Kinetics and Impact Factors for Nanoscale Zinc Adsorption of Arsenite from Water
-
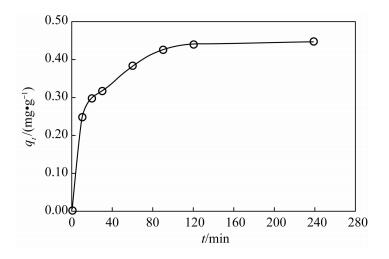
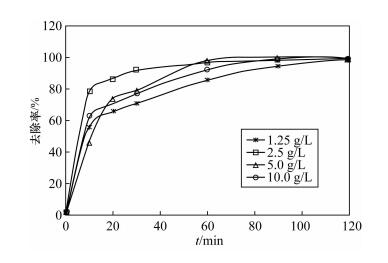
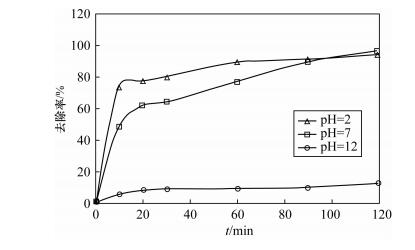
摘要: As(Ⅲ)毒性高,易迁移,且是厌氧条件下地下水中主要存在形式。纳米铁颗粒在含砷水体处理中受到广泛关注,而锌具有比铁更低的氧化还原电位且更易保存,被认为是用于氯代有机化合物还原的最佳金属,但有关纳米锌用于水体中砷的研究很少。本文研究了纳米锌吸附As(Ⅲ)的反应动力学性质和吸附As(Ⅲ)的主要影响因素。通过应用准一级动力学、准二级动力学和粒内扩散三种模型对吸附过程进行模拟,结果显示纳米锌吸附As(Ⅲ)的过程更符合二级反应动力学模型,速率常数k2为0.18 g/(mg·min),吸附量为0.47 mg/g,且去除机理以化学吸附为主。批实验结果表明,纳米锌对As(Ⅲ)吸附最佳条件为:振荡时间120 min,纳米锌投加量2.5 g/L,pH值2~7。在最佳实验条件下,纳米锌对起始浓度为0.565 mg/L As(Ⅲ)和0.568 mg/L As(Ⅴ)进行吸附试验,As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)的去除率均能达到99.5%以上,表明纳米锌对As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)都有很好的去除效果,可作为处理水体中砷的吸附材料之一。以纳米锌作为吸附材料与传统方法相比,并不需要将As(Ⅲ)预氧化成As(Ⅴ),在实际应用中可简化水处理程序,节约处理成本。Abstract: As(Ⅲ) is a highly toxic, mobile, and predominant arsenic species in anoxic groundwater.The removal of arsenic in contaminated water by using nanoscale iron particles has received extensive attention. The reduction potential and storage of Zn is lower and easier than that of Fe. Therefore, Zn is considered to be the best choice for the reduction of chlorinated organic compounds. To our knowledge, there is little research on the reduction of arsenic with nanoscale zinc in water. The objectives of this study were to investigate kinetics and impact factors by batch experiments. Pseudo-first-order, second-order kinetics and the intraparticle diffusion model were applied to simulate the sorption process. The sorption process was best fitted by the pseudo-second-order kinetic with reaction rate constants (k2) of 0.18 g/(mg·min). The adsorption capacity of nanoscale zinc for As(Ⅲ) was 0.47 mg/g. Chemical adsorption is the main mechanism of As(Ⅲ) removal by nanoscale zinc. The shaking time for optimum removal of As(Ⅲ) has been noted as 120 min for nanoscale zinc. The adsorbent dose for nanoscale zinc is 2.5 g/L. Maximum removal of As(Ⅲ) was observed in the pH range of 2-7. Over 99.5% As(Ⅲ) and As(Ⅴ) were removed within 120 min in an initial concentration of 0.565 g/L. These results suggest that nanoscale zinc particles can be used for treating As-affected groundwater that contains substantial As(Ⅲ) without preoxidation of As(Ⅲ) to As(Ⅴ). In comparison with traditional methods, the removal of As(Ⅲ) by nanoscale zinc is simple, inexpensive and has a high efficiency for application in water treatment facilities.
-
Key words:
- nanoscale zinc particles /
- As(Ⅲ) /
- adsorption /
- kinetics /
- impact factors
-

-
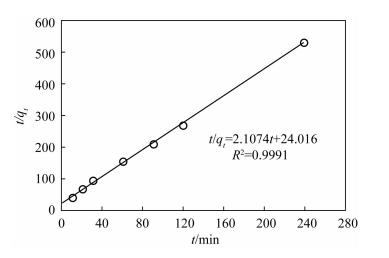
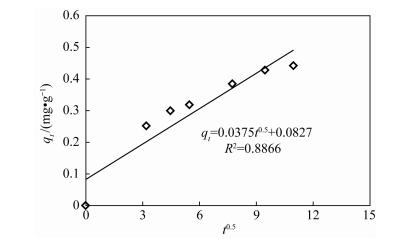
表 1 在20℃时三种动力学模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of three kinetic models at 20℃
qe实验值
(mg/g)一级动力学模型 二级动力学模型 粒内扩散模型 k1
(min-1)qe
(mg/g)R21 k2
mg/(g·min)qe
(mg/g)R22 kid
mg/(g·min)c
(mg/g)R32 0.45 0.0404 0.40 0.9562 0.1849 0.47 0.9991 0.0375 0.0827 0.8866 -
[1] Mohan D, Pittman Jr C U.Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2007, 142:1-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.006
[2] Nickson R, McArthur J, Burgess W, Ahmed K M, Ravenscroft P, Rahman M.Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater [J].Nature, 1998, 385:338.
[3] Watkims C D, de Groot P H.A perspective on the FOCUS Conference on Eastern regional ground water issues [J].Ground Water Management, 1991, 7:967-978.
[4] Das D, Chatterjee A, Mandal B K, Samanta G, Chakraborti D, Chanda B.Arsenic in ground water in six districts of West Bengal, India:The biggest arsenic callamity in the word (Part 2). Arsenic concentration in drinking water, hair, nails, urine, skin-scale, and liver tissue (biopsy) of the affected people [J].Analyst, 1995, 120:917-924. doi: 10.1039/an9952000917
[5] 肖唐付,洪冰,杨中华,杨帆.砷的水地球化学及环境效应[J].地质科技情报,2001,20(1):71-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200101016.htm
[6] 庄金陵.砷对世界地下水源的污染[J].矿产与地质, 2003, 17(2):177-178. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200302015.htm
[7] Hering J G, Chen P Y, Wilkie J A, Elimelech M.Arsenic removal from drinking water during coagulation[J].Journal of Environment Engineering, 1997, 123(8):800-807. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1997)123:8(800)
[8] Borho M, Wilderer P.Optimized removal of arsenate(Ⅲ) by adaptation of oxidation and precipitation processes to the filtration step [J].Water Science Technology, 1996, 34(9):25-31.
[9] 苑宝玲,李坤林,邓临莉,张之东.多功能高铁酸盐去除饮用水中砷的研究[J].环境科学, 2006, 27(2):281-284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200602015.htm
[10] Daus B, Wennrich R, Weiss H.Sorption materials for arsenic removal from water:A comparative study [J].Water Research, 2004, 38:2948-2954. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.003
[11] Boddu V M, Abburi K, Talbott J L, Smith E D, Haasch R.Removal of arsenic(Ⅲ) and arsenic(Ⅴ) from aqueous medium using chitosan-coated biosorbent [J].Water Research, 2008, 42:633-642. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.014
[12] Jaeshin K, Benjamin M M.Modeling a novel ion exchange process for arsenic and nitrate removal [J].Water Research, 2004, 38:2053-2062. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.01.012
[13] Sato Y, Kang M, Kamei T, Magara Y.Performance of nanofiltration for arsenic removal[J].Water Research, 2002, 36:3371-3377. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00037-4
[14] van der Bruggen B, Vandecasteele C.Removal of pollutants from surface water and groundwater by nanofiltration:Overview of possible applications in the drinking water industry [J].Environment Pollution, 2003, 122:435-445. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00308-1
[15] Gholami M M, Mokhtari M A, Aameri A, Alizadeh F M R.Application of reverse osmosis technology for arsenic removal from drinking water [J].Desalination, 2006, 200(1-3):725-727. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2006.03.504
[16] Zouboulis A I, Katsoyiannis I A.Recent advances in the bioremediation of arsenic-contaminated groundwaters [J].Environment International, 2005, 31:213-219. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2004.09.018
[17] Al Rmalli S W, Harrington C F, Ayub M, Haris P I.A biomaterial based approach for arsenic removal from water [J].Journal Environment Monitoring,2005, 7:279-282. doi: 10.1039/b500932d
[18] Mondal P, Majumder C B, Mohanty B.Removal of trivalent arsenic [As(Ⅲ)] from contaminated water by calcium chloride (CaCl2)-impregnated rice husk carbon[J].Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research,2007, 46:2550-2557. doi: 10.1021/ie060702i
[19] Li Z, Beachner R, McManama Z, Hanlie H.Sorption of arsenic by surfactant modified zeolite and kaolinite [J].Microporous Materials,2007, 105:291-297. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.03.038
[20] Streat M, Hellgardt K, Newton N L R.Hydrous ferric oxide as an adsorbent in water treatment. Part 2. Adsorption studies [J].Process Safety Environmental Protection,2008, 86:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2007.10.008
[21] Guo H, Stüben D, Berner Z.Adsorption of arsenic(Ⅲ) and arsenic(Ⅴ) from groundwater using natural siderite as the adsorbent[J].Journal of Colloid Interface Science,2007, 315:47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.06.035
[22] 汪大翠,徐新华,宋爽.工业废水中专项污染物处理手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2000:66-79.
[23] 杨杰,顾海红,赵浩,徐炎华.含砷废水处理技术研究进展[J].工业水处理,2003,23(6):14-18. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2003.23(6).14
[24] 黄园英,秦臻,刘菲.纳米铁去除饮用水中As(Ⅲ)和As(Ⅴ)[J].岩矿测试,2009,28(6):529-534. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200906007.htm
[25] 黄园英,刘丹丹,刘菲.纳米铁用于饮用水中As(Ⅲ)去除效果[J].生态环境学报,2009,18(1):83-87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200901019.htm
[26] 朱慧杰,贾永峰,吴星,王赫.负载型纳米铁吸附剂去除饮用水中As(Ⅲ)的研究[J].环境科学,2009, 30(6):1644-1648. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200906013.htm
[27] Boronina T N, Lagadic I, Sergeev G B, Klabunde K J.Activated and nonactivated forms of zinc powder:Reactivity toward chlorocarbons in water and AFM studies of surface morphologies[J].Environmental Science & Technology,1998, 32:2614-2622.
[28] Choia J H, Kim Y H.Reduction of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol with zero-valent zinc and catalyzed zinc [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 166:984-991. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.004
[29] Roberts A L, Totten L A, Arnold W A, Burris D R, Campbell T J.Reductive elimination of chlorinated ethylenes by zero-valent metals [J].Environmental Science & Technology,1996,30:2654-2659.
[30] Arnold W A, Roberts A L.Pathways of chlorinated ethylene and chlorinated acetylene reaction with Zn(0)[J].Environmental Science & Technology,1998, 32:3017-3025.
[31] Fennelly J P, Roberts A L.Reaction of 1,1,1-trichloroethane with zero-valent metals and bimetallic reductants[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1998, 32:1980-1988.
[32] Ho Y S.Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions [J].Scientometrics, 2004, 59:171-177. doi: 10.1023/B:SCIE.0000013305.99473.cf
[33] Azizian S.Kinetic models of sorption:A theoretical analysis [J].Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2004, 276:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.048
[34] Lagergren S.About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substance [J].Kungliga Svenska Vetenskap-sakademiens Handlingar, 1898, 24(4):1-39.
[35] Ho Y S.Review of second-order models for adsorption systems [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 136:681-689. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
[36] Borah D, Satokawa S, Kato S, Kojima T.Sorption of As(Ⅴ) from aqueous solution using acid modified carbon black [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009,162:1269-1277. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.015
[37] Ozdes D, Gundogdu A, Kemer B, Duran C, Senturk H B, Soylak M. Removal of Pb(Ⅱ) ions from aqueous solution by a waste mud from copper mine industry:Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009, 166:1480-1487. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.073
[38] Reed B E, Vaughan R, Jiang L. As(Ⅲ), As(Ⅴ), Hg and Pb removal by Fe-oxide impregnated activated carbon [J]. Journal of Environment Engineering, 2000, 126: 869-873. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2000)126:9(869)
[39] Mondal P, Balomajumder C, Mohanty B.A laboratory study for the treatment of arsenic, iron, and manganese bearing ground water using Fe3+ impregnated activated carbon:Effects of shaking time, pH and temperature [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 144:420-426. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.10.078
[40] 杨力.砷污染及含砷废水治理[J].有色金属加工,1999(4):27-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJF199904009.htm
[41] Pattanayak J, Mondal K, Mathew S, Lalvani S B.A paraletric evaluation of the removal of As(Ⅴ) and As(Ⅲ) by carbon-based adsorbents [J].Carbon, 2000, 38(4):589-596. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00144-X
[42] Ning R Y.Arsefiic removal by reverse osnosis [J].Desalination, 2002,143(3):237-241. doi: 10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00262-X
-




 下载:
下载: