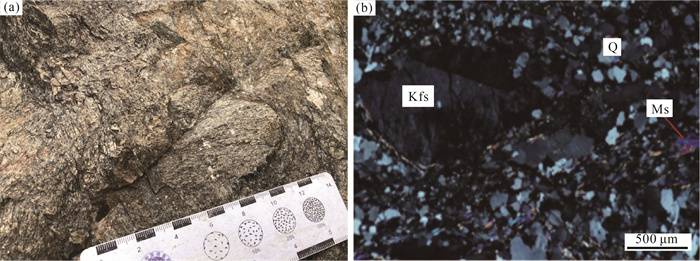
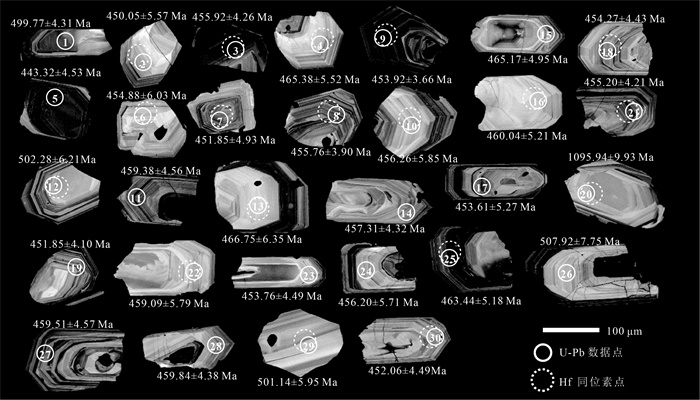
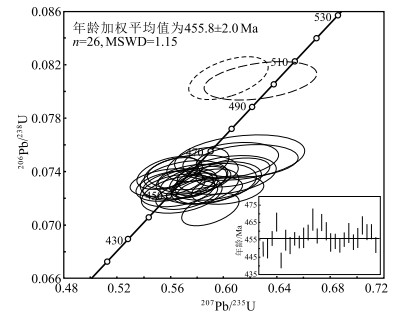
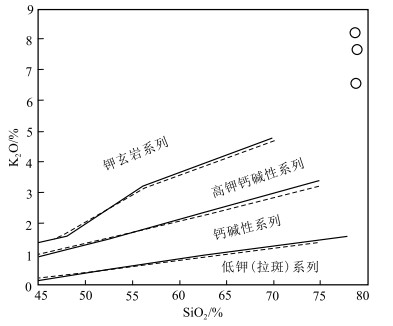
Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of Early Paleozoic granite from the Jitang area in eastern Xizang and its insight into the evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean
-
摘要:
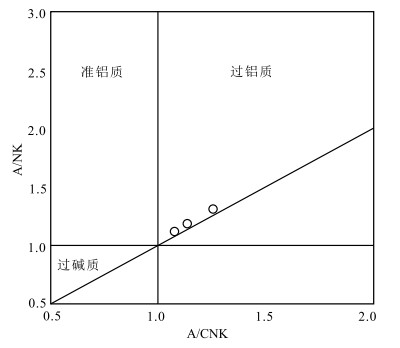
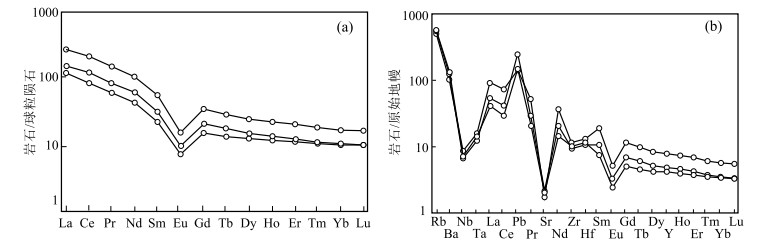
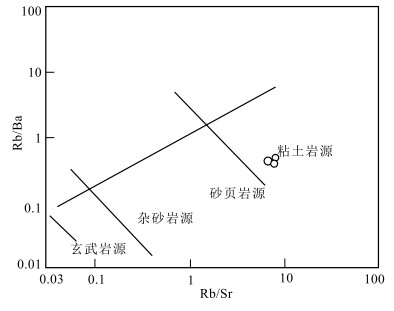
以前对藏东吉塘地区的早古生代岩浆事件鲜有报道,在吉塘地区的浪拉山新发现了中—晚奥陶世花岗岩。采用LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得该花岗岩的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为455±2.0 Ma(WSWD=1.15,n=26),属于中—晚奥陶世。岩石地球化学特征表明,该花岗岩具有高SiO2(78.72%~79.48%)、富钾(K2O/Na2O=5.55~10.20),低MgO(0.10%~0.25%)的特征,铝饱和指数A/CNK为1.08~1.26,岩石属于高钾钙碱性强过铝S型花岗岩。岩石稀土元素总体表现为轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的特征,具强烈负Eu异常,δEu值为0.35~0.39;在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图上,明显富集Rb、Th、Nd、Pb等元素,亏损Ba、Nb、Sr、P、Ti等元素。结合区域地质资料分析,该岩体是由原特提斯洋俯冲消减引起古老地壳物质部分熔融形成的,是原特提斯洋俯冲消减的岩浆事件响应;说明在中—晚奥陶世吉塘地区存在原特提斯洋的俯冲消减作用。
Abstract:There is little report on the Early Paleozoic magmatic events in the Jitang area, eastern Xizang.The Middle-Late Ordovician granites have been discovered in Langla Mountain, Jitang.The weighted average U-Pb age of the granite is 455±2.0 Ma(WSWD=1.15, n=26) by the LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of the zircon, indicating that it was emplaced in Middle-Late Ordovician.The geochemical characteristics indicate that the granite has high SiO2(78.72%~79.48%), high potassium(K2O/Na2O=5.55~10.20), low MgO(0.10%~0.25%), with aluminum supersaturated index A/CNK values ranging from 1.08 to 1.26, and the rock is a high-potassium-calcium- alkali-strong over aluminum S-type granite.The REE contents of rocks are enriched in LREE and depleted in HREE, with a negative Eu anomaly and δEu values ranging from 0.35 to 0.39.They are also enriched in LILEs (Rb, Th, Nd and Pb), but depleted in HFSEs (Ba, Nb, Sr, P and Ti).Combined with regional geological data, it is suggested that the granites might have originated from partial melting of ancient crustal materials, caused by the subduction of the Proto-Tethys, and is the response of the magmatic events during subduction of the Proto-Tethys.
-
Key words:
- Proto-Tethys Ocean /
- Langla Mountain granite /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- Hf isotope /
- geochemistry /
- eastern Xizang
-

-
表 1 花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of granite
点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U Pb Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ YX-5GS-01 91.4 292.3 696.1 0.42 0.0577 0.0016 0.5724 0.0154 0.0723 0.0007 516.71 67.58 459.59 9.95 449.77 4.31 YX-5GS-02 91.5 358.1 485.4 0.74 0.0572 0.0020 0.5685 0.0201 0.0723 0.0009 501.89 71.29 457.05 13.04 450.05 5.57 YX-5GS-03 429.9 1531.3 2785.1 0.55 0.0573 0.0012 0.5827 0.0126 0.0733 0.0007 505.60 46.29 466.19 8.08 455.92 4.26 YX-5GS-04 120.5 506.9 572.6 0.89 0.0587 0.0023 0.6050 0.0236 0.0749 0.0009 553.74 87.02 480.43 14.93 465.38 5.52 YX-5GS-05 440.9 1665.2 2868.6 0.58 0.0599 0.0015 0.5898 0.0144 0.0712 0.0008 598.17 53.69 470.72 9.19 443.32 4.53 YX-5GS-06 89.4 397.6 418.2 0.95 0.0584 0.0024 0.5882 0.0239 0.0731 0.0010 542.63 90.73 469.69 15.30 454.88 6.03 YX-5GS-07 183.8 812.4 967.9 0.84 0.0560 0.0018 0.5654 0.0183 0.0726 0.0008 453.75 67.59 455.01 11.90 451.85 4.93 YX-5GS-08 198.9 849.2 1174.7 0.72 0.0563 0.0016 0.5718 0.0151 0.0733 0.0006 464.86 28.70 459.20 9.73 455.76 3.90 YX-5GS-09 464.6 1813.1 2925.8 0.62 0.0569 0.0011 0.5779 0.0119 0.0730 0.0006 487.08 44.44 463.10 7.69 453.92 3.66 YX-5GS-10 81.9 324.9 451.9 0.72 0.0567 0.0023 0.5711 0.0223 0.0733 0.0010 483.38 90.73 458.69 14.42 456.26 5.85 YX-5GS-11 271.3 1176.2 1472.2 0.80 0.0547 0.0013 0.5607 0.0134 0.0739 0.0008 466.71 53.70 451.98 8.71 459.38 4.56 YX-5GS-13 41.7 140.8 228.0 0.62 0.0600 0.0034 0.6127 0.0322 0.0751 0.0011 605.58 120.36 485.25 20.30 466.75 6.35 YX-5GS-14 133.1 539.6 740.7 0.73 0.0568 0.0018 0.5781 0.0180 0.0735 0.0007 483.38 68.51 463.22 11.56 457.31 4.32 YX-5GS-15 118.1 518.7 594.8 0.87 0.0603 0.0027 0.6175 0.0251 0.0748 0.0008 612.98 96.28 488.25 15.74 465.17 4.95 YX-5GS-16 77.0 305.1 412.4 0.74 0.0565 0.0022 0.5769 0.0225 0.0740 0.0009 477.82 85.18 462.48 14.49 460.04 5.21 YX-5GS-17 215.2 985.1 1094.0 0.90 0.0586 0.0017 0.5863 0.0165 0.0729 0.0009 553.74 56.47 468.47 10.56 453.61 5.27 YX-5GS-18 155.1 640.1 894.0 0.72 0.0561 0.0017 0.5658 0.0176 0.0730 0.0007 453.75 66.66 455.31 11.42 454.27 4.43 YX-5GS-19 211.7 883.3 1119.1 0.79 0.0589 0.0016 0.5894 0.0165 0.0726 0.0007 564.85 65.73 470.48 10.56 451.85 4.10 YX-5GS-21 172.2 711.9 970.2 0.73 0.0550 0.0017 0.5568 0.0178 0.0732 0.0007 409.31 68.51 449.44 11.63 455.20 4.21 YX-5GS-22 74.2 272.2 400.0 0.68 0.0595 0.0024 0.6022 0.0246 0.0738 0.0010 587.07 88.88 478.60 15.60 459.09 5.79 YX-5GS-23 129.3 456.4 840.4 0.54 0.0554 0.0017 0.5600 0.0168 0.0729 0.0007 431.53 66.66 451.55 10.96 453.76 4.49 YX-5GS-24 90.8 364.1 486.5 0.75 0.0586 0.0023 0.5941 0.0230 0.0733 0.0009 553.74 78.69 473.48 14.67 456.20 5.71 YX-5GS-25 353.2 1342.4 2168.1 0.62 0.0562 0.0015 0.5800 0.0154 0.0745 0.0009 461.16 59.25 464.48 9.88 463.44 5.18 YX-5GS-27 200.2 789.9 1231.5 0.64 0.0547 0.0016 0.5599 0.0165 0.0739 0.0008 466.71 60.18 451.48 10.72 459.51 4.57 YX-5GS-28 148.7 662.8 791.7 0.84 0.0593 0.0018 0.6068 0.0183 0.0739 0.0007 575.96 66.66 481.52 11.54 459.84 4.38 YX-5GS-30 138.6 633.6 719.9 0.88 0.0600 0.0018 0.6029 0.0177 0.0726 0.0007 605.58 97.21 479.08 11.24 452.06 4.49 表 2 花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析数据
Table 2. Zircon Lu-Hf isotope data of granite
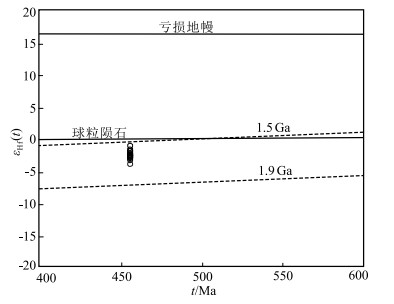
测试点 年龄/Ma 176Hf/177Hf 1σ 176Lu/177Hf 1σ 176Yb/177Hf 1σ εHf(t) 1σ TDM1/Ma TDM2/Ma fLu/Hf YX2018-5GS-02 456 0.282460 0.000017 0.002453 0.000085 0.088962 0.002450 -1.8 0.8 1165 1407 -0.93 YX2018-5GS-03 456 0.282436 0.000008 0.002236 0.000010 0.084752 0.000672 -2.5 0.6 1193 1450 -0.93 YX2018-5GS-04 456 0.282471 0.000009 0.001853 0.000041 0.068869 0.001328 -1.2 0.6 1129 1374 -0.94 YX2018-5GS-06 456 0.282441 0.000011 0.002102 0.000041 0.075693 0.000840 -2.3 0.7 1181 1437 -0.94 YX2018-5GS-07 456 0.282450 0.000011 0.002148 0.000039 0.086728 0.002714 -2.0 0.7 1170 1421 -0.94 YX2018-5GS-08 456 0.282418 0.000009 0.001261 0.000004 0.047822 0.000273 -2.9 0.6 1187 1469 -0.96 YX2018-5GS-09 456 0.282424 0.000008 0.001815 0.000003 0.069138 0.000197 -2.8 0.6 1196 1466 -0.95 YX2018-5GS-10 456 0.282415 0.000010 0.000868 0.000001 0.032192 0.000120 -2.8 0.6 1178 1467 -0.97 YX2018-5GS-12 456 0.282432 0.000010 0.002054 0.000044 0.078081 0.001551 -2.6 0.7 1192 1453 -0.94 YX2018-5GS-13 456 0.282421 0.000011 0.000552 0.000006 0.020079 0.000154 -2.5 0.7 1160 1450 -0.98 YX2018-5GS-16 456 0.282438 0.000008 0.000727 0.000007 0.027462 0.000379 -2.0 0.6 1142 1420 -0.98 YX2018-5GS-18 456 0.282432 0.000008 0.001011 0.000002 0.038956 0.000094 -2.3 0.6 1159 1437 -0.97 YX2018-5GS-21 456 0.282412 0.000009 0.001064 0.000006 0.041036 0.000369 -3.0 0.6 1190 1477 -0.97 YX2018-5GS-22 456 0.282421 0.000010 0.000784 0.000002 0.029737 0.000081 -2.6 0.6 1168 1455 -0.98 YX2018-5GS-25 456 0.282408 0.000009 0.001762 0.000012 0.069045 0.000549 -3.4 0.6 1218 1497 -0.95 YX2018-5GS-29 456 0.282406 0.000008 0.000563 0.000007 0.021216 0.000229 -3.1 0.6 1182 1480 -0.98 YX2018-5GS-30 456 0.282383 0.000011 0.000992 0.000002 0.038857 0.000093 -4.0 0.7 1227 1532 -0.97 表 3 花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 3. Major, trace elements and REE analytical resultes of granite
样品编号 YX-5H1 YX-5H2 YX-5H3 样品编号 YX-5H1 YX-5H2 YX-5H3 SiO2 78.33 78.72 79.48 Ag 0.14 0.17 0.14 Al2O3 11.86 11.43 11.37 Cd 0.67 0.07 0.07 Fe2O3 0.76 0.34 0.21 In 0.04 0.02 0.01 MgO 0.25 0.13 0.10 Sn 2.85 2.16 1.69 CaO 0.20 0.17 0.16 Sb 0.30 0.36 0.35 Na2O 1.18 0.81 0.90 Cs 2.62 1.83 1.98 K2O 6.55 8.27 7.56 Ba 691.00 911.00 852.00 MnO 0.01 0.01 0.01 La 63.2 27.8 36.4 P2O5 0.04 0.04 0.04 Ce 128.00 51.3 73.1 TiO2 0.30 0.26 0.23 Pr 13.9 5.62 7.95 烧失量 1.10 0.75 0.82 Nd 48.5 19.6 27.7 总计 100.58 100.93 100.87 Sm 8.35 3.33 4.72 Na2O+K2O 7.77 9.06 8.46 Eu 0.87 0.41 0.55 A/CNK 1.26 1.08 1.14 Gd 6.91 3.03 4.14 K2O/Na2O 5.55 10.21 8.40 Tb 1.05 0.49 0.65 Li 2.31 1.10 1.30 Dy 6.02 3.09 3.79 Be 1.20 0.75 0.62 Ho 1.21 0.65 0.76 Sc 5.32 4.25 3.62 Er 3.31 1.82 2.04 V 11.0 8.61 8.20 Tm 0.45 0.26 0.28 Cr 2.13 3.93 3.61 Yb 2.80 1.67 1.74 Co 0.54 0.60 0.84 Lu 0.41 0.25 0.25 Ni 1.48 2.35 3.41 Hf 4.02 3.51 3.28 Cu 1.24 1.60 1.80 Ta 0.65 0.58 0.50 Zn 66.1 10.5 10.3 W 1.68 2.36 0.78 Ga 14.0 10.5 10.1 Tl 0.72 0.93 0.93 Ge 1.16 0.84 0.81 Pb 9.97 10.3 17.4 As 0.94 1.58 2.68 Bi 0.04 0.04 0.13 Rb 309.00 352.00 339.00 Th 20.8 15.6 13.8 Sr 36.5 43.5 46.6 U 1.74 1.37 1.36 Y 35.7 19.2 21.9 ΣREE 284.98 119.31 164.06 Zr 127.00 112.00 104.00 LREE 262.82 108.06 150.42 Nb 6.12 5.09 4.77 HREE 22.16 11.25 13.64 Mo 0.26 0.19 0.26 LREE/HREE 11.86 9.60 11.03 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6;A/CNK=摩尔Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O);δEu=EuN/[1/2(SmN+GdN)];(La/Yb)N=LaN/YbN;(Gd/Yb)N=GdN/YbN -
[1] 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 尹福光, 等. 中国大地构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 1-617.
[2] 彭智敏, 耿全如, 王立全, 等. 青藏高原羌塘中部本松错花岗质片麻岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59: 2621-2629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201426014.htm
[3] 胡培远, 李才, 苏犁, 等. 青藏高原羌塘中部蜈蚣山花岗片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年——泛非与印支事件的年代学记录[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4): 1050-1061. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.019
[4] 彭智敏, 张辑, 关俊雷, 等. 滇西"三江"地区临沧花岗岩基早-中奥陶世花岗质片麻岩的发现及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8): 2571-2585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808003.htm
[5] 王冬兵, 罗亮, 唐渊, 等. 昌宁-孟连结合带牛井山早古生代埃达克岩锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(8): 2317-2329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608006.htm
[6] 李才. 龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带与石炭二叠纪冈瓦纳北界[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1987, 17(2): 155-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ198702003.htm
[7] 李才. 青藏高原龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(1): 105-119 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.012
[8] 杜斌, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 等. 锆石Hf和全岩Nd同位素填图研究进展: 以三江特提斯造山带为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(8): 2555-2570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608022.htm
[9] Deng J, Wang C M, Zi J W, et al. Constraining subduction-collision processes of the Paleo-Tethys along the Changning-Menglian Suture: New zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf oisotopes of the Lincang Batholith[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 62: 75-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.10.008
[10] 潘桂棠, 陈智梁, 李兴振, 等. 东特提斯地质构造形成演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 1-198.
[11] Pan G T, Xu Q, Wang L Q, et al. The frame mechanism of multiple island arc basin system in Xizang plaieau[J]. Mineral Petrol, 2001, 9: 186-189. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200103028.htm
[12] Pan G T, Wang L Q, Yin F G, et al. Charm of langding of plate tectonics on the continent as viewed from the study of the archipelagic arc-basic system[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23: 9-10. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zgqydz200409016
[13] 李才, 谢尧武, 沙绍礼, 等. 藏东八宿地区泛非期花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(1): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.01.005 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080105&flag=1
[14] 樊炳良, 王新然, 白涛, 等. 西藏卡贡地区晚寒武世错多勤石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(4): 471-479. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200406&flag=1
[15] 康朝龙, 代克刚, 李海波, 等. 西藏八宿吉利地区发现寒武纪变质花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2019, 39(2): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.02.001
[16] 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48: 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2002S1006.htm
[17] Middlemost E A K. Naming Materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035302893810_0b9a.html
[18] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and Refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[19] Ludwig K R. Users manual for Isoplot 3.00. a Geochronological toolkit for microsoft excel[J]. California: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003, 35: 1-39. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303107803_User's_manual_for_Isoplot_36_A_geochronological_toolkit_for_microsoft_excel_Berkeley_Geochronology_Center
[20] Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations if zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Reserch, 2004, 28(3): 353-370. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
[21] 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010
[22] Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Gao S, et al. Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmercone and jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogenby laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27(9): 1391-1399. doi: 10.1039/c2ja30078h
[23] Fisher C M, Vervoort J D, Hanchar J M. Guidelines for reporting zircon Hf isotopic data by LA-MC-ICPMS and potential pitfalls in the interpretation of these data[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 363(1): 125-133. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Christopher_Fisher4/publication/259085842_Guidelines_for_reporting_zircon_Hf_isotopic_data_by_LA-MC-ICPMS_and_potential_pitfalls_in_the_interpretation_of_these_data._Chem_Geol/links/550b3ed60cf290bdc111dee1.pdf
[24] Blichert-Toft J, Albarède F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1/2): 243-258.
[25] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/oup/petroj/2010/00000051/F0020001/art00023
[26] Soderlund U, Patchett P J, Vervoort J D et al. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219(3/4): 311-324. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X04000123
[27] Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al. The Hf isotope composition ofcratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1): 133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
[28] Simon L H, Nigel M K. Zircon tiny but timely[J]. Elements, 2007, (1): 13-18. http://qe3gw7ge4p.search.serialssolutions.com/?ctx_ver=Z39.88-2004&ctx_enc=info%3Aofi%2Fenc%3AUTF-8&rfr_id=info:sid/xueshu.baidu.com&rft_val_fmt=info:ofi/fmt:kev:mtx:journal&rft.genre=article&rft.atitle=Zircon%20Tiny%20but%20Timely&rft.jtitle=Elements
[29] 吴荣新. 锆石阴极发光和U-Pb年龄特征研究[J]. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 28(4): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2008.04.001
[30] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm
[31] Vervoort J D, Pachelt P J, Gehrels G E, et al. Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996, (379): 624-627. http://www.nature.com/articles/379624a0.pdf
[32] Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N. Early-middle Archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J]. Geochimical et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, (64): 4205-4225. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Alex_Halliday2/publication/222888843_Amelin_Y_Lee_D-C_Halliday_A_N_Early-middle_Archaean_crustal_evolution_deduced_from_Lu-Hf_and_U-Pb_isotopic_studies_of_single_zircon_grains_Geochim_Cosmochim_Acta_64_4205-4225/links/0c96052d64af58a9c0000000.pdf
[33] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implication for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunder A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Special Publication, 1989, 2: 313-345.
[34] Alther R, Holl A, Hegner E. High-potassium, calc-alkaline plutonism in the European Variscides: northern Vosges(France) and northern Schwarzwald(Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50: 51-73. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00052-3
[35] Zhou X M, Li W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in South eastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 326(3/4): 269-287. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001207
[36] 孙载波, 胡绍斌, 周坤, 等. 滇西南勐海布朗山奥陶纪花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(11): 2044-2054. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20181110&flag=1
[37] Sylvester P J. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, (45): 29-44. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paul_Sylvester/publication/223458063_Post-collisional_strongly_peraluminous_granites._Lithos/links/00b7d51c4ff86b1f39000000.pdf
[38] Vielzeuf D, Montel J M. Partial melting of metagreywackes. PartⅠ: Fluid-absent experiments and phase relationships[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 117: 375-393. doi: 10.1007/BF00307272
[39] Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S W, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ anaysis of Hf Isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3/4): 237-269. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493702000828
[40] Peter D K, Roland M. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope system in zircon[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 327-341. doi: 10.2113/0530327
[41] Ferry J M, Watson E B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-Zircon and Zr-in-Rutile the rmometers[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 154(4): 429-437. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0
[42] Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2): 295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
[43] King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and Origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3): 371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
[44] 潘桂棠, 王立全, 李荣社, 等. 多岛弧盆系构造模式: 认识大陆地质的关键[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(3): 1-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2012.03.001
[45] 王立全, 潘桂棠, 李才, 等. 藏北羌塘中部果干加年山早古生代堆晶辉长岩的锆石SHRIM P U-Pb年龄——兼论原-古特提斯洋的演化[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(12): 2045-2056. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.12.010 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20081210&flag=1
[46] 王保弟, 王立全, 潘桂棠, 等. 昌宁-孟连结合带南汀河早古生代辉长岩锆石年代学及地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(4): 344-354. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201304009.htm
[47] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa terrane, southern Xizang: record of an early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc in the Australian proto-Tethy an margin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328: 290-308. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.12.024
[48] 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 牛耀龄, 等. 拉萨地体的起源和古生代构造演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2012, 18(1): 1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.001
[49] 李再会, 林仕良, 丛峰, 等. 滇西高黎贡山群变质岩的锆石年龄及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5): 1529-1541. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205017.htm
[50] 刘琦胜, 叶培盛, 吴中海. 滇西高黎贡山南段奥陶纪花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(Z1): 250-257. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2012020306&flag=1
[51] 王晓先, 张进江, 杨雄英, 等. 藏南吉隆地区早古生代大喜马拉雅片麻岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(2): 127-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201102014.htm
[52] 宋述光, 季建清, 魏春景, 等. 滇西北怒江早古生代片麻状花岗岩的确定及其构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(8): 927-930. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.08.013
[53] 陆松年. 初论"泛华夏造山作用"与加里东和泛非造山作用的对比[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10): 952-958. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200409169&flag=1
[54] Cawood P A, Buchan C. Linking accretionary orogenesis with supercontinent assembly[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2007, 82: 217-256. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.03.003
[55] 刘强, 邓玉彪, 向树元, 等. 藏南仲巴地体早奥陶世构造-热事件及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(6): 881-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201706003.htm
[56] 刘桂春, 孙载波, 曾文涛, 等. 滇西双江县勐库地区湾河蛇绿混杂岩的形成时代、岩石地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(2): 163-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.02.003
[57] Nie X M, Fen g Q L, Qian X, et al. Magmatic record of Proto-tethyan evolution in SW Yunnan, China: Geochemieal, zircon U-Pb geochrono1ogica1 and Lu- Hf isotopic evidence from the Huim in metavolcanic rocks in the Southern Laneangjiang Zone[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(2): 757-768. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.05.011
[58] Xing X W, Zhang Y Z, Wang Y J, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of the Ordovician granitic gneisses in Ximeng area, West Yunnan Province[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 2015, 39(3): 470-480. http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DGYK201503011&dbcode=CJFD&year=2015&dflag=pdfdown
[59] 韩文文, 彭智敏, 张辑, 等. 滇西澜沧群纳长浅粒岩锆石U-Pb测年、Hf同位素组成及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(4): 1282-1294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.04.017
[60] 胡金锋, 彭智敏, 付于真, 等. 滇西早古生代增生杂岩中钠长片岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学及Hf同位素研究[J]. 中国地质, 2020. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200724.1727.008.html.
[61] Pullen A, Kapp P, Gehrels G E, et al. Metamorphic rocks in central Xizang: Lateral variations and implications for crustal structure[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 2011, 123: 585-600. doi: 10.1130/B30154.1
-



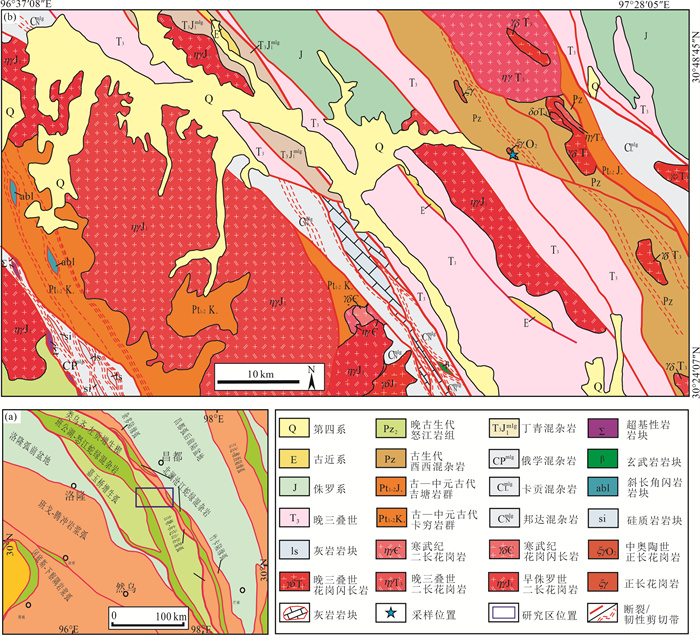
 下载:
下载: