Constructing a county-level landscape ecological restoration pattern of agricultural and forestry interlacing based on the "Source-Sink" theory: A case study of Oroqen Banner
-
摘要:
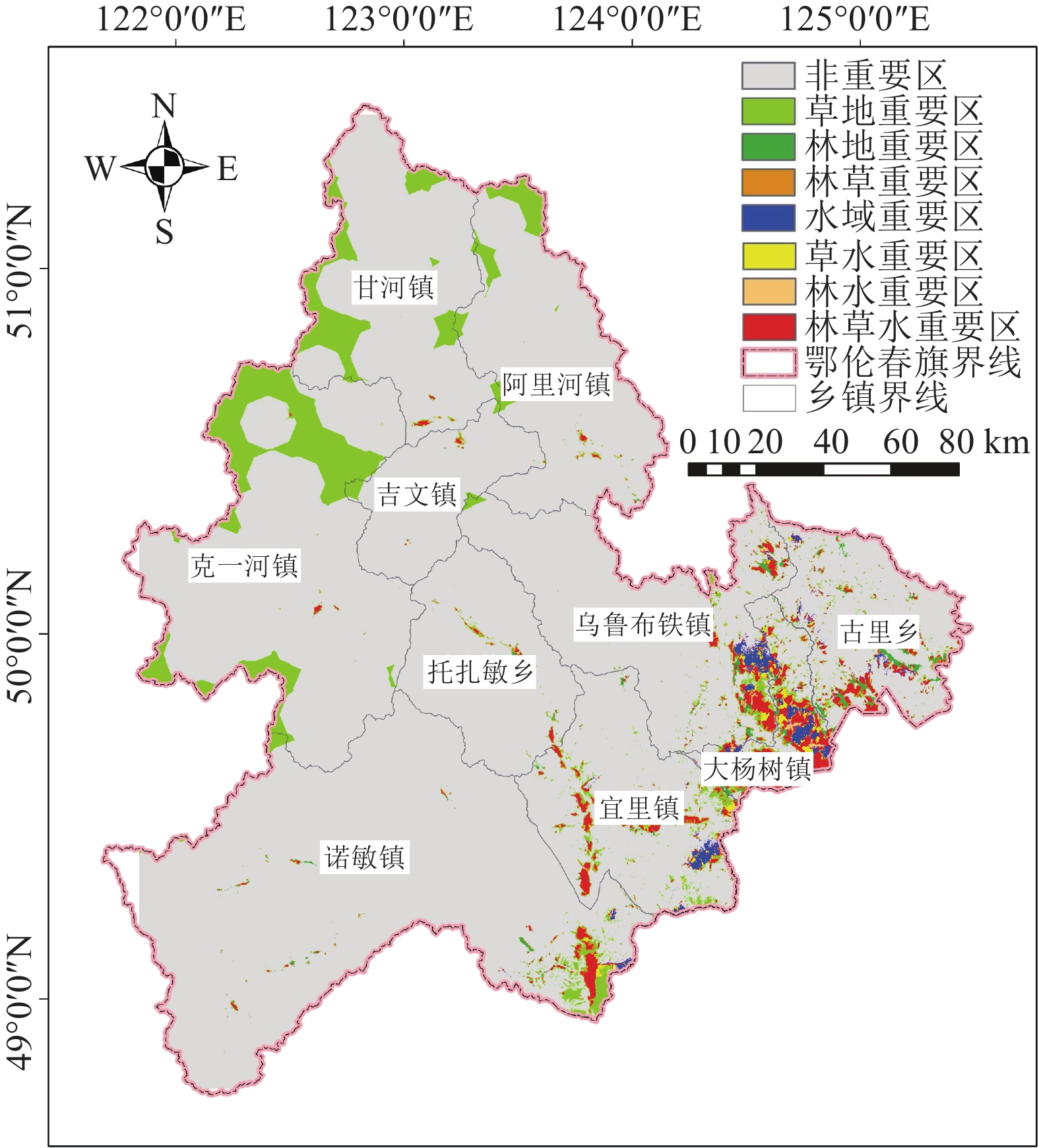
基于“源-汇”理论,运用最小累计阻力模型,通过ArcGIS软件分析计算,构建内蒙古鄂伦春旗地区景观生态修复格局。通过对区域“源”、“汇”景观识别,分析区域各类型源景观阻力面,划分出5级生态功能分区,提出修复区的空间修复次序。结果表明,鄂伦春旗地区林地源景观面积28054.2 km2,草地源景观面积2912.9 km2,水域源景观面积141.4 km2,源景观占鄂伦春旗总面积的85.58 %,生态功能及生态质量整体较好,但是旗南部均以耕地为主,南北部景观生态安全质量差异较大。针对各类修复区生态问题的严重程度及分布区域范围,修复次序为林草水修复重要区>林草修复重要区>草水修复重要区>林水修复重要区>草地修复重要区>水域修复重要区>林地修复重要区。创新提出了研究区生态保护核心区及重点生态修复区分布范围,构建了“点、线、面”三位一体的立体空间廊道和“四横二纵”的生态修复格局,为以林地和耕地为主要景观的欠发达县域地区生态环境保护体系做出示例。可广泛应用于存在较多类型生态保护区且农林混杂交错的县域地区,为区域生态保护、空间规划管制、构建生态修复格局提供参考。
Abstract:This study focuses on Oroqen Banner as the research subject and utilizes the "source-sink" theory and the Minimum Cumulative Resistance model (MCR) to establish a landscape ecological restoration pattern in the region. By employing the third national land survey vector data and conducting analysis and calculations through ArcGIS software, the study constructs and discusses the ecological restoration pattern in Oroqen Banner. The identification of source and sink landscapes, along with the analysis of resistance surfaces for different types of source landscapes, allows for the delineation of a 5-level ecological functional zoning. Moreover, a spatial restoration sequence is proposed for the restoration areas. The results indicate that the forest source landscape covers an area of 28054.2 km2 in the study area, while the grassland source landscape spans 2912.9 km2, and the water source landscape occupies 141.4 km2. These source landscapes account for 85.58% of the total area of the banner, demonstrating a generally favorable ecological function and quality. However, the southern part of the banner is primarily characterized by cultivated land, exhibiting significant disparities in landscape ecological security compared to the northern part. Based on the severity of ecological issues and the distribution range of various restoration areas, the restoration sequence is as follows: forest and grassland restoration important area > forest and grassland restoration important area > grassland and water restoration important area > forest and water restoration important area > grassland restoration important area > water restoration important area > forest restoration important area. In contrast to previous research, this study innovatively proposes the distribution range of ecological core areas and key ecological restoration areas within the study area. Additionally, it constructs a "point-line-surface three-in-one" three-dimensional spatial corridor and a "four-horizontal and two-vertical" ecological restoration pattern, serving as an exemplary instance for the ecological environment protection system in underdeveloped county-level areas dominated by forest and cultivated land. The findings have broad applicability to county-level areas with abundant ecological protection areas and a complex mixture of agricultural and forestry landscapes. Accordingly, it will provide valuable references for regional ecological protection and the establishment of ecological restoration patterns in spatial planning and control.
-

-
[1] Mangun, William R. 2010. Impact assessment for federal wildlife policy[J]. Review of Policy Research, 6(3/4): 84−94.
[2] Zhang Z, Hu B, Jiang W, et al. 2023. Construction of ecological security pattern based on ecological carrying capacity assessment 1990–2040: A case study of the Southwest Guangxi Karst−Beibu Gulf[J]. Ecological Modelling, 479: 110322. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2023.110322
[3] 陈利顶, 傅伯杰, 赵文武. 2006. “源”“汇”景观理论及其生态学意义[J]. 生态学报, 36(5): 1444−1449.
[4] 程晰钰. 2020. 基于“源-汇”景观格局理论的南四湖流域非点源污染控制研究[D]. 曲阜师范大学硕士学位论文.
[5] 程迎轩, 王红梅, 刘光盛, 等. 2016. 基于最小累计阻力模型的生态用地空间布局优化[J]. 农业工程学报, 32(16): 248−257. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.16.034
[6] 关凤峻, 刘连和 , 刘建伟, 等. 2021. 系统推进自然生态保护和治理能力建设——《全国重要生态系统保护和修复重大工程总体规划(2021—2035年)》专家笔谈[J]. 自然资源学报, (2): 290−299.
[7] 贾玉雪, 帅红, 韩龙飞. 2020. 基于“源-汇”理论的资江下游地区非点源污染风险区划[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(10): 3518−3528.
[8] 蒋贵彦, 运迎霞, 任利剑. 2019. 基于GIS-MCR高寒藏区城镇生态安全格局构建及空间发展策略——以青海省玉树市为例[J]. 现代城市研究, (4): 106−111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6000.2019.04.015
[9] 李航鹤, 马腾辉, 王坤, 等. 2020. 基于最小累积阻力模型(MCR)和空间主成分分析法(SPCA)的沛县北部生态安全格局构建研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(8): 1036−1045.
[10] 李立峰, 徐进勇, 祝文明, 等. 2020. 县域生态空间系统化修复路径与实践[J]. 规划师, 36(22): 12−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2020.22.002
[11] 李哲. 2019. 哈尔滨市水环境管控单元的划分及非点源污染应对策略[D]. 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文.
[12] 林雨菡, 杨培峰. 2021. 基于“源-汇”理论的县域国土空间生态修复分区研究——以四川省威远县为例[C]//. 中国风景园林学会2021年会论文集. 299-305.
[13] 刘健, 郭璨, 刘亚秋, 等. 2022. 平原农区适宜性-集约性耦合协调的乡村空间重构[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 39(2): 394−405.
[14] 蒙吉军, 王雅, 王晓东, 等. 2016. 基于最小累积阻力模型的贵阳市景观生态安全格局构建[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 25(7): 1052−1061. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201607006
[15] 木皓可, 汤大为, 张子灿, 等. 2019. 基于“源”-“汇”景观理论的北京浅山地区生态空间格局构建研究[C]//中国风景园林学会2019年会论文集(下册). 319−323.
[16] 那音太. 2014. 内蒙古自治区主体功能区规划体系研究[J]. 经济论坛, (06): 33−35.
[17] 田雅楠, 张梦晗, 许荡飞, 等. 2019. 基于“源-汇”理论的生态型市域景观生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态学报, 39(7): 2311−2321.
[18] 王琦, 付梦娣, 魏来, 等. 2016. 基于源-汇理论和最小累积阻力模型的城市生态安全格局构建——以安徽省宁国市为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(12): 4546−4554.
[19] 张红伟, 王占岐, 柴季, 等. 2018. 基于“源”“汇”景观理论的山区农村居民点整治适宜性评价研究——以湖北省十堰市房县为例[J]. 中国土地科学, 32(11): 65−72.
[20] 张艺璇, 位宏, 那嘉明, 等. 2021. 基于MCR模型的城市生态安全格局构建——以甘肃省平凉市为例[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 44(3): 54−62.
[21] 张玉娟, 宋娟, 赵梓涵, 等. 2022. 基于“源-汇”理论和MCR的哈尔滨市生态安全格局变化[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 45(3): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2022.03.002
[22] 张云路, 李雄, 田野. 2018. 基于景观生态学“源-汇”理论的市域尺度生态功能分区——以内蒙古通辽市为例[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 65−72.
-



 下载:
下载: