Geomorphology of channel sandbodies in fluvially dominated shallow water delta front: taking the Lower Member of the Minghuazhen Formation in BZ34 Oilfield of the Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin as an example
-
摘要:
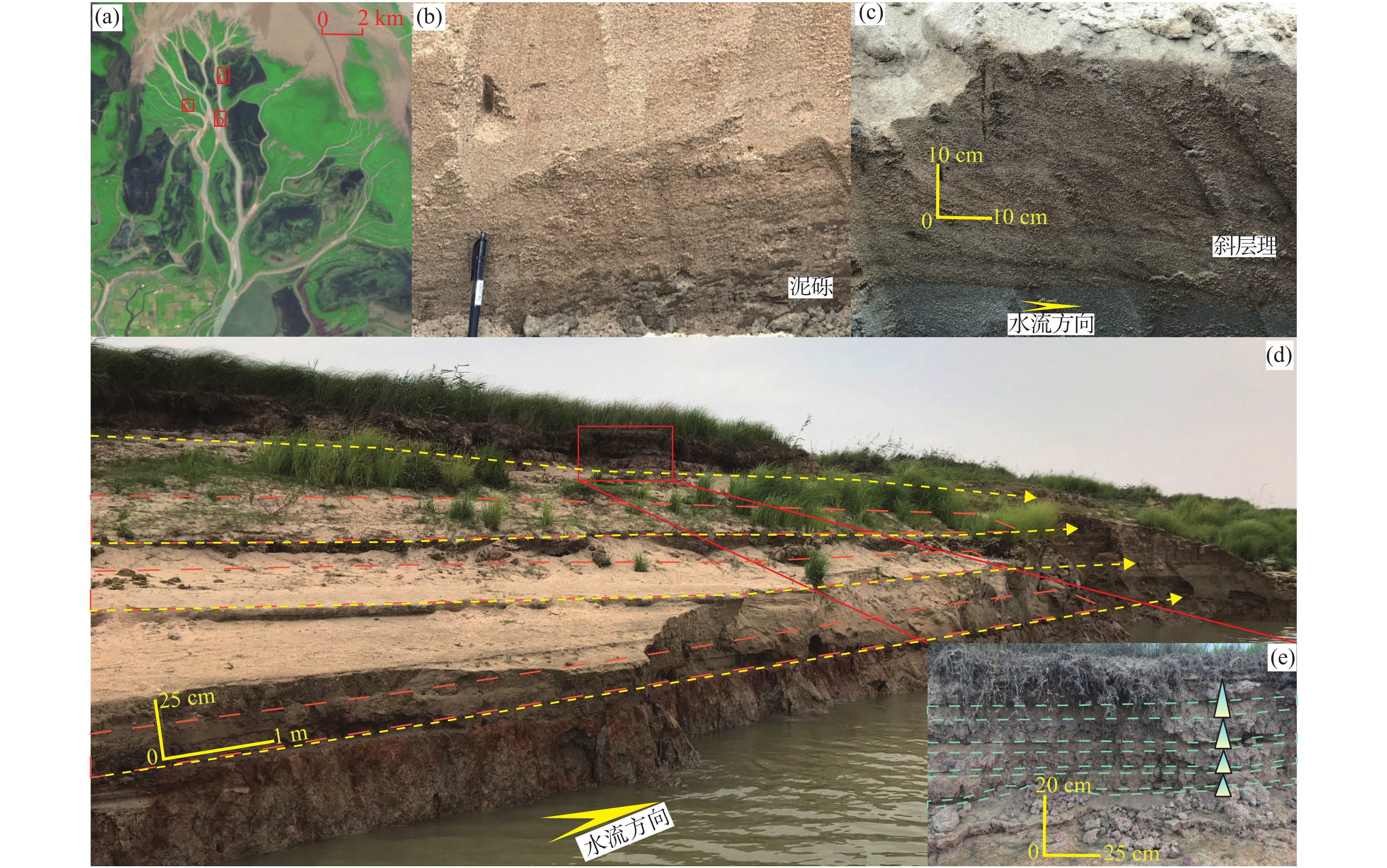
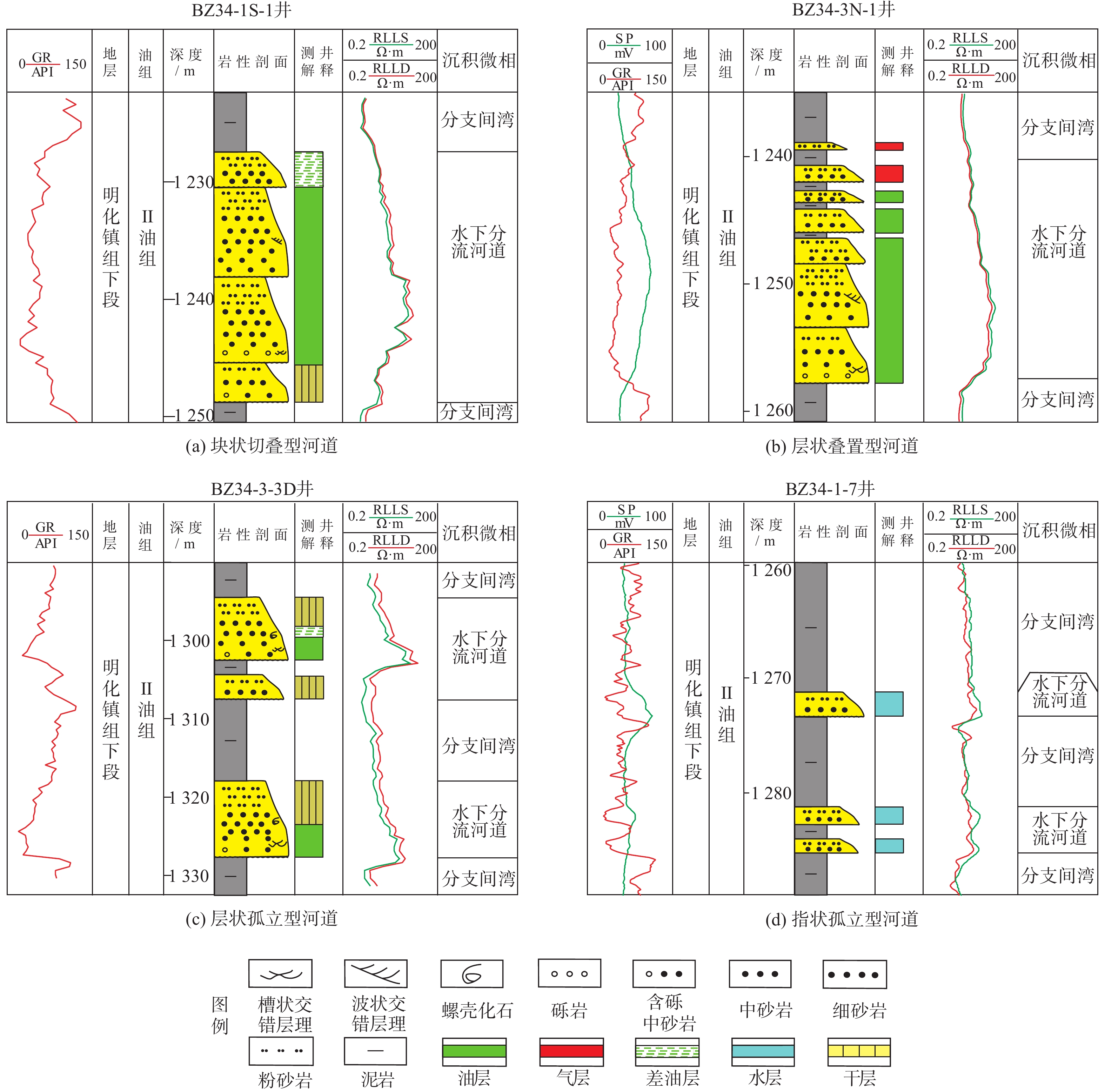
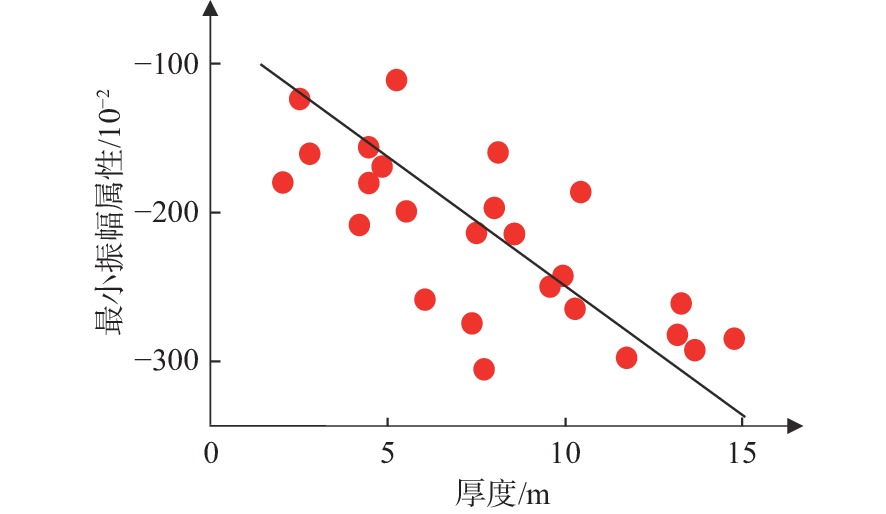
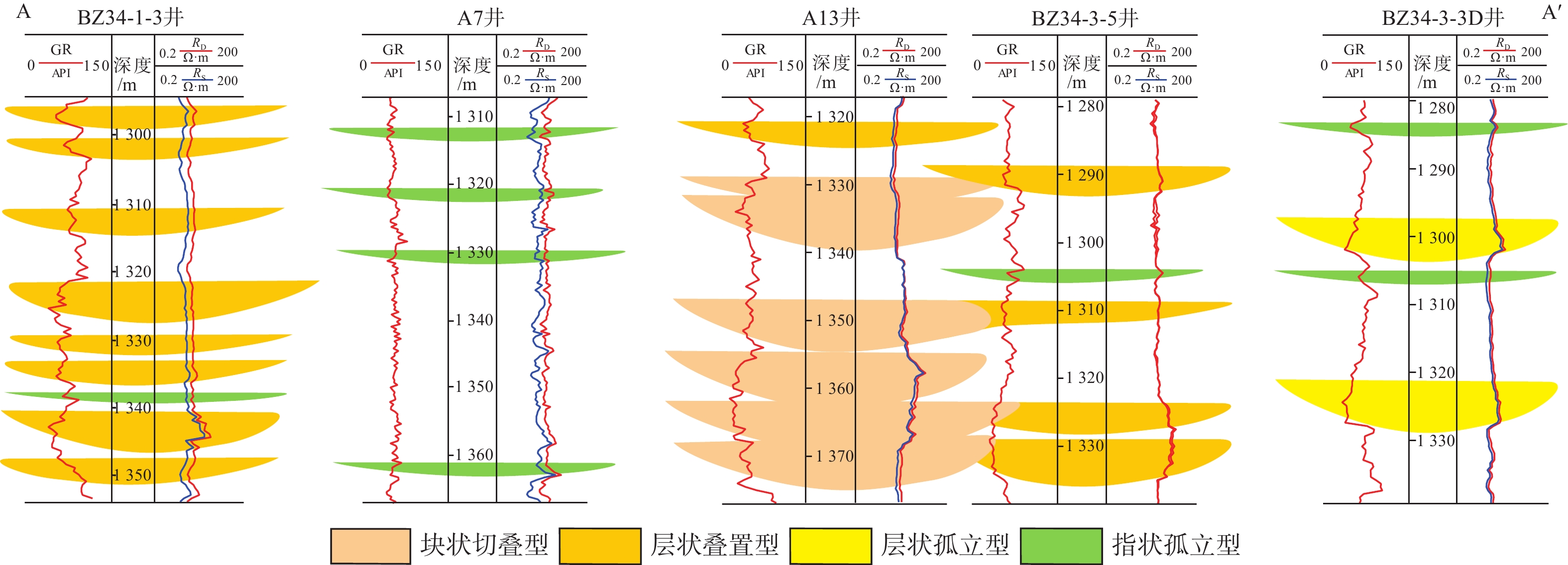
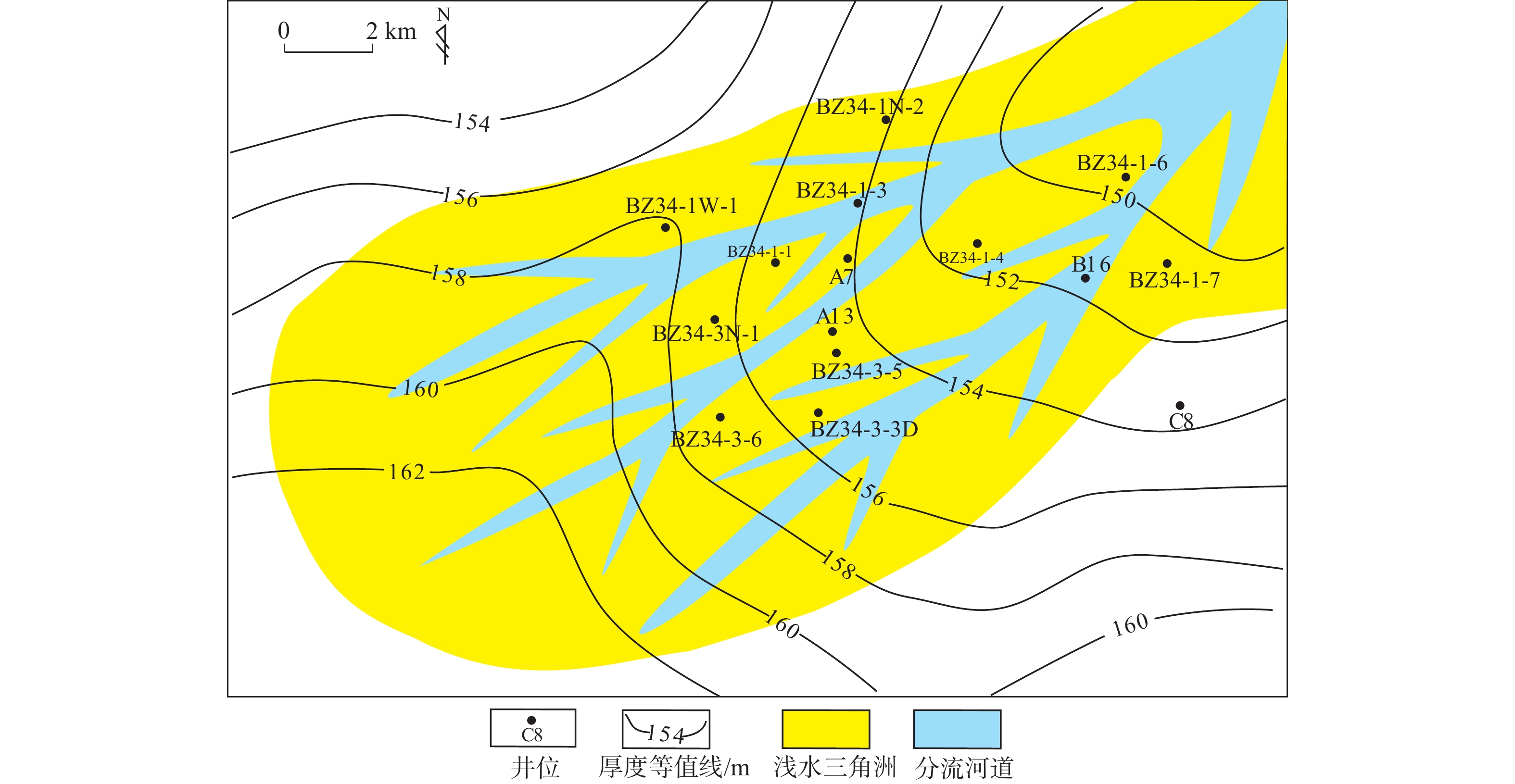
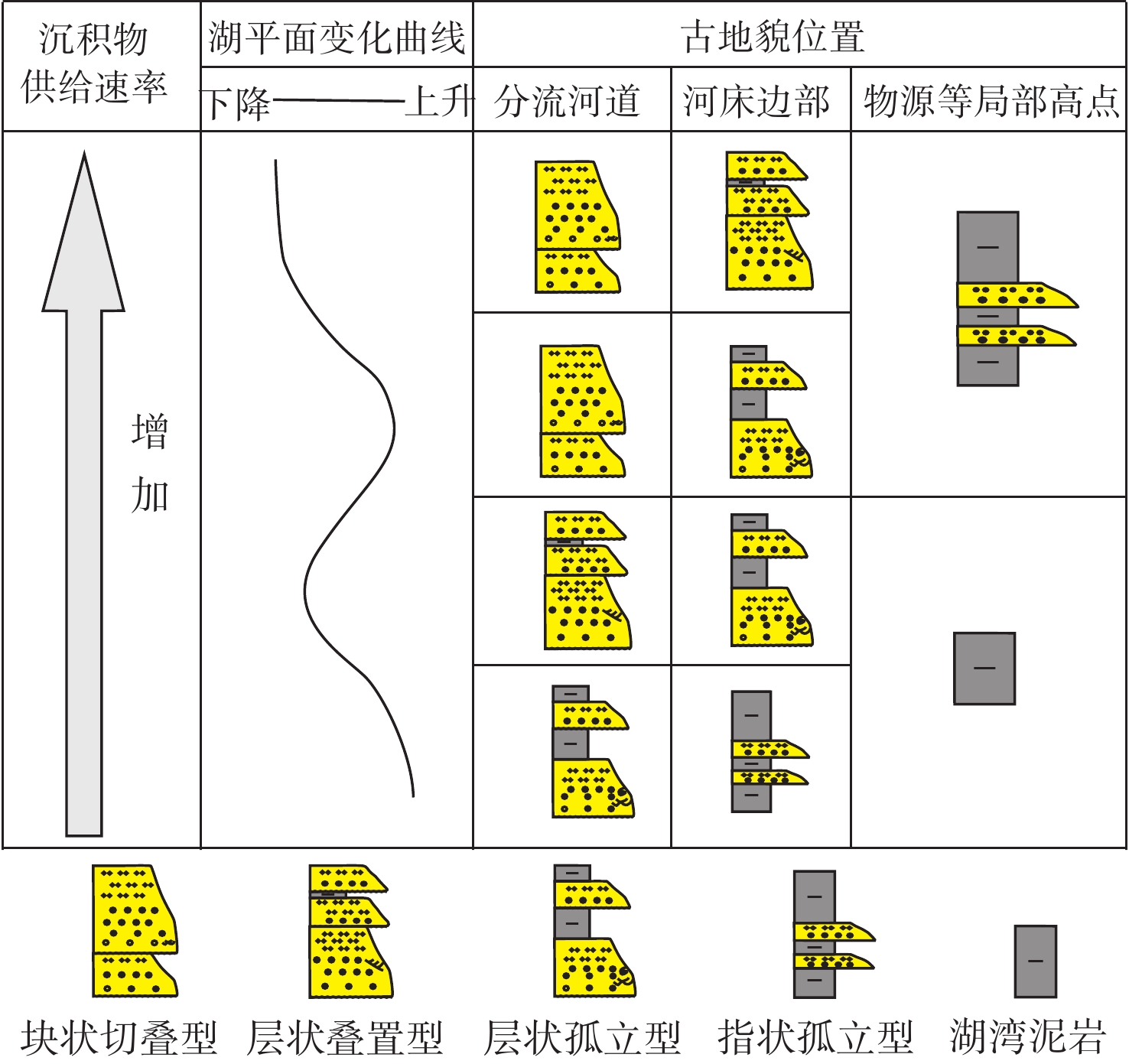
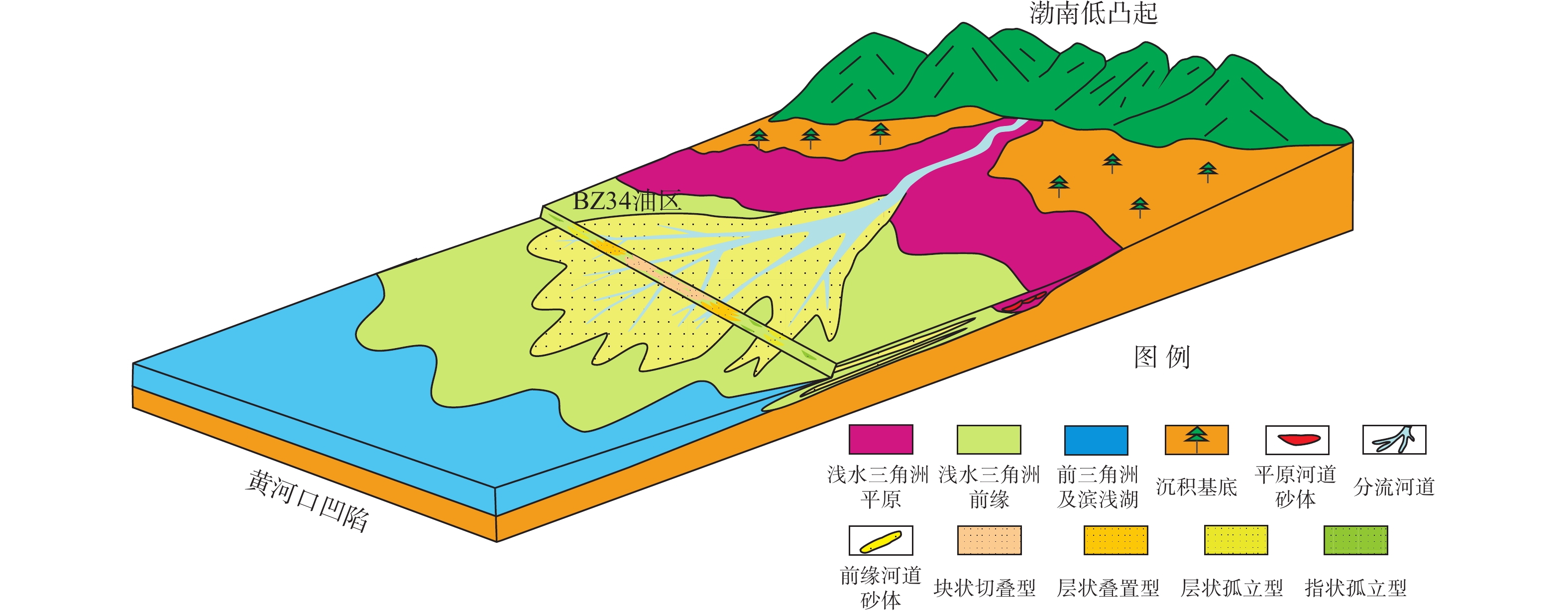
新近系明化镇组下段(明下段,N1ml)为黄河口凹陷BZ34油区的主力含油层段,该时期主要发育河控型浅水三角洲前缘沉积。为更好地表征前缘砂体的结构特征及展布规律,以BZ34油区明下段Ⅱ油组为例,综合应用岩芯、地震属性和测井等资料,分析总结了该地区的砂体沉积类型、砂体结构及沉积模式。研究结果表明:BZ34油区明下段Ⅱ油组砂体以浅水三角洲前缘水下分流河道为主;依据测井形态和叠置关系,将其砂体结构类型划分为4种:块状切叠型河道、层状叠置型河道、层状孤立型河道和指状孤立型河道;砂体结构展布特征及成因主要受古地形、沉积物供给速率、基准面旋回和古气候等因素影响。BZ34油区的水下分流河道沉积,具有垂向上交错叠置、平面上摆动连片的分布特征,与鄱阳湖现代河控浅水三角洲河道的沉积特征类似。该研究对BZ34油区后期部署加密调整井和剩余油挖潜工作具有指导意义。
Abstract:The Lower Member of the Neogene Minghuazhen Formation (N1ml) is the main oil-bearing sand body unit in the BZ34 Oilfield in Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, North China, in which delta front deposits in fluvially dominated shallow waters were developed. To better characterize the structural characteristics and distribution of the front sand bodies, taking the second oil unit of N1ml as an example, the sedimentary types, geomorphological structures, and depositional models of the sand body were analyzed based on the data from coring, seismic profiling, and logging. Results show that the sand bodies are dominated by underwater distributary channels in shallow water delta front. According to the logging curves and overlapping of the sand bodies, four channel types were recognized: massive incised river channel, layered overlapping channel, layered isolated channel, and finger-shaped isolated channel. The distribution and genesis of the sand bodies were affected mainly by paleotopography, sediment supply rate, base level cycle, and paleoclimate. The underwater distributary channel deposits in the BZ34 Oil Field are characteristic of incisive superposition in vertical direction and meandering patchy distribution in horizontal, which is similar to the modern case of fluvially dominated shallow water delta channels in Poyang Lake, South China. This study provided a guidance for infill adjustment and potential tapping in later stage for the remaining oil in BZ34 Oilfield.
-
Key words:
- fluvially dominated shallow water deposit /
- sand body morphology /
- N1ml /
- BZ34 Oilfield /
- Huanghekou Sag
-

-
表 1 BZ34油区明下段Ⅱ油组泥岩X衍射黏土矿物成分数据
Table 1. X-ray diffraction result of clay mineral composition of mudstone of the N1ml in BZ34 Oilfield
井名 深度/m 伊利石/% 高岭石/% 绿泥石/% 伊/蒙混层/% A9井 1 359.10 4 5 4 87 1 364.12 8 11 8 73 1 368.92 10 11 7 72 -
[1] 朱伟林,李建平,周心怀,等. 渤海新近系浅水三角洲沉积体系与大型油气田勘探[J]. 沉积学报,2008,26(4):575-582. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2008.04.016
[2] 徐长贵,姜培海,武法东,等. 渤中坳陷上第三系三角洲的发现、沉积特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 沉积学报,2002,20(4):588-594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.04.009
[3] 吴小红,吕修祥,周心怀,等. BZ34油区明下段浅水三角洲沉积特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 东北石油大学学报,2009,33(5):32-36,40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2009.05.008
[4] 吴穹螈,穆朋飞,孙广义,等. 浅水三角洲分流砂坝精细刻画新方法[J]. 断块油气田,2020,27(2):176-181.
[5] 楼章华,卢庆梅,蔡希源,等. 湖平面升降对浅水三角洲前缘砂体形态的影响[J]. 沉积学报,1998,16(4):27-31. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.1998.04.005
[6] 赵汉卿,张建民,李栓豹,等. 长周期基准面下降半旋回内浅水三角洲沉积演化规律及其在开发中的应用:以渤海A油田明下段为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(5):71-79.
[7] 宋光永,朱超,李森明,等. 油砂山地区浅水三角洲-滨浅湖沉积及其对储层的控制[J]. 断块油气田,2018,25(2):146-150.
[8] 邹才能,赵文智,张兴阳,等. 大型敞流坳陷湖盆浅水三角洲与湖盆中心砂体的形成与分布[J]. 地质学报,2008,82(6):813-825. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.06.011
[9] 刘桂珍,高伟,张丹丹,等. 姬塬地区长81亚油层组浅水型三角洲砂体结构及成因[J]. 岩性油气藏,2019,31(2):16-23. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190203
[10] 张家强,李士祥,周新平,等. 志丹地区长82砂层组缓坡浅水三角洲前缘砂体发育模式及成因[J]. 岩性油气藏,2020,32(1):36-50. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200105
[11] 任双坡,姚光庆,毛文静. 三角洲前缘水下分流河道薄层单砂体成因类型及其叠置模式:以古城油田泌浅10区核三段Ⅳ-Ⅵ油组为例[J]. 沉积学报,2016,34(3):582-593. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2016.03.016
[12] OLARIU C,BHATTACHARYA J P. Terminal distributary channels and delta front architecture of river-dominated delta systems[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2006,76(2):212-233.
[13] 张兴强,尹太举,宋亚开,等. 叠覆式浅水三角洲储层结构分析:以东濮凹陷文79南断块沙二下亚段为例[J]. 断块油气田,2019,26(5):555-560.
[14] LEMONS D R,CHAN M A. Facies architecture and sequence stratigraphy of fine-grained lacustrine deltas along the eastern margin of late Pleistocene Lake Bonneville,northern Utah and southern Idaho[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1999,83(4):635-665.
[15] 涂丹凤,牛成民,张新涛,等. 黄河口凹陷BZ34-1复杂断块油藏滚动勘探实践[J]. 石油地质与工程,2015,29(5):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2015.05.018
[16] 沈孝秀,张婕茹,缪飞飞,等. 黄河口凹陷明化镇组下段储层特征及其对产能的影响[J]. 石油地质与工程,2020,34(1):55-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2020.01.012
[17] 加东辉,吴小红,赵利昌,等. 渤中25-1 南油田浅水三角洲各微相粒度特征分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2005,25(4):87-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2005.04.015
[18] 朱筱敏,赵东娜,曾洪流,等. 松辽盆地齐家地区青山口组浅水三角洲沉积特征及其地震沉积学响应[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(5):889-897. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2013.05.009
[19] 庞小军,王清斌,解婷,等. 黄河口凹陷北缘古近系物源及其对优质储层的控制[J]. 岩性油气藏,2020,32(2):1-13.
[20] 邓鹏,孙善磊,黄鹏年. 气候变化对鄱阳湖流域径流的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(1):39-45. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2020.01.006-
[21] 秦润森,岳红林,周凤军,等. 河控浅水三角洲前缘席状砂沉积特征及沉积模式探讨:以黄河口凹陷渤中34地区明下段为例[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(2):429-439.
-




 下载:
下载: