-
摘要: 测定水和土壤的氮氧同位素组成能够识别硝酸盐来源和研究氮素的迁移转化过程,用在线高温热解法测试硝酸盐的15N和18O同位素是目前应用最广泛、最流行的高新技术。但是由于离子源内NO的干扰,使该方法测定的δ18O值不准确,而采用He稀释法则可有效减少该项干扰。本文选取4个国际标准样品(IAEA-No-3、USGS32、USGS34和USGS35)和一个实验室标准样品(CUGL-No-1),使用元素分析仪耦合MAT 253稳定同位素比值质谱仪(EA-IRMS),在8个月时间内对100多个地下水样品进行238次测试,对在线高温热解测试硝酸盐15N和18O技术进行了检验,验证其实用性。得到三点新认识:① 用KNO3作为靶样品形式成本低,且便于和国际标准对比;② 在线高温热解法测定标准和样品中硝酸盐的15N和18O同位素组成需样量仅为500 μg的KNO3,一次进样可同时测定NO3-的δ15N和δ18O,消耗时间仅720 s,δ15N和δ18O的测试精度分别为0.25‰、0.6‰,达到了国外相应水平,速度快,效率高;③ He稀释法可减少离子源内NO对δ18O测试的干扰,不必改变EA-IRMS系统的任何硬件。Abstract: The studying of 15N and 18O in soil and water can be used to identify the origin, transportation and transformation of the nitrate, which provides reliable evidence for the remediation of the polluted environment. At present, high-temperature pyrolysis is the most widely used method for assessing 15N and 18O. However, NO from the ion source may interfere with the measurement of δ18O, which is efficiently reduced by the He dilution method. In this article, the selection of four international standards (IAEA-No-3, USGS32, USGS34 and USGS35) and one laboratory standard (CUGL-No-1) are documented to verify the practicability of high-temperature pyrolysis. Over the course of eight months, 238 tests were conducted for 100 groundwater samples by using coupled elemental analyser and MAT 253 stable isotope ratio mass spectrometer (EA-IRMS). Three new conclusions were obtained through the study. Firstly, the low cost target sample of KNO3 was convenient for the comparison to the international standards. Secondly, it was concluded that online high-temperature pyrolysis was the best method to study 15N and 18O in nitrate of standards and samples. In this research, the sample amount of KNO3 was only 500 μg. Moreover, the values of δ15N and δ18O were determined simultaneously in one sample input, which took just 720 s and had the added advantages of being rapid and having high efficiency. The accuracies of δ15N and δ18O were 0.25‰ and 0.6‰, respectively, which were close to the corresponding international level. Thirdly, the He dilution method reduced the interference to δ18O without any improvement of the EA-IRMS system.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- nitrate /
- nitrogen and oxygen isotopes /
- online high temperature pyrolysis
-

-
表 1 标准物质氮同位素测试结果
Table 1. Analytical results of the standard of δ15N in nitrate
标准样品编号 化学形式 同位素组成 测定日期(2011年)和测试结果 推荐值 测试平均值和误差 1月21日 1月22日 1月24日 1月26日 8月13日 8月17日 CUGL-No-1(实验室标准) KNO3 δ15N (‰,空气) 14.59±15(n=6)
14.82±0.18(n=5)14.80±0.32(n=6) 14.45±0.26(n=5)
14.24±0.16(n=5)14.56±0.32(n=6)
14.59±0.24(n=5)14.78±0.18(n=9) 14.96±0.27(n=13) - 14.64±0.22(n=9) IAEA-No-3 KNO3 δ15N(‰,空气) 4.70±0.15(n=5) 4.70±0.31(n=5) 4.70±0.17(n=6)
4.70±0.23(n=6)4.70±0.24(n=6) 4.70±0.18(n=14) 4.70±0.24(n=15) 4.70 - USGS32 KNO3 δ15N(‰,空气) - 179.54±0.17(n=6) 179.23±0.25(n=3)
179.87±0.28(n=3)179.35±0.24(n=4) 180.12±0.33(n=9) 180.34±0.27(n=13) 180.00 179.74±0.44(n=6) USGS34 KNO3 δ15N (‰,空气) - 1.69±0.22(n=6) -1.14±0.23(n=6)
-1.81±0.20(n=4)1.42±0.16(n=4) -1.59±0.23(n=14) -1.50±0.25(n=13) -1.80 1.53±0.23(n=6) USGS35 NaNO3 δ15N (‰,空气) - 3.02±0.09(n=6) 2.75±0.18(n=4)
2.75±0.18(n=4)2.90±0.33(n=5) 3.14±0.19(n=13) 3.38±0.18(n=9) 2.70 2.99±0.24(n=6) 表 2 标准物质氧同位素测试结果
Table 2. Analytical results of the standard of δ18O in nitrate
标准样品编号 化学形式 同位素组成 测定日期(2011年)和测试结果 推荐值 测试平均值和误差 1月21日 1月22日 1月24日 1月26日 8月13日 8月17日 CUGL-No-1(实验室标准) KNO3 δ18O(‰,VSMOW) 24.18±0.34(n=6)
24.88±0.48(n=4)25.54±0.39(n=6) 24.21±0.32(n=6) 25.2±1.85(n=5) 23.57±0.41(n=10) 24.22±0.65(n=11) - 24.54±0.69(n=7) IAEA-No-3 KNO3 δ18O(‰,VSMOW) 25.6±0.51(n=5) 25.6±0.20(n=5) 25.6±0.42(n=4)
25.6±0.53(n=6)25.6±0.83(n=3) 25.6±0.45(n=12) 25.6±0.45(n=14) 25.6 - USGS32 KNO3 δ18O(‰,VSMOW) 25.98±0.37(n=6) 26.26±0.28(n=6) 25.64±0.37(n=5)
26.04±0.25(n=3)27.48±0.28(n=3) 25.54±0.37(n=12) 25.56±0.25(n=13) 25.7 26.07±0.68(n=7) USGS34 KNO3 δ18O(‰,VSMOW) - -26.71±0.49(n=6) -27.25±0.49(n=4)
-27.72±0.39(n=4)-28.20±0.21(n=4) -26.89±0.47(n=13) -27.51±0.45(n=13) -27.9 -27.38±0.55(n=6) USGS35 NaNO3 δ18O(‰,VSMOW) - 57.89±0.19(n=6) - 57.70±0.61(n=3) 57.20±0.24(n=10) 56.58±0.38(n=8) 57.5 57.34±0.59(n=4) -
[1] Kendall C, Grim E. Combustion tube method for measurement of nitroge isotope ratios using calcium oxide for total removal of carbon dioxide and water [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1990,62: 526-529. doi: 10.1021/ac00204a019
[2] Kendall C, Silva S R, Chang C C Y, Burns D A, Campbell D H, Shanley J B. Use of δ18O and δ15N of Nitrate to Determine Sources of Nitrate in Early Spring Runoff in Forested Catchments[C]//Internation Symposium on Isotope in Water Resources Management. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency,1995.
[3] Silva S R, Kendall C, Wilkison D H, Ziegler A C, Chang C C Y, Avanzino R J. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2000, 228: 22-36. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00205-X
[4] Wassenaar L I. Evaluation of the origin and fate of nitrate in the Abbotsford aquifer using the isotopes of 18O and 15N in NO3-[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1995, 10: 391-405. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(95)00013-A
[5] Revesz K, Böhlke J K, Yoshinari T. Determination of δ18O and δ15N in nitrate [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1997, 69: 4375-4380. doi: 10.1021/ac9610523
[6] 蔡鹤生, 刘存富, 周爱国, 杨琰.硝酸盐中15N和18O测试新技术 [J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001,20(4): 421-424.
[7] Werner R A, Kornexl B E, Roβmann A, Schmidt H L. On-line determination of δ18O values of organic substan-ces [J]. Analytical Chimica Acta, 1996, 319: 159-164. doi: 10.1016/0003-2670(95)00468-8
[8] Koziet J. Isotope ratio mass spectrometric method for the on-line determination of oxygen-18 in organic matter [J]. Mass Spectrometry, 1997, 32: 103. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9888
[9] Farquhar G D, Henry B K, Styles J M. A rapid on-line technique for determination of oxygen isotope composition of nitrogen-containing organic matter and water [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 1997, 11: 1554. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0231
[10] Brand W A, Tegtmeyer A R, Hilkert A. Compound-specific isotope analysis: Extending toward 15N/14N and 18O/16O [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1994, 21: 585-594. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(94)90004-3
[11] Begley I S, Scrimgeour C M. High-precision δ2H and δ18O measurement for water and volatile organic compounds by continuous-flow pyrolysis isotope ratio mass spectrometry [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1997, 69: 1530. doi: 10.1021/ac960935r
[12] Kornexl B E, Gehre M, Höfling R, Werner R A. On-line δ18O measurement of organic and inorganic substances [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 1999, 13: 1685-1693. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0231
[13] Böhlke J K, Mroczkowski S J, Coplen T B. Oxygen isotopes in nitrate: New reference materials for 18O : 17O : 16O measurements and observations on nitrate-water equilibration [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2003, 17: 1835-1846. doi: 10.1002/rcm.v17:16
[14] Gehre M, Strauch G. High-temperature element analysis and pyrolysis techniques for stable isotope analysis [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2003, 17: 1497-1503. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0231
[15] Werner R A. The online 18O/16O analysis: Development and application [J]. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 2003, 39: 85-104. doi: 10.1080/1025601031000108642
[16] Accoe F, Berglund M, Geypens β, Taylor P. Method to reduce interference effect in thermal conversion elemental analyzer/continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry δ18O measurements of nitrogen-containing compounds [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2008, 22: 2280-2286. doi: 10.1002/rcm.3609
[17] Brand W A, Coplen T B, Aerts-Bijma A T, Böhlke J K, Gehre M, Geilmann H, Gröning M, Jansen H G, Meijer H A J, Mroczkowski S J, Qi H P, Soergel K, Stuart-Williams H S, Weisl S M, Werner R A. Comprehensive inter-laboratory calibration of reference materials for δ18O versus VSMOW using various on-line high-temperature conversion techniques [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2009, 23: 999-1019. doi: 10.1002/rcm.v23:7
[18] Hunsinger G B, Hagopian W M, Jahren A H. Offline oxygen isotope analysis of organic compounds with high N : O [J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2010, 24: 3182-3186. doi: 10.1002/rcm.4752
[19] Huber B, Bernasconi S M, Luster J, Pannatier E G. A new isolation procedure of nitrate from freshwater for nitrogen and oxygen isotope analysis [J]. Rapid Communication in Mass Spectrometry, 2011, 25: 3056-3062. doi: 10.1002/rcm.5199
[20] Li S L, Liu C Q, Lan Y C, Zhao Z Q, Zhou Z H. Tracing the sources of nitrate in karstic groundwater in Zunyi, Southwest China: A combined nitrogen isotope and water chemistry approach [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, DOI10(100)/s12665-009-0277-0. doi: 10(100)/s12665-009-0277-0
[21] Li S L, Liu C Q, Li J, Liu X L, Chetelat B, Wang B L, Wang F S. Assessment of the source of nitrate in the Changjiang River, China: Using a nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44: 1573-1578.
[22] 马传明, 刘存富, 蔡鹤生, 岳向冰, 王嫣然.微量水硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐在线测试新技术——两阶段化学转化法[M]//同位素水文学新技术学习方法.武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2010: 182-193.
-

| 引用本文: | 徐文, 周建伟, 刘存富, 甘义群, 刘运德, 张彦鹏. 地下水硝酸盐15N和18O同位素在线测试技术研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(2): 305-312. |
| Citation: | Wen XU, Jian-wei ZHOU, Cun-fu LIU, Yi-qun GAN, Yun-de LIU, Yan-peng ZHANG. Online Measurement Technique on 15N and 18O Isotopes of Nitrate in Groundwater[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(2): 305-312. |
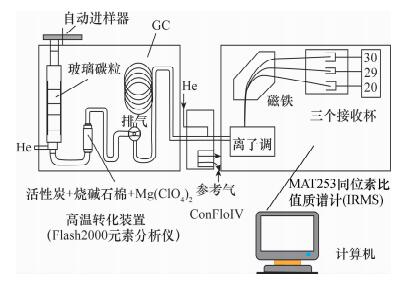
- Figure 1. Schematic diagram of HTP-IRMS for δ15N and δ18O measurements of nitrate
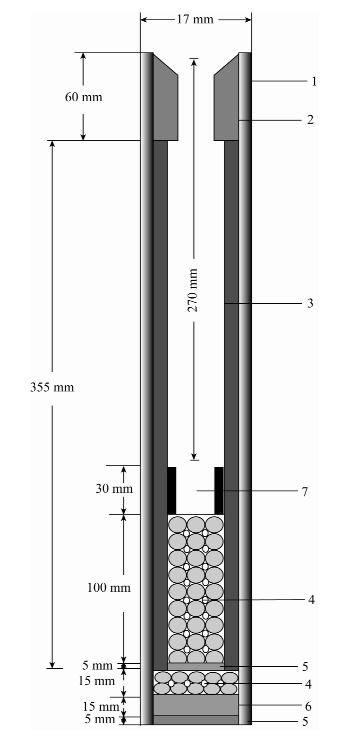
- Figure 2. Special ceramic reactor
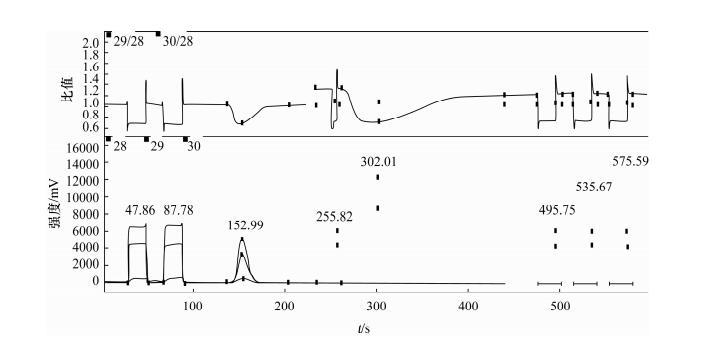
- Figure 3. The mass spectrogram of N2 and CO from KNO3 and the ratio of 30/28


 下载:
下载: