Summary and Prospect of Steel Slag Treatment Technology at the “Double Carbon” Goal
-
摘要:
这是一篇冶金工程领域的论文。作为炼钢过程中产生的一种固体废弃物,钢渣具有产量大、温度高、化学组成复杂和安定性不良等特点。我国钢渣的资源化利用率低于30%,造成钢渣所含有价资源的浪费,大量钢渣的堆存也会占用大量的土地,造成土壤和水体的污染。钢渣的资源化利用和其处理技术密切相关,基于此本文对钢渣的一次处理工艺,如有压热闷法、常压池式热闷法、滚筒法等进行了简单介绍,重点对钢渣还原提铁、以钢渣为原料制备高附加值材料和高温钢渣余热回收的研究进行了综述分析,指出钢渣的资源化利用不仅包括物质的回收和利用,也包括钢渣所含热能的回收。在“双碳”目标下,应该关注并加强熔融钢渣中金属铁、尾渣和热能的全量化回收和利用,才能真正助力“双碳”目标的实现。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of metallurgical engineering. As a solid waste produced in the process of steelmaking, the steel slag has the characteristics of large output, high temperature, complex chemical composition and poor stability. The resource utilization rate of steel slag in China is less than 30%, resulting in the waste of valuable resources contained in steel slag. The stockpiling of a large number of steel slag will also occupy a large amount of land and cause soil and water pollution. The resource utilization of steel slag is closely related to its treatment technology. Based on this, this paper briefly introduces the primary treatment processes of steel slags, such as pressurized hot stuffy method, the atmospheric tank hot stuffy method, the drum method, etc., and focuses on the reduction and iron extraction of steel slag, the preparation of high value-added materials with steel slag as raw materials, and the waste heat recovery of high-temperature steel slag. It is pointed out that the resource utilization of steel slag not only includes the recovery and utilization of materials, but also the recovery of heat energy contained in steel slag. At the goal of "double carbon", we should pay attention to and strengthen the full quantitative recovery and utilization of metal iron, tailings and heat energy in molten steel slag, so as to truly help achieve the goal of "double carbon".
-
Key words:
- Steel slag /
- Treatment and utilization /
- "Double carbon" goal /
- Iron recovery /
- Modification /
- Waste heat recovery
-

-
[1] 刘仕业, 王占军, 彭犇, 等. 高炉渣对钢渣改性的物理化学基础研究[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(5):557-564.LIU S Y, WANG Z J, PENG B, et al. Fundamental research on the physics and chemistry of steelmaking slag modified with hot blast furnace slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(5):557-564.
LIU S Y, WANG Z J, PENG B, et al. Fundamental research on the physics and chemistry of steelmaking slag modified with hot blast furnace slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(5):557-564.
[2] 朱金伟, 王凡, 任洪岩, 等. 钢渣作为湿法脱硫吸收剂的实验研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2011, 1(3):205-209.ZHU J W, WANG F, REN H Y, et al. Experimental study on steel slag used as wet flue gas desulfurization absorbent[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2011, 1(3):205-209.
ZHU J W, WANG F, REN H Y, et al. Experimental study on steel slag used as wet flue gas desulfurization absorbent[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2011, 1(3):205-209.
[3] 刘国威, 朱李俊, 金强, 等. 钢渣沥青混凝土研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2016(2):11-16.LIU G W, ZHU L J, JIN Q, et al. Research progress of steel slag asphalt concrete[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016(2):11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.02.002
LIU G W, ZHU L J, JIN Q, et al. Research progress of steel slag asphalt concrete[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016(2):11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.02.002
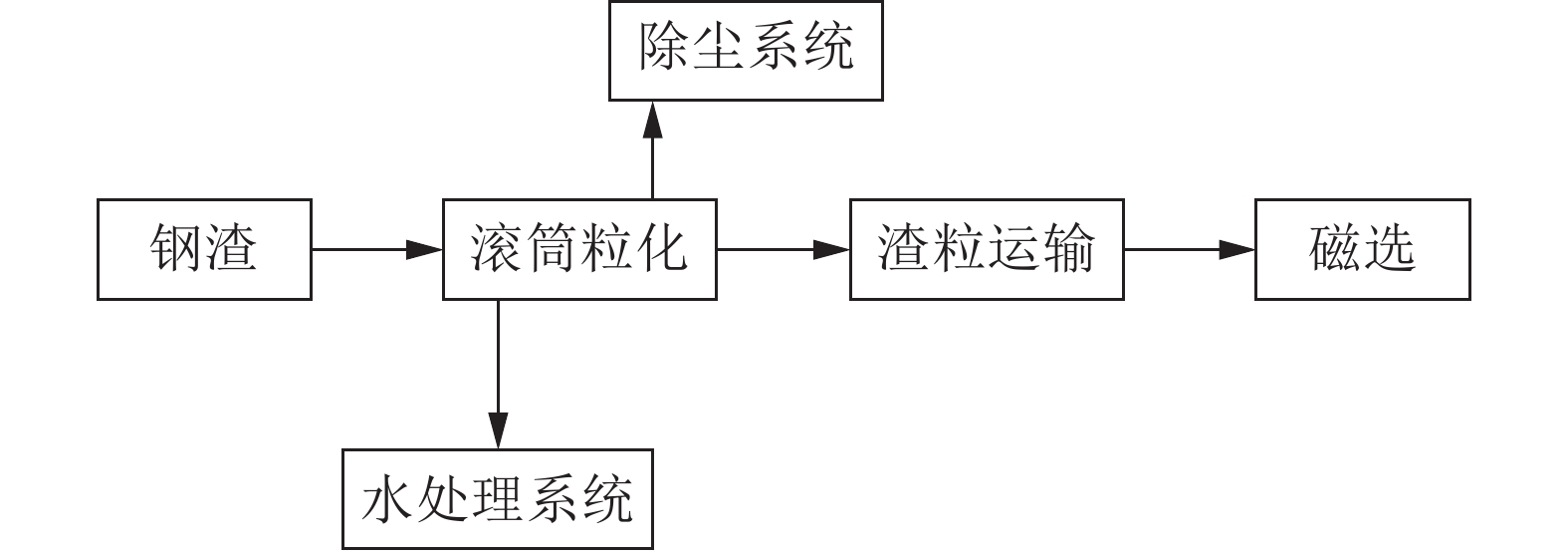
[4] 王会刚, 吴龙, 彭犇, 等. 中外钢渣一次处理技术特点及进展[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(13):5025-5031.WANG H G, WU L, PENG B, et al. Characteristics and research progress of steel slag primary treatment technology at home and abroad[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(13):5025-5031.
WANG H G, WU L, PENG B, et al. Characteristics and research progress of steel slag primary treatment technology at home and abroad[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(13):5025-5031.
[5] 吴燕开, 胡锐, 赵位莹, 等. 钢渣粉固化淤泥质水泥土强度特性试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(15):306-311.WU Y K, HU R, ZHAO W Y, et al. Study on strength characteristic of muddy cement soil stabilized by steel slag powder[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(15):306-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.15.050
WU Y K, HU R, ZHAO W Y, et al. Study on strength characteristic of muddy cement soil stabilized by steel slag powder[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(15):306-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.15.050
[6] 周朝刚, 杨会泽, 艾立群, 等. 转炉含磷钢渣循环利用技术的研究现状及展望[J]. 钢铁, 2021, 56(2):22-39.ZHOU C G, YANG H Z, AI L Q, et al. Research status and prospect of recycling technology of converter slag containing phosphorus[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021, 56(2):22-39.
ZHOU C G, YANG H Z, AI L Q, et al. Research status and prospect of recycling technology of converter slag containing phosphorus[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021, 56(2):22-39.
[7] 苏严, 刘淑贤 , 徐平安, 等. 钢渣易磨性研究现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(3): 95-99.SU Y, LIU S X, XU P A, et al. Research status of the grindability of steel slag [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(3): 95-99.
SU Y, LIU S X, XU P A, et al. Research status of the grindability of steel slag [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(3): 95-99.
[8] 郭辉. 转炉钢渣中铁的还原回收及制备高胶凝性水淬渣的方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.GUO H. Iron recovery and preparation of water-quenched slag with high cementitious performance from BOF slag by means of reduction[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
GUO H. Iron recovery and preparation of water-quenched slag with high cementitious performance from BOF slag by means of reduction[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
[9] 郭丽霞. 废旧钢渣在道路工程中的应用研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017.GUO L X. Research of application of steel slag on road construction[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2017.
GUO L X. Research of application of steel slag on road construction[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2017.
[10] 高本恒, 郝以党, 张淑苓, 等. 钢渣综合利用现状及发展趋势[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(S1): 776-779.GAO B H, HAO Y D, ZHANG S L, et al. Development trend and comprehensive utilization of steel slag[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(S1): 776-779.
GAO B H, HAO Y D, ZHANG S L, et al. Development trend and comprehensive utilization of steel slag[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(S1): 776-779.
[11] 胡绍洋, 戴晓天, 那贤昭. 钢渣的处理工艺及综合利用[J]. 铸造技术, 2019, 40(2):220-224.HU S Y, DAI X T, NA X Z. Treatment process and comprehensive utilization of steel slag[J]. Foundry Technology, 2019, 40(2):220-224.
HU S Y, DAI X T, NA X Z. Treatment process and comprehensive utilization of steel slag[J]. Foundry Technology, 2019, 40(2):220-224.
[12] 彭犇, 邱桂博, 王晟, 等. 钢渣有压热闷爆炸原因分析及防控措施[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(11):158-161+146.PENG B, QIU G B, WANG S, et al. Explosion cause analysis and control measures of steel slags under self-pyrolytic slaking with pressure[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(11):158-161+146.
PENG B, QIU G B, WANG S, et al. Explosion cause analysis and control measures of steel slags under self-pyrolytic slaking with pressure[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(11):158-161+146.
[13] 张健, 祝妍熙, 张宇, 等. 钢渣有压热闷工艺尘汽捕集净化系统探讨[J]. 中国冶金, 2016, 26(4):62-64.ZHANG J, ZHU Y X, ZHANG Y, et al. Discussion on dust steam catcher purification system for hot stuffy with pressure of molten slag[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016, 26(4):62-64.
ZHANG J, ZHU Y X, ZHANG Y, et al. Discussion on dust steam catcher purification system for hot stuffy with pressure of molten slag[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016, 26(4):62-64.
[14] 高本恒, 郝以党, 张淑苓, 等. 转炉钢渣资源化处理及热闷生产工艺应用实例研究[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(11):99-101+79.GAO B H, HAO Y D, ZHANG S L, et al. The application of converte steel slag resource utilization and the hot stuffy process[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(11):99-101+79.
GAO B H, HAO Y D, ZHANG S L, et al. The application of converte steel slag resource utilization and the hot stuffy process[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(11):99-101+79.
[15] 周溪滢. 钢渣生态工业园的设计与实践[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2014.ZHOU X Y. The design and practice of steel-slag eco-industrial park[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2014.
ZHOU X Y. The design and practice of steel-slag eco-industrial park[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2014.
[16] 吴龙, 孙健, 胡天麒, 等. 一种钢渣余热有压热闷可燃气体安全防控装置及方法: CN105039614A[P]. 2015-11-11.WU L, SUN J, HU T Q, et al. A kind of steel slag waste heat pressurized heat boring combustible gas safety prevention and control device and method:CN105039614A[P]. 2015-11-11.
WU L, SUN J, HU T Q, et al. A kind of steel slag waste heat pressurized heat boring combustible gas safety prevention and control device and method: CN105039614A[P]. 2015-11-11.
[17] 吴龙, 孙健, 胡天麒, 等. 一种钢渣余热有压热闷可燃气体安全防控装置: CN204981915U[P]. 2016-01-20.WU L, SUN J, HU T Q, et al. A kind of steel slag waste heat pressurized heat boring combustible gas safety prevention and control device:CN204981915U[P]. 2016-01-20.
WU L, SUN J, HU T Q, et al. A kind of steel slag waste heat pressurized heat boring combustible gas safety prevention and control device: CN204981915U[P]. 2016-01-20.
[18] 陈荣凯, 刘坤. 钢渣有压热闷磁选工艺的海外应用分析[J]. 炼钢, 2018, 34(6):75-78.CHEN K R, LIU K. Analysis and application of steel slag hot stuffing with pressure and magenetic separation purification process in overseas projects[J]. Steelmaking, 2018, 34(6):75-78.
CHEN K R, LIU K. Analysis and application of steel slag hot stuffing with pressure and magenetic separation purification process in overseas projects[J]. Steelmaking, 2018, 34(6):75-78.
[19] 黄丽, 徐杰. 浅谈钢渣热闷的现状及发展[J]. 工业加热, 2016, 45(4):68-70.HUANG L, XU J. The status and development of steel slag hot stew method[J]. Industrial Heating, 2016, 45(4):68-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2016.04.019
HUANG L, XU J. The status and development of steel slag hot stew method[J]. Industrial Heating, 2016, 45(4):68-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2016.04.019
[20] 钱强. 新型热闷钢渣综合利用分析[J]. 鞍钢技术, 2019(2):7-9+16.QIAN Q. Analysis on comprehensive utilization of new type of hot steaming steel slag[J]. Angang Technology, 2019(2):7-9+16.
QIAN Q. Analysis on comprehensive utilization of new type of hot steaming steel slag[J]. Angang Technology, 2019(2):7-9+16.
[21] 杨刚, 蒋兴浩, 张健, 等. 宝钢BSSF法处理的钢渣综合利用方向分析[J]. 工业建筑, 2010, 40(S1):835-836+772.YANG G, JIANG X H, ZHANG J, et al. Analysis of trend of comprehensive utilization of steel slag treated BSSF method in Bao Steel[J]. Industrial Construction, 2010, 40(S1):835-836+772.
YANG G, JIANG X H, ZHANG J, et al. Analysis of trend of comprehensive utilization of steel slag treated BSSF method in Bao Steel[J]. Industrial Construction, 2010, 40(S1):835-836+772.
[22] 王有龙, 胡治春, 金焰, 等. 宝钢滚筒型渣处理装置用钢球磨损分析[J]. 钢铁研究, 2012, 40(2):50-55.WANG Y L, HU Z C, JIN Y, et al. Wear analysis of steel ball in rotary drum-type slag treatment at Baosteel[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2012, 40(2):50-55.
WANG Y L, HU Z C, JIN Y, et al. Wear analysis of steel ball in rotary drum-type slag treatment at Baosteel[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2012, 40(2):50-55.
[23] 刘钰天, 沈恒根, 晏维华, 等. BSSF滚筒法液态钢渣水淬尾气净化工艺的分析[J]. 环境工程, 2011, 29(4):78-81+89.LIU Y T, SHEN H G, YAN W H, et al. The analysis of purification process of the gas from steel slag water quenching by BSSF roller method[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2011, 29(4):78-81+89.
LIU Y T, SHEN H G, YAN W H, et al. The analysis of purification process of the gas from steel slag water quenching by BSSF roller method[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2011, 29(4):78-81+89.
[24] 王军峰. 项目管理在滚筒连续化生产技术提升研究中的应用[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2010.WANG J F. The application of project management in roller continuous production technology promotion research[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2010.
WANG J F. The application of project management in roller continuous production technology promotion research[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2010.
[25] 王申. 熔融钢渣有压热闷及显热回收工艺研究[D]. 北京: 中冶集团建筑研究总院, 2012.WANG S. The Process research on hot stuffy with pressure and sensible heat recovery of the molten slag[D]. Beijing: Central Research Institute of Building and Construction Co. , Ltd. , MCC Group, 2012.
WANG S. The Process research on hot stuffy with pressure and sensible heat recovery of the molten slag[D]. Beijing: Central Research Institute of Building and Construction Co. , Ltd. , MCC Group, 2012.
[26] 孙明明. 冶金钢渣风淬回收工艺排风系统的研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2010.SUN M M. Research on air ventilation system of air quenched recycling process for metallurgical slag[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2010.
SUN M M. Research on air ventilation system of air quenched recycling process for metallurgical slag[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2010.
[27] 胡东风, 仵增瑞. 转炉钢渣风碎技术在石钢30t转炉的应用[J]. 河北冶金, 1997(1):36-40.HU D F, WU Z R. Application of slag wind-crushing technology of 30-ton converter of Shijiazhuang iron and steel plant[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 1997(1):36-40.
HU D F, WU Z R. Application of slag wind-crushing technology of 30-ton converter of Shijiazhuang iron and steel plant[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 1997(1):36-40.
[28] 叶斌. 转炉钢渣气碎工艺技术及产业化[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2003.YE B. Gas blowing grinding technology of BOF slag and its industrialization[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2003.
YE B. Gas blowing grinding technology of BOF slag and its industrialization[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2003.
[29] 李明阳. 钢渣处理工艺的设计思路[J]. 中国冶金, 2014, 24(5):1-4.LI M Y. Design conception of steelmaking slag utilization process[J]. China Metallurgy, 2014, 24(5):1-4.
LI M Y. Design conception of steelmaking slag utilization process[J]. China Metallurgy, 2014, 24(5):1-4.
[30] 许建雄, 范永明, 李泽平, 等. 钢渣热闷工艺及装备研究[J]. 包钢科技, 2019, 45(1):37-41.XU J X, FAN Y M, LI Z P, et al. Study on technology and equipment of hot tight covering for steel slag[J]. Science and Technology of Baotou Steel, 2019, 45(1):37-41.
XU J X, FAN Y M, LI Z P, et al. Study on technology and equipment of hot tight covering for steel slag[J]. Science and Technology of Baotou Steel, 2019, 45(1):37-41.
[31] 王延兵, 宋善龙, 范永平. 一种钢渣有压热闷处理新技术[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(S1):664-666.WANG Y B, SONG S L, FAN Y P. The new techniques of rolling and crushing and pressure hot stuffy steel slag[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(S1):664-666.
WANG Y B, SONG S L, FAN Y P. The new techniques of rolling and crushing and pressure hot stuffy steel slag[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(S1):664-666.
[32] 李术川, 陈晓曦, 刘明亮. 环境友好型钢渣热闷技术的设计和生产实践[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2011, 33(7): 90-93.LI S C, CHEN X X, LIU M L. Design and production practice of environment-friendly hot pressing technology of steel slag [J]. Environmental pollution and Prevention, 2014, 32(S1): 664-666.
LI S C, CHEN X X, LIU M L. Design and production practice of environment-friendly hot pressing technology of steel slag [J]. Environmental pollution and Prevention, 2014, 32(S1): 664-666.
[33] 朱桂林, 孙树杉, 范永平, 等. 一种熔融钢渣热闷处理方法: CN101397595[P]. 2009-04-01.ZHU G L, SUN S S, FAN Y P, et al. A hot smothering treatment method for molten steel slag:CN101397595[P]. 2009-04-01.
ZHU G L, SUN S S, FAN Y P, et al. A hot smothering treatment method for molten steel slag: CN101397595[P]. 2009-04-01.
[34] 柴轶凡, 彭军, 安胜利. 钢渣综合利用及钢渣热闷技术概述[J]. 内蒙古科技大学学报, 2012, 31(3):250-253.CHAI Y F, PENG J, AN S L. Overview of comprehensive utilization of steel slag and hot pressing technology of steel slag[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, 2012, 31(3):250-253.
CHAI Y F, PENG J, AN S L. Overview of comprehensive utilization of steel slag and hot pressing technology of steel slag[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, 2012, 31(3):250-253.
[35] 吴康, 郑毅, 杨和平, 等. 梅钢转炉上应用滚筒处理钢渣的研究[J]. 中国冶金, 2011, 21(10):11-14.WU K, ZHENG Y, YANG H P, et al. Study of BSSF slag in the converter of Meishan steelmaking plant[J]. China Metallurgy, 2011, 21(10):11-14.
WU K, ZHENG Y, YANG H P, et al. Study of BSSF slag in the converter of Meishan steelmaking plant[J]. China Metallurgy, 2011, 21(10):11-14.
[36] 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013: 75.HUANG X H. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 75.
HUANG X H. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 75.
[37] 潘晓, 陈文海, 刘锐. 钢渣直接还原铁在转炉中的应用试验[J]. 硅谷, 2013, 6(13): 136+133.PAN X, CHEN W H, LIU R. Application test of steel slag direct reduction iron in converter[J]. Silicon Valley, 2013, 6(13): 136+133.
PAN X, CHEN W H, LIU R. Application test of steel slag direct reduction iron in converter[J]. Silicon Valley, 2013, 6(13): 136+133.
[38] 殷素红, 郭辉, 余其俊, 等. 还原铁法重构钢渣及其矿物组成[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 292(7):966-971.YIN S H, GUO H, YU Q J, et al. Reconstruction of steel slag by reduced iron method and its mineral composition[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 292(7):966-971. doi: 10.7521/j.issn.0454-5648.2013.07.14
YIN S H, GUO H, YU Q J, et al. Reconstruction of steel slag by reduced iron method and its mineral composition[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 292(7):966-971. doi: 10.7521/j.issn.0454-5648.2013.07.14
[39] 杨志杰, 李宇, 苍大强, 等. AlO含量对提铁后的钢渣及粉煤灰微晶玻璃结构与性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(12):4631-4636.YANG Z J, LI Y, CANG D Q, et al. Effect of AlO content on the structure and properties of steel slag and fly ash glass ceramics after iron extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(12):4631-4636.
YANG Z J, LI Y, CANG D Q, et al. Effect of AlO content on the structure and properties of steel slag and fly ash glass ceramics after iron extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(12):4631-4636.
[40] 张艺伯, 朱桂林, 孙树杉, 等. 重熔还原法处理转炉钢渣研究[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 41(7):111-114.ZHANG Y B, ZHU G L, SUN S S, et al. Study on treatment of converter steel slag by remelting reduction method[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 41(7):111-114.
ZHANG Y B, ZHU G L, SUN S S, et al. Study on treatment of converter steel slag by remelting reduction method[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 41(7):111-114.
[41] 梁晓杰, 叶正茂, 常钧. 碳酸化钢渣复合胶凝材料早期水化活性[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2012, 40(2):226-233.LIANG X J, YE Z M, CHANG J. Early hydration activity of carbonated steel slag composite cementitious material[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 40(2):226-233.
LIANG X J, YE Z M, CHANG J. Early hydration activity of carbonated steel slag composite cementitious material[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 40(2):226-233.
[42] 赵贵州, 李宇, 代文彬, 等. 采用一步烧结法的钢渣基微晶玻璃制备机理[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2014, 33(12):3288-3294.ZHAO G Z, LI Y, DAI W B, et al. Preparation mechanism of steel slag based glass ceramics by one-step sintering[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 33(12):3288-3294.
ZHAO G Z, LI Y, DAI W B, et al. Preparation mechanism of steel slag based glass ceramics by one-step sintering[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 33(12):3288-3294.
[43] 李建新, 韦江雄, 赵三银, 等. 重构钢渣的胶凝性分析[J]. 水泥, 2010(10):16-19.LI J X, WEI J X, ZHAO S Y, et al. Cementitious analysis of reconstituted steel slag[J]. Cement, 2010(10):16-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9877.2010.10.004
LI J X, WEI J X, ZHAO S Y, et al. Cementitious analysis of reconstituted steel slag[J]. Cement, 2010(10):16-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-9877.2010.10.004
[44] 胡天麒, 杨景玲, 朱桂林, 等. 重熔改性后钢渣成分与胶凝性能的研究[J]. 中国钢铁业, 2013(4):19-21.HU T Q, YANG J L, ZHU G L, et al. Study on composition and cementitious properties of steel slag after remelting modification[J]. China Steel Industry, 2013(4):19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2013.04.006
HU T Q, YANG J L, ZHU G L, et al. Study on composition and cementitious properties of steel slag after remelting modification[J]. China Steel Industry, 2013(4):19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2013.04.006
[45] 代文彬, 李宇, 苍大强. 热处理过程对钢渣微晶玻璃结构和性能的影响规律[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(11):966-971.DAI W B, LI Y, CANG D Q. Effect of heat treatment on structure and properties of steel slag glass ceramics[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013, 35(11):966-971.
DAI W B, LI Y, CANG D Q. Effect of heat treatment on structure and properties of steel slag glass ceramics[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013, 35(11):966-971.
[46] 张宇, 张健, 张天有, 等. 钢渣处理与余热回收技术的分析[J]. 中国冶金, 2014, 24(8):33-37.ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG T Y, et al. Analysis of steel slag treatment and waste heat recovery technology[J]. China Metallurgical, 2014, 24(8):33-37.
ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG T Y, et al. Analysis of steel slag treatment and waste heat recovery technology[J]. China Metallurgical, 2014, 24(8):33-37.
[47] SHIGAKI N, TOBO H, OZAWA S, et al. Heat recovery process from packed bed of hot slag plates[J]. ISIJ International, 2015, 55(10):2258-2265. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-169
[48] ZHANG T H, QIU G B, WANG H G, et al. In-suit industrial tests of the highly efficient recovery of waste heat and reutilization of the hot steel slag[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 2021, 9:3955-3962. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c00081
-




 下载:
下载: