Determination of Major Elements in Stream Sediments and Soils by X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Using Pressed-superfine Powder Pellets
-
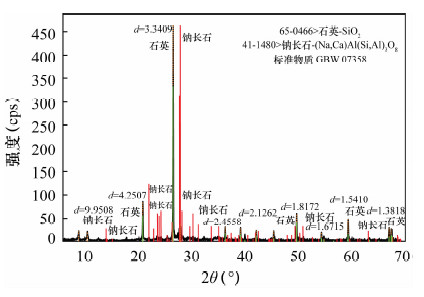
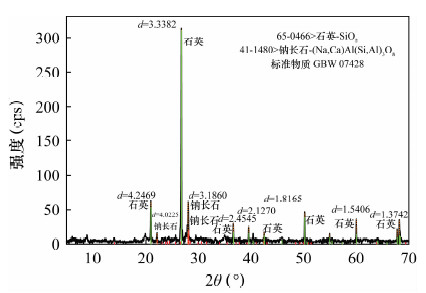
摘要: X射线荧光光谱分析中,粉末压片法是一种理想的绿色环保制样技术,操作简单、制样效率高,但由于受到粒度效应和矿物效应的影响,其测定误差在5%左右,因而限制了这种技术在常量元素检测方面的应用,目前主要应用于痕量元素的测定以及对分析精度要求不高的分析领域。本文运用行星式粉碎制样机,将水系沉积物和土壤标准物质在几分钟内粉碎至平均粒径4~5 μm左右,建立了超细粉末压片制样X射线荧光光谱测定SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO、MgO等主量元素的方法。该方法绝大多数主量元素的测量精密度(RSD)小于2%;检出限为0.003%~0.021%,优于熔融法的检出限(0.006%~0.081%),特别是原子序数小的钠元素,检出限改善4倍。本文针对水系沉积物和土壤研制的超细粉末压片法,由于样品粉碎至几微米,最大限度地减小了粒度效应的影响;X射线衍射分析表明制备样品的矿物成分以石英为主,矿物组成简单,矿物效应可以忽略不计。同时对测量数据加入烧失量进行归一化处理,各元素归一化的测量结果与标准值基本一致,方法准确度比常规压片法获得显著提高。Abstract: The powder pellet compression method for X-ray Fluorescence analysis is an ideal environmentally friendly sample preparation technique with the added advantages of being simple and having high efficiency. However, due to the impact of particle effects and mineral effects, its measurement error is within about 5%, which hinders the application of this technology in the detection of major elements. Powder pellet technology is mainly used in the determination of trace elements as well as the analysis field with less precision. In this study, the stream sediment and soil reference material were crushed to an average particle size about 4-5 μm within a few minutes by ultra-high-speed planetary pressure prototype. The method of ultra-fine pressed powder pellet sample to determine SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, CaO, MgO and other major elements was established by using X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. Measurement precision (RSD) of the method for most of the major elements is less than 2%, and detection limits are 0.003%-0.021%, which is an improvement on the melting method detection limit (0.006%-0.081%), especially for small atomic sodium with four times improvement on the detection limit. The development of this ultra-fine powder compression method for stream sediment and soil, minimizes the impact of the particle size effect by crushing the sample into several microns. X-ray Diffraction analysis demonstrates that the mineral composition of river sediments and soil preparation is dominated by quartz. Therefore, the mineral composition is simple with negligible mineral effect. Measured data with added LOI normalized processing shows that normalized measurements for each element is consistent with the standard value. The accuracy of the method is a significant over the conventional pellet sampling method.
-
Key words:
- stream sediment /
- soil /
- ultrafine powder pellet /
- X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
-

-
表 1 分析元素的测量条件
Table 1. Measurement condition for elements by XRF
元素 分析线 分析晶体 探测器 2 θ(°) 背景(o) 测量时间(s) PHA LL DL SiO2 Kα RX4 F-PC 144.60 140.00 20 10 10 35 Al2O3 Kα PET F-PC 144.78 140.00 20 10 7 35 Fe2O3 Kα LiF200 SC 57.52 55.00 40 20 7 35 MgO Kα TAP F-PC 45.17 48.00 40 20 7 35 CaO Kα LiF200 F-PC 113.18 110.00 40 20 10 35 Na2O Kα TAP F-PC 55.17 58.00 40 20 7 35 K2O Kα LiF200 F-PC 136.70 144.00 40 10 10 35 P2O5 Kα Ge111 F-PC 140.96 143.02 40 20 7 35 TiO2 Kα LiF200 F-PC 86.20 88.50 40 20 10 35 MnO Kα LiF200 F-PC 63.01 64.50 40 20 10 35 Rh Kc LiF200 SC 18.45 - 10 - 7 35 注:X射线管激发电压50 kV,电流 50 mA,粗准直器,真空光路,SC为闪烁计数器,F-PC为流气正比计数器。 表 2 标准物质含量范围
Table 2. The content range of major elements in standard materials
主量元素 含量(%) 主量元素 含量(%) SiO2 32.69~80.58 Al2O3 10.31~29.26 Fe2O3 1.53~18.76 MgO 0.15~4.66 CaO 0.10~13.12 Na2O 0.080~8.99 K2O 0.20~5.34 P2O5 0.012~0.12 TiO2 0.11~2.02 MnO 0.022~0.18 表 3 标准物质粒度分析结果
Table 3. Analytical results of particle size for standard reference materials
GBW 07304a GBW 07404 测量项目 测量值 测量项目 测量值 平均体积直径 5.18 μm 平均体积直径 5.42 μm 平均数量直径 0.78 μm 平均数量直径 0.79 μm 平均面积直径 2.00 μm 平均面积直径 2.08 μm 比表面积 3.00 m2/g 比表面积 2.88 m2/g 相对标准偏差 4.06% 相对标准偏差 4.19% 平均粒径 4.40 μm 平均粒径 4.58 μm 相对标准偏差 4.49% 相对标准偏差 4.65% 偏度 0.61 偏度 0.60 峰值 1.28 峰值 1.28 表 4 标准物质分析结果(归一化前后的测量值)
Table 4. The analytical results of major elements in national standard materials (unnormalized values and normalized values)
元素 含量(%) GBW 07303a GBW 07308a GBW 07358 GBW 07360 GBW 07366 GBW 07403 GBW 07447 GBW 07451 GBW 07453 GBW 07454 SiO2 测定值 72.21 72.82 69.03 62.11 64.61 74.10 60.30 67.60 68.32 61.85 归一化的测定值 72.32 73.17 69.57 62.16 64.33 74.83 60.47 68.28 68.69 61.39 标准值 72.45 73.58 69.40 61.96 64.35 74.72 60.40 68.23 69.11 60.93 Al2O3 测定值 12.59 13.14 10.95 12.97 13.92 12.09 10.45 13.76 13.91 11.53 归一化的测定值 12.61 13.20 10.03 12.98 13.86 12.20 10.48 13.90 13.99 11.44 标准值 12.45 13.25 11.06 12.94 13.61 12.24 10.56 13.89 13.58 11.76 Fe2O3 测定值 4.68 3.66 6.89 3.70 6.86 1.97 3.60 3.96 4.89 4.33 归一化的测定值 4.69 3.67 6.95 3.70 6.83 1.99 3.61 4.00 4.91 4.30 标准值 4.72 3.70 7.00 3.80 7.05 2.00 3.63 4.06 4.97 4.30 MgO 测定值 0.71 0.45 1.66 1.33 1.27 0.56 2.64 1.46 1.18 1.96 归一化的测定值 0.72 0.45 1.67 1.33 1.26 0.57 2.65 1.48 1.18 1.94 标准值 0.72 0.47 1.70 1.29 1.25 0.58 2.58 1.47 1.16 1.99 CaO 测定值 0.44 0.17 2.89 2.04 1.62 1.26 6.78 1.06 0.34 7.22 归一化的测定值 0.44 0.17 2.91 2.04 1.61 1.27 6.80 1.07 0.34 7.17 标准值 0.44 0.17 2.96 2.08 1.64 1.27 6.80 1.09 0.34 7.18 MnO 测定值 0.099 0.083 0.18 0.19 0.13 0.040 0.067 0.097 0.090 0.081 归一化的测定值 0.099 0.083 0.18 0.19 0.12 0.040 0.068 0.098 0.090 0.081 标准值 0.10 0.084 0.18 0.19 0.13 0.039 0.068 0.098 0.093 0.081 TiO2 测定值 0.70 0.48 0.53 0.47 0.75 0.37 0.55 0.63 0.75 0.63 归一化的测定值 0.68 0.48 0.53 0.46 0.75 0.37 0.55 0.63 0.75 0.63 标准值 0.72 0.48 0.53 0.48 0.75 0.37 0.53 0.63 0.75 0.65 P2O5 测定值 0.10 0.050 0.13 0.25 0.14 0.071 0.14 0.099 0.096 0.19 归一化的测定值 0.10 0.050 0.13 0.25 0.13 0.071 0.14 0.10 0.099 0.19 标准值 0.099 0.050 0.13 0.25 0.13 0.073 0.14 0.10 0.094 0.20 K2O 测定值 2.87 4.27 2.30 3.12 2.78 2.97 2.08 2.95 2.49 2.26 归一化的测定值 2.87 4.29 2.31 3.12 2.77 3.00 2.08 2.98 2.50 2.24 标准值 2.87 4.32 2.35 3.17 2.76 3.04 2.11 2.97 2.48 2.28 Na2O 测定值 0.39 0.37 1.41 2.00 0.42 2.66 3.03 2.82 0.85 1.73 归一化的测定值 0.39 0.37 1.42 2.04 0.41 2.69 3.03 2.85 0.85 1.72 标准值 0.39 0.38 1.40 2.09 0.41 2.71 3.05 2.84 0.83 1.75 表 5 方法精密度
Table 5. Precision tests of the method
元素 GBW 07428 元素 GBW 07450 测定平均值(%) RSD(%) 测定平均值(%) RSD(%) SiO2 64.34 0.1 SiO2 60.52 0.2 Al2O3 14.66 0.1 Al2O3 11.75 0.5 Fe2O3 5.26 0.4 Fe2O3 4.07 0.8 MgO 1.99 0.3 MgO 2.06 1.5 CaO 2.46 0.3 CaO 7.41 0.4 MnO 0.07 0.8 MnO 0.070 0.8 TiO2 0.4 0.8 TiO2 0.37 0.7 P2O5 0.070 1.8 P2O5 0.060 3.8 K2O 2.45 0.2 K2O 2.41 0.4 Na2O 1.52 0 Na2O 2.01 0.6 表 6 方法检出限
Table 6. Detection limits of the method
元素 检出限(%) 元素 检出限(%) 本法(压片法) 熔融法 本法(压片法) 熔融法 SiO2 0.021 0.081 MnO 0.003 0.009 Al2O3 0.015 0.052 TiO2 0.005 0.026 Fe2O3 0.005 0.028 P2O5 0.003 0.006 MgO 0.004 0.026 K2O 0.004 0.027 CaO 0.004 0.012 Na2O 0.005 0.038 -
[1] 卓尚军.X射线荧光光谱分析[J].分析试验室,2009,28(7):112-122. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY200104034.htm
[2] Bertin E P.Principles and Practice of X-ray Spectrometric Analysis (Second Edition) [M].New York: Plenum Press,1975:397-429.
[3] 特希昂R,克莱特F,著.高新华,译.X射线荧光定量分析原理[M].北京:冶金部钢铁研究总院,1982:280-302.
[4] 张勤,李国会,樊守忠.X射线荧光光谱法测定土壤和水系沉积物等样品中碳、氮、氟、氯、硫、溴等42种主次和痕量元素[J].分析试验室,2008,27(11):51-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2008.11.014
[5] 徐海,刘琦,王龙山.X射线荧光光谱法测定土壤样品中碳氮硫氯等31种组分[J].岩矿测试,2007,26(6):490-492. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200706013.htm
[6] 刘磊夫,张孟星,曲淑凡.岩石、土壤中23种主次痕量元素的XRF测定[J].现代科学仪器,2008(2):75-77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYQ200802026.htm
[7] 孙芹.熔融法X 射线荧光光谱测定岩石主成分含量[J].化学分析计量,2012,2(3):49-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ201202016.htm
[8] 殷勇. X射线荧光分析在区域地球化学勘查样品分析中的应用[J].中国测试技术,2008,34(6):89-91. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYCS200806027.htm
[9] 张勤,樊守忠,潘宴山,李国会,李小莉.Minipal 4便携式能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪在勘查地球化学中的应用[J].岩矿测试,2007,26(5):377-380. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200705006.htm
[10] Longerich H P.Analysis of pressed pellets of geological samples using wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].X-Ray Spectrometry, 1995, 24:123-126. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4539
[11] 徐婷婷,张波,张红.X射线荧光光谱法同曲线测定海洋沉积物和陆地地化样品中的29个主次痕量元素[J].海洋地质动态,2007, 23(2):31-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200702008.htm
[12] 徐婷婷,夏宁,张波.熔片制样-X射线荧光光谱法测定海洋沉积物样品中主次量组分[J].岩矿测试,2008,27(1):74-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200801021.htm
[13] Xia N, Zhang Q, Yao D, Li G H.Geochemical analysis of marine sediments using fused glass disc by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008, 26(4):475-479. doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0475-8
[14] 李小莉,张勤.粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法测定土壤、水系沉积物和岩石样品中15中稀土元素[J].冶金分析,2013,33(7):35-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201307007.htm
[15] 郑荣华,刘建坤.粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法测定矿石中钨、锡[J].理化检验(化学分册),2013,49(1):66-68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201301023.htm
[16] 赵合琴,郑先君,魏丽芳,魏明宝.X射线荧光光谱分析中样品制备方法评述[J].河南化工,2006, 23(10):8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3467.2006.10.003
[17] 王祎亚,詹秀春,樊兴涛,温宏利,李迎春,许祖银,殷绍泉.粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法测定地质样品中痕量硫的矿物效应佐证实验及其应用[J].冶金分析,2010,30(1):7-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201001001.htm
[18] 刘尚华,陶光仪,吉昂.X射线荧光光谱分析中的粉末压片制样法[J].光谱实验室,1998,15(6):9-15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GPSS806.002.htm
[19] 王毅民,王晓红,高玉淑.地球科学中的现代分析技术地球科学进展[J].地球科学进展,2003,18(3):476-482. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200303022.htm
[20] 吴淑琪,王晓红,屈文俊.南非"Geoanalysis 2009"——第七届国际地质与环境材料分析大会[J].岩矿测试, 2009,28(6):600-601. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200906023.htm
[21] 王晓红,何红蓼,王毅民,孙德忠,樊兴涛,高玉淑,温宏利,夏月莲.超细样品的地质分析应用[J].分析测试学报,2010,29(6):578-583. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TEST201006011.htm
[22] 王晓红,高玉淑,王毅民.超细地质标准物质及其应用[J].自然科学进展,2006,16(3):309-315. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200603011.htm
[23] National Institute of Standards & Technology.Certificate of Analysis Standard Reference Materials 2703-Sediment for Solid Sampling (Small Sample) Analytical Techniques[S].2005:1-9.
[24] Wang X H, Wang Y M, Gao Y S, Huang Y Y, Wang Z Y, Shi X F.Preparation of five China sea and continental shelf sediment reference materials (MSCS-1~5) with ultra-fine particle size distributions[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2009, 33(3):357-368. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2009.33.issue-3
[25] 王毅民,高玉淑,王晓红,黄永样,王振宇,石学法.中国海大陆架沉积物超细标准物质系列研制[J].分析化学,2009,37(11):1700-1705. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2009.11.028
[26] 侯运丰,刘雨.气流粉碎技术的发展[J].中国非金属矿工业导刊,2007,63(5):39-42. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-2002101957.htm
-



 下载:
下载: