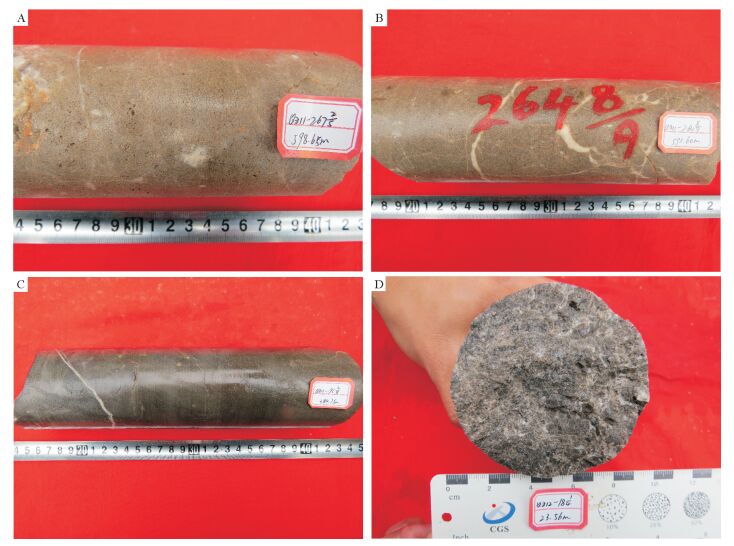
Geochemical features of oil-bearing samples from the well in Buqu Formation in the Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet, and their implications
-
摘要:
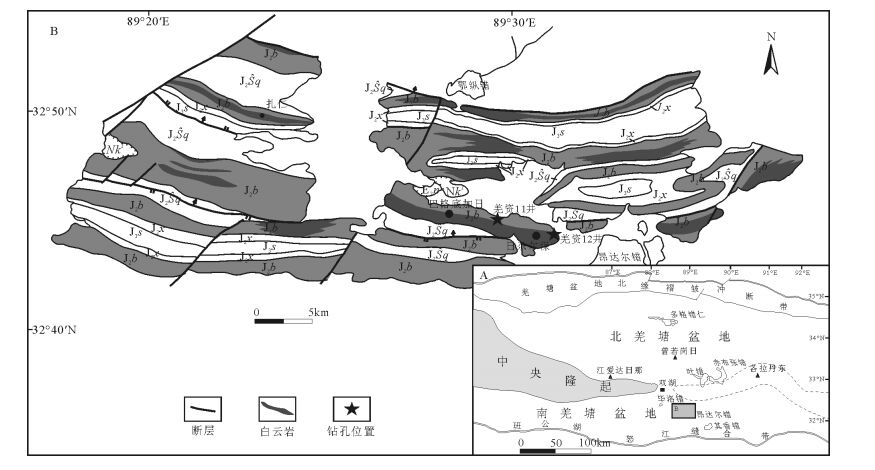
羌资11、12井是羌塘盆地揭示隆鄂尼-昂达尔错古油藏展布规律的资料井。对这2口钻井揭示的含油岩层进行取样分析,结合前人该区石油地质调查报告中羌资2井布曲组、夏里组及曲色组烃源岩的分析数据,从类异戊二烯烃、甾烷、萜烷等系列生物标志化合物参数方面进行油-岩对比研究。研究表明,羌资11、12井揭示的原油为同一种类型,但11井原油生物降解程度强于12井。各原油的母质主要来源于低等水生生物和藻类;各原油的母质形成于还原-弱还原、盐度值不高的咸水环境。原油中类异戊二烯烃、萜烷、甾烷等生物标志化合物参数与羌资2井布曲组泥晶灰岩与夏里组和曲色组烃源岩之间具有较好的亲缘性。结合南羌塘地区烃源岩有机碳资料,油源可能主要来自于曲色组,混入了部分夏里组及布曲组的油源,具有混源的特征。该研究结果对下一步油气勘探具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:The Qiangzi-11 and 12 wells are the data well to reveal the distribution regularities of Longeni-Angdaerco palaeo-oil reservoirs. Together with the hydrocarbon source rock data of Buqu Formation, Xiali Formation, and Quse Formation from Qiangzi-2 well, the authors analyzed the oil-rock correlations based on the biomarker parameters composed of isoprenoid, steranes, and ter-panes. The property of crude oil from Qiangzi-11 and 12 wells is of the same type. However, the biodegradation degree from Qiang-zi-11 well is higher than that from Qiangzi-12. The biomarker parameters reveal that the organic matter mainly originated from al-gae. The crude oil was formed under weak reduction-reduction conditions and in a slightly salty water environment. The biomarkers of crude oil, composed of isoprenoid, terpane, and sterane, are closely related to those of the Buqu Formation in Qiangzi-2 well, and also show good correlation with those of the Xiali Formation and Quse Formation in Qiangzi-2 well. Combined with the TOC data of the hydrocarbon source rock in south Qiangtang Basin, the authors hold that the crude oil of the Longeni-Angdaerco palaeo-oil reservoir was mainly from the source rocks of Quse Formation, and partly from the Xiali and Buqu Formations, suggesting a mixture of sources. The result of this study may have some guidance significance for further oil-gas exploration.
-
Key words:
- biomarker /
- oil-bearing dolomite /
- Buqu Formation /
- oil-rock correlation /
- Qiangtang Basin
-

-
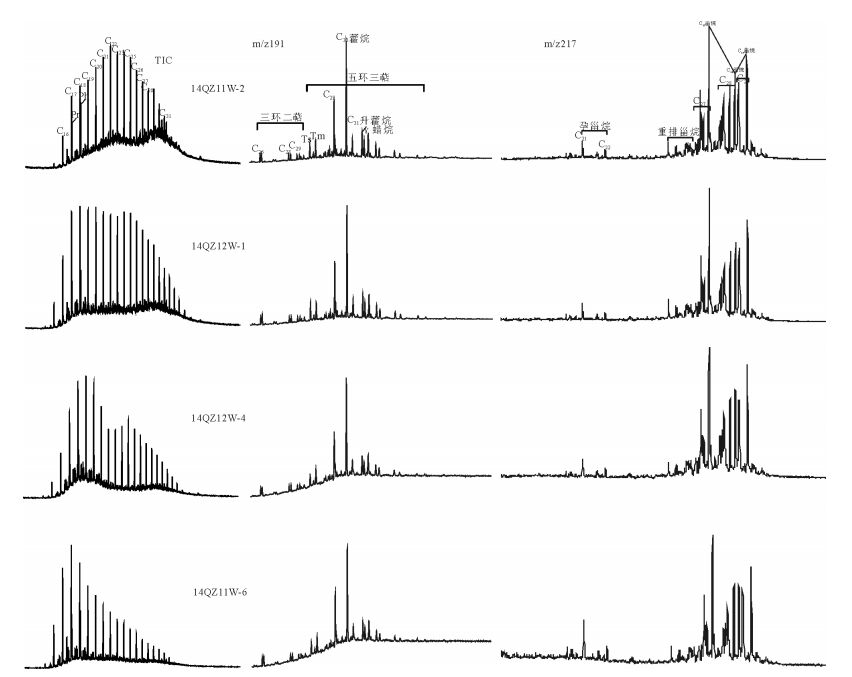
表 1 羌资11、12井样品氯仿沥青“A”及族组分含量
Table 1. The concentrations of chloroform bitumen"A"and group composition in the sample from Well Qiangzi-11 and 12
样品号 井深/m 岩性 氯仿沥青
“A”/%族组分/% 饱和烃 芳烃 非烃 沥青质 非烃+沥青质 14QZ11W-1 591 含油白云岩 0.0017 42.86 11.11 39.68 6.35 46.03 14QZ11W-2 593.95 含油白云岩 0.0004 37.52 12.48 43.75 6.25 50.00 14QZ11W-3 596.55 含油白云岩 0.0009 37.93 10.34 44.82 6.91 51.73 14QZ11W-4 598.81 含油白云岩 0.0007 30.43 13.04 47.82 8.71 56.53 14QZ12W-1 23 含油白云岩 0.0013 45.45 11.36 38.64 4.55 43.19 14QZ12W-2 34.5 含油白云岩 0.0012 46.34 17.07 31.71 4.88 36.59 14QZ12W-3 58.5 含油白云岩 0.0017 64.41 18.64 11.86 5.09 16.95 14QZ12W-4 71 含油白云岩 0.0009 65.51 17.24 10.34 6.91 17.25 14QZ11W-5 370.22 含油灰岩 0.011 46.02 34.66 14.77 4.55 19.32 14QZ11W-6 377.56 含油灰岩 0.007 46.99 31.33 18.07 3.61 21.68 14QZ11W-7 384.83 含油灰岩 0.0051 40.98 22.95 26.23 9.84 36.07 14QZ11W-8 396.78 含油灰岩 0.0024 39.58 18.75 35.42 6.25 41.67 表 2 羌资11、12井样品正构烷烃与类异戊二烯烃分析结果
Table 2. The analytical results of n-alkanes and isoprenoid alkanes in the samples from Well Qiangzi-11 and 12
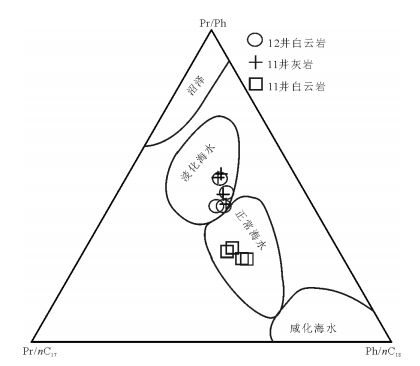
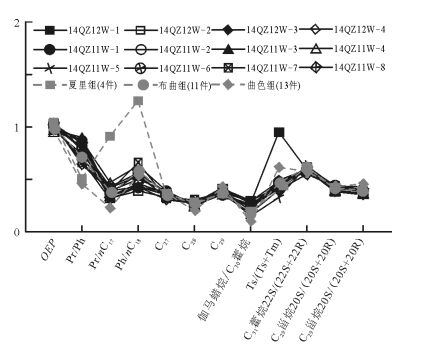
样品号 井深/m 岩性 主峰碳 C21-/ C22+ Pr/Ph Pr/nC17 Ph/nC18 CPI OEP 14QZ11W-1 591 含油白云岩 nC25 0.58 0.58 0.61 0.98 1.27 1.02 14QZ11W-2 593.95 含油白云岩 nC25 0.55 0.67 0.72 0.92 1.11 0.97 14QZ11W-3 596.55 含油白云岩 nC21 1.23 0.55 0.56 0.96 1.12 0.93 14QZ11W-4 598.81 含油白云岩 nC25 0.63 0.71 0.69 0.96 1.06 0.96 14QZ12W-1 23 含油白云岩 nC25 0.61 0.74 0.42 0.53 1.04 0.97 14QZ12W-2 34.5 含油白云岩 nC18 0.68 0.78 0.32 0.39 1.04 1.03 14QZ12W-3 58.5 含油白云岩 nC18 0.74 0.68 0.31 0.43 1.02 1.01 14QZ12W-4 71 含油白云岩 nC19 0.82 0.64 0.39 0.43 1.06 1.03 14QZ11W-5 370.22 含油灰岩 nC17 1.22 0.87 0.36 0.42 1.05 1.01 14QZ11W-6 377.55 含油灰岩 nC17 1.34 0.8 0.39 0.5 1.06 1 14QZ11W-7 384.83 含油灰岩 nC17 1.52 0.9 0.34 0.43 0.97 0.97 14QZ11W-8 396.78 含油灰岩 nC17 1.69 0.87 0.47 0.63 0.98 0.95 表 3 羌资11、12井样品萜烷、甾烷分析结果
Table 3. The analytical results of terpane and sterane in the samples from Well Qiangzi-11 and 12
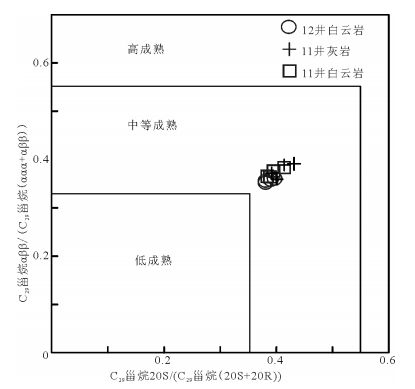
样品号 井深/m A B C D E F G H I 规则甾烷 C27 C28 C29 14QZ11W-1 591 0.41 0.41 0.38 0.57 0.35 0.22 0.59 0.06 0.90 0.34 0.29 0.37 14QZ11W-2 593.9 0.43 0.38 0.36 0.57 0.27 0.28 0.59 0.11 1.07 0.39 0.25 0.36 14QZ11W-3 596.6 0.43 0.39 0.37 0.57 0.27 0.28 0.60 0.10 1.00 0.37 0.26 0.37 14QZ11W-4 598.8 0.41 0.39 0.36 0.57 0.29 0.25 0.60 0.09 1.02 0.37 0.26 0.37 14QZ12W-1 23 0.95 0.38 0.36 0.55 0.27 0.30 0.59 0.12 1.12 0.40 0.25 0.36 14QZ12W-2 34.5 0.43 0.39 0.36 0.55 0.30 0.38 0.59 0.14 1.09 0.39 0.24 0.36 14QZ12W-3 58.5 0.49 0.38 0.35 0.57 0.20 0.20 0.59 0.19 1.10 0.39 0.26 0.35 14QZ12W-4 71 0.41 0.4 0.36 0.53 0.27 0.33 0.59 0.10 1.02 0.37 0.26 0.37 14QZ11W-5 370.2 0.48 0.41 0.39 0.56 0.29 0.41 0.58 0.30 1.03 0.39 0.24 0.37 14QZ11W-6 377.6 0.41 0.43 0.39 0.58 0.23 0.33 0.59 0.25 1.08 0.39 0.25 0.36 14QZ11W-7 384.8 0.46 0.39 0.37 0.57 0.23 0.48 0.60 0.43 1.00 0.38 0.24 0.38 14QZ11W-8 396.8 0.45 0.4 0.36 0.57 0.26 0.42 0.60 0.18 1.10 0.39 0.25 0.36 注:A=Ts/(Ts+Tm);B=C29甾烷20S/(20S+20R);C=C29甾烷ββ/(αα+ββ);D=C32藿烷22S/(22S+22R);E=伽马蜡烷/αβ-C30藿烷;F=三环萜烷/藿烷;G=C31升藿烷22S/(22S+22R);H=孕甾烷/C29-ααα-20R甾烷;I=ααα-20R甾烷C27/C29 -
[1] 王成善, 伊海生, 刘池洋, 等.西藏羌塘盆地古油藏发现及其意义[J].石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2):139-143. doi: 10.11743/ogg20040204
[2] 黄汲清, 陈炳蔚.中国及邻区特提斯海的演化[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987:36-47.
[3] 王剑, 谭富文, 李亚林, 等.青藏高原重点沉积盆地油气资源潜力分析[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004:1-88.
[4] 付修根, 廖忠礼, 刘建清, 等.南羌塘盆地扎仁地区中侏罗统布曲组沉积环境特征及其对油气地质条件的控制作用[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(4):599-605. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200704008.htm
[5] 赵正璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等.羌塘盆地南部海相侏罗系古油藏例析[J].海相油气地质, 2002, 7(3):34-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200203007.htm
[6] 陈文彬, 廖忠礼, 刘建清, 等.西藏羌塘盆地扎仁地区白云岩油苗地球化学特征[J].新疆石油地质, 2008, 29(2):214-218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200802026.htm
[7] 杜佰伟, 陈明, 李忠雄, 等.羌塘盆地扎仁地区中侏罗统布曲组烃源岩评价[J].新疆石油地质, 2010, 31(1):40-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201203007.htm
[8] 刘建清, 杨平, 陈文彬, 等.羌塘盆地中央隆起带南侧隆额尼-昂昂达尔错布曲组古油藏白云岩特征及成因机制[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(1):311-321. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001030.htm
[9] 付修根, 廖忠礼, 王剑, 等.藏北南羌塘盆地扎仁地区油苗地球化学特征及意义[J].沉积学报, 2008, 26(4):697-704. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200804024.htm
[10] 李忠雄, 王剑, 汪正江, 等.藏北羌塘盆地羌资2井中侏罗统布曲组碳酸盐岩岩石学及储集物性特征[J].地球学报, 2009, 30(5):590-598. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200905005.htm
[11] 李忠雄, 何江林, 杜佰伟, 等.羌塘盆地羌资2井布曲组碳酸盐岩生物标志物特征及意义[J].石油实验地质, 2010, 32(2):175-185. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201002175
[12] 和钟铧, 李才, 杨的明, 等.西藏羌塘盆地的构造沉积特征及演化[J].长春科技大学学报, 2000, 30(4):347-352. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200004007.htm
[13] 王剑, 丁俊, 王成善, 等.青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009:227-270.
[14] 丁文龙, 李超, 苏爱国, 等.西藏羌塘盆地中生界海相烃源岩综合地球化学剖面研究及有利生烃区预测[J].岩石学报, 2000, 27(3):878-896. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103025.htm
[15] 李忠雄, 杜佰伟, 汪正江, 等.藏北羌塘盆地中侏罗统石油地质特征[J].石油学报, 2008, 29(6):797-803. doi: 10.7623/syxb200806002
[16] 包建平, 朱翠山.生物降解作用对辽河盆地原油甾萜烷成熟度参数的影响[J].中国科学 (D辑), 2008, 38(增刊Ⅱ):38-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S2007.htm
[17] Peters K E, Fraser T H, Amris W, et al. Geochemistry of crude oils form eastern Indonesia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(12):1927-1942. http://www.academia.edu/16059123/Geochemistry_of_crude_oils_from_Eastern_Indonesia
[18] 国朋飞, 何生, 朱生奎, 等.利用三环萜烷对比泌阳凹陷生物降解油油源[J].石油实验地质, 2015, 37(1):80-87. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201501080
[19] Peters K E, Walters C C, Moldowan J M. The biomarker guide, bio-markers and isotopes in petroleum exploration and earth history[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2005:1-704.
[20] 范璞.塔里木油气地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1990.
[21] Summons R E, Volkman J K, Boreham C J. Dinosterane and other steroidal hydrocarbons of dinoflagellate origin in sediments and pe-troleum[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(11):3075-3082. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90381-4
[22] Volkman J K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrige-nous organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(2):83-99. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(86)90089-6
[23] 刘全有, 刘文汇, 孟仟祥, 等.塔里木盆地侏罗系煤岩热模拟生物标志化合物特征研究[J].沉积学报, 2004, 22(4):724-728. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200404026.htm
[24] 王铁冠.生物标志物地球化学研究[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1990.
[25] 范善发, 周中毅, 潘长春, 等.塔里木盆地下古生界生物标志物分布与沉积环境的关系[J].石油与天然气地质, 1991, 12(2):169-176. doi: 10.11743/ogg19910209
[26] 段毅, 吴保祥, 张辉, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地西峰油田原油地球化学特征及成因[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(2):301-310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200602027.htm
[27] 聂志阳, 黄清华, 席党鹏, 等.松辽盆地松科1井烃源岩生物标志化合物特征[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(2):265-274. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201402023.htm
[28] Mackenzie A S, Brassell S C, Eglinton G, et al. Chemical fossilsthe geological fate of steroids[J]. Science, 1982, 217(4559):491-504. doi: 10.1126/science.217.4559.491
[29] Moldowan J M, Albercht P, Philip R P, et al. Biological markers in sediments and petroleum[M]. New Jersey:Prentice Hall, 1992:268-280.
[30] 季长军, 伊海生, 陈志勇, 等.西藏羌塘盆地羌D2井原油类型及勘探意义[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(6):1070-1076. doi: 10.7623/syxb201306005
[31] 林金辉, 尹海生, 李勇, 等.藏北高原双湖地区中侏罗统海相油页岩生物标志化合物分布特征及其意义[J].沉积学报, 2001, 19(2):287-292. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200102020.htm
[32] Zeng Y H, Fu X G, Zeng S Q, et al. Organic geochemical charac-teristics of the Bilong Co oil shale (China):implications for paleoen-vironment and petroleum prospects[J]. Oil Shale, 2011, 28(3):398-414. doi: 10.3176/oil.2011.3.04
[33] 陈文彬, 廖忠礼, 刘建清, 等.羌塘盆地扎仁地区中上侏罗统烃源岩生物标志物特征[J].油气地质与采收率, 2008, 15(5):17-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200805007.htm
[34] 南征兵, 张艳玲, 李永铁, 等.羌塘盆地中侏罗统布曲组烃源岩评价[J].油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(3):15-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201203007.htm
[35] 伍新和, 张丽, 王成善, 等.西藏羌塘盆地中生界海相烃源岩特征[J].石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(3):348-354. doi: 10.11743/ogg20080310
[36] 陈文彬, 廖忠礼, 刘建清, 等.西藏南羌塘盆地侏罗系烃源岩地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(4):654-661. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201004002.htm
[37] 肖睿, 祝有海, 王平康, 等.藏北羌塘盆地QK-1井中侏罗统烃源岩地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(1):163-170. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201501020.htm
[38] Fu X. G, Wang J, Chen W. B, et al. Elemental geochemistry of the early Jurassic black shales in the Qiangtang Basin, eastern Tethys:constraints for palaeoenvironment conditions[J]. Geological Journal, 2016, 51(3):443-454. doi: 10.1002/gj.v51.3 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271081199_Elemental_geochemistry_of_the_early_Jurassic_black_shales_in_the_Qiangtang_Basin_eastern_Tethys_Constraints_for_palaeoenvironment_conditions
-



 下载:
下载: