Platinum-group elements characteristics of the Hejiaya Ni-Co intrusion in the south of Lüeyang County, Shaanxi Province: Constraints on the process of sulfide melting segregation
-
摘要:
陕西何家垭镍钴含矿岩体位于南秦岭碧口地块,是近年来秦岭造山带中镍、钴战略性矿产找矿取得的重要新发现之一。该岩体由辉长岩、辉长闪长岩和少量辉石岩、角闪石岩组成,矿(化)体主要赋存在蚀变辉长岩中。基于对不同结构类型矿石铂族元素地球化学和硫化物原位硫同位素分析,探讨了岩浆性质和硫化物熔离过程。结果表明,各类矿石铂族元素(PGE)丰度均较低(3.93×10−9 ~ 87.85×10−9,平均为27.88×10−9)。铂族元素地球化学特征反映,岩体母岩浆为高镁玄武质岩浆,受后期热液作用影响较弱。铂族元素和原位硫同位素特征显示,镁铁质矿物分离结晶是引起矿床中硫演化至饱和并发生深部硫化物熔离的重要因素。矿石中Pt元素的显著亏损可能是含Pt矿物结晶导致。南秦岭略阳何家垭岩体具有较好的镍钴成矿条件和找矿潜力,有望在秦岭造山带岩浆型铜镍硫化物矿床勘查评价方面取得重大突破。
Abstract:Hejiaya Ni−Co mineralized intrusion is located in Bikou block of South Qinling. It is one of the important new discoveries of nickel, cobalt and other strategic minerals in Qinling orogenic belt in recent years.The rock mass is mainly composed of gabbro, gabbro−diorite and a small amount of pyroxenite, amphibolite, and the mineral bodies is mainly hosted by the altered gabbro.Based on the analysis of platinum−group element geochemistry and in situ sulfur isotope of sulfide in ores of different structural types, the magmatic properties and the process of sulfide melting segregation are discussed. The results showed that the abundance of platinum−group elements (PGE) was low in all kinds of ores (3.93×10−9 ~ 87.85×10−9, average 27.88×10−9). The geochemical characteristics of platinum−group elements indicate that the primary magma of the rock mass is high magnesium basaltic magma, which is weakly affected by the late hydrothermal process. The characteristics of platinum−group elements and in situ sulfur isotopes indicate that the separation and crystallization of mafic minerals is an important factor that causes sulfur evolution to saturation and deep sulfide melting segregation.The significant depletion of Pt element in the ore may be the result of Pt−containing mineral crystallization. The Lüeyang Hejiaya rock mass in South Qinling has good Ni−Co metallogenic conditions and prospecting potential, which is expected to make a major breakthrough in the exploration and evaluation of magmatic Cu−Ni sulfide deposit in Qinling orogenic belt.
-
Key words:
- mineralization /
- platinum group element /
- Ni−Cu deposit /
- Hejiaya /
- Shaanxi Province
-

-
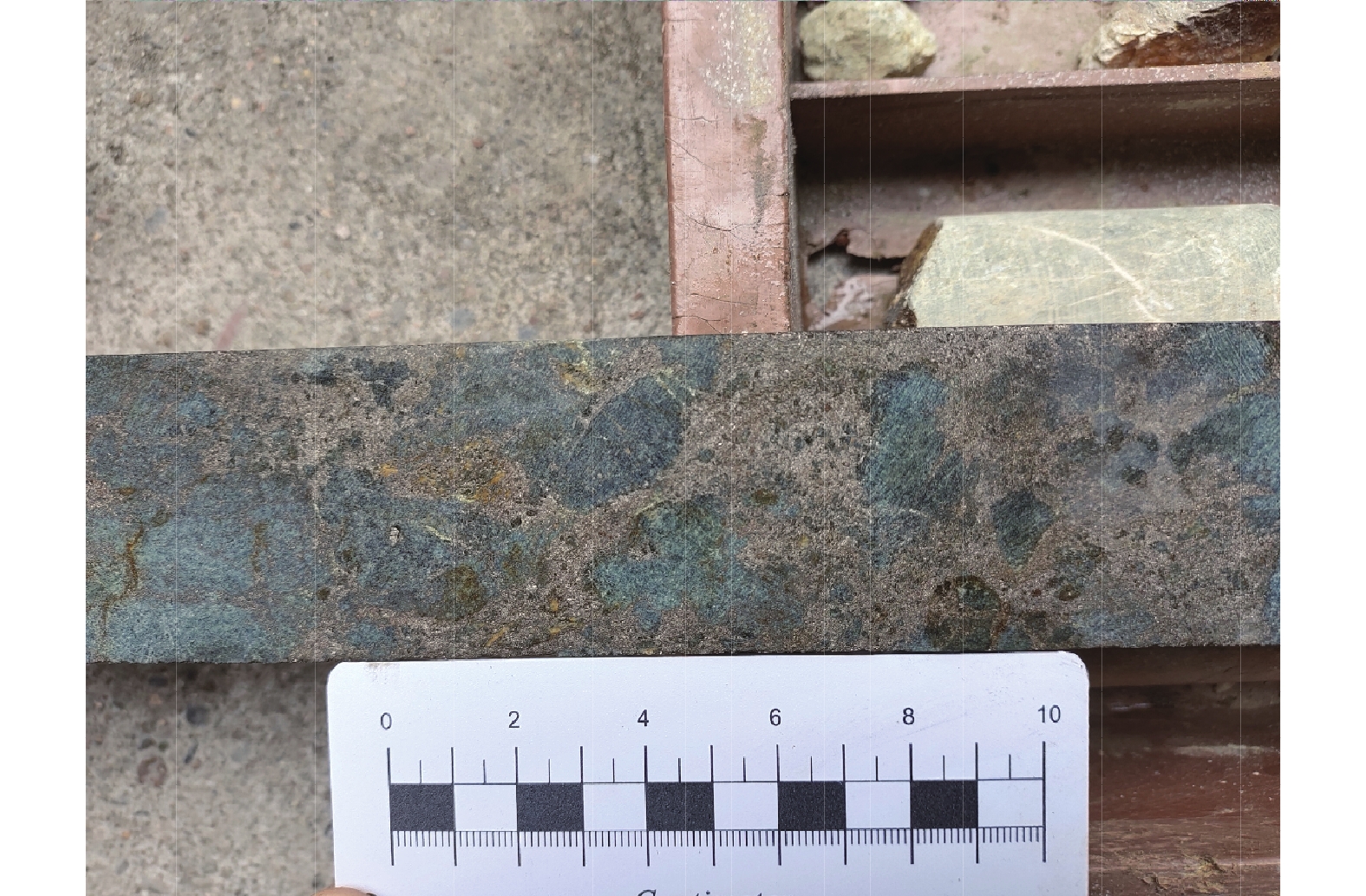
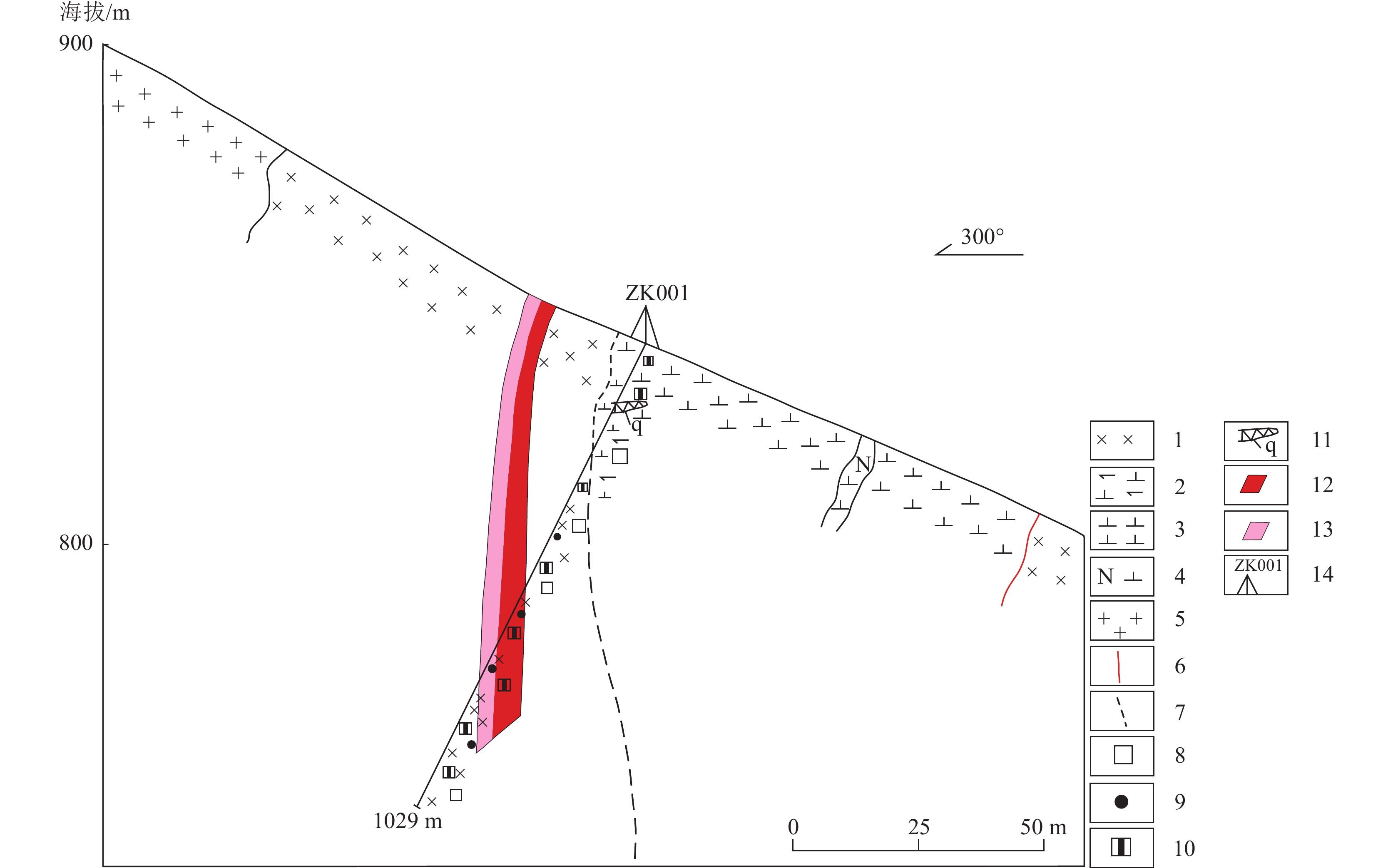
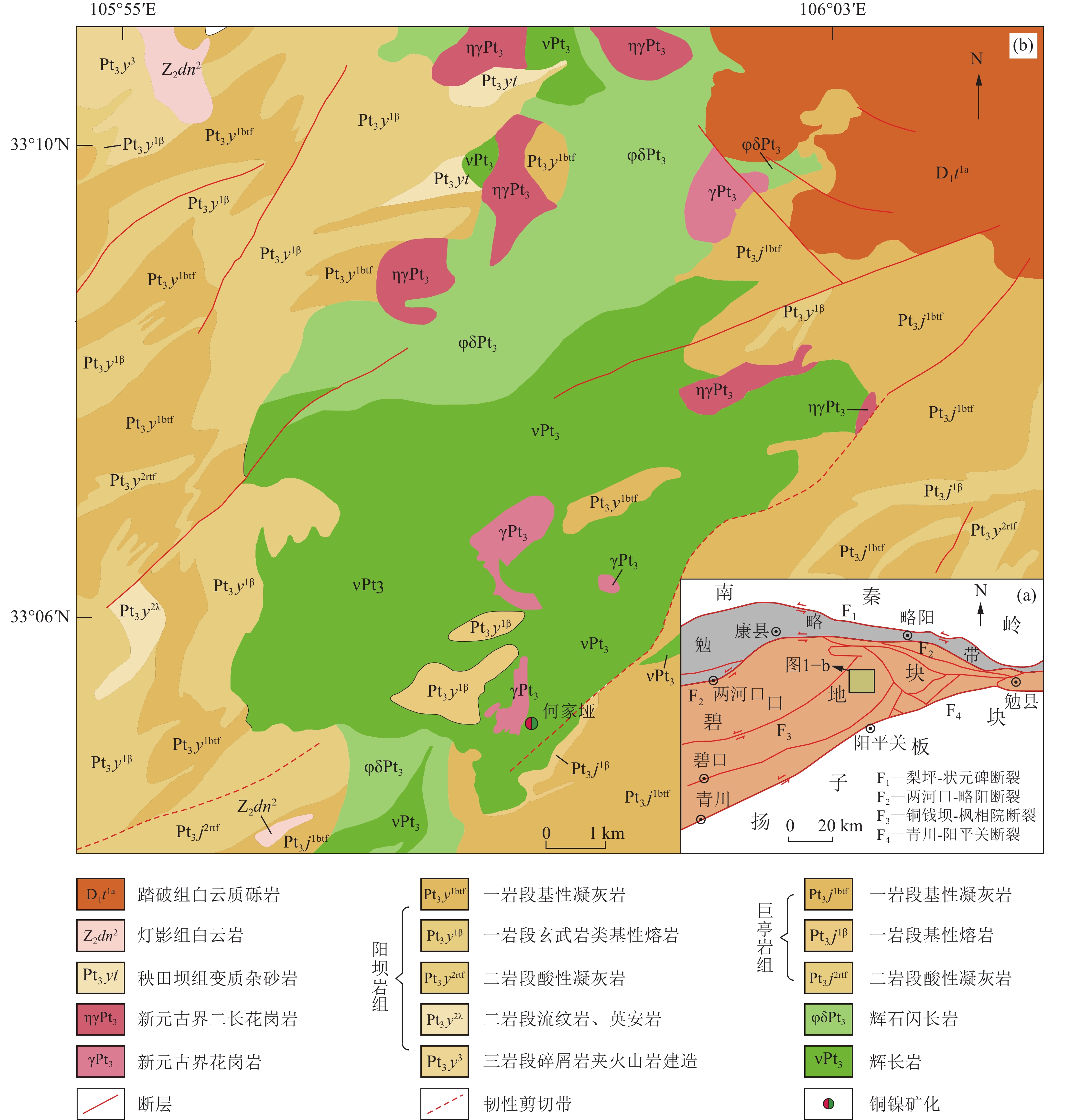
图 1 扬子北缘碧口地块东段地质构造略图(a,据Yang et al.,2015)及陕西白雀寺一带地质矿产略图(b,据张小明等,2018)
Figure 1.
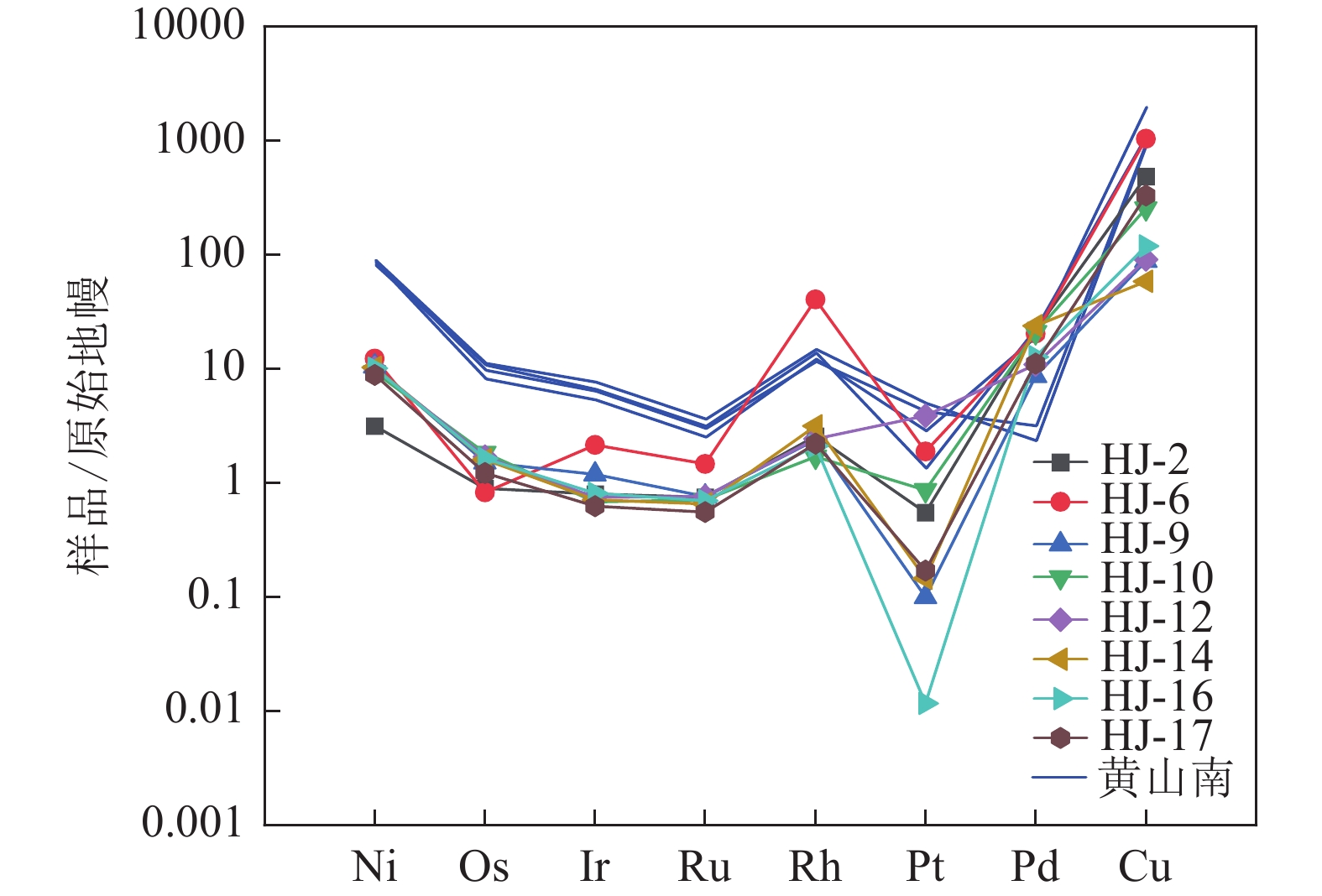
图 6 何家垭镍钴含矿岩体矿石原始地幔标准化PGE配分曲线图(黄山南数据据Mao et al.,2017)
Figure 6.
图 8 何家垭镍钴含矿岩体矿石Ni/Cu−Pd/Ir关系图解(底图据Barnes et al.,1988)
Figure 8.
表 1 何家垭镍钴含矿岩体铂族元素分析结果
Table 1. Analysis result of platinum group elements in Hejiaya Ni−Co intrusion
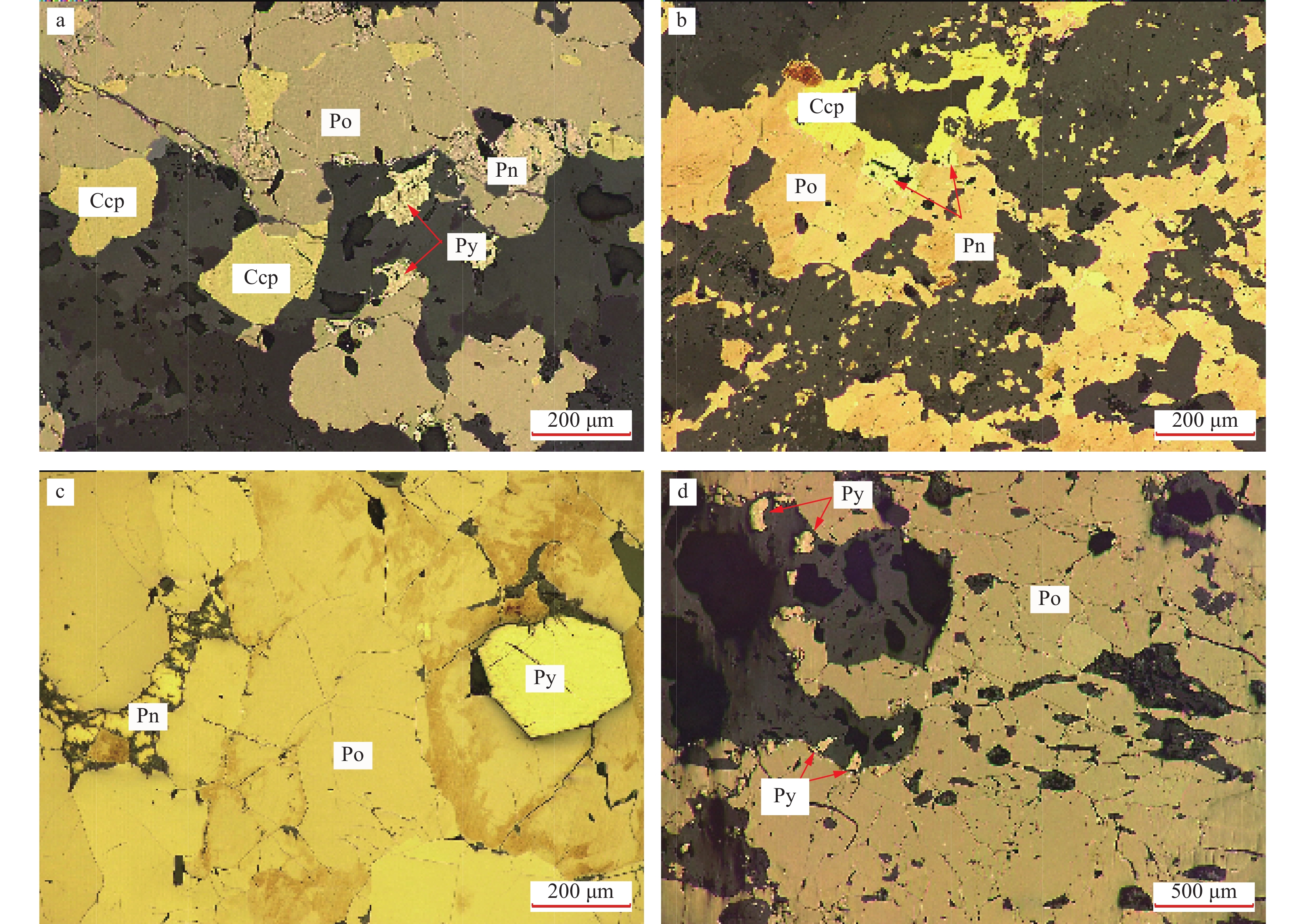
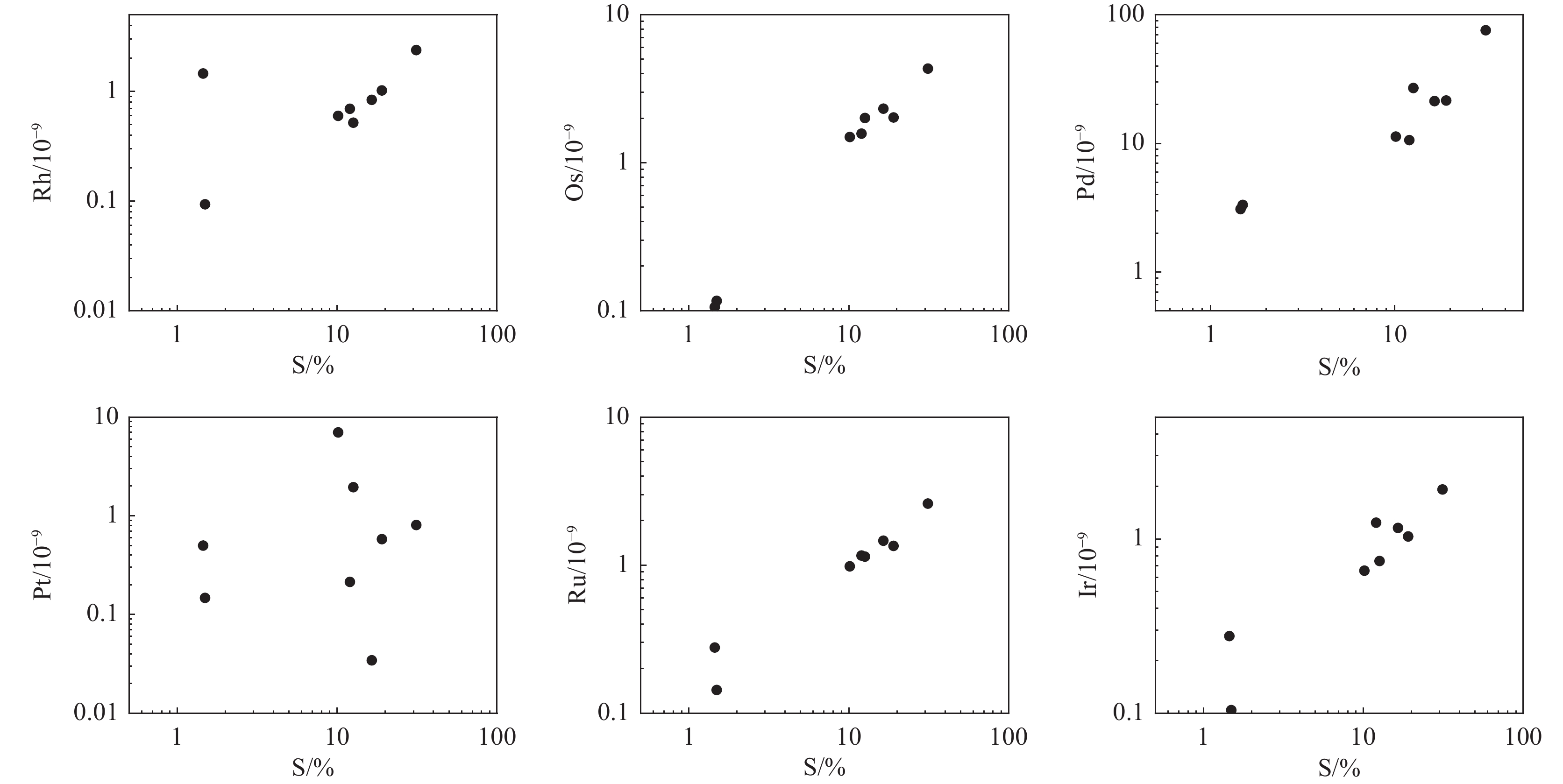
样品编号 样品岩性 Os Ir Ru Rh Pt Pd Cu Ni S ΣPGE HJ-2 星点状矿石 0.12 0.10 0.14 0.09 0.15 3.33 0.052 0.12 1.49 3.93 HJ-6 星点状矿石 0.11 0.28 0.28 1.46 0.50 3.09 0.11 0.189 1.45 5.71 HJ-9 稀疏浸染状矿石 1.57 1.24 1.16 0.70 0.21 10.6 0.076 0.71 12 15.49 HJ-10 稀疏浸染状矿石 2.01 0.75 1.14 0.52 1.95 26.9 0.23 0.667 12.62 33.31 HJ-12 稠密浸染状矿石 1.49 0.66 0.98 0.60 7.01 11.3 0.066 0.599 10.14 22.04 HJ-14 块状矿石 4.33 1.92 2.61 2.38 0.81 75.8 0.13 1.65 31.25 87.85 HJ-16 团块状矿石 2.32 1.16 1.46 0.84 0.03 21.3 0.14 0.901 16.46 27.15 HJ-17 稠密浸染状矿石 2.02 1.03 1.35 1.02 0.58 21.6 0.45 0.908 19.04 27.57 注:除Cu、Ni、S元素含量单位为10−2外,其余均为10−9 表 2 何家垭含矿岩体矿石原位硫同位素测试结果
Table 2. In situ sulfur isotope test results of Hejiaya Ni−Co intrusion
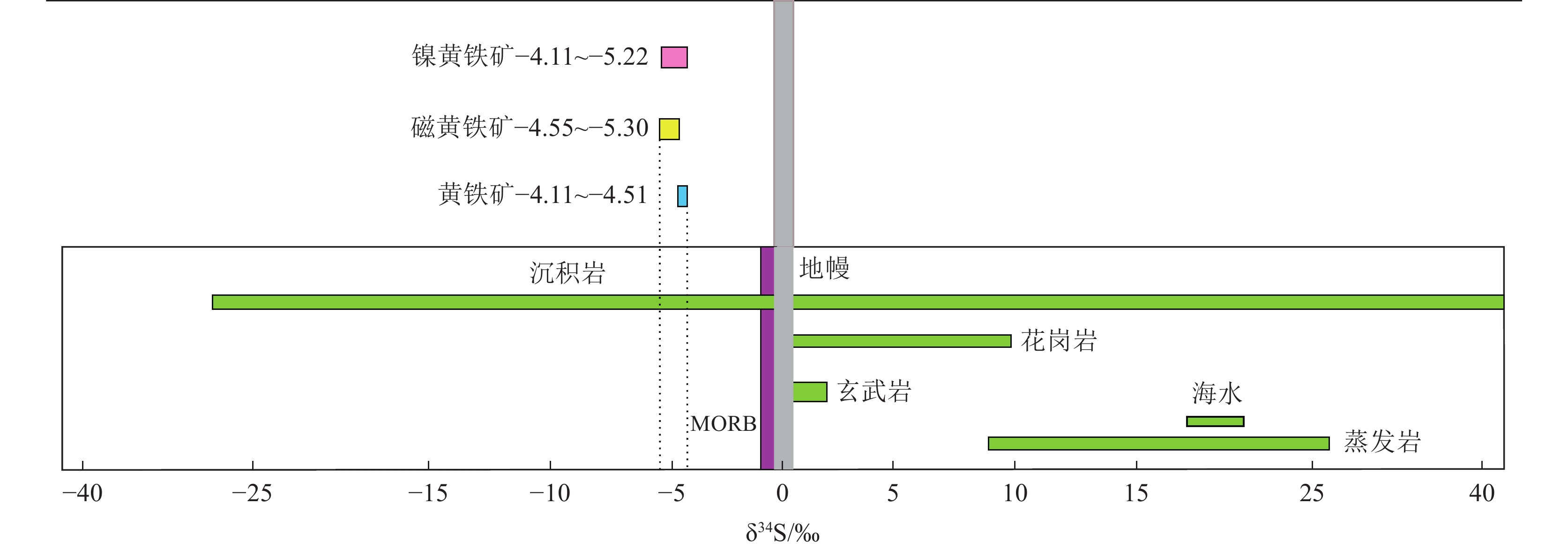
样品编号 样品类型 δ34S/‰ 样品编号 样品类型 δ34S/‰ HJ-11-1 镍黄铁矿 −4.58 HJ-17-3 黄铁矿 −4.11 HJ-11-3 镍黄铁矿 −4.57 HJ-17-5 黄铁矿 −4.32 HJ-14-1 镍黄铁矿 −4.11 HJ-11-4 磁黄铁矿 −4.80 HJ-14-4 镍黄铁矿 −5.22 HJ-14-2 磁黄铁矿 −4.52 HJ-17-7 镍黄铁矿 −4.32 HJ-14-3 磁黄铁矿 −5.26 HJ-17-8 镍黄铁矿 −4.64 HJ-14-5 磁黄铁矿 −4.77 HJ-11-2 黄铁矿 −4.19 HJ-17-2 磁黄铁矿 −5.30 HJ-11-5 黄铁矿 −4.23 HJ-17-4 磁黄铁矿 −4.55 HJ-14-6 黄铁矿 −4.42 HJ-17-6 磁黄铁矿 −4.45 HJ-17-1 黄铁矿 −4.51 -
[1] Barnes S J, Boyd R, Korneliussen A, et al. 1988. The use of mantle normalization and metal ratios in discriminating between the effects of partial melting, crystal fractionation and sulphide segregation on platinum−group elements, gold, nickel and copper: Examples from Norway[M]. Berlin: Springer Netherlands.
[2] Barnes S J, Maier W D. 1999. The fractionation of Ni, Cu, and the noble metals in silicate and sulphide liquids[J]. Geological Association Canada, Short Course Notes, 13: 69−106.
[3] Barnes S J, Naldrett A J, Gorton M P. 1985. The origin of the fractionation of platinum−group elements in terrestrial magmas[J]. Chemical Geology, 53: 303−323. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(85)90076-2
[4] Brügmann G E, Naldrett A J, Asif M, et al. 1993. Siderophile and chalcophile metals as tracers of the evolution of the Siberian trap in the Noril’sk region, Russia[J]. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta, 57: 2001−2018. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90089-F
[5] Campbell I H, Naldrelt A J. 1979. The influence of silicate: Sulfide ratios on the geochemistry of magmatic sulfides[J]. Economic Geology, 74: 1503−1506. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.74.6.1503
[6] Chaussidon M, Albarede F, Sheppard S M F. 1989. Sulphur isotope variations in the mantle from ion microprobe analyses of micro-sulphide inclusions[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 92(2): 144−156.
[7] Chen M Y, Pang C Y, Xiao M H. 1994. Characteristics of metallogensis of Jianchaling Ni−deposit[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinnica, (Z1): 138−144 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Crocket J H, Fleet M E, Stone W E. 1997. Implications of composition for experimental partitioning of platinum−group elements and gold between sulfide liquid and basalt melt: The significance of nickel content[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(19): 4139−4149. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00234-2
[9] Du W, Ling J L, Zhou W, et al. 2014. Geological characteristics and genesis of Xiarihamu nickel deposit in East Kunlun[J]. Mineral Deposits, 33(4): 713−726 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Fleet M E, Crocket J H, Stone W E. 1996. Partitioning of platinumgroup elements (Os, Ir, Ru, Pt, Pd) and gold between sulfide liquid and basalt melt[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60: 2397−2412. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00100-7
[11] Francis R D. 1990. Sulfide globules in mid−ocean ridge basalts (MORB) and the effect of oxygen abundance in Fe−S−O liquids on the ability of those liquids to partition metals from MORB and komatiitic magmas[J]. Chemical Geology, 85: 199−213. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(90)90001-N
[12] Fryer B J, Greentough J D. 1995. Search results for evidence for mantle heterogeneity from platinum−group element abundances in Indian Ocean basalts[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 29: 2329−2339.
[13] Irvine T N. 1975. Crystallization sequences in the Muskox intrusion and other layered intrusions—II. Origin of chromitite layers and similar deposits of other magmatic ores[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39: 991−1020. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(75)90043-5
[14] Keays R R, Lightfoot P C. 2010. Crustal sulfur is required to form magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposits: Evidence from chalcophile element signatures of Siberian and Deccan trap basalts[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 45: 241−257. doi: 10.1007/s00126-009-0271-1
[15] Keays R R. 1995. The role of komatiitic and picritic magmatism and S−saturation in the formation of ore deposits[J]. Lithos, 34: 1−18. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(95)90003-9
[16] Lehmann J, Arndt N T, Windley B, et al. 2007. Field relationships and geochemical constraints on the emplacement of the Jinchuan intrusion and its Ni−Cu−PGE sulfide deposit, Gansu, China[J]. Economic Geology, 102(1): 75−94. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.1.75
[17] Maier W D, Barnes S J, De Klerk W J, et al. 1996. Cu/Pd and Cu/Pt of silicate rocks in the Bushveld Complex: Implications for platinum−group element exploration[J]. Economic Geology, 91(6): 1151−1158. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.91.6.1151
[18] Maier W D, Barnes S J, De Waal S A. 1998. Exploration for magmatic Ni−Cu−PGE sulphide deposits: A review of recent advances in the use of geochemical tools, and their application to some south African ores[J]. South African Journal of Geology, 101(3): 237−253.
[19] Maier W D, Barnes S J, Gartz V, et al. 2003. Pt−Pd reefs in magnetitites of the Stella layered intrusion, South Africa: A world of new exploration opportunities for platinum group elements[J]. Geology, 31(10): 885−888. doi: 10.1130/G19746.1
[20] Mao Y J, Qin K Z, Barnes S J, et al. 2017. Genesis of the Huangshannan high−Ni tenor magmatic sulfide deposit in the Eastern Tianshan, northwest China: Constraints from PGE geochemistry and Os–S isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 591−606. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.05.015
[21] Munteanu M, Wilson A H, Yao Y, et al. 2011. The Lengshuiqing Ni−Cu deposit, Sichuan, Southeastern China: Ore characteristics and genesis[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 49(6): 1599−1626. doi: 10.3749/canmin.49.6.1599
[22] Naldrett A J. 1999. World−class Ni−Cu−PGE deposits: Key factors in their genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 34: 227−240. doi: 10.1007/s001260050200
[23] Naldrett A J. 2004. Magma sulfide deposits: Geology, geochemistry and exploration[M]. Berlin: Springer.
[24] Patten C, Barnes S J, Mathez E A, et al. 2013. Partition coefficients of chalcophile elements between sulfide and silicate melts and the early crystallization history of sulfide liquid: LA−ICP−MS analysis of MORB sulfide droplets[J]. Chemical Geology, 358: 170−188. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.08.040
[25] Pei X Z, Zhang G W, Lai S C, et al. 2002. Main geological features of the Mianlue tectonic belt on the southern margin of the West Qinling[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(8/9): 486−494 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Qi L, Gao J F, Huang X W, et al. 2011. An improved digestion technique for determination of platinum group elements in geological samples[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 26: 1900−1904. doi: 10.1039/c1ja10114e
[27] Qi L, Gao J F, Zhou M F, et al. 2013. The design of Re−usable carius tubes for the determination of rhenium, osmium and platinum−group elements in geological samples[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 37: 345−451. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908x.2012.00211.x
[28] Qi L, Zhou M F, Gao J F, et al. 2010. An improved carius tube technique for determination of low concentrations of Re and Os in pyrites[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 25: 585−589. doi: 10.1039/b919016c
[29] Ripley E M. 1984. Application of stable isotopic studies to problems of magmatic sulfide ore genesis with special reference to the Duluth Complex, Minnesota[C]//Geology and Metallogeny of Copper Deposits: Proceedings of the Copper Symposium 27th International Geological Congress, Moscow, 1984. Berlin Heidelberg Springer: 25−42.
[30] Roeder P L, Jamieson H E. 1992. Composition of chromite and co−existing Pt−Fe alloy at magmatic temperatures[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 39(3): 419−426. doi: 10.1080/08120099208728034
[31] Song X Y, Hu R Z, Chen L M. 2009. Geochemical natures of copper, nickel and PGE and their significance for the study of origin and evolution of mantle−derived magmas and magmatic sulfide deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(4): 287−305 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Su B X, Qin K Z, Jiang S Y, et al. 2023. Mineralization regularity, scientific issues, prospecting technology and research prospect of Co−Ni deposits in China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 39(4): 968−980 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.04.02
[33] Tang Z L, Li X H. 2006. Small intrusions forming large deposits in two types of magma[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(S1): 35−38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Wang R T, He Y, Wang D S, et al. 2003. The study on ore−forming process of Jianchaling large cobalt−bearing nickel ore deposit[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 32(2): 185−190 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Wang R T, Mao J W, Ren X H, et al. 2005. Isotopic geochemical evidence of rock−forming and ore−forming processes in the Jianchaling sulfide nickel deposit, Lueyang County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 25(6): 513−519 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Wang R T. 2002. The comparative study on mineralization of Jianchaling and Jinchuan nickel−copper sulfide deposits[D]. PhD thesis of Northwest University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Yang C. 2011. The tectonic evolution of Bikou terrane[D]. Master Thesis of Northwest University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yang L Q, Deng J, Qiu K F, et al. 2015. Magma mixing and crust−mantle interaction in the Triassic monzogranites of Bikou Terrane, central China: Constraints from petrology, geochemistry, and zircon U−Pb−Hf isotopic systematics[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 320−341. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.023
[39] Yang Y J, Han X, Bian X W, et al. 2020. An analysis of sedimentary environment and prototype basin of Lueyang Group in the Mian−Lue−Ning triangle area, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 39(10): 1549−1560 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Yang Y J, Yu H B, You J, et al. 2018. Characteristics and tectonic significance of the back−arc CFB volcanic rock in the Mianlue−Ning triangle area, Shaanxi[J]. Mineral Exploration, 9(9): 1768−1778 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Yang Y, Wang M Z, Zhang J A, et al. 2022. The discovery and prospecting direction of Cu−Ni ores in the Baiquesi basic complex in south Lüeyang County of Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 58(4): 756−766 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] You J, Zhang X M, Yang Y J, et al. 2018. Zircon U−Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Baiquesi−Shiwengzi bimodal intrusive rocks in Lueyang, and their significance[J]. Mineral Exploration, 9(12): 2365−2377 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhang X M, Wu Y Z, Zeng Z C, et al. 2022. Discovery of a new nickel−cobalt mineralization body of the basic complex in Mian−Lue−Ning area, Shaanxi[J]. Geology in China, 9(2): 669−670 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Zhang X M, You J, Yang Y J. 2018. Analysis of iron−nickel metallogenic conditions of Baiquesi basic complex in Lueyang County, southern Shaanxi Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 9(9): 1643−1653 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] 陈民扬, 庞春勇, 肖孟华. 1994. 煎茶岭镍矿床成矿作用特征[J]. 地球学报, (Z1): 138−144.
[46] 杜玮, 凌锦兰, 周伟, 等. 2014. 东昆仑夏日哈木镍矿床地质特征与成 因[J]. 矿床地质, 33(4): 713−726. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2014.04.004
[47] 裴先治, 张国伟, 赖绍聪, 等. 2002. 西秦岭南缘勉略构造带主要地质特征[J]. 地质通报, 21(8/9): 486−494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.08.006
[48] 宋谢炎, 胡瑞忠, 陈列锰. 2009. 铜、镍、铂族元素地球化学性质及其在幔源岩浆起源、演化和岩浆硫化物矿床研究中的意义[J]. 地学前缘, 16(4): 287−305. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.04.028
[49] 苏本勋, 秦克章, 蒋少涌, 等. 2023. 我国钴镍矿床的成矿规律、科学问题、勘查技术瓶颈与研究展望[J]. 岩石学报, 39(4): 968−980. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.04.02
[50] 汤中立, 李小虎. 2006. 两类岩浆的小岩体成大矿[J]. 矿床地质, 25(S1): 35−38.
[51] 王瑞廷, 赫英, 王东生, 等. 2003. 煎茶岭含钴硫化镍矿床成矿作用研 究[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 32(2): 185−190.
[52] 王瑞廷, 毛景文, 任小华, 等. 2005. 煎茶岭硫化镍矿床成岩成矿作用的同位素地球化学证据[J]. 地球学报, 25(6): 513−519. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2005.06.005
[53] 王瑞廷. 2002. 煎茶岭与金川镍矿床成矿作用比较研究[D]. 西北大学博士学位论文.
[54] 杨晨. 2011. 碧口地块构造演化[D]. 西北大学硕士学位论文.
[55] 杨渊, 王明志, 张瑾爱, 等. 2022. 陕西略阳南部白雀寺基性杂岩体何家垭铜镍矿的发现及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 58(4): 756−766. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2022.04.005
[56] 杨运军, 韩旭, 边小卫, 等. 2020. 陕西勉略宁三角区略阳群沉积环境及原型盆地分析[J]. 地质通报, 39(10): 1549−1560. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.10.006
[57] 杨运军, 于恒彬, 游军, 等. 2018. 陕西勉略宁三角区弧后裂解型火山岩特征及其构造意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 9(9): 1768−1778. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2018.09.016
[58] 游军, 张小明, 杨运军, 等. 2018. 略阳白雀寺-石瓮子双峰式侵入岩锆石U−Pb定年、地球化学特征及意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 9(12): 2365−2377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2018.12.010
[59] 张小明, 吴应忠, 曾忠诚, 等. 2022. 陕西勉略宁地区基性杂岩体中新发现镍钴矿化体[J]. 中国地质, 9(2): 669−670.
[60] 张小明, 游军, 杨运军. 2018. 陕南略阳县白雀寺基性杂岩铁-镍成矿条件分析[J]. 矿产勘查, 9(9): 1643−1653. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2018.09.004
-



 下载:
下载: