The Early Cretaceous gabbro in Yare area, middle Lhasa Block: Magmatism response to the slab break-off of the southward subduction Bangong-Nujiang Ocean lithosphere
-
摘要:
为深入认识拉萨地块中北部地区早白垩世构造-岩浆过程,对中拉萨地块西段亚热地区早白垩世辉长岩进行了研究。辉长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为115.5±0.5 Ma。岩石属于拉斑玄武岩系列,具有与洋岛玄武岩(OIB)相似的稀土元素特征,Mg#值(46.07~48.05)、Cr(6.97×10-6~18.5×10-6)和Ni(6.87×10-6~11.2×10-6)元素含量较低,Rb、Ba、K、Sr等大离子亲石元素富集,Th、U和Pb元素呈现明显的正异常,Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf、P、Ti等高场强元素表现为负异常,显示具有部分弧火山岩性质;具有正的锆石εHf(t)值(+4.3~+7.9)和较年轻的Hf亏损地幔模式年龄(TDM1=489~614 Ma)。综合分析认为,亚热地区早白垩世辉长岩形成于南向俯冲的班公湖-怒江特提斯洋岩石圈板片断离的构造背景,可能是受近期俯冲板片熔体或超临界流体交代的软流圈地幔部分熔融的产物,并经历了不同程度的分离结晶作用。
Abstract:In order to understand the Early Cretaceous tectonic-magmatic process in the central and north Lhasa Block, the Early Cretaceous gabbro in the Yare area of western part of middle Lhasa Block were studied.The zircon U-Pb age of gabbro is 115.5±0.5 Ma.The rocks belong to tholeiite series, and their characteristics of rare earth elements are similar to those of oceanic island basalt (OIB).Mg# value (46.07~48.05) and contents of Cr (6.97×10-6~18.5×10-6), Ni (6.87×10-6~11.2×10-6) are relatively low.The large ion lithophile elements such as Rb, Ba, K, Sr of gabbro samples are relatively enriched, Th、U and Pb show positive anomalies, and the high field strength elements such as Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, P and Ti show negative anomalies, indicating that the gabbro samples have some "arc volcanic rock" properties.The gabbro show positive zircon εHf (t) values (+4.3~+7.9) and younger Hf-depleted mantle model ages (TDM1) of 489~614 Ma.By comprehensive analysis, it is proposed that the Early Cretaceous gabbro in the Yare area is most likely triggered by the slab break-off of the southward subducting Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean lithosphere, and can be considered as the product of partial melting of the asthenosphere mantle which was metasomatized by recent melts or supercritical fluids from the subduction slab, and subsequently experienced varying degrees of fractional crystallization.
-
Key words:
- middle Lhasa Block /
- Yare area /
- Early Cretaceous /
- gabbro /
- slab break-off
-

-
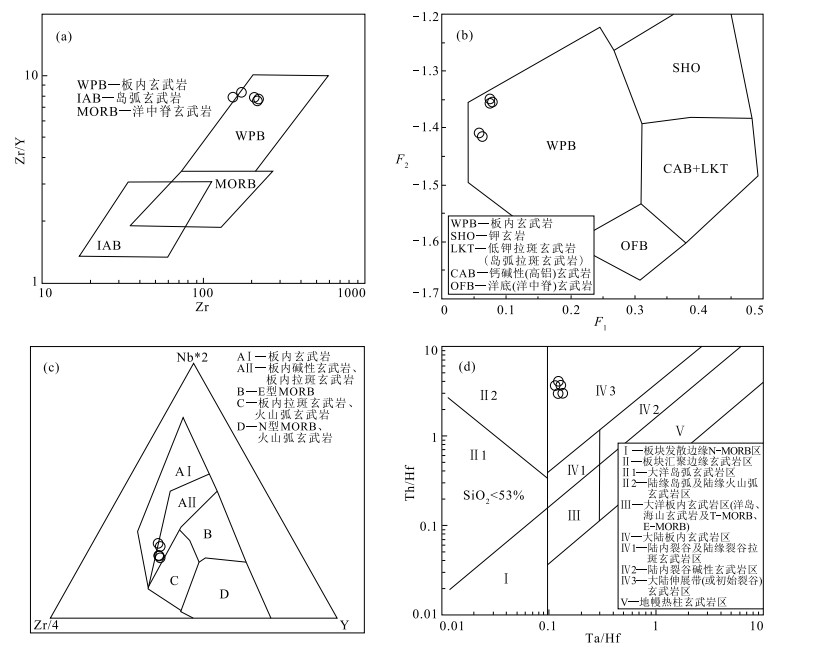
图 1 拉萨地块构造简图(a) (据参考文献[19]修改)和研究区地质简图(b)
Figure 1.
表 1 亚热地区早白垩世辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb定年结果
Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating results of the Early Cretaceous gabbro in the Yare area
测点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ YR03-N1:细粒辉长岩, 115.5±0.5 Ma(MSWD=0.24, n=24) 1 63.8 3149 2424 1.30 0.0497 0.0023 0.1239 0.0059 0.0180 0.0003 119 5.3 115 1.9 2 58.1 2004 2455 0.82 0.0463 0.0019 0.1160 0.0046 0.0181 0.0002 111 4.2 116 1.2 3 101.8 6586 3422 1.92 0.0483 0.0024 0.1198 0.0056 0.0180 0.0002 115 5.1 115 1.3 4 171 12027 5389 2.23 0.0507 0.0014 0.1264 0.0039 0.0180 0.0002 121 3.5 115 1.4 5 67.5 2940 2638 1.11 0.0475 0.0018 0.1187 0.0045 0.0180 0.0002 114 4.1 115 1.1 6 113.5 7009 3855 1.82 0.0474 0.0018 0.1192 0.0048 0.0182 0.0002 114 4.4 116 1.3 7 46.7 1560 1988 0.78 0.0469 0.0020 0.1167 0.0049 0.0180 0.0002 112 4.5 115 1.3 8 128.9 7023 4503 1.56 0.0467 0.0015 0.1183 0.0039 0.0183 0.0002 114 3.5 117 1.1 9 119.3 6708 4287 1.56 0.0480 0.0016 0.1213 0.0040 0.0182 0.0002 116 3.6 116 1.0 10 72.9 3814 2756 1.38 0.0479 0.0015 0.1185 0.0035 0.0180 0.0002 114 3.2 115 1.1 11 150.9 8583 5442 1.58 0.0463 0.0013 0.1158 0.0033 0.0181 0.0002 111 3.0 115 1.1 12 73.1 4645 2553 1.82 0.0459 0.0038 0.1146 0.0096 0.0180 0.0003 110 8.7 115 2.1 13 82.5 4571 3123 1.46 0.0488 0.0019 0.1212 0.0045 0.0181 0.0002 116 4.0 115 1.5 14 100.7 4763 3927 1.21 0.0485 0.0016 0.1216 0.0039 0.0181 0.0002 117 3.6 116 1.1 15 98.5 4945 3703 1.34 0.0505 0.0018 0.1265 0.0044 0.0181 0.0002 121 4.0 116 1.0 16 109.7 6310 3925 1.61 0.0494 0.0018 0.1231 0.0045 0.0180 0.0002 118 4.1 115 1.3 17 72.0 2447 3092 0.79 0.0481 0.0017 0.1193 0.0042 0.0180 0.0002 114 3.8 115 1.1 18 52.2 2851 1877 1.52 0.0496 0.0023 0.1228 0.0056 0.0180 0.0002 118 5.1 115 1.4 19 61.9 3042 2365 1.29 0.0519 0.0023 0.1281 0.0055 0.0180 0.0002 122 5.0 115 1.3 20 149 10657 4758 2.24 0.0496 0.0016 0.1242 0.0040 0.0181 0.0002 119 3.6 116 1.1 21 48.5 1558 2072 0.75 0.0483 0.0019 0.1215 0.0049 0.0181 0.0002 116 4.4 116 1.1 22 73.4 3844 2798 1.37 0.0507 0.0020 0.1277 0.0050 0.0182 0.0002 122 4.5 116 1.3 23 137.8 8344 4834 1.73 0.0471 0.0016 0.1182 0.0041 0.0180 0.0002 113 3.7 115 1.1 24 29.7 1446 1117 1.29 0.0523 0.0038 0.1317 0.0093 0.0182 0.0003 126 8.4 116 2.2 表 2 亚热地区早白垩世辉长岩锆石Hf同位素组成
Table 2. Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of the Early Cretaceous gabbro in the Yare area
测点 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 1σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM1 /Ma TDM2 /Ma fLu/Hf 1 115 0.034591 0.001233 0.282841 0.000011 0.282839 2.5 4.9 586 859 -0.96 2 116 0.031632 0.001115 0.282837 0.000009 0.282835 2.3 4.8 590 868 -0.97 3 115 0.036831 0.001321 0.282869 0.000009 0.282866 3.4 5.9 547 797 -0.96 4 115 0.106599 0.003638 0.282931 0.000009 0.282924 5.6 7.9 489 668 -0.89 5 115 0.035429 0.001266 0.282831 0.000009 0.282828 2.1 4.5 601 883 -0.96 6 116 0.054628 0.001919 0.282835 0.000012 0.282831 2.2 4.6 606 877 -0.94 7 115 0.023673 0.000850 0.282848 0.000008 0.282846 2.7 5.1 571 843 -0.97 8 117 0.045489 0.001628 0.282852 0.000009 0.282848 2.8 5.3 577 837 -0.95 12 115 0.072057 0.002395 0.282882 0.000011 0.282877 3.9 6.2 545 773 -0.93 13 115 0.028848 0.001027 0.282824 0.000009 0.282821 1.8 4.3 608 898 -0.97 16 115 0.047060 0.001653 0.282874 0.000008 0.282870 3.6 6.0 545 788 -0.95 17 115 0.032015 0.001215 0.282855 0.000011 0.282852 2.9 5.4 566 829 -0.96 19 115 0.034776 0.001250 0.282842 0.000007 0.282839 2.5 4.9 585 858 -0.96 20 116 0.054467 0.001885 0.282829 0.000009 0.282825 2.0 4.4 614 890 -0.94 21 116 0.014140 0.000527 0.282833 0.000007 0.282832 2.2 4.7 586 873 -0.98 22 116 0.045963 0.001585 0.282854 0.000011 0.282850 2.9 5.3 574 833 -0.95 24 116 0.060981 0.002101 0.282888 0.000009 0.282883 4.1 6.5 532 759 -0.94 表 3 亚热地区早白垩世辉长岩主量、微量和稀土元素数据
Table 3. Major, trace and rare earth element concentrations of the Early Cretaceous gabbro in the Yare area
编号 YR03-H1 YR03-H2 YR03-H3 YR03-H4 YR03-H5 编号 YR03-H1 YR03-H2 YR03-H3 YR03-H4 YR03-H5 SiO2 51.38 50.14 51.25 50.68 50.5 Zr 173 208 153 221 217 TiO2 0.9 0.96 0.87 0.9 0.92 Nb 13.3 12.9 11.3 13.7 12.9 Al2O3 18.7 16.76 19.16 17.2 17.27 Cs 3.98 2.07 3.6 1.34 1.58 Fe2O3 9.38 11.01 9.46 10.36 10.47 Ba 375 449 407 632 588 MnO 0.16 0.19 0.15 0.19 0.19 La 54.3 71.3 42.9 80.2 79.3 MgO 4.38 4.86 4.08 4.52 4.63 Ce 101 134 87 149 147 CaO 8.74 9.5 8.95 9.04 9.24 Pr 10.6 14 9.03 15.6 15.5 Na2O 3.29 2.63 3.25 2.92 2.78 Nd 37.8 51 32.8 55.7 56.8 K2O 1.28 1.89 1.34 1.79 1.77 Sm 7.12 9.77 6.24 10.8 10.9 P2O5 0.41 0.69 0.34 0.59 0.59 Eu 1.99 2.5 1.81 2.88 2.86 烧失量(LOI) 1.24 1.18 1.01 1.62 1.42 Gd 5.84 8.02 5.19 8.78 8.89 总和 99.86 99.81 99.86 99.81 99.78 Tb 0.74 0.99 0.68 1.09 1.1 TFeO 8.44 9.91 8.51 9.32 9.42 Dy 3.96 5.21 3.77 5.69 5.73 K2O+Na2O 4.57 4.52 4.59 4.71 4.55 Ho 0.72 0.94 0.7 1.02 1.02 K2O/Na2O 0.39 0.72 0.41 0.61 0.64 Er 2.03 2.5 1.99 2.71 2.75 Mg# 48.05 46.65 46.07 46.36 46.69 Tm 0.27 0.34 0.27 0.37 0.38 δ 2.49 2.86 2.55 2.89 2.76 Yb 1.78 2.17 1.75 2.4 2.4 F1 0.06 0.08 0.06 0.08 0.07 Lu 0.27 0.32 0.26 0.36 0.35 F2 -1.42 -1.35 -1.41 -1.35 -1.36 Hf 4.05 4.86 3.79 5.36 5.33 Sc 23.5 24.3 22.1 25.3 25.6 Ta 0.55 0.63 0.46 0.66 0.61 V 247 271 268 277 276 Pb 12.6 12.9 12.5 15.1 14.3 Cr 18.5 9.96 6.97 11.4 10.7 Th 12.1 18 11.2 22 19.4 Co 27.6 28.7 27 28.8 29.3 U 2.38 4.33 2.28 4.81 4.2 Ni 11.2 8.64 6.87 8.63 8.36 ΣREE 228.42 303.06 194.39 336.60 334.98 Cu 58.6 192 14.1 160 105 LREE/HREE 18.42 19.24 16.31 19.38 19.19 Zn 122 103 103 104 109 (La/Yb)N 21.46 23.11 17.24 23.50 23.24 Ga 24 20.2 23.5 21.7 21.6 δEu 0.96 0.87 0.98 0.92 0.90 Ge 1.52 1.49 1.43 1.59 1.59 Zr/Ba 0.46 0.46 0.38 0.35 0.37 Rb 39.8 54.6 35.2 56.1 55.5 (Th/Ta)N 10.61 13.78 11.74 16.08 15.34 Sr 828 882 790 1166 1116 (La/Nb)N 4.24 5.74 3.94 6.08 6.38 Y 20.7 26.4 19.4 28.6 28.7 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6;Mg#=100×(MgO/40.304)/(MgO/40.304+2×Fe2O3/159.691+FeO/71.846); 里特曼指数δ=(K2O+Na2O)2/(SiO2-43); F1=0.0088(SiO2)-0.0774(TiO2)-0.0102(Al2O3)+0.0066(TFeO)-0.0017(MgO)-0.0143(CaO)-0.0155(Na2O)-0.0007(K2O); F2=-0.0130(SiO2)-0.0185(TiO2)-0.0129(Al2O3)-0.0134(TFeO)-0.0300(MgO)-0.0204(CaO)-0.0481(Na2O)+0.0715(K2O); δEu= EuN / $\sqrt {{\rm{S}}{{\rm{m}}_{\rm{N}}} * {\rm{G}}{{\rm{d}}_{\rm{N}}}} $ -
[1] Coulon C, Maluski H, Bollinger C, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic rocks from central and southern Xizang: 39Ar/40Ar dating, petrological characteristics and geodynamical significance[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(3/4): 281-302. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X8690186X
[2] Ding L, Kapp P, Zhong D L, et al. Cenozoic volcanismin Xizang: evidence for a transition from oceanic to continental subduction[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(10): 1833-1865. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egg061
[3] Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Xizang[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119(7/8): 917-932. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037062951610_8f69.html
[4] 马国林, 岳雅慧. 西藏拉萨地块北部白垩纪火山岩及其对冈底斯岛弧构造演化的制约[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(5): 525-538. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.05.008
[5] 崔浩杰, 苟正彬, 刘函, 等. 拉萨地块西段尼雄地区早白垩世晚期花岗闪长岩的成因及构造意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2019, 39(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.01.001
[6] 康志强, 许继峰, 董彦辉, 等. 拉萨地块中北部白垩纪则弄群火山岩: Slainajap洋南向俯冲的产物[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(2): 303-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200802012.htm
[7] 张彤, 黄波, 罗改, 等. 西藏中冈底斯带北部早白垩世构造属性: 来自则弄群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学的制约[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(2): 75-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202002008.htm
[8] 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏冈底斯带措勤地区则弄群火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学格架及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(3): 401-412. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200803001.htm
[9] 康志强, 许继峰, 王保弟, 等. 拉萨地块北部白垩纪多尼组火山岩的地球化学: 形成的构造环境[J]. 地球科学, 2009, 34(1): 89-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200901010.htm
[10] 高顺宝, 郑有业, 王进寿, 等. 西藏班戈地区侵入岩年代学和地球化学: 对班公湖-怒江洋盆演化时限的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7): 1973-1982. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107007.htm
[11] 黄瀚霄, 李光明, 董随亮, 等. 西藏班戈地区青龙花岗闪长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(6): 852-859. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.06.004 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120604&flag=1
[12] Qu X M, Wang R J, Xin H B, et al. Age and petrogenesis of A-type granites in the middle segment ofthe Bangonghu-Nujiang suture, Xizang plateau[J]. Lithos, 2012, 146/147: 264-275. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.006
[13] 张予杰, 刘伟, 朱同兴, 等. 西藏申扎县买巴地区早白垩世侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1): 50-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.004
[14] 隋清霖. 西藏拉萨地块盐湖地区早白垩世岩浆岩年代学、岩石成因及构造意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2014.
[15] Wu H, Li C, Xu M J, et al. Early Cretaceous adakitic magmatism in the Dachagou area, northern Lhasa terrane, Xizang: Implications for slab roll-back and subsequent slab breakoff of the lithosphere of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 51-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.014
[16] 齐宁远, 赵志丹, 唐演, 等. 西藏中拉萨地块西段左左乡晚侏罗世-早白垩世花岗岩年代学、地球化学与岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(2): 405-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201902009.htm
[17] 尹滔, 李威, 尹显科, 等. 西藏阿翁错地区早白垩世花岗闪长岩——班公湖-怒江洋壳南向俯冲消减证据[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5): 1105-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201905012.htm
[18] Zhu D C, Mo X X, Niu Y L, et al. Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa Terrane, Xizang[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(3/4): 298-312.
[19] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1/2): 241-255. http://community.dur.ac.uk/yaoling.niu/MyReprints-pdf/2010ZhuEtAl-EPSL.pdf
[20] 张亮亮, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏北冈底斯巴尔达地区岩浆作用的成因: 地球化学、年代学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(6): 1871-1886. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201006020.htm
[21] 张亮亮, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏申扎早白垩世花岗岩类: 板片断离的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7): 1938-1946. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107004.htm
[22] 张晓倩, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏措勤麦嘎岩基的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和锆石Hf同位素: 对中部拉萨地块早白垩世花岗岩类岩石成因的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5): 1615-1634. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205025.htm
[23] Chen Y, Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, et al. Slab breakoff triggered Ca. 113Ma mamgatism around Xainza area of the Lhasa Terrane, Xizang[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(2): 449-463. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.005
[24] Sui Q L, Wang Q, Zhu D C, et al. Compositional diversity of ca. 110 Ma magmatism in the northern Lhasa Terrane, Xizang: Implications for the magmatic origin and crustal growth in a continent-continent collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168/169: 145-159. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493713000273
[25] 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 521-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603001.htm
[26] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[27] Hu Z C, Zhang W, Liu Y S, et al. "Wave" signal-smoothing and mercury-removing device for laser ablation quadrupole and multiple collector ICPMS analysis: Application to lead isotope analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(2): 1152-1157. doi: 10.1021/ac503749k
[28] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm
[29] Wu Y B, Zheng Y F. Genesis of Zircon and Itsconstraints On Interpretation of U-Pb Age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15): 1554-1569. doi: 10.1007/BF03184122
[30] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
[31] 杨婧, 王金荣, 张族, 等. 全球多弧玄武岩数据挖据——在玄武岩判别图解上的表现及初步解释[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(12) 1937-1949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.12.001 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20161201&flag=1
[32] Ormerod D S, Hawkesworth C J, Rogers N W, et al. Tectonic and magmatic transitions in the western Great Basin, USA[J]. Nature, 1988, 333(6171): 349-353. doi: 10.1038/333349a0
[33] Zhou Z H, Mao J W, Peter L. Geochronology and isotopic geochemistry of the A-type granites from the Huanggang Sn-Fe deposit, southern Great Hinggan Range, NE China: Implication for their origin and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 49: 272-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.01.015
[34] 彭树华, 孙立新, 时学忠, 等. 冀北三面井岩体时代、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2013, 32(4): 694-706 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.04.006
[35] 杨岳衡, 张宏福, 谢烈文, 等. 华北克拉通中、新生代典型火山岩的岩石成因: Hf同位素新证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6): 1665-1671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200606023.htm
[36] Shi Y R, Liu D Y, Miao L C, et al. Devonian A-type granitic magmatism on the northern margin of the North China Craton: SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating and Hf-isotopes of the Hongshan granite at Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 17(4): 632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2009.11.011
[37] 第五春荣, 孙勇, 王倩. 华北克拉通地壳生长和演化: 来自现代河流碎屑锆石Hf同位素组成的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(11): 3520-3530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201211009.htm
[38] 杨浩田, 杨德彬, 师江朋, 等. 鲁西早白垩世岩石圈地幔的属性: 大昆仑辉长岩和辉绿岩年代学、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(11): 3327-3340 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201811016.htm
[39] 岳维好, 周家喜. 青海都兰县阿斯哈石英闪长岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄与Hf同位素特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(2/3): 328-338. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2019020314&flag=1
[40] 许强伟, 王玭, 王志强, 等. 内蒙古克什克腾旗长岭子斜长花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄、成因与碰撞造山作用[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(1): 229-246. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202101017.htm
[41] 梁国科, 吴祥珂, 蔡逸涛, 等. 桂北罗城地区云煌岩成因——地球化学及U-Pb年龄约束[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(2/3): 267-278. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2020020310&flag=1
[42] Neal C R, Mahoney J J, Chazey W J. Mantle sources and the highly variable role of continental lithosphere in basalt petrogenisis of the Kerguelen Plateau and Broken Ridge LIP: Results from ODP leg 183[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2002, 43(7): 1177-1205 doi: 10.1093/petrology/43.7.1177
[43] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等. 青藏高原中部中生代OIB型玄武岩的识别: 年代学、地球化学及其构造环境[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(9): 1312-1328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.008
[44] Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry(Second Edition). Oxford: Elsevier, 2014, 4: 1-51.
[45] Zhao J H, Zhou M F. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district(Sichuan Province, SW China): implications for subduction-related metasomatism in the upper mantle[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 152(1): 27-47. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030192680600218X
[46] 杨崇辉, 杜利林, 任留东, 等. 中条山铜矿峪变质火山岩的时代、构造背景及对成矿的制约[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(5): 613-633. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201505012.htm
[47] Kessel R, Schmidt M W, Ulmer P, et al. Trace element signature of subduction-zone fluids, melts and supercritical liquids at 120-180 km depth[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(29): 724-727. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Peter_Ulmer/publication/7571924_Kessel_R._Schmidt_M._Ulmer_P.__Pettke_T._Trace_element_signature_of_subduction-zone_fluids_melts_and_supercritical_liquids_at_120-180_km_depth._Nature_437_724-727/links/0deec5278d40d6bdc5000000.pdf
[48] Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lave from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Thorpe R S. Orogenic andesites and related rocks. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 1982: 528-548.
[49] 杨逸云, 赵志丹, 雷杭山, 等. 云南腾冲全新世火山岩岩浆演化和岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(2): 472-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201902013.htm
[50] Yu Y, Huang X L, Sun M, et al. Missing Sr-Nd isotopic decoupling in subduction zone: Decoding the multi-stage dehydration and melting of subducted slab in the Chinese Altai[J]. Lithos, 2020, 362/363, 105465: 1-14.
[51] Woodhead J D, Hergt J M, Davidson J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for conservative element mobility during subduction zone process[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 192(3): 331-346. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00453-8
[52] Kohut E J, Stern R J, Kent A R L, et al. Evidence for adiabatic decompression melting in the Southern Mariana Arc from high-Mg lavas and melt inclusions[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 152(2): 201-221. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0102-7
[53] Li W C, Ni H W. Dehydration at subduction zones and the geochemistry of slab fluids[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2020, 63(12): 1925-1937. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9655-1
[54] Xiong X L, Liu X C, Li L, et al. The partitioning behavior of trace elements in subduction zones: Advances and prospects[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2020, 63(12): 1938-1951. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9631-6
[55] 邱检生, 胡建, 蒋少涌, 等. 鲁西中、新生代镁铁质岩浆作用与地幔化学演化[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(6): 646-658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200506001.htm
[56] 徐向珍, 熊发挥, 杨经绥, 等. 冈底斯中段卡热辉长岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(10): 2542-2555. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.10.011
[57] Frey F A, Green D H, Roy S D. Integrated models of basalt petrogenesis: A study of quartz tholeiites to olivine melilitites from southeastern Australia utilizing geochemical and experimental petrological data[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1978, 19(3): 463-513. doi: 10.1093/petrology/19.3.463
[58] Hess P C. Phase equilibria constraints on the origin of ocean floor basalts[C]//Morgan J P, Blackman D K, Sinton J M. Mantle Flow and Melt Generation at Mid-Ocean Ridges. 1992, 71: 67-102.
[59] 李永军, 沈锐, 王冉, 等. 新疆西准噶尔巴尔努克早石炭世富Nb岛弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(12): 3501-3511. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201412002.htm
[60] 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等. 利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1): 77-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2007.01.011
[61] Pearce J A. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins[C]//Hawkesworth C J, Norry M J. Continental basalts and mantle xenoliths. Nantwich, Cheshire: Shiva Publications, 1983: 230-249.
[62] Pearce J A. Statistical analysis of major element patterns in basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1976, 17(1): 15-43. doi: 10.1093/petrology/17.1.15
[63] Meschede M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56(3/4): 207-218. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035296655110_4aed.html
[64] 汪云亮, 张成江, 修淑芝. 玄武岩类形成的大地构造环境的Th/Hf-Ta/Hf图解判别[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(3): 413-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200103008.htm
[65] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Xizang Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 23(4): 1429-1454. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yildirim_Dilek/publication/257518261_The_origin_and_pre-Cenozoic_evolution_of_the_Tibetan_Plateau._Gondwana_Res/links/02e7e5283ff902333b000000.pdf
[66] Zhu D C, Li S M, Cawood P A, et al. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang Terranes in Central Xizang by divergent double subduction[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245: 7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023
[67] Ferrari L. Slab detachment control on mafic volcanic pulse and mantle heterogeneity in Central Mexico[J]. Geology, 2004, 32(1): 77-80. doi: 10.1130/G19887.1
[68] Duretz T, Gerya T V, May D A. Numerical modelling of spontaneous slab breakoff and subsequent topographic response[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 502(1/2): 244-256. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Thibault_Duretz/publication/229366368_Numerical_modeling_of_spontaneous_slab_breakoff_and_subsequent_topographic_response/links/5671a3af08ae3aa2fcedaa8b/Numerical-modeling-of-spontaneous-slab-breakoff-and-subsequent-topographic-response.pdf
[69] 于枫. 西藏冈底斯盐湖南部花岗岩的岩石学、地球化学与成因[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2010: 1-68.
[70] 于玉帅, 高原, 杨竹森, 等. 西藏措勤尼雄矿田滚纠铁矿侵入岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7): 1949-1960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107005.htm
[71] 曲晓明, 辛洪波, 杜德道, 等. 西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带中段碰撞后A型花岗岩的时代及其对洋盆时间的约束[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(1): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201201002.htm
[72] 苟正彬, 刘函, 李俊, 等. 拉萨地块中北部尼雄地区早白垩世火山岩的成因及构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8): 2780-2794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808019.htm
-



 下载:
下载: