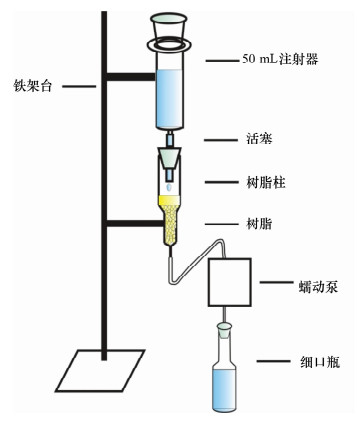
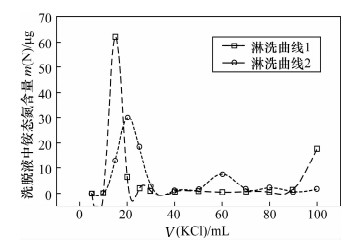
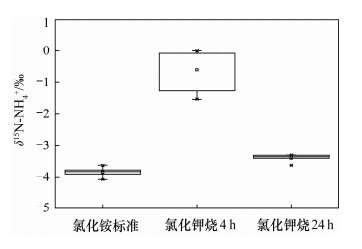
Determination of Nitrogen Isotope of Water Samples with Low Ammonium Nitrogen by Ion Exchange Method
-
摘要: 采用氯化铵、氯化钾为原料的离子交换色层法结合扩散法处理低浓度铵态氮水样,测定其铵态氮同位素时,减小全流程空白、避免同位素分馏、获取准确的铵态氮同位素值是需解决的关键问题。本文建立一套尽可能密闭的离子交换系统,避免了在大气环境下低浓度铵态氮水样在离子交换色层预处理过程中的污染;采用蠕动泵过柱的方法,调节蠕动泵的转速控制氯化铵溶液的过柱速率为1.2 L/h,洗脱速率为0.2 L/h,缩短了样品处理时间,减少了空气对铵态氮样品的污染,样品中的NH4+可完全被阳离子交换树脂吸附,铵态氮回收率为93.5%~102.8%,且不会引起氮同位素分馏;将优级纯氯化钾试剂置于450℃马弗炉中灼烧24 h,降低了氯化钾试剂引入的铵态氮污染。建立的方法使全流程的铵态氮空白浓度低于检出限0.02 mg/L,解决了在大气环境下采用离子交换色层法处理低浓度铵态氮水样的污染问题,加速了样品前处理的过程,提高了样品处理效率。
-
关键词:
- 低浓度铵态氮水样 /
- 铵态氮同位素 /
- 离子交换色层法 /
- 扩散法 /
- 元素分析仪-同位素比值质谱法
Abstract: When the δ15N-NH4+ in water samples is pretreated by using the ion exchange and diffusion method with NH4Cl and KCl, the key problem is how to reduce the blank, avoid isotopic fractionation and yield accurate isotope results. In this study, a closed ion exchange system was set up to prevent the small amount of NH4+ contamination to the water samples. Furthermore, the sample and elution flow rates of 1.2 L/h and 0.2 L/h respectively were achieved by adjusting the speed of a peristaltic pump. Thus, both the experiment time and the contamination were reduced. In addition, all of the NH4+ in the sample is absorbed on the ion exchange resin and the N recoveries were from 93.5% to 102.8%. Therefore, the whole process will not cause isotopic fractionation. The blank introduced by KCl was reduced by being heated at 450℃ for 24 h. As a result, the blank ion exchange was reduced to below the detection limit of 0.02 mg/L by using the closed ion exchange system. The problem of contamination for water sample pretreatment in air was solved. The process was accelerated and efficiency was improved -

-
表 1 开放系统和尽量密闭系统中离子交换流程空白和回收率
Table 1. Blank and yield of N for NH4+ ion exchange under air and closed system
离子交换树脂柱编号 样品 处理体积V/mL ρB/(mg·L-1) 洗脱液NH4+-N含量m/mg 回收率/% NH4+-N-上柱前 NH4+-N-上柱后 1# 流程空白1a 450 0.00 0.17 nd nd 2# 流程空白2a 700 0.00 0.38 nd nd 3# 流程空白3a 1500 0.00 nd 0.66 nd 4# 标准溶液1a 450 0.12 0.17±0.01(n=5) nd nd 5# 标准溶液2a 700 0.12 0.45±0.01(n=5) nd nd 6# 标准溶液3a 1500 0.12 nd 0.66 nd 7# 流程空白1b 450 0.00 <0.02 小于检出限 nd 8# 流程空白2b 1500 0.00 <0.02 小于检出限 nd 9# 标准溶液1b 450 0.56 <0.02 0.24 94.8 10# 标准溶液2b 1500 0.10 <0.02 0.15 102.7 注:a和b分别表示在开放系统和尽量密闭的系统下进行离子交换过程。nd表示未检出。 表 2 过柱和洗脱速率对离子交换过程的影响
Table 2. Effect of column rate and eluting rate on ion exchange procedure
离子交换
树脂柱编号ρ(NH4+-N)/
(mg·L-1)V/mL 过柱速率/
(L·h-1)洗脱速率/
(L·h-1)回收率/
%1# 0.5 500 0.3 0.05 95.1 2# 0.5 500 1.2 0.05 103.2 3# 0.5 500 1.2 0.05 101.2 4# 0.5 450 0.9 0.05 96.1 5# 0.5 450 0.9 0.05 93.5 6# 0.1 1500 0.9 0.2 102.8 7# 0.1 1500 0.9 0.2 102.8 -
[1] Hastings M G, Jarvis J C, Steig E J. Anthropogenic impacts on nitrogen isotopes of ice-core nitrate [J].Science, 2009, 324: 1288. doi: 10.1126/science.1170510
[2] 罗绪强,王世杰,刘秀明.稳定氮同位素在环境污染示踪中的应用进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2007, 26(3): 295-299. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200703018.htm
[3] Xing M, Liu W G. Variations in the concentration and isotopic composition of nitrate nitrogen in wet deposition and their relation with meteorological conditions in Xi′an city, Northwest China [J].Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27: 831-840. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.01.003
[4] Liu W G, Xing M. Isotopic indicators of carbon and nitrogen cycles in river catchments during soil erosion in the arid Loess Plateau of China [J].Chemical Geology, 2012, 296-297: 66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.12.021
[5] 李思亮,刘丛强,肖化云,陶发祥,郎贇超,韩贵琳.δ15N在贵阳地下水氮污染来源和转化过程中的辨识应用[J].地球化学, 2005, 34(3): 257-262.
[6] 金赞芳,叶红玉.氮同位素方法在地下水氮污染源识别中的应用[J].环境污染与防治,2006,28(7): 531-535. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR200607014.htm
[7] 宁卓,张翠云,张胜.地下水铵污染及其氮同位素研究[J].南水北调与水利科技, 2011, 9(3): 129-132. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201103033.htm
[8] 曹亚澄,孙国庆,施书莲.土壤中不同含氮组分的δ15N质谱测定法[J].土壤通报, 1993, 24(2): 87-90.
[9] Rock L, Ellert B H. Nitrogen-15 and oxygen-18 natural abundance of potassium chloride extractable soil nitrate using the denitrifier method [J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2007, 71: 355-361. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2006.0266
[10] Silva S R, Kendalla C, Wilkisonb D H, Ziegler A C, Chang C C Y, Avanzino R J. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios [J].Journal of Hydrology, 2000, 228: 22-36. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00205-X
[11] Sigman D M, Casciotti K L, Andreani M, Barford C, Galanter M, Böhlke J K. A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater [J].Analytical Chemistry, 2001,73: 4145-4153. doi: 10.1021/ac010088e
[12] 肖化云,刘丛强.水样氮同位素分析预处理方法的研究现状与进展[J].岩矿测试, 2001, 20(2): 125-130. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200102009.htm
[13] Johnston A M, Scrimgeour C M, Kennedy H, Handley L L.Isolation of ammonium-N as 1-sulfonato-iso-indole for measurement of δ15N [J].Rapid Communication in Mass Spectrometry, 2003, 17: 1099-1106. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0231
[14] Xing M, Liu W G. An improved method of ion exchange for nitrogen isotope analysis of water nitrate [J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2011, 686: 107-114. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.11.051
[15] Huber B, Bernasconi S M, Luster J, Pannatier E G. A new isolation procedure of nitrate from freshwater for nitrogen and oxygen isotope analysis [J].Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2011, 25: 3056-3062. doi: 10.1002/rcm.5199
[16] Velinsky D J, Pennock J R, Sharp J H, Cifuentes L A, Fogel M L. Determination of the isotopic composition of ammonium-nitrogen at the natural abundance level from estuarine waters [J].Marine Chemistry, 1989, 26: 351-361. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(89)90040-6
[17] Goerges T, Dittert K. Improved diffusion technique for 15N:14N analysis of ammonium and nitrate from aqueous samples by stable isotope spectrometry [J].Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1998, 29(3-4): 361-368. doi: 10.1080/00103629809369950
[18] Holmes R M, McClelland J W, Sigman D M, Fry B, Peterson B J. Measuring 15N-NH4+ in marine, estuarine and fresh waters: An adaption of the ammonia diffusion method for samples with low ammonium concentrations [J].Marine Chemistry, 1998, 60: 235-243. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(97)00099-6
[19] Sebilo M, Mayer B, Grably M, Billiou D, Mariotti A. The use of the ‘ammonium diffusion’ method for 15N-NH4+ and 15N-NO3- measurements: Comparison with other techniques [J].Environmental Chemistry, 2004, 1: 99-103. doi: 10.1071/EN04037
[20] Stephan K, Kavanagh K L. Suitability of the diffusion method for natural abundance nitrogen-15 analysis [J].Soil Science Society of American Journal, 2009, 73: 293-302. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2007.0079
[21] Downs M, Michener R, Fry B. Nadelhoffer K.Routine measurement of dissolved inorganic 15N in precipitation and streamwater [J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 1999, 55: 211-220. doi: 10.1023/A:1006194307747
[22] Xiao H Y, Liu C Q. A fast method to prepare water samples for 15N analysis [J].Science in China (Series E), 2001, 44: 105-107. doi: 10.1007/BF02916798
[23] Lehmann M F, Bernasconi S M, McKenzie J A. A method for the extraction of ammonium from freshwaters for nitrogen isotope analysis [J].Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73: 4717-4721. doi: 10.1021/ac010212u
[24] 肖化云,刘丛强.水样硝酸盐氮同位素分析预处理方法探讨[J].岩矿测试, 2002,21(2): 105-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200202003.htm
[25] Mulvaney R L, Khan S A. Use of diffusion to determine inorganic nitrogen in a complex organic matrix [J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1999, 63: 240-246. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300010035x
[26] Brooks P D, Stark J M, McInteer B B, Preston T. Diffusion method to prepare soil extracts for automated nitrogen-15 analysis [J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1989, 53: 1707-1711. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300060016x
[27] Stark J M, Hart S C. Diffusion technique for preparing salt solutions, kjeldahl digests, and persulfate digests for nitrogen-15 analysis [J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1996, 60: 1846-1855. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1996.03615995006000060033x
[28] Mulvaney R L, Khan S A, Stevens W B, Mulvaney C S. Improved diffusion methods for determination of inorganic nitrogen in soil extracts and water [J].Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1997, 24: 413-420. doi: 10.1007/s003740050266
[29] 胡婧,刘卫国.扩散法-EA-IRMS测定天然水体铵态氮同位素实验条件研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2010, 29(1): 31-37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201001005.htm
[30] Robinson D.δ15N as an integrator of the nitrogen cycle [J].Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2001, 16(3): 153-162.
[31] 肖化云,刘丛强.氮同位素示踪贵州红枫湖河流季节性氮污染[J].地球与环境, 2004, 32(1): 71-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200401012.htm
[32] 肖化云,刘丛强,李思亮.贵阳地区夏季雨水硫和氮同位素地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 2003, 32(3): 248-254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200303005.htm
-




 下载:
下载: