Application of Stripping Voltammetry with a Solid Amalgam Electrode for Determination of Copper in a Tracer and Groundwater Tracing Experiment
-
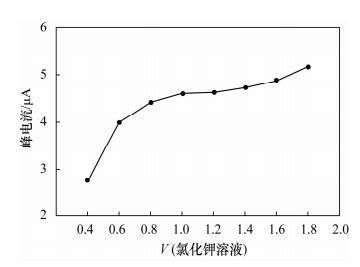
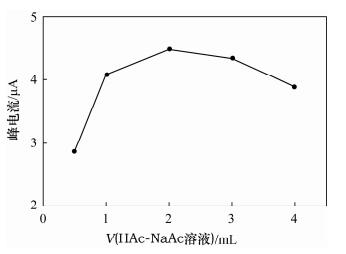
摘要: 用易溶于水的金属盐类试剂作示踪剂,是岩溶地下水示踪试验中广泛采用的有效方法,通过野外现场测定人工示踪剂中的金属离子可以揭示岩溶地下水的运动特征。传统极谱法所用的液态汞操作不便,且容易造成环境污染。本文制作了固体汞电极,采用溶出伏安法测定地下水示踪剂中的铜,在地下水样品中加入醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲溶液,氯化钾溶液作为支持电解质,采用固体汞电极扫描,记录溶出曲线。实验了氯化钾溶液、醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲溶液用量对100 ng/mL铜标准工作溶液峰电流的影响,在选定最佳实验条件下,铜浓度在0~1000 ng/mL范围内与峰电流呈现良好的线性关系,相关系数大于0.999,方法检出限为0.58 ng/mL,加标回收率为96.4%~101.7%。地下水中可能存在的一些离子对测定不产生干扰。该方法应用于地下水示踪试验,铜的测定结果与极谱法基本吻合,且简单快速,适合野外现场测定,同时避免了极谱法液态汞的污染问题。Abstract: Using water-soluble metal salts as tracers, provides an effective method for karst groundwater tracing experiments, which reveal the motion law of karst groundwater by the instant determination of metal ions with artificial tracers in the field. Liquid mercury used in traditional polarography is inconvenient to operate and easily pollutes the environment. In this work, a solid amalgam electrode was made and used for the determination of copper ion in groundwater tracer by stripping voltammetry, in which method the buffer solution of HAc-NaAc was added to the groundwater sample and potassium chloride solution was used as a supporting electrolyte, while the solid amalgam electrode sweeping was employed and the stripping diagram was recorded. Effects of the amount of potassium chlorate solution and HAc-NaAc buffer solution on peak current with a concentration of 100 ng/mL copper standard solution were studied. Copper concentration in the range of 0-1000 ng/mL demonstrated a good linear relationship with the peak current under the selected optimal conditions. The correlation coefficient was greater than 0.999, the detection limit was 0.58 ng/mL and the addition standard recoveries were 96.4%-101.7%. The results were not interfered with by the ions possibly existing in groundwater. When applied to groundwater tracing experiments, stripping voltammetry results for copper ions agree well with those obtained by polarography. This method provides a simple and rapid procedure, which is suitable for field spot determination while avoiding pollution by liquid mercury.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- tracer /
- copper /
- solid amalgam electrode /
- stripping voltammetry
-

-
表 1 水样分析测定结果及加标回收率
Table 1. Determination results of water samples and the spiked recovery
水样 ρ(Cu)/(ng·mL-1) 回收率/% 本底值 加入量 测定值 归安地下河天窗 4.12 5.00 9.02 98.0 社泉水样 4.96 10.0 15.13 101.7 融江河水样 7.20 5.00 12.11 98.2 浮桥水潭水样 7.63 10.0 17.27 96.4 表 2 水样监测结果
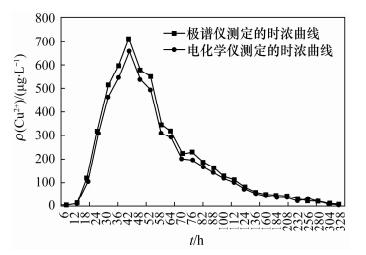
Table 2. Monitoring results of water samples
取样时间
t/hρ(Cu2+)/(μg·L-1) 极谱法 本法 6 5.00 4.90 12 10.0 7.50 18 120 105 24 320 308 30 516 464 36 595 546 42 710 659 48 576 536 52 549 496 58 345 311 64 320 292 70 220 202 76 230 197 82 186 169 88 160 142 100 130 117 112 110 101 124 80 75.1 136 55 49.1 160 50 45.8 184 40 40.2 208 45 38.9 232 30 26.4 256 25 27.8 280 20 21.2 304 10 12.2 328 5.00 5.10 352 5.00 5.00 -
[1] 吴法伟,刘群昌,王宏伟.辽宁本溪水洞地下暗河的补给源研究[J].地下水,2007,29(1): 43-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU200701014.htm
[2] 邓振平,周小红,何师意,罗英.西南岩溶石山地区岩溶地下水示踪试验与分析——以湖南湘西大龙洞为例[J].中国岩溶,2007,26(2): 163-169. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200702013.htm
[3] 张祯武.岩溶地下水管流场类型与示踪曲线对应关系及在生产中的应用[J].中国岩溶,1990, 9(3): 211- 219. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199003002.htm
[4] Carlier E, Boulemia C.A method for the analysis of tracer tests in groundwater [J].Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology & Hydrogeology,2002,35(3): 291-294. doi: 10.1144/1470-9236/2000-14
[5] 张祯武,杨胜强.岩溶水示踪探测技术的新进展[J].工程勘察,1999(5): 40-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC905.011.htm
[6] 樊引琴,高宏,李立阳,穆伊舟,卿松.自动监测站在水资源质量监测与评价中的应用[J].水资源保护,2006, 22(5): 71-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200605018.htm
[7] 贾秀梅,刘满杰,孙继朝,齐继祥,臧逸中,鲁静.万家寨水库右岸岩溶渗漏试验研究[J].地球学报, 2005, 26(2): 179-182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200502012.htm
[8] 李敬兰,李益民.广西龙布排泥库地下水多元示踪试验研究[J].安全与环境工程,2004,11(1): 59-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ200401019.htm
[9] 裴建国,谢运球,章程.湘中溶蚀丘陵区示踪试验——以湖南新化为例[J].中国岩溶,2000,19(4): 366-371. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200004014.htm
[10] 黄保健,张之淦,陈伟海,高明刚.高山峡谷岩溶水示踪试验——以川西锦屏地区为例[J].中国岩溶,1995,14(4): 362-371. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR504.010.htm
[11] 汪进良, 姜光辉,侯满福,陈定宁.自动化监测电导率在盐示踪试验中的应用——以云南八宝水库盐示踪试验为例[J].地球学报,2005,26(4): 371-374. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200504014.htm
[12] 陈学民,周云.示踪试验中的浓度测定[J].甘肃环境研究与监测,1995,8(1): 5-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSHJ501.001.htm
[13] Yosypchuk B, Novtny L. Copper solid amalgam electrodes [J].Elector Analysis, 2003, 15(2): 121-125.
[14] 李建平,杜亚琳.新型固体汞电极在仪器分析实验中的应用[J].大学化学,2006,21(2): 56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8438.2006.02.016
[15] 李建平,彭图治,张雪君.铋膜电极电位溶出法测定痕量铅、镉、锌[J].分析化学,2002,30(9): 1092-1095. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX200209016.htm
[16] 邓振平,周小红,杜亚琳,李建平.用于示踪分析的固体汞合金电极线性扫描伏安法测痕量钼[J].分析试验室,2007,26(12): 44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2007.12.011
-




 下载:
下载: