Applications of X-ray Diffraction in Natural Gas Hydrate Research
-
摘要: 天然气水合物是一种由气体分子(包括烃类和CO2、H2S等非烃类气体)和水分子在高压低温环境中形成的笼型水合物,主要有Ⅰ型(立方晶体结构)、Ⅱ型(菱形晶体结构)和H型(六方晶体结构)三种晶体结构。研究水合物的结构特征及变化规律,对于认识水合物形成机理、微观动力学、相态转化及水合物样品鉴定等具有重要意义。X射线衍射(XRD)是一种利用X射线照射晶体(或某些非晶态物质)时产生的衍射来研究晶体内部结构(即内部原子排布)的分析技术。该技术应用于天然气水合物研究,不仅能准确获取水合物的结构类型及晶格参数等重要信息,还能观测水合物生成分解的微观动力学过程。本文阐述了XRD技术应用于水合物结构特征研究、水合物生成/分解动力学过程原位观测以及野外水合物样品鉴定等方面的研究进展。已知结构Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型水合物立方晶体的边长分别约为12.0×10-10 m和17.3×10-10 m,而结构H型水合物六方晶体a轴和c轴的边长分别约为12.2×10-10 m和10.0×10-10 m,因此,通过XRD技术准确测量水合物晶体的晶格参数,即可判定水合物晶体的结构类型,该技术在国外已应用于海洋和冻土区钻获的天然气水合物样品鉴定并获得结构信息。此外,通过测定不同条件下生成的水合物晶体参数的变化,可研究水合物的结构转换及其影响规律,研究表明混合气体的组成、客体分子体积及直径大小、温度等都对水合物晶体参数及结构产生影响。通过在高压环境下的XRD原位技术,可测定水合物的生成与分解过程中衍射峰的变化,研究水合物生成/分解动力学过程,研究表明水合物生成/分解主要分两个阶段,即在气液(固)表面的快速生成/分解过程及气体分子在液(固)体内部的扩散过程,后一个阶段控制着反应速度。目前,国外在水合物研究中应用XRD技术已相对成熟,而我国才刚刚起步。本文认为,将XRD技术应用到天然气水合物的研究中,可解决水合物的结构类型鉴别及晶格参数测量等基本的科学问题,而且XRD技术与核磁共振、红外光谱、X-CT等分析技术的联用,尚有很大的发展空间,将为天然气水合物相关的理论研究提供强有力的技术支撑。Abstract: Natural gas hydrates are clathrate hydrates formed from gas molecules (e.g. hydrocarbon gases and non-hydrocarbon gases such as CO2 and H2S) and water molecules under high pressure and low temperature, with three types of crystal structure, such as cubic (Ⅰ), rhombus (Ⅱ) and hexagonal (H). The structural characteristics and variation rule of clathrate hydrate is significant for understanding the formation mechanism, micro-kinetic, phase transformation and identification of gas hydrate. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) is an analytical technique that is used to analyze the crystal micro-structure (i.e. atom orientation) based on the diffraction pattern produced by X-ray irradiating the crystal or some non-crystal substances. When XRD is applied in gas hydrate research, not only can it provide the important information such as structure type and lattice parameter of gas hydrate, but it can also be used to observe the micro-kinetic process of hydrate formation and dissociation. Several applications of XRD in natural gas hydrates research, such as structural characteristics, in situ observation of gas hydrates formation/dissociation, and hydrate sample identification on field are reviewed in this paper. It is well known that the crystal lattice of structure Ⅰ and Ⅱ is approximately 12.0×10-10 m and 17.3×10-10 m, respectively, and approximately 12.2×10-10 m and 10.0×10-10 m along a and c axis for structure H. Therefore, the crystal structure type can be easily identified with the accurate lattice parameters measured by XRD. Now, the XRD technique has been already conducted in identifying and obtaining the structural information of gas hydrate samples recovered from marine and permafrost region overseas. In addition, the structure transformation and influencing factors of gas hydrate can be investigated based on the lattice parameter variation of gas hydrate, which was measured under different conditions. The experimental results show that all the mixture composition, the volume and diameter of guest molecules as well as the temperature can affect the lattice parameter and structure of gas hydrate. In situ XRD technique under high pressure is also used to measure the variation of diffraction peaks during gas hydrate formation/dissociation, and eventually to investigate the kinetic processes of gas hydrate formation and dissociation. The results show that two stages were observed during gas hydrate formation/dissociation, the fast process of hydrate formation/dissociation on the gas-liquid (solid) surface and the gas molecules diffusion process in the liquid (solid). The last stage controls the whole reaction speed. At present, although the XRD technique is widely used in gas hydrate research abroad, it is just beginning in China. It is believed that the XRD technique can be used in gas hydrate research to resolve the basic scientific problems such as structure type identification and lattice parameter measurement, and will provide a powerful technological support for gas hydrate relevant theory research once it combines with other analytical techniques like NMR, IR and X-CT.
-
Key words:
- X-ray diffraction /
- natural gas hydrate /
- structure type /
- lattice parameter /
- in-situ observation
-

-
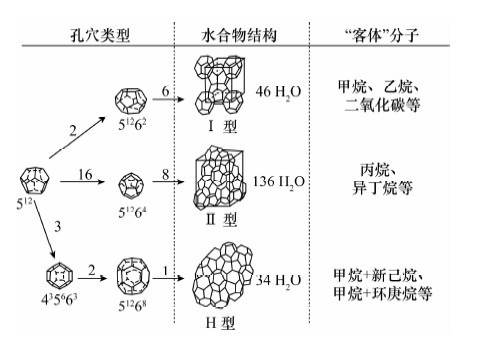
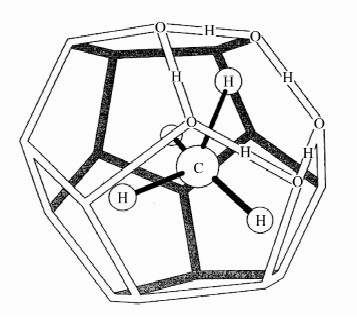
图 1 天然气水合物晶体结构模型[33]
Figure 1.
图 2 三种类型水合物单体晶体结构图[33]
Figure 2.
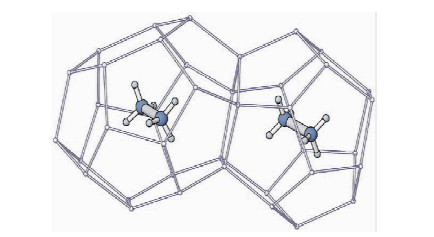
图 3 立方结构的Ⅰ型水合物,乙烷分子在大小孔穴中[10]
Figure 3.
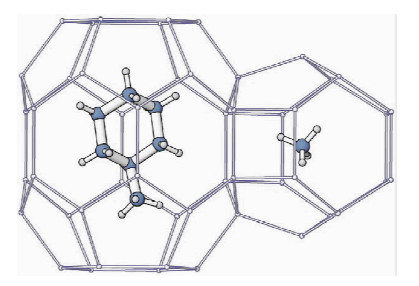
图 4 H型水合物,甲基环己烷分子和甲烷分子分别在大孔穴和小孔穴中[10]
Figure 4.
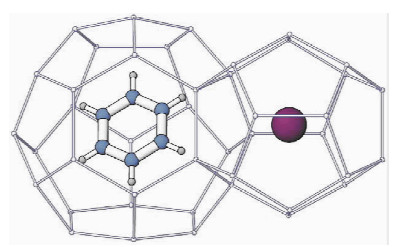
图 5 立方结构的Ⅱ型水合物,苯分子在大孔穴而氙分子在小孔穴中[10]
Figure 5.
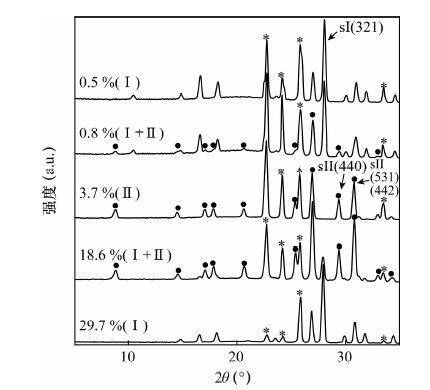
图 6 不同乙烷含量时,CH4-C2H6混合气水合物的X射线衍射图谱[11]
Figure 6.
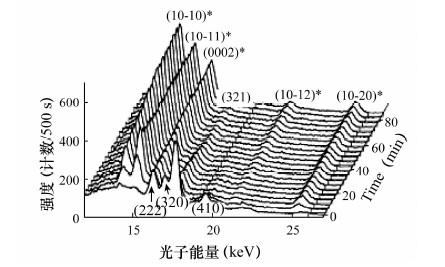
图 7 XRD原位观测从甲烷水合物到Ih冰的转化过程[37]
Figure 7.
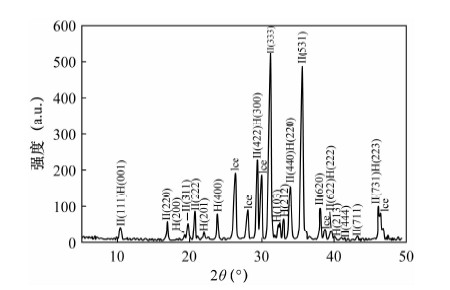
图 8 温哥华近海天然气水合物的XRD图谱[68]
Figure 8.
表 1 三种类型天然气水合物晶体结构参数[33]
Table 1. The crystal structure parameters of three types of gas hydrate [33]
孔穴规格 Ⅰ型天然气水合物 Ⅱ型天然气 水合物 H型天然气 水合物 小 大 小 大 小 中 大 孔穴结构 512 51262 512 51264 512 435663 51268 孔穴数目 2 6 16 8 3 2 1 孔穴半径(10-10 m) 3.91 4.33 3.91 0.473 3.91 4.06 5.71 晶格大小(10-10 m) a≈12.0 a≈17.3 a≈12.2,c≈10.0 空间群 Pm3n Fd3m P6/mmm 晶体 立方体 菱形 六面体 表 2 客体分子的大小和体积及在-100℃形成的Ⅱ型水合物晶胞参数 [10]
Table 2. Sizes and volumes of the guests and the lattice parameters of structure Ⅱ hydrate at -100℃ [10]
Ⅱ型水合物的 客体分子 分子直径 Dmax (×10-10 m) 分子体积 (×10-10 m) 单位晶胞参数 (×10-10 m) 环氧丙烷 6.01 56 17.182 1,3-二氧戊烷 6.19 63 17.157 丙酮 6.26 59 17.181 三氯甲烷 6.50 69 17.236 四氯化碳 6.50 82 17.330 四氢呋喃 6.95 82 17.316 苯+氙 7.07 76 17.363 -
[1] Milkov A V.Global estimates of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments: How much is really out there [J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2004, 66(3):183-197.
[2] Lu H, Ripmeester J A. A laboratory protocol for the analysis of natural gas hydrates [C]//6th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Vancouver, British Columbia, CANADA, 2008.
[3] Rojas Y, Lou X.Instrumental analysis of gas hydrates properties [J].Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2010, 5(2):310-323. doi: 10.1002/apj.v5:2
[4] 夏宁,刘昌岭,业渝光,孟庆国,林学辉,贺行良.显微激光拉曼光谱测定天然气水合物的方法研究[J].岩矿测试,2011,30(4):416-422. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201104009.htm
[5] 刘昌岭,孟庆国,业渝光.固体核磁共振技术在气体水合物研究中的应用[J].波谱学杂志,2012, 29(3):465-474. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PPXZ201203017.htm
[6] 刘昌岭,业渝光,孟庆国.显微激光拉曼光谱测定甲烷水合物的水合指数[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2010, 30(4):963-966. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201004024.htm
[7] Udachin K A, Ratcliffe C I, Ripmeester J A. Structure, composition, and thermal expansion of CO2 hydrate from single crystal X-ray diffraction measurements[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2001, 105(19):4200-4204. doi: 10.1021/jp004389o
[8] Uchida T, Takeya S, Kamata Y, Ikeda I Y, Nagao J, Ebinuma T, Narita H, Zatsepina O, Buffett B A. Spectroscopic observations and thermodynamic calculations on clathrate hydrates of mixed gas containing methane and ethane: Determination of structure, composition and cage occupancy[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(48):12426-12431. doi: 10.1021/jp025884i
[9] Uchida T, Takeya S, Kamata Y, Ohmura R, Narita H.Spectroscopic measurements on binary, ternary, and quaternary mixed-gas molecules in clathrate structures [J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(14):5080-5087.
[10] Udachin K A, Ratcliffe C I, Ripmeester J A.Single crystal diffraction studies of structure Ⅰ, Ⅱ and H hydrates: Structure, cage occupancy and composition [J].Journal of Supramolecular Chemistry, 2002, 2(4):405-408.
[11] Takeya S, Kamata Y, Uchida T, Nagao J, Ebinuma T, Narita H, Hori A, Hondoh T.Coexistence of structure Ⅰ and Ⅱ hydrates formed from a mixture of methane and ethane gases [J].Canadian Journal of Physics, 2003, 81(1-2):479-484. doi: 10.1139/p03-038
[12] Takeya S, Uchida T, Kamata Y, Nagao J, Kida M, Minami H, Sakagami H, Hachikubo A, Takahashi N, Shoji H, Khlystov O, Grachev M, Soloviev V.Lattice expansion of clathrate hydrates of methane mixtures and natural gas[J].Angewandte Chemie, 2005, 117(42):7088-7091. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3757
[13] Takeya S, Hori A, Uchida T, Ohmura R.Crystal lattice size and stability of type H clathrate hydrates with various large-molecule guest substances[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2006, 110(26):12943-12947. doi: 10.1021/jp060198v
[14] Susilo R, Ripmeester J A, Englezos P.Characterization of gas hydrates with PXRD, DSC, NMR, and Raman spectroscopy[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(15):3930-3939. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2007.03.045
[15] Davidson D W, Garg S K, Gough S R, Handa Y P, Ratcliffe C I, Ripmeester J A, Tse J S.Laboratory analysis of a naturally occurring gas hydrate from sediment of the Gulf of Mexico[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(4):619-623. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90110-9
[16] Lu H L, Moudrakovski I, Riedel M, Spence G, Dutrisac R, Ripmeester J, Wright F, Dallimore S.Occurrence and structural characterization of gas hydrates associated with a cold vent field, offshore Vancouver Island [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,2005, 110(B10):10-18.
[17] Lee J W, Kim D Y, Lee H.Phase behavior and structure transition of the mixed methane and nitrogen hydrates [J].Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2006, 23(2):299-302. doi: 10.1007/BF02705731
[18] Jeffrey G A, McMullan R K.The clathrate hydrates[J].Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, 2007, 8:43-108.
[19] Klapproth A, Goreshnik E, Staykova D, Klein H, Kuhs W F.Structural studies of gas hydrates[J].Canadian Journal of Physics, 2003, 81(1-2):503-518. doi: 10.1139/p03-024
[20] Seo Y T, Lee H.Structure and guest distribution of the mixed carbon dioxide and nitrogen hydrates as revealed by X-ray diffraction and 13C NMR spectroscopy[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(2):530-534. doi: 10.1021/jp0351371
[21] Tse J S, McKinnon W R, Marchi M.Thermal expansion of structure Ⅰ ethylene oxide hydrate[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1987, 91(15):4188-4193. doi: 10.1021/j100299a047
[22] Tse J S.Dynamical properties and stability of clathrate hydrates[J].Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1994, 715(1):187-206.
[23] Takeya S, Nagaya H, Matsuyama T, Hondoh T, Lipenkov V Y.Lattice constants and thermal expansion coefficient of air clathrate hydrate in deep ice cores from Vostok, Antarctica[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000, 104(4):668-670. doi: 10.1021/jp993344o
[24] Takeya S, Kida M, Minami H, Sakagamib H, Hachikubob A, Takahashib N, Shojib H, Solovievc V, Wallmannd K, Biebowe N, Obzhirovf A, Salomatinf A, Poortg J.Structure and thermal expansion of natural gas clathrate hydrates[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(8):2670-2674. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2005.11.049
[25] Koh C A, Savidge J L, Tang C C.Time-resolved in-situ experiments on the crystallization of natural gas hydrates[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(16):6412-6414. doi: 10.1021/jp960094s
[26] Takeya S, Hondoh T, Uchida T.In situ observation of CO2 hydrate by X-ray diffraction[J].Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2000, 912(1):973-982.
[27] Huo Z, Hester K, Sloan E D, Miller K T.Methane hydrate nonstoichiometry and phase diagram[J].AIChE Journal, 2003, 49(5):1300-1306. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905
[28] Uchida T, Takeya S, Wilson L D, Tulk C A, Ripmeester J A, Nagao J, Ebinuma T, Narita H.Measurements of physical properties of gas hydrates and in situ observations of formation and decomposition processes via Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction[J].Canadian Journal of Physics, 2003, 81(1-2):351-357. doi: 10.1139/p03-017
[29] Uchida T, Ohmura R, Ikeda I Y, Nagao J, Takeya S, Hori A.Phase equilibrium measurements and crystallographic analyses on structure-H type gas hydrate formed from the CH4-CO2-neohexane-water system[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(10):4583-4588. doi: 10.1021/jp056503e
[30] Feklistov V V, Timchenko A K, Ancharov A I, Sheromov M A, Manakov A Y.A chamber for X-ray diffractometry of gas hydrates samples for pressures of up to 700 atm[J].Instruments and Experimental Techniques, 2005, 48(6):826-828. doi: 10.1007/s10786-005-0146-3
[31] Kurnosov A, Dubrovinsky L, Kuznetsov A, Dmitriev V.High-pressure/high-temperature behavior of the methane-ammonia-water system up to 3 GPa[J].Zeitschrift Fur Naturforschung B, 2006, 61(12):1573-1576.
[32] Takeya S, Shimada W, Kamata Y, Ebinuma T, Uchida T, Nagao J, Narita H.In situ X-ray diffraction measurements of the self-preservation effect of CH4 hydrate[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2001, 105(42):9756-9759. doi: 10.1021/jp011435r
[33] Sloan E D.Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates[J].Nature,2003, 426(6964):353-363. doi: 10.1038/nature02135
[34] Claussen W F.A second water structure for insert gas hydrates[J].Journal of Chemical Physics,1951, 19:1425-1426.
[35] Claussen W F.Suggested structures of water in inert gas hydrates[J].Journal of Chemical Physics, 1951, 19:662.
[36] Ripmeester J A, John S T, Ratcliffe C I, Powell B M.A new clathrate hydrate structure[J].Nature, 1987, 325(6100):135-136. doi: 10.1038/325135a0
[37] Takeya S, Ebinuma T, Uchida T, Nagao J, Narita H.Self-preservation effect and dissociation rates of CH4 hydrate[J].Journal of Crystal Growth, 2002, 237:379-382.
[38] Muromachi S, Takeya S, Yamamoto Y, Ohmura R.Characterization of tetra-n-butylphosphonium bromide semiclathrate hydrate by crystal structure analysis[J].CrystEngComm, 2014, 16:2056-2060. doi: 10.1039/c3ce41942h
[39] Shpakov V P, Tse J S, Tulk C A, Kvammec B, Belosludov V R.Elastic moduli calculation and instability in structure Ⅰ methane clathrate hydrate[J].Chemical Physics Letters, 1998, 282(2):107-114. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2614(97)01241-4
[40] Collett T S, Lee M W.Reservoir characterization of marine and permafrost associated gas hydrate accumulations with downhole well logs[J].Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2000, 912(1):51-64.
[41] Stern L A, Circone S, Kirby S H, Durham W B.Anomalous preservation of pure methane hydrate at 1 atm[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2001, 105(9):1756-1762. doi: 10.1021/jp003061s
[42] Ikeda-Fukazawa T, Hondoh T, Fukumura T, Fukazawa H, Mae S.Variation in N2/O2 ratio of occluded air in Dome Fuji Antarctic ice[J].Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres (1984—2012), 2001, 106(D16):17799-17810. doi: 10.1029/2000JD000104
[43] Shin K, Moudrakovski I L, Davari M D, Alavi S, Ratcliffe C I, Ripmeester J A.Crystal engineering the clathrate hydrate lattice with NH4F[J].CrystEngComm, 2014, Advance Article.DOI: 10.1039/C3CE41661E.
[44] Hendriks E M, Edmonds B, Moorwood R A S, Szczepanski R.Hydrate structure stability in simple and mixed hydrates[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1996, 117(1):193-200.
[45] Subramanian S, Kini R A, Dec S F, Sloan E D.Evidence of structure Ⅱ hydrate formation from methane+ ethane mixtures[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2000, 55(11):1981-1999. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00389-9
[46] Subramanian S, Ballard A L, Kini R A, Dec S F, Sloan E D.Structural transitions in methane+ethane gas hydrates—part Ⅰ: Upper transition point and applications[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2000, 55(23):5763-5771. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(00)00162-7
[47] Ballard A L, Sloan E D.Optimizing thermodynamic parameters to match methane and ethane structural transition in natural gas hydrate equilibria[J].Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2000, 912(1):702-712.
[48] Schicks J M, Naumann R, Erzinger J, Hester K C, Koh C A, Sloan E D.Phase transitions in mixed gas hydrates: Experimental observations versus calculated data[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(23):11468-11474. doi: 10.1021/jp0612580
[49] Schicks J M, Ripmeester J A.The coexistence of two different methane hydrate phases under moderate pressure and temperature conditions: Kinetic versus thermodynamic products[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2004, 43(25):3310-3313. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773
[50] Staykova D K, Kuhs W F, Salamatin A N, Hansen T.Formation of porous gas hydrates from ice powders: Diffraction experiments and multistage model [J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107(37):10299-10311. doi: 10.1021/jp027787v
[51] Matsumoto Y, Grim R G, Khan N M, Sugahara T, Ohgaki K, Sloan E D, Koh C A, Sum A K.Investigating the thermodynamic stabilities of hydrogen and methane binary gas hydrates[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(7):3783-3788. doi: 10.1021/jp411140z
[52] Kondo W, Ohtsuka K, Ohmura R, Takeya S, Mori Y H.Clathrate-hydrate formation from a hydrocarbon gas mixture: Compositional evolution of formed hydrate during an isobaric semi-batch hydrate-forming operation [J].Applied Energy, 2014, 113:864-871. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.08.033
[53] Luzi M, Schicks J M, Naumann R, Erzinger J.Systematic kinetic studies on mixed gas hydrates by Raman spectroscopy and powder X-ray diffraction[J].The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2012, 48:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2011.12.004
[54] Lee H H, Ahn S H, Nam B U, Kim B S, Lee G W, Moon D, Shin H J, Han K W, Yoon J H.Thermodynamic stability, spectroscopic identification, and gas storage capacity of CO2-CH4-N2 mixture gas hydrates: Implications for landfill gas hydrates[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(7):4184-4190.
[55] Seo Y, An S, Park J W, Kim B S, Komai T, Yoon J H.Occupation and release behavior of guest molecules in CH4, CO2, N2 and acetone mixture hydrates: An in situ study by Raman spectroscopy[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53 (14):6179 6184.
[56] Lee H, Seo Y, Seo Y T, Moudrakovski I L, Ripmeester J A.Recovering methane from solid methane hydrate with carbon dioxide[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2003, 42(41):5048-5051. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773
[57] Kuhs W F, Klapproth A, Gotthardt F, Techmer K, Heinrichs T.The formation of meso- and macroporous gas hydrates[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(18):2929-2932. doi: 10.1029/2000GL006112
[58] Uchida T, Moriwaki M, Takeya S, Ikeda I Y, Ohmura R, Nagao J, Minagawa H, Ebinuma T, Narita H, Gohara K, Mae S.Two-step formation of methane propane mixed gas hydrates in a batch-type reactor[J].AIChE Journal, 2004, 50(2):518-523. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905
[59] Yakushev V S, Istomin V A.Gas-hydrates self preser-vation effect[J].Physics and Chemistry of Ice, 1992:136-140.
[60] Stern I A, Kirky S H, Durham W B.Peculiarities of methane clathrate hydrate formation and solid-state deformation, including possible superheating of water ice[J].Science-AAAS-Weekly Paper Edition, 1996, 273(5283):1843-1847.
[61] Stern L A, Circone S, Kirby S H, Durham W B.Temperature, pressure, and compositional effects on anomalous or "self" preservation of gas hydrates[J].Canadian Journal of Physics, 2003, 81(1-2):271-283. doi: 10.1139/p03-018
[62] Circone S, Stern L A, Kirby S H.The role of water in gas hydrate dissociation[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(18):5747-5755. doi: 10.1021/jp0362584
[63] Komai T, Kang S P, Yoon J H, Yamamoto Y, Kawamura T, Ohtake M.In situ Raman spectroscopy investigation of the dissociation of methane hydrate at temperatures just below the ice point[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2004, 108(23):8062-8068. doi: 10.1021/jp0310955
[64] Takeya S, Uchida T, Nagao J, Ohmura R, Shimada W, Kamata Y, Ebinuma T, Narita H.Particle size effect of CH4 hydrate for self-preservation[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(5):1383-1387. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2004.10.011
[65] Gutt C, Asmussen B, Press W, Merkl C, Casalta H, Greinert J, Bohrmann G, Tse J S, H ller A.Quantum rotations in natural methane-clathrates from the Pacific sea-floor[J].EPL (Europhysics Letters), 1999, 48(3):269. doi: 10.1209/epl/i1999-00476-x
[66] Tulk C A, Ratcliffe C I, Ripmeester J A.Chemical and physical analysis of natural gas hydrate from the JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L-38 gas hydrate research well[J].Bulletin-Geological Survey of Canada, 1999:251-262.
[67] Yousuf M, Qadri S B, Knies D L, Grabowski K S, Coffin R B, Pohlman J W.Novel results on structural investigations of natural minerals of clathrate hydrates[J].Applied Physics A, 2004, 78(6):925-939. doi: 10.1007/s00339-003-2091-y
[68] Chazallon B, Focsa C, Charlou J L, Bourry C, Donval J.A comparative Raman spectroscopic study of natural gas hydrates collected at different geological sites[J].Chemical Geology, 2007, 244(1):175-185.
[69] Kim D Y, Uhm T W, Lee H, Lee Y J, Ryu B J, Kimet J H.Compositional and structural identification of natural gas hydrates collected at Site 1249 on Ocean Drilling Program Leg 204[J].Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2005, 22(4):569-572. doi: 10.1007/BF02706645
[70] Ripmeester J A, Lu H, Moudrakovski I L, Dutrisac R, Wilson L D, Wright F, Dallimore S R.Structure and composition of gas hydrate in sediment recovered from the JAPEX/JNOC/GSC et al.Mallik 5L-38 gas hydrate production research well, determined by X-ray diffraction and Raman and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J].Bulletin-Geological Survey of Canada, 2005, 585:106.
[71] Udachin K A, Lu H, Enright G D, Ratcliffe C I, Ripmeester J A, Chapman N R, Riedel M, Spence G.Single crystals of naturally occurring gas hydrates: The structures of methane and mixed hydrocarbon hydrates[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 46(43):8220-8222. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773
[72] Kida M, Hachikubo A, Sakagami H, Minami H, Krylov A, Yamashita S, Takahashi N, Shoji H, Khlystov O, Poort J, Narita H.Natural gas hydrates with locally different cage occupancies and hydration numbers in Lake Baikal[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2009, 10(5):1-8.
[73] Khlystov O, Batist M D, Shoji H, Hachikubo A, Nishio S, Naudts L, Poort J, Khabuev A, Belousov O, Manakov A.Gas hydrate of Lake Baikal: Discovery and varieties[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62:162-166. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.03.009
[74] Klapp S A, Bohrmann G, Kuhs W F, Murshed M M, Pape T, Klein H, Techmer K S, Heeschena K U, Abegg F.Microstructures of structure Ⅰ and Ⅱ gas hydrates from the Gulf of Mexico[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(1):116-125. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.03.004
[75] Klapp S A, Murshed M M, Pape T, Klein H, Bohrmann G, Brewer P G, Kuhs W F.Mixed gas hydrate structures at the Chapopote Knoll, southern Gulf of Mexico[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 299(1):207-217.
[76] Kida M, Jin Y, Watanabe M,Konno Y, Yoneda J, Egawa K, Ito T, Nakatsuka Y, Suzuki K, Nagao J.Characteristics of hydrate-bound gases from the Eastern Nankai Trough [C]//AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts San Francisc: The Smithsonian/NASA Astrophysics Data System, 2013:1605.
[77] Miyakawa A, Saito S, Yamada Y, Tomaru H, Kinoshita M, Tsuji T.Gas hydrate saturation at Site C0002, IODP Expeditions 314 and 315, in the Kumano Basin, Nankai trough[J].Island Arc, 2014.Advance Article. DOI:10.1111/iar.12064.
[78] Lu H, Lorenson T D, Moudrakovski I L, Ripmeester J A, Collett T S, Hunter R B, Ratcliffe C I.The characteristics of gas hydrates recovered from the Mount Elbert Gas Hydrate Stratigraphic Test Well, Alaska North Slope[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(2):411-418. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.01.002
[79] Lu H, Seo Y, Lee J, Moudrakovski I,Ripmeester J A, Chapman N R, Coffin R B, Gardner G, Pohlman J.Complex gas hydrate from the Cascadia margin[J].Nature, 2007, 445(7125):303-306. doi: 10.1038/nature05463
-



 下载:
下载: