Geochemical Characteristics and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in the Lower Tarim River Reclamation Area
-
摘要:
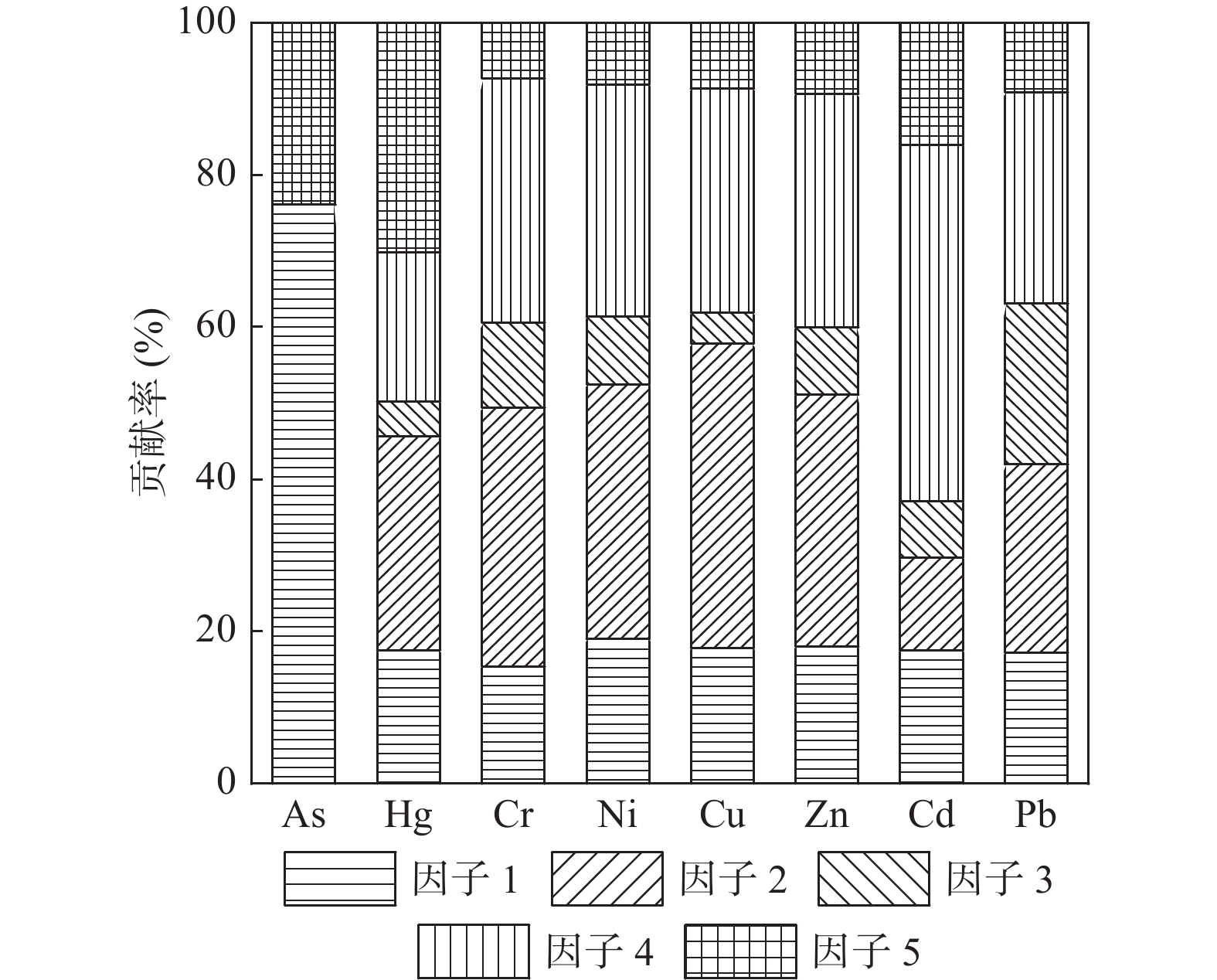
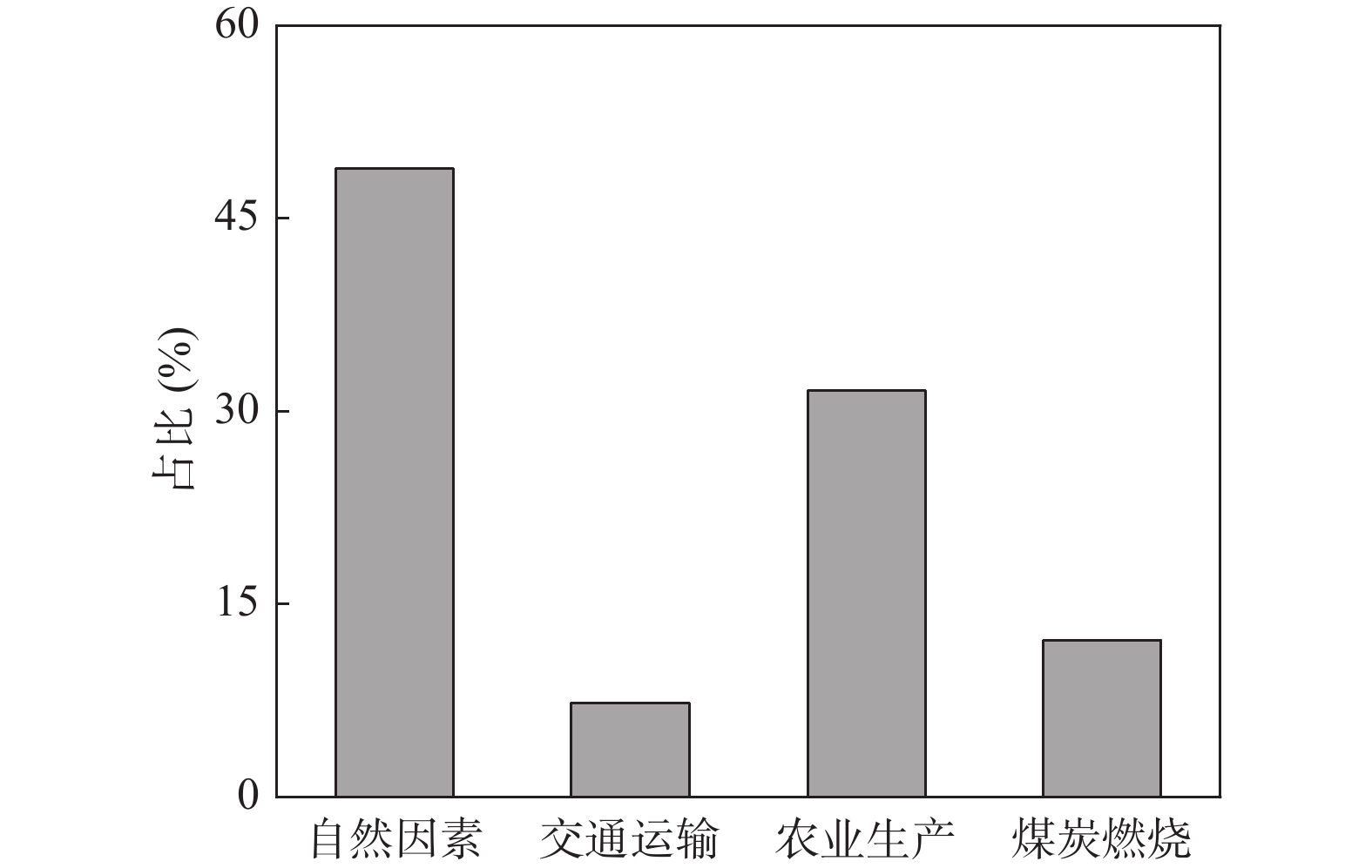
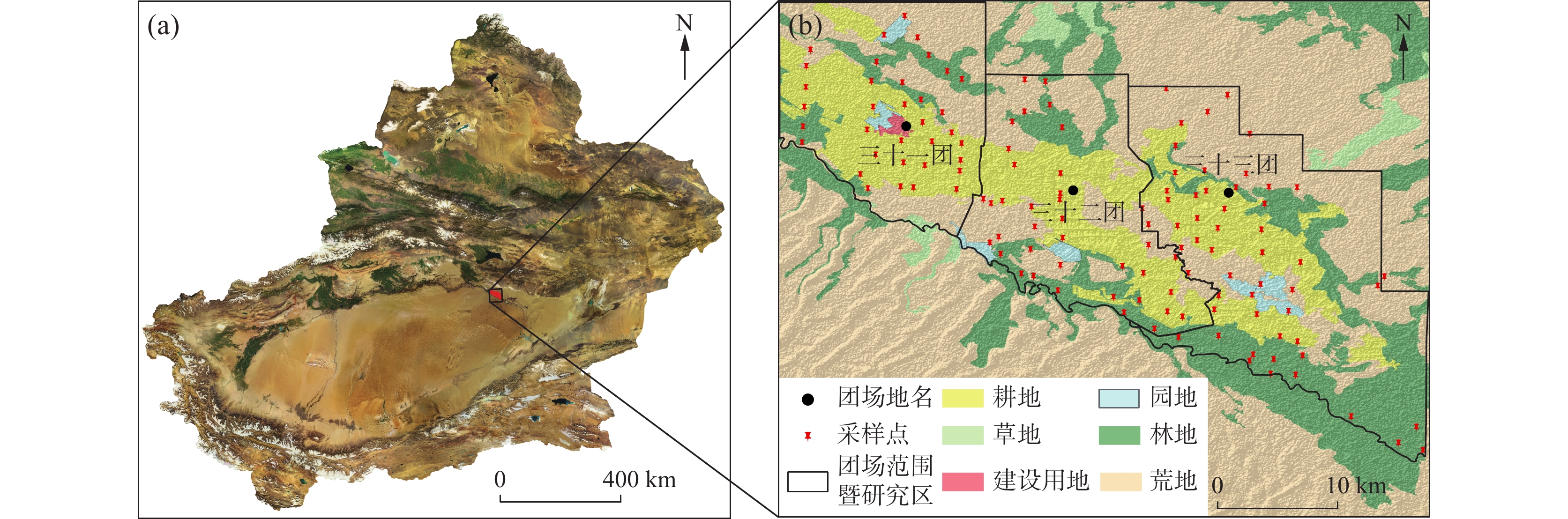
为查明塔里木河下游垦区土壤重(类)金属地球化学特征及潜在生态风险,采集表层土壤样品125件,测定其As、Hg、Ni、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb 8种元素含量和pH值大小,基于地统计学、内梅罗综合污染指数法(Nemerow Comprehensive Pollution Index,Pn)和潜在生态风险指数法(Potential ecological Risk Index,RI)对土壤重(类)金属潜在生态风险进行评价,利用正定矩阵模型(Positive Matrix Factorization,PMF)对重(类)金属来源进行解析。结果表明:①研究区内所有重(类)金属元素的含量均值未超过国家农用地土壤污染风险管控筛查值,含量整体处于正常水平。②研究区RI指数的变化范围为50.75~179.07,生态风险轻微、中等、较强的样点分别占29.37%、63.63%和7%,说明研究区整体处于中等生态风险等级。③PMF模型结果表明,研究区土壤重(类)金属主要来自于自然因素(48.88%),其含量与地质背景密切相关;其次为农业生产(31.63%),大量化肥、农药的使用导致耕地区重(类)金属含量较高;煤炭燃烧(12.20%)和交通运输(7.29%)对重(类)金属元素累积也有一定的贡献。
Abstract:To identify the geochemical characteristics and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soils of the lower Tarim River reclamation area, 125 surface soil samples were collected and their As, Hg、Ni、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd and Pb concentrations and pH values were determined. The potential ecological risk of soil heavy metals was evaluated based on geostatistics, Nemerow Comprehensive Pollution Index(Pn)and Potential Ecological Risk Index(RI), and the sources of heavy metals were analysed using Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF). The results show that:①The average values of all heavy (class) metal elements in the study area did not exceed the national screening values for soil pollution risk control on agricultural land, and the levels were generally at normal levels. ②The range of variation of the index in the study area was 50.75 to 179.07, with 29.37%, 63.63% and 7% of the sample points with slight, medium and strong ecological risk respectively, indicating that the study area as a whole was in the medium ecological risk class. ③The results of the PMF model show that the heavy (class) metals in the study area come mainly from natural factors (48.88%) and their content is closely related to the geological background; followed by agricultural production (31.63%), the use of large amounts of chemical fertilisers and pesticides leads to a high content of heavy (class) metals in the cultivated area; coal combustion (12.20%) and transportation (7.29%) also contribute to the accumulation of heavy (class) metal elements. Coal combustion (12.20%) and transportation (7.29%) also contribute to the accumulation of heavy (class) metals.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- Lower Tarim River /
- reclamation area /
- geochemical characteristics /
- ecological risk
-

-
表 1 土壤重(类)金属描述性统计表(n=125)
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of soil heavy metals(n=125)
元素 最小值
(mg/kg)最大值
(mg/kg)平均值
(mg/kg)标准差
(mg/kg)偏度 峰度 变异
系数(%)新疆背景值
(mg/kg)国国家筛查值(mg/kg) As 2.40 24.60 9.63 3.71 1.07 1.49 38 11.20 25.00 Hg 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.89 −0.04 42 0.02 3.40 Cr 23.29 75.70 42.19 10.48 0.69 0.12 25 49.30 250.00 Ni 11.71 39.20 21.39 5.61 0.55 −0.18 26 26.60 190.00 Cu 8.92 40.90 18.96 6.79 0.93 0.62 36 26.70 100.00 Zn 29.68 93.10 52.15 13.91 0.53 −0.32 27 68.80 300.00 Cd 0.07 0.26 0.14 0.04 0.72 0.46 26 0.12 0.60 Pb 10.08 32.58 17.48 3.06 1.29 3.79 17 19.40 170.00 pH 8.01 9.46 8.66 0.29 0.25 0.05 3.3 — — 注:背景值参照新疆土壤元素地球化学背景值(2011)(叶盼青等,2022)。 表 2 相关理论参数及最优拟合模型
Table 2. Related theoretical parameters and optimal fitting model
元素 理论模型 块金值C0 基台值Sill 块金比(%) 变程(m) 决定系数R2 残差RSS As 指数 0.02 0.14 0.89 4920.00 0.77 6.10×10−5 Hg 高斯 0.02 0.14 0.84 3222.00 0.18 1.08×10−4 Cr 指数 0.01 0.06 0.87 4200.00 0.35 9.66×10−5 Ni 指数 0.01 0.07 0.89 3570.00 0.22 4.01×10−5 Cu 指数 0.01 0.12 0.89 2520.00 0.23 1.16×10−4 Zn 指数 0.01 0.07 0.89 3240.00 0.24 4.20×10−5 Cd 高斯 0.01 0.06 0.83 2286.00 0.24 5.15×10−5 Pb 高斯 0.00 0.04 0.83 3186.00 0.38 8.35×10−6 pH 高斯 0.00 0.00 0.84 3984.00 0.21 1.76×10−8 表 3 不同污染级别的样本数占总样本数的百分数(n=125)
Table 3. The number of samples with different contamination levels is a percentage of the total number of samples (n=125)
指数 元素 无污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 单因子污染指数(Pr) As 69.93% 29.37% 0.70% 0 Hg 72.03% 29.97% 0 0 Cr 78.32% 21.68% 0 0 Ni 81.82% 18.18% 0 0 Cu 88.81% 11.19% 0 0 Zn 86.71% 13.29% 0 0 Cd 38.46% 60.83% 0.70% 0 Pb 78.32% 21.68% 0 0 内梅罗综合污染指数(Pn) — 48.95% 51.05% 0 0 表 4 调整前后潜在生态风险评价标准
Table 4. Evaluation criteria of potential ecological risks before and after adjustment
指标 生态危害等级 轻微 中等 强 很强 极强 调整前 单项生态风险指数(Er) <40 40~80 80~160 160~320 >320 综合生态风险指数(RI) <150 150~300 300~600 >600 调整后 单项生态风险指数(Er) <30 30~60 60~120 120~240 >240 综合生态风险指数(RI) <70 70~140 140~280 >280 表 5 潜在生态风险评价
Table 5. Assessment of potential ecological risks
潜在生态风险系数(Er) 综合潜在生态
污染指数(RI)元素 As Hg Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb 最小值 2.14 14.12 0.94 2.20 1.67 0.43 18.32 2.60 50.75 最大值 21.96 75.29 3.07 7.37 7.66 1.35 66.00 8.40 179.07 均值 8.60 34.03 1.71 4.02 3.55 0.76 34.76 4.51 91.93 -
[1] 阿吉古丽·马木提, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 艾尼瓦尔·买买提, 等. 开都河下游绿洲耕地土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(6): 2331-2341
MAMUT Ajigul, EZIZ Mamattursun, MAMUTI Aniwar, et al. Heavy metal contamination and potential ecological risks in the soil of the lower Kaidu River oasis[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(6): 2331-2341.
[2] 比拉力·依明, 阿不都艾尼·阿不里, 师庆东, 等. 基于PMF模型的准东煤矿周围土壤重(类)金属污染及来源解析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(9): 185-192
BILAL Imin, ABDUGHENI Abliz, SHI Qingdong, et al. Analysis of heavy metal pollution and sources in soils around Zhundong coal mine based on PMF model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(9): 185-192.
[3] 曹佰迪, 李文明, 周一凡, 等. 鄱阳湖流域沉积物中重金属元素分布特征及生态风险浅析[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(4): 343-353
CAO Baidi, LI Wenming, ZHANG Yifan, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risks of heavy metal elements in sediments of Poyang Lake basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(4): 343-353.
[4] 陈锦, 郭锦. 单因子法及综合污染指数法在矿山土壤重金属污染评价中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020(9): 281-282 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2020.09.135
CHEN Jin, GUO Jin. Application of single factor method and integrated pollution index method in the evaluation of heavy metal pollution in mine soils[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020(9): 281-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2020.09.135
[5] 陈明, 王琳玲, 曹柳, 等. 基于PMF模型的某铅锌冶炼城市降尘重金属污染评价及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 44(6): 3450-3462
CHEN Ming, WANG Linling, CAO Liu, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution from dustfall in a lead-zinc smelting city based on PMF model[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 44(6): 3450-3462. .
[6] 陈喜, 黄日超, 黄峰, 等. 西北内陆河流域水循环和生态演变与功能保障机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(5): 12-21
CHEN Xi, HUANG Richao, HUANG Feng, et al. Study on water cycle and ecological evolution and function guarantee mechanism of inland river basins in Northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(5): 12-21.
[7] 冯博鑫, 徐多勋, 张宏宇, 等. 基于最小数据集的周至地区土壤重金属地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(1): 284-292
FENG Boxin, XU Duoxun, ZHANG Hongyu, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of heavy metals in soils of Zhouzhi area based on minimum data set[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(1): 284-292.
[8] 冯娟. 浅析实施塔里木河干流下游生态输水工程的重要意义[J]. 中国水运, 2015, 15(2): 138-139
FENG Juan. An analysis of the importance of implementing the ecological water transfer project in the downstream of the main stream of Tarim River[J]. China Water Transport, 2015, 15(2): 138-139.
[9] 奉大博, 董树义, 杨棣, 等. 广东韶关乐昌铅锌矿土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 矿物岩石, 2022, 42(3): 123-133
FENG Dabo, DONG Shuyi, YANG Di, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal contamination in soils of Shaoguan Lechang Pb-Zn mine, Guangdong[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2022, 42(3): 123-133.
[10] 胡明, 薛娇, 严玉林, 等. 北京市特征河流沉积物重金属污染评价与来源解析[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37(23): 73-81
HU Ming, XUE Jiao, YAN Yulin, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in sediments of characteristic rivers in Beijing[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2021, 37(23): 73-81.
[11] 林丽钦. 应用毒理学安全评价数据推算重金属毒性系数的探讨: 2009重金属污染监测、风险评价及修复技术高级研讨会[C], 中国山东青岛, 2009.
[12] 马建华, 韩昌序, 姜玉玲. 潜在生态风险指数法应用中的一些问题[J]. 地理研究, 2020, 39(6): 1233-1241 doi: 10.11821/dlyj020190632
MA Jianhua, HAN Changxu, JIANG Yuling. Some issues in the application of potential ecological risk index method[J]. Geographical Research, 2020, 39(6): 1233-1241. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020190632
[13] 麦尔耶姆·亚森, 买买提·沙吾提, 尼格拉·塔什甫拉提, 等. 渭干河-库车河绿洲土壤重金属分布特征与生态风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(20): 226-233 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.028
YASEN Maieryemu, SAWUT Mamat, TAXIPULATI Nigela, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal distribution and ecological risk evaluation in the oasis soil of Weigan River-Kuche River[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(20): 226-233. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.028
[14] 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 阿吉古丽·马木提, 艾尼瓦尔·买买提. 新疆焉耆盆地辣椒地土壤重金属污染及生态风险预警[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(3): 1075-1086
EZIZ Mamattursun, MAMUT Ajigul, MAMUTI Aniwar. Early warning of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in pepperlands of Yanqi Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 1075-1086.
[15] 孟晓飞, 郭俊娒, 杨俊兴, 等. 石家庄市栾城区农田土壤重金属分布特征及作物风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(9): 4779-4790
MENG Xiaofei, GUO Junym, YANG Junxing, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Luancheng District Shijiazhuang and evaluation of crop risk[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(9): 4779-4790.
[16] 汪家权, 刘万茹, 钱家忠, 等. 基于单因子污染指数地下水质量评价灰色模型[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2002(5): 697-702
WANG Jiaquan, LIU Wanru, QIAN Jiazhong, et al. A grey model for groundwater quality evaluation based on single factor pollution index[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2002(5): 697-702.
[17] 王海江, 董天宇, 朱永琪, 等. 玛纳斯河流域长期连作棉田土壤重金属剖面分布特征分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(11): 2216-2225
WANG Haijiang, DONG Tianyu, ZHU Yongqi, et al. Characterization of soil heavy metal profiles in long-term continuous crop cotton fields in the Manas River basin[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(11): 2216-2225.
[18] 王雪婷. 沈阳市农村土壤环境质量监测与重金属污染评价[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2022
WANG Xueting. Monitoring the quality of rural soil environment and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in Shenyang[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2022.
[19] 王幼奇, 白一茹, 王建宇. 基于GIS的银川市不同功能区土壤重金属污染评价及分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(2): 710-716
WANG Youqi, BAI Yiru, WANG Jianyu. GIS-based evaluation and distribution characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution in different functional areas of Yinchuan City[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(2): 710-716.
[20] 吴梅, 刘属灵, 袁余洋, 等. 土壤重金属潜在生态风险指数法优化研究-以重庆市城口县为例[J]. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(2): 473-480
WU Mei, LIU Zhiling, YUAN Yuyang, et al. Optimization of the potential ecological risk index method for soil heavy metals in Chengkou County, Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2023, 54(2): 473-480.
[21] 息朝庄, 戴塔根, 黄丹艳. 湖南株洲市土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 中国地质, 2008(3): 524-530
XI Chaozhuang, DAI Tagen, HUANG Danyan. Characteristics of soil heavy metals distribution and pollution evaluation in Zhuzhou, Hunan[J]. Geology in China, 2008(3): 524-530.
[22] 杨淑媛. 植酸改性生物炭对土壤中Pb、Zn、Cd形态转化的影响研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2022
YANG Shuyuan. Study on the effect of phytate modified biochar on the morphological transformation of Pb、Zn、Cd in soil[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2022.
[23] 杨秀敏, 任广萌, 李立新, 等. 土壤pH值对重金属形态的影响及其相关性研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(6): 79-83
YANG Xiumin, REN Guangmeng, LI Lixin, et al. Study on the influence of soil pH on heavy metal morphology and its correlation[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(6): 79-83.
[24] 叶盼青, 阿不都艾尼·阿不里, 孙小丽, 等. 天山北坡经济带土壤重金属污染评价及来源分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(10): 4704-4712
YE Panqing, ABLIZ Abdugheni, SUN Xiaoli, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution in the economic zone on the north slope of Tianshan Mountain[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(10): 4704-4712.
[25] 尹芳, 封凯, 尹翠景, 等. 青海典型工业区耕地土壤重金属评价及源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(11): 5217-5226 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.11.030
YIN Fang, FENG Kai, YIN Cuijing, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metals in arable soils of typical industrial areas in Qinghai[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(11): 5217-5226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.11.030
[26] 余飞, 王佳彬, 王锐, 等. 基于乡镇尺度的地质高背景区耕地土壤重金属来源分析与风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(5): 2838-2848
YU Fei, WANG Jia-bin, WANG Rui, et al. Source analysis and risk assessment of heavy metals in arable soils in a high geological background area based on township scale[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(5): 2838-2848.
[27] 张慧文, 马剑英, 张自文, 等. 地统计学在土壤科学中的应用[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 45(6): 14-20, 27.
ZHANG Huiwen, MA Jianying, ZHANG Ziwen, et al. Application of geostatistics in soil science[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 45(6): 14-20.
[28] 郑行泉. 重金属铜对动物的急性毒性试验[J]. 福建畜牧兽医, 2018, 40(5): 14-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4331.2018.05.007
ZHENG Xingquan. Acute toxicity test of heavy metal copper to animals[J]. Fujian Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 40(5): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4331.2018.05.007
[29] 周雪明, 郑乃嘉, 李英红, 等. 2011~2012北京大气PM_2.5中重金属的污染特征与来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10): 4054-4060
ZHOU Xueming, ZHENG Naijia, LI Yinghong, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in atmospheric PM_2.5 in Beijing from 2011 to 2012[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10): 4054-4060.
[30] 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 王松涛, 等. 新疆若羌县农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(9): 87-91
ZENG Yanyan, ZHOU Jinlong, WANG Songtao, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal distribution and pollution evaluation in agricultural soils of Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(9): 87-91.
[31] Ajani G E, Popoola S O, Oyatola O O. Evaluation of the Pollution Status of Lagos Coastal Waters and Sediments using Physicochemical Characteristics Contamination Factor Nemerow Pollution Index Ecological Risk and Potential Ecological Risk Index[J]. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change, 2021, 2(4): 1-16.
[32] Begum B A, Biswas S K, Hopke P K. Key issues in controlling air pollutants in Dhaka, Bangladesh[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2010, 45(40): 7705-7713.
[33] Cai L, Xu Z, Ren M, et al. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2012, 78(1): 2-8.
[34] Chai L, Wang Y, Wang X, et al. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil and associated model uncertainty[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 215(1): 112150-112150.
[35] Gray C W, McLaren R G, Roberts A H C, et al. The effect of long-term phosphatic fertiliser applications on the amounts and forms of cadmium in soils under pasture in New Zealand[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 1999, 54(3): 267-277. doi: 10.1023/A:1009883010490
[36] Hu W, Wang H, Dong L, et al. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 237(3): 650-661.
[37] Nalan K, DENGİZ O. Assessment of potential ecological risk index based on heavy metal elements for organic farming in micro catchments under humid ecological condition[J]. Eurasian Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 9(3): 194-201.
[38] Zhuang P, Lu H, Li Z, et al. Multiple exposure and effects assessment of heavy metals in the population near mining area in South China[J]. Plos One, 2017, 9(4): 94484-94485.
-



 下载:
下载: