冻土区天然气水合物的找矿选区及其资源潜力[J].天然气工业, 2011, 31(1):13-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201101004.htm
[10] 徐学祖, 程国栋, 俞祁浩.青藏高原多年冻土区天然气水合物的研究前景和建议[J].地球科学进展. 1999, 14(2):201-204. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ902.017.htm
[11] 张立新, 徐学祖, 马巍.青藏高原多年冻土区与天然气水合物[J].天然气地球科学, 2001, 12(1/2):22-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYS201102015.htm
[12] 黄朋, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.青藏高原天然气水合物资源预测[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(11):794-798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.11.019 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2002011176&journal_id=gbc
[13] 伊海生, 时志强, 刘文军.青藏高原多年冻土区天然气水合物形成潜力及远景[J].西藏地质, 2002, 20(1):46-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200901020.htm
[14] 刘怀山, 韩晓丽.西藏羌塘盆地天然气水合物地球物理特征识别与预测[J].西北地质, 2004, 37(4):33-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200404006.htm
[15] 陈多福, 王茂春, 夏斌.青藏高原冻土带天然气水合物的形成条件与分布预测[J].地球物理学报, 2005, 48(1):165-172. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200501022.htm
[16] 吴青柏, 蒋观利, 蒲毅彬, 等.青藏高原天然气水合物的形成与多年冻土的关系[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2):29-33. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060106&journal_id=gbc
[17] 库新勃, 吴青柏, 蒋观利.青藏高原多年冻土区天然气水合物可能分布范围研究[J].天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(4):588-592. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200704024.htm
[18] 郭祖军, 陈志勇, 胡素云, 等.天然气水合物分布及青藏高原有利勘探区[J].新疆石油地质, 2012, 33(3):266-271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201203001.htm
[19] He J, Wang J, Fu X, et al. Assessing in the conditions favorable for the occurrence of gas hydrate in the Tuonamu area Qiangtang Ba-sin, Qinghai-Tibetan, China[J]. Energy Conversion and Manage-ment, 2012, 53:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2011.08.012
[20] Fu X, Wang J, Tan F, et al. Gas hydrate formation and accumula-tion potential in the Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet, China[J]. En-ergy Conversion and Management, 2013, 73:186-194. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2013.04.020
[21] 刘增乾, 徐宪, 潘桂棠.青藏高原大地构造与形成演化[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990:9-34.
[22] 余光明, 王成善.西藏特提斯沉积地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990:94-98.
[23] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等.青藏高原羌塘盆地石油地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:1-367.
[24] 王剑, 丁俊, 王成善, 等.青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.
[25] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等.青藏高原大地构造特征及盆地演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000.
[26] 王成善, 伊海生, 李勇, 等.西藏羌塘盆地地质演化与油气远景评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001:224-225.
[27] 王成善, 伊海生, 刘池洋, 等.西藏羌塘盆地古油藏发现及其意义[J].石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2):139-143. doi: 10.11743/ogg20040204
[28] Xu W, Ruppel C. Predicting the occurrence, distribution, and evo-lution of methane gas hydrate in porous marine sediments[J]. Jour-nal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B3):5081-5095. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900092
[29] Bunz S, Mienert J, Bemdt C. Geological controls on the storage gas-hydrate system of the mid-Norweigian continental margian[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 209:291-307. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00097-9
[30] Milkov A V, Clapool G, Lee Y J, et al. Gas hydrate systems at Hy-drate Ridge offshore Oregon inferred from molecular and isotopic properties of hydrate-bound and void gases[J]. Geochimica et Cos-mochimica Acta, 2005, 69(4):1007-1026. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.08.021
[31] 吴能友, 张海啟, 杨胜雄, 等.南海神狐海域天然气水合物成藏系统初探[J].天然气工业, 2007, 27(9):1-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200709004.htm
[32] 吴能友, 梁金强, 王宏斌, 等.海洋天然气水合物成藏系统研究进展.现代地质, 2008, 22(3):356-362. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200803003.htm
[33] 卢振权, 吴能友, 陈建文, 等.试论天然气水合物成藏系统.现代地质, 2008, 22(3):363-375. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200803004.htm
[34] Collett T S, Johnson A, Knapp C, et al. Natural Gas Hydrate-A Review[C]//Collett T S, Johnson A, Knapp C, et al. Natural Gas Hydrates-Energy Resource Potential and Associated Geologic Haz-ards. AAPG Memoir, 2009, 89:153-162.
[35] 王平康, 祝有海, 卢振权, 等. 浅析祁连山冻土区天然气水合物成藏体系[C]//海峡两岸天然气水合物学术交流会论文集, 2010: 52.
[36] 卢振权, 祝有海, 张永勤, 等. 祁连山冻土区天然气水合物成藏系统[C]//中国地质学会2013年学术年会, 2013: 459-461.
[37] 翟刚毅, 卢振权, 卢海龙, 等.祁连山冻土区天然气水合物成矿系统[J].矿物岩石, 2014, 34(4):79-92. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ201310012067.htm
[38] 王平康, 祝有海, 张旭辉, 等.羌塘盆地冻土结构特征及其对天然气水合物成藏的影响[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2015, 35(1):57-67. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201501008.htm
[39] 戴金星.各类天然气的成因鉴别[J].中国海上油气:地质, 1992, 1:11-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199201005.htm
[40] 肖睿. 西藏羌塘盆地天然气水合物气源研究[D]. 中国地质科学院硕士学位论文, 2015.
[41] 杨润田, 林凤桐.多年冻土区水文地质及工程地质学[M].哈尔滨:东北林业大学出版社, 1986:134.
[42] 陈俊, 王鹤年.地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2004:116.
① 成都地质矿产研究所.《吐错幅》(I45C003004)(比例尺1:250000)地质调查报告. 2010.
-



 下载:
下载: