Stable Isotope Characteristics and Geological Significance of Acid Wastewater in a Stone Coal Mining Area
-
摘要:
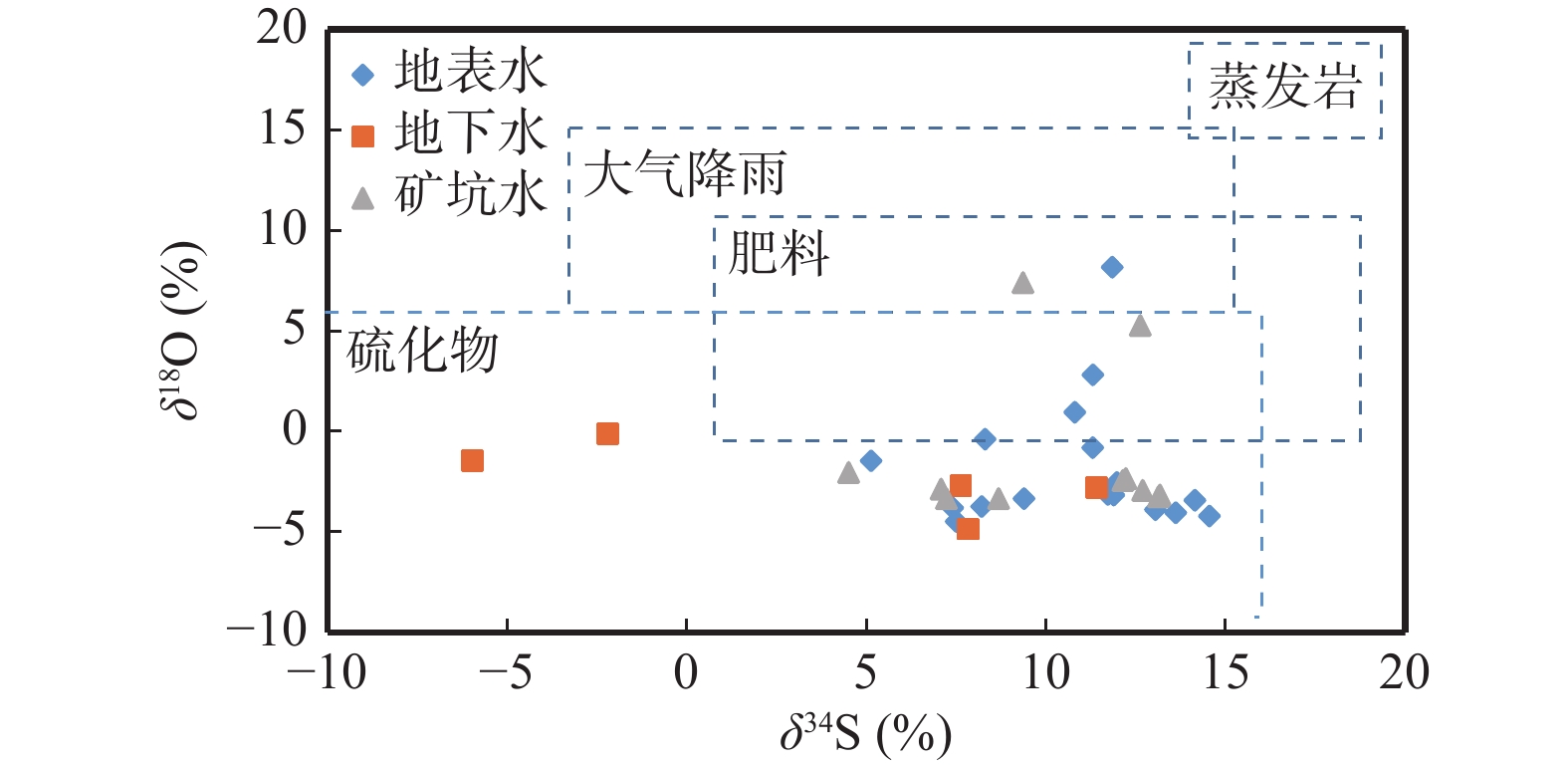
紫阳石煤矿区水体硫酸盐浓度超标,污染日趋严重,识别硫酸盐的来源对于矿区水体硫酸盐污染防治和饮用水安全保障极为重要。笔者应用硫酸盐S、O同位素示踪矿区酸性废水对地下水的污染。紫阳石煤矿区酸性废水中硫酸根离子浓度高而pH值低,其硫酸盐S、O同位素显著富集轻同位素,表明石煤中黄铁矿开采后氧化是其产生的主要机制。通过IsoSource质量守恒模型,计算了石煤矿区酸性废水对地下水硫酸盐的贡献率约为36.5%。应用多种同位素综合识别酸性废水硫酸盐来源及其对地下水影响的定量研究提供了一种新方法,为矿山开发与生态环境保护修复提供了科学依据。
Abstract:The sulfate concentration of the water body in the Ziyang stone coal mining area exceeds the standard, and the pollution is becoming more and more serious. Identifying the source of sulfate pollution is extremely important for the prevention of pollution and the guarantee of drinking water safety. The production mechanism of acid wastewater was analyzed and identified using sulfate and oxygen stable isotopes. The results show that the sulfate produced by the sulfide oxidation of stone coal was the main source of sulfate in acid wastewater. Calculated by the IsoSource mass conservation model, the contribution rate of acid wastewater to groundwater sulfate is about 36.5%. The application of multiple isotopes provides a new approach for the comprehensive identification of sulfate sources in acid wastewater and the quantitative study of its impacts on groundwater and provides a scientific basis for mine development and ecological environmental protection and restoration.
-
Key words:
- sulfate /
- isotope /
- acid wastewater /
- stone coal /
- source
-

-
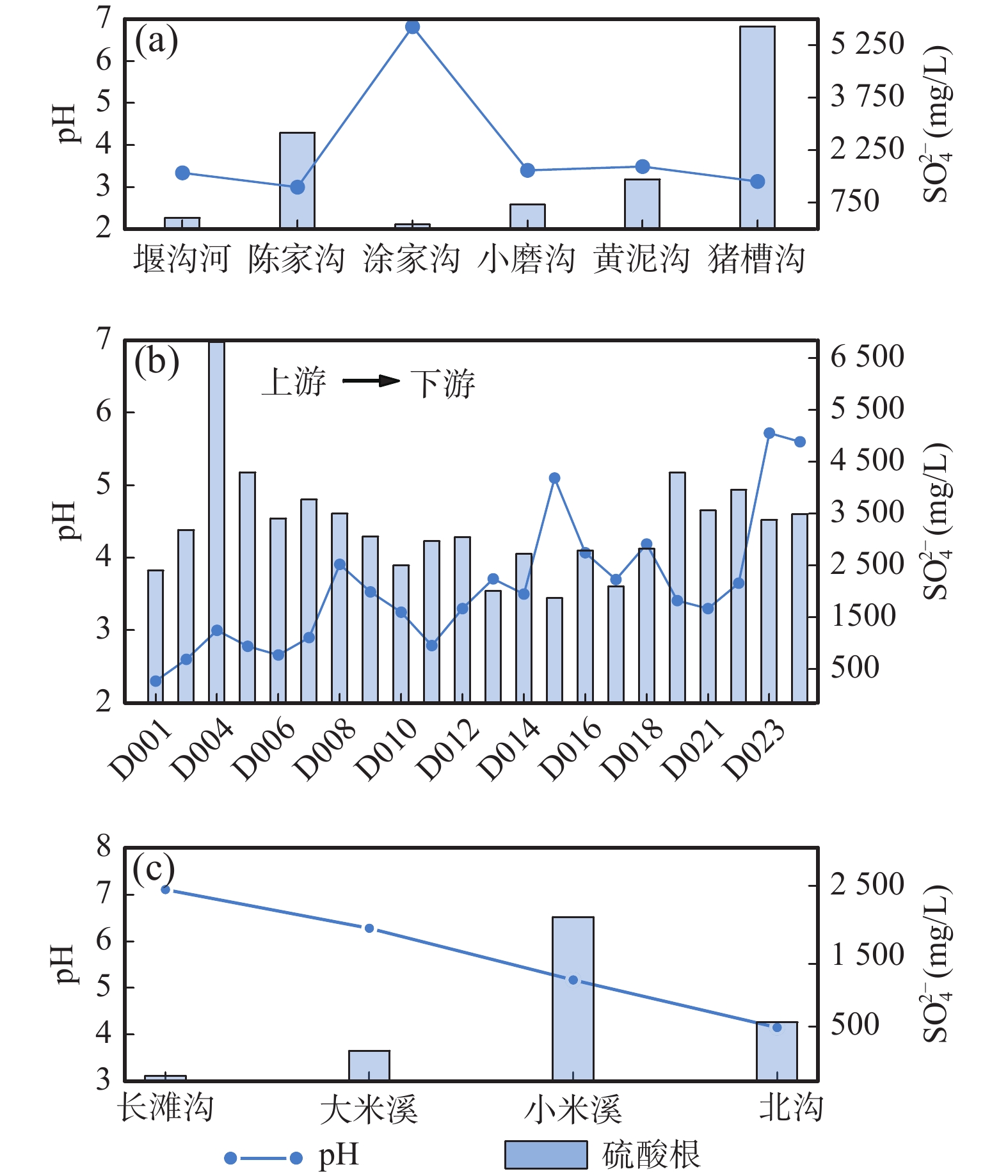
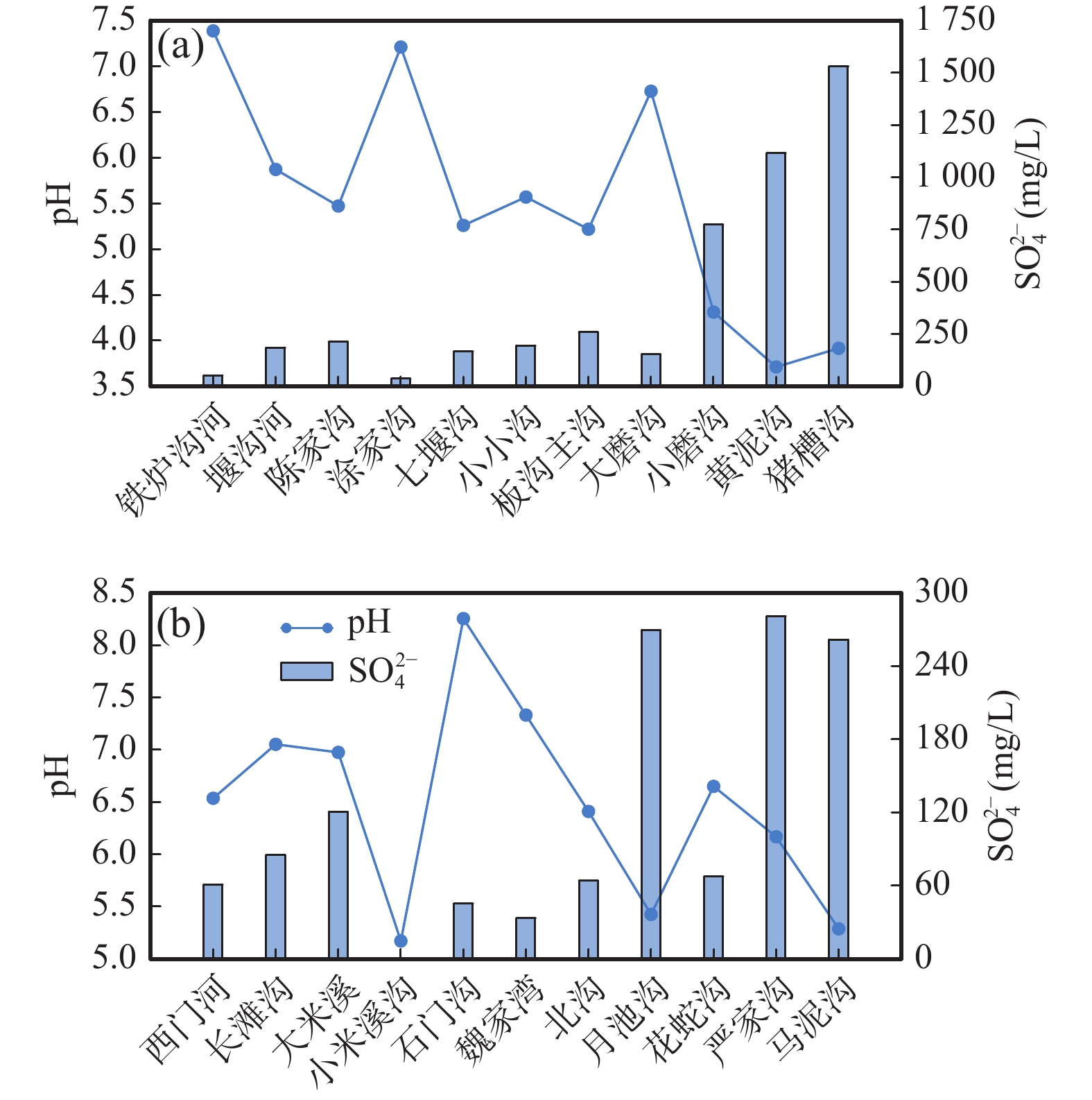
表 1 紫阳石煤矿区水样化学组成及同位素组成
Table 1. The chemical and isotope composition of water samples in Ziyang stone coal mining area
样品编号 取样点位置 样品类型 pH SO42−(mg/L) δ18O (‰) δ34S (‰) δD (‰) δ18O (‰) ZK-1 废渣坝 地下水 3.14 3870 −3.18 12.62 −53.11 −10.05 D001 米溪梁 地表水 2.3 2550 −3.42 14.14 −61.05 −9.88 D002 米溪梁 地表水 2.6 3336.7 2.82 11.30 −51.51 −8.45 D004 米溪梁 地表水 3 6963 −4.21 14.55 −61.07 −9.92 D005 米溪梁 地表水 2.78 4450 −3.73 8.21 −60.80 −9.85 D006 米溪梁 地表水 2.66 3560 −4.48 7.50 −60.51 −9.74 D007 米溪梁 地表水 2.9 3920 −4.04 13.61 −61.09 −9.76 D008 米溪梁 地表水 3.91 3650 0.96 10.80 −59.79 −9.51 D009 米溪梁 地表水 3.53 3210 −2.54 11.97 −61.33 −9.69 D010 米溪梁 地表水 3.25 2650 −3.34 9.39 −60.90 −9.59 D011 米溪梁 矿坑水 2.79 3117 −3.16 13.17 −60.53 −9.79 D012 米溪梁 矿坑水 3.3 3200 −3.25 13.13 −59.60 −9.65 D013 米溪梁 矿坑水 3.71 2160 −2.34 12.22 −58.94 −9.46 D014 米溪梁 矿坑水 3.5 2870 −2.44 12.14 −58.63 −9.39 D015 米溪梁 矿坑水 5.1 2020 −3.33 8.68 −59.60 −9.55 D016 米溪梁 矿坑水 4.07 2940 −2.93 12.69 −58.05 −9.22 D017 米溪梁 地下水 3.7 2250 −4.86 7.83 −58.45 −9.34 D018 米溪梁 地下水 4.19 2970 −2.69 7.63 −60.62 −9.55 D019 米溪梁 地下水 3.41 4440 −2.81 11.42 −60.21 −9.42 D021 米溪梁 矿坑水 3.3 3710 −3.34 7.23 −58.54 −9.68 D022 米溪梁 矿坑水 3.65 4110 −2.87 7.08 −58.70 −9.67 D023 米溪梁 矿坑水 5.72 3530 7.41 9.36 −63.17 −10.13 D024 米溪梁 地下水 5.6 3640 −1.45 −5.97 −61.30 −9.85 D025 大磨沟 地表水 6.05 59.9 −1.46 5.13 −62.01 −9.85 续表1 样品编号 取样点位置 样品类型 pH SO42−(mg/L) δ18O (‰) δ34S (‰) δD (‰) δ18O (‰) D026 大磨沟 矿坑水 / / −2.04 4.50 −58.14 −9.31 D027 小磨沟 矿坑水 4.26 223 5.28 12.62 −60.96 −9.80 D028 小磨沟 地表水 6.24 25.8 −3.13 11.72 −62.66 −9.81 D029 小米溪沟 地下水 5.95 254 −0.11 −2.20 −61.57 −9.97 D030 月池沟 地表水 4.16 1500 −3.89 13.04 −59.60 −9.72 D031 月池沟 地表水 / / −0.80 11.30 −61.21 −9.96 D032 小米溪沟 地表水 3.14 3870 −3.17 11.89 −58.30 −9.54 D033 小米溪沟 地表水 3.18 3320 8.17 11.84 −60.79 −9.87 D037 铁炉沟 地表水 6.34 140 −0.38 8.30 −67.33 −10.78 D038 铁炉沟 地表水 6.52 69.7 −3.80 7.40 −63.44 −10.05 YS01 蒿坪镇 大气降水 6.19 319 / / −10.44 −4.30 YS02 陈家沟 雨水 6.67 305 / / −9.21 −4.17 YS03 陈家沟 雨水 5.7 114 / / −10.46 −4.54 YS04 陈家沟 雨水 6.09 49.1 / / −15.09 −5.17 YS05 大米溪沟 雨水 3.34 319 / / −20.76 −5.97 YS06 大米溪沟 雨水 7.19 29.7 / / −23.18 −6.46 YS07 大米溪沟 雨水 4.81 113 / / −23.78 −6.42 YS08 大米溪沟 雨水 / / / / −20.56 −5.97 表 2 不同来源硫酸盐含量及同位素组成
Table 2. Sulphate content and isotopic composition of different sources
类型 

备注 降雨 −3~+9 +7~+17 顾慰祖,2011;
邱述兰,2012肥料 10.5±9.2 6.7±5.5 Laura et al.,2004 硫化物 <+18 <+5 Qibo et al.,2016 石膏(蒸发岩) +15~+25 +15~+20 顾慰祖等,2000 -
[1] 丁坤, 王瑞廷, 刘凯, 等. 南秦岭柞水-山阳矿集区龙头沟金矿床硫化物微量元素和硫同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(5): 969-980.
DING Kun, WANG Ruiting, LIU Kai, et al. Sulfide trace elements and sulfur isotope geochemistry of the Longtougou gold deposit, Zhashui - Shanyang ore district, South Qinling[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57( 5) : 0969 - 0980.
[2] 顾慰祖. 同位素水文学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011
GU Weizu. Isotope hydrology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011
[3] 顾慰祖, 林曾平, 费光灿, 等. 环境同位素硫在大同南寒武-奥陶系地下水资源研究中的应用[J]. 水科学进展, 2000, 11(01): 14-20
GU Weizu, LIN Zengping, FEI Guangchan, et al. The use of environmental sulphur isotopes in the study of the Cambrian-Ordovician aquifer system in the south of Datong[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2000, 11(01): 14-20.
[4] 胡德银, 张宏德, 王化锋等. 浅议安康石煤地质特征及“十二五”开发设想[J]. 科技信息, 2011, (23): 45-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2011.23.030
HU Deyin, ZHANG Hongde, WANG Huafeng, et al. Yee Shallow AnKang Stone Coal Geological Features and " Second Five " Development Vision[J], SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY INFORMATION, 2011, (23): 45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2011.23.030
[5] 庞振甲, 成欢, 冀月飞. 陕西省略阳县陶家沟地区地质地球物理特征及找矿预测[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(1): 93-100
PANG Zhenjia, CHENG Huan, JI Yuefei. Geophysical Characteristics and Prospecting Prediction of Taojiagou Area in Lueyang County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(1): 93-100.
[6] 邱述兰. 利用多同位素($ \delta {}^{34}{\text{S}} $, $ \delta {}^{15}{\text{N}} $, $ {}^{87}{\text{Sr/}}{}^{86}{\text{Sr}} $和$ \delta {}^{13}{{\text{C}}_{DIC}} $)方法示踪岩溶农业区地下水中硝酸盐和硫酸盐的污染[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2012
QIU Shulan. Use of multiple environmental isotopes($ \delta {}^{34}{\text{S}} $, $ \delta {}^{15}{\text{N}} $, $ {}^{87}{\text{Sr/}}{}^{86}{\text{Sr}} $and $ \delta {}^{13}{{\text{C}}_{DIC}} $)to trace sulfate and nitrate contaminations of karst groundwater in an agricultural area-A case from Wingmuguan Subterranean Stream System[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2012
[7] 徐友宁, 张江华, 何芳, 等. 西北地区矿山地质环境调查与防治研究[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 129-139
XU Youning, ZHANG Jianghua, HE Fang, et al. Investigation and Preventive Research of Mine Geological Environment in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 129-139.
[8] 张俊, 尹立河, 顾小凡, 等. 同位素水化学指示的新疆孔雀河流域地下水与地表水关系[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(1): 185-195
ZHANG Jun, YIN Lihe, GU Xiaofan, et al. Study on the Relationship Between Groundwater and Surface Water in Xinjiang Kongque River Basin Using Isotopes and Hydrochemistry method[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(1): 185-195.
[9] 张卫国, 侯恩科, 李军, 等. 陕南石煤及煤灰中磷元素的迁移规律[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2021, 41(02): 316-322
ZHANG Weiguo, HOU Enke, LI Jun, et al. Migration law of Phosphorus in stone coal and coal ash in southern Shaanxi province[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2021, 41( 2): 316-322.
[10] 张亚丽, 张志敏, 张继军, 等. 安康西部农田土壤硒形态及农作物富硒特征[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(3): 229-235
ZHANG Yali, ZHANG Zhimin, ZHANG Jijun, et al. Soil Selenium Speciation in Cropland of Western Ankang and the Characteristics of Crop Selenium Enrichment[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(3): 229-235.
[11] Balci N, Iii W, Mayer B, et al. Oxygen and sulfur isotope systematics of sulfate produced by bacterial and abiotic oxidation of pyrite[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(15), 3796-3811. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.017
[12] Banfield J F, Nealson K H, Lovley D R. Geomicrobiology: Interactions between microbes and minerals[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1998, 62(5), 725-726.
[13] Bottrell S, Tellam J, Bartlett R, et al. Isotopic composition of sulfate as a tracer of natural and anthropogenic influences on groundwater geochemistry in an urban sandstone aquifer, Birmingham, UK[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23(8), 2382-2394. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.03.012
[14] Everdingen R O V, Krouse H R. Isotope composition of sulphates generated by bacterial and abiological oxidation[J]. Nature, 1985, 315(6018): 395-396. doi: 10.1038/315395a0
[15] Jezierski P, Szynkiewicz A, Jedrysek M O. Natural and Anthropogenic Origin Sulphate in an Mountainous Groundwater System: S and O Isotope Evidences[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 2006, 173(1/4): 81-101.
[16] Laura V . Fertilizer characterization: isotopic data (N, S, O, C, and Sr). [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(12): 3254. DOI:doi:10.1021/es0348187.
[17] Lewis J S , Krouse H R . Isotopic composition of sulfur and sulfate produced by oxidation of FeS[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1969, 5(6): 425-428.
[18] Mingyu W , Sheng H , Bianfang C , et al. A review of processing technologies for vanadium extraction from stone coal[J]. Mineral Processing & Extractive Metallurgy, 2018: 1-9.
[19] Qibo H , Xiaoqun Q , Qiyong Y , et al. Identification of dissolved sulfate sources and the role of sulfuric acid in carbonate weathering using δ13CDIC and δ34S in karst area, northern China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4873-x
[20] Schippers A , Sand W . Bacterial Leaching of Metal Sulfides Proceeds by Two Indirect Mechanisms via Thiosulfate or via Polysulfides and Sulfur[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(1): 319.
[21] Stempvoort D R V, Krouse H R . Controls of δ18O in sulphate: Review of experimental data and application to specific environments[J]. Environmental Geochemistry of Sulfide Oxidation, 1994.
[22] Taylor B E , Wheeler M C , Nordstrom D K . Isotope composition of sulphate in acid mine drainage as measure of bacterial oxidation[J]. Nature, 1984, 308(5959): 538-541. doi: 10.1038/308538a0
[23] Tuttle M L W , Breit G N , Cozzarelli I M . Processes affecting δ34S and δ18O values of dissolved sulfate in alluvium along the Canadian River, central Oklahoma, USA[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 265(3-4): 455-467. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.05.009
[24] Wang X , Zhang Y, Liu T, et al. Phase Transformation and Dissolution Behavior of Pyrite in the Roasting-Sulfuric Acid Leaching Process of Vanadium-Bearing Stone Coal[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(6): 526-535 doi: 10.3390/min10060526
-




 下载:
下载: